- 2011 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2004 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 1997 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2007 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2008 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2005 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2006 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2009 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 1998 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2001 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 1999 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2003 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2010 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2002 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driver Controls
on the
3. Press the SET + control and release it. 4. Take your foot off the accelerator pedal. 5. The indicator light instrument cluster will turn on. Note: • Vehicle speed may vary momentarily when driving up and down a • If the vehicle speed increases above the set speed on a downhill, you • If the vehicle speed decreases more than 10 mph (16 km/h) below • If the vehicle speed decreases to 30 mph (48 km/h) or less, your
your set speed on an uphill, your speed control will disengage.
may want to apply the brakes to reduce the speed.
steep hill.
speed control will disengage
Disengaging speed control To disengage the speed control: • Depress the brake pedal or • Depress the clutch pedal (if equipped). Disengaging the speed control will not erase previous set speed. Note: When you use the clutch pedal to disengage the speed control, the engine speed may briefly increase, this is normal. Resuming a set speed Press the RES (resume) control and release it. This will automatically return the vehicle to the previously set speed. The RES control will not work if the vehicle speed is not faster than 30 mph (48 km/h).
53
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driver Controls
Increasing speed while using speed control There are three ways to set a higher speed: • Press and hold the SET + control until you get to the desired speed, then release the control. • Press and release the SET +
control to operate the Tap-Up function. Each tap will increase the set speed by 1 mph (1.6 km/h).
• Use the accelerator pedal to get to the desired speed. When the vehicle reaches that speed press and release the SET + control.
Reducing speed while using speed control There are three ways to reduce a set speed: • Press and hold the CST - control until you get to the desired speed, then release the control. • Press and release the CST -
control to operate the Tap-Down function. Each tap will decrease the set speed by 1 mph (1.6 km/h). • Depress the brake pedal or the clutch pedal (if equipped) until the desired vehicle speed is reached, press the SET + control.
Turning off speed control There are two ways to turn off the speed control: • Press the speed control OFF • Turn OFF the ignition. Note: When you turn off the speed control or the ignition, your speed control set speed memory is erased.
control.
54
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driver Controls
CARGO AREA FEATURES
Cargo area shade (if equipped) Your vehicle may be equipped with notches in the side trim panels that are used for a cargo area shade. See your authorized dealer for more information.
BEDRAILS (IF EQUIPPED) • This bedrail is for appearance use only.
To help prevent injury, do not use bedrail to retain cargo.
• Retain cargo with the pickup tie down hooks. BED EXTENDER (IF EQUIPPED) Your vehicle may be equipped with a bed extender designed to extend the pickup box for longer loads. To extend the bed extender: 1. Lower tailgate. 2. Pull the round knobs on each side of the extender to release it from the pickup box. 3. Pivot extender on to the tailgate.
4. Evenly push down on the extender and push the round knobs in on each side locking it in place. Green markings on the shaft indicate the locked position. The locking clip screws below the middle bar can be tightened counterclockwise for extra security. Note: If the red marking on the shaft is visible, the bed extender is not locked or properly secured. To stow the bed extender, follow Steps 1 through 4 in reverse order.
55
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driver Controls
The bed extender may be used to secure a load of up to 100 lb. (46 kg) on the tailgate. The bed extender should always be kept in the stowed position with the tailgate closed when not in use. When driving the vehicle off road, the bed extender should be in the stowed position and the tailgate closed. To remove the bed extender: 1. Extend the bed extender. 2. Pull the round knobs on each side of the extender to unlock it. Make sure the locking clip screws are loose before removing the extender. 3. Press the locking clips below the middle bar on each side and lift the extender out of the bed. Note: Remove and store the bed extender when not in use. To install the bed extender, follow the removal procedure in reverse order.
56
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
KEYS The key operates all locks on your vehicle. You should always carry a second key with you in a safe place in case you require it in an emergency. Your keys are coded to your vehicle; using a non-coded key will not permit your vehicle to start. If you lose your dealer supplied keys, replacement keys are available through your authorized dealer.
POWER DOOR LOCKS (IF EQUIPPED) Press the top of the control to unlock all doors and the bottom to lock all doors.
UNLOCK
LOCK
REMOTE ENTRY SYSTEM (IF EQUIPPED) This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules and with RS-210 of Industry Canada. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment. The typical operating range for your remote entry transmitter is approximately 33 feet (10 meters). A decrease in operating range could be caused by: • weather conditions, • nearby radio towers, • structures around the vehicle, or • other vehicles parked next to your vehicle.
57
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
a key.
Your vehicle is equipped with a remote entry system which allows you to: • unlock the vehicle doors without • lock all the vehicle doors without • activate the personal alarm.
a key.
• If
and release to unlock the driver’s door. Note: The interior
If there are problems with the remote entry system, make sure to take ALL remote entry transmitters with you to your authorized dealer in order to aid in troubleshooting the problem. Unlocking the doors 1. Press lamps will illuminate. 2. Press doors. Locking the doors • Press
and release to lock all the doors. The park lamps will flash once to confirm lock; if any of the doors are not properly closed, the lamps will not flash.
and release again within three seconds to unlock all the
is pressed a second time within three seconds, the lamps will
flash again and the horn will chirp to confirm all doors are locked and closed. If either door is ajar the lamps will not flash and the horn will chirp twice.
Sounding a panic alarm Press to activate the alarm. The horn will sound and the parklamps will flash for approximately 3 minutes. Press again or turn the ignition to the 4 (ON) position to deactivate, or wait for the alarm to timeout in 3
minutes. Note: The panic alarm will only operate when the ignition is in the 1
(ACCESSORY), 2 (LOCK) or 3 (OFF) position. Replacing the battery The remote entry transmitter uses one coin type three-volt lithium battery CR2032 or equivalent.58
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
To replace the battery: 1. Twist a thin coin between the two halves of the remote entry transmitter near the key ring. DO NOT TAKE THE RUBBER COVER AND CIRCUIT BOARD OFF THE FRONT HOUSING OF THE REMOTE ENTRY TRANSMITTER.
2. Do not wipe off any grease on the battery terminals on the back surface of the circuit board.
3. Remove the old battery. Note: Please refer to local regulations when disposing of transmitter batteries. 4. Insert the new battery. Refer to the diagram inside the remote entry transmitter for the correct orientation of the battery. Press the battery down to ensure that the battery is fully seated in the battery housing cavity. 5. Snap the two halves back together. Note: Replacement of the battery will not cause the remote transmitter to become deprogrammed from your vehicle. The remote transmitter should operate normally after battery replacement. Replacing lost remote entry transmitters If you would like to have your remote entry transmitter reprogrammed because you lost one, or would like to buy additional remote entry transmitters, you can either reprogram them yourself, or take all remote entry transmitters to your authorized dealer for reprogramming. How to reprogram your remote entry transmitters You must have all remote entry transmitters (maximum of four) available before beginning this procedure.
59
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
To reprogram the remote entry transmitters: 1. Ensure the vehicle is electronically unlocked. 2. Put the key in the ignition. 3. Turn the key from the 2 (LOCK) position to 3 (OFF). 4. Cycle eight times rapidly (within 10 seconds) between the 3 (OFF) position and 4 (ON). Note: The eighth turn must end in the 4 (ON) position. 5. The doors will lock, then unlock, to confirm that the programming mode has been activated. 6. Within 20 seconds press any button on the remote entry transmitter. Note: If more than 20 seconds have passed you will need to start the procedure over again. 7. The doors will lock, then unlock, to confirm that this remote entry transmitter has been programmed. 8. Repeat Step 6 to program each additional remote entry transmitter. 9. Turn the ignition to the 3 (OFF) position after you have finished programming all of the remote entry transmitters. Note: After 20
seconds, you will automatically exit the programming mode. 10. The doors will lock, then unlock, to confirm that the programming mode has been exited.Illuminated entry The interior lamps illuminate when the remote entry system is used to unlock the door(s) or sound the personal alarm. The illuminated entry system will turn off the interior lights if: • the ignition switch is turned to the ON position, or • the remote transmitter lock control is pressed, or • after 25 seconds of illumination. The inside lights will not turn off if: • they have been turned on with the dimmer control, or • any door is open. The battery saver will shut off the interior lamps after several minutes if they are left on accidentally.
60
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
SECURILOCK姟 PASSIVE ANTI-THEFT SYSTEM (IF EQUIPPED) SecuriLock娂 passive anti-theft system is an engine immobilization system. This system is designed to help prevent the engine from being started unless a coded key programmed to your vehicle is used. The use of the wrong type of coded key may lead to a “no-start” condition. Your vehicle comes with two coded keys; additional coded keys may be purchased from your authorized dealer. The authorized dealer can program your spare keys to your vehicle or you can program the keys yourself. Refer to Programming spare keys for instructions on how to program the coded key. Note: The SecuriLock娂 passive anti-theft system is not compatible with non-Ford aftermarket remote start systems. Use of these systems may result in vehicle starting problems and a loss of security protection. Note: Large metallic objects, electronic devices that are used to purchase gasoline or similar items, or a second coded key on the same key chain may cause vehicle starting issues. You need to prevent these objects from touching the coded key while starting the engine. These objects will not cause damage to the coded key, but may cause a momentary issue if they are too close to the key when starting the engine. If a problem occurs, turn the ignition off, remove all objects on the key chain away from the coded key and restart the engine.
Anti-theft indicator The anti-theft indicator is located in the instrument cluster.
• When the ignition is in the 2 (LOCK) position, the indicator will flash
once every 2 seconds to indicate the SecuriLock娂 system is functioning as a theft deterrent.
• When the ignition is in the 4 (ON) position, the indicator will glow for
3 seconds, then turn off to indicate normal system functionality.
If a problem occurs with the SecuriLock娂 system, the indicator will flash rapidly or glow steadily when the ignition is in the 4 (ON) position. If this occurs, the vehicle should be taken to an authorized dealer for service.
61
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
Replacement keys If your keys are lost or stolen and you don’t have an extra coded key, you will need to have your vehicle towed to an authorized dealer. The key codes need to be erased from your vehicle and new coded keys will need to be programmed. Replacing coded keys can be very costly. Store an extra programmed key away from the vehicle in a safe place to help prevent any inconveniences. Please visit an authorized dealer to purchase additional spare or replacement keys.
Programming spare keys You can program your own coded keys to your vehicle. Please read and understand the entire procedure before you begin. Tips: • A maximum of eight keys can be coded to your vehicle. • Only use Securilock娂 keys. • You must have two previously programmed coded keys (keys that already operate your vehicle’s engine) and the new unprogrammed key(s) readily accessible.
• If no previously programmed coded keys are available, you must take
your vehicle to your authorized dealer to have the spare key(s) programmed.
1. Insert a previously programmed coded key into the ignition. 2. Turn the ignition from the 3
(OFF) position to the 4 (ON) position. Keep the ignition in the 4
(ON) position for at least one second, but no more than 10
seconds. 3. Turn the ignition to the 3 (OFF) position, and remove the coded key from the ignition.62
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Locks and Security
4. Within ten seconds of removing the previously programmed coded key, insert the other previously programmed coded key into the ignition. 5. Turn the ignition from the 3 (OFF) position to the 4 (ON) position. Keep the ignition in the 4 (ON) position for at least one second but not more than 10 seconds. 6. Turn the ignition to the 3 (OFF) position, and remove the second key from the ignition. 7. Within twenty seconds of removing the previously programmed coded key, insert the unprogrammed key (new/valet key) into the ignition. 8. Turn the ignition from the 3 (OFF) position to the 4 (ON) position. Keep the ignition in the 4 (ON) position for at least one second. 9. Your new unprogrammed key is now programmed. If the key has been successfully programmed it will start the vehicle’s engine and the theft indicator light will illuminate for three seconds and then go out. If the key was not successfully programmed, it will not start your vehicle’s engine and the theft indicator light will flash on and off rapidly. If failure repeats, bring your vehicle to your authorized dealer to have the new key(s) programmed. To program additional new unprogrammed key(s), repeat this procedure from Step 1 for each additional key.
63
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
SEATING Notes:
Reclining the seatback can cause an occupant to slide under the seat’s safety belt, resulting in severe personal injuries in the
event of a collision.
Do not pile cargo higher than the seatbacks to reduce the risk of injury in a collision or sudden stop.
Before returning the seatback to its original position, make sure that cargo or any objects are not trapped behind the seatback.
After returning the seatback to its original position, pull on the seatback to ensure that it has fully latched. An unlatched seat may become dangerous in the event of a sudden stop or collision.
Adjusting the front manual seat
Never adjust the driver’s seat or seatback when the vehicle is moving.
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap belt snug and low across the hips.
Lift the release bar to move seat forward or backward. Ensure that the seat is locked into place.
64
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Pull lever located at the side of the seat cushion up to adjust seatback.
60/40 seat (if equipped) To gain access to the storage compartment in your armrest (if equipped), lift the latch to open lid. The 60/40 seat cupholder (if equipped) is detachable for cleaning. • Firmly grasp the bottom of the
cup holder and pull up.
To re-attach: • Slide the cupholder over the two pins located on the front of the 60% • Press down until it is firmly latched into place.
driver’s seat.
Using the manual lumbar support (if equipped) Turn the lumbar support control clockwise to increase firmness. Turn the lumbar support control counterclockwise to increase softness.
65
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Passenger side rear access Pull up on the recliner handle. The seat will lean forward. Lift the release bar to move the seat forward to access the rear area of the cab.
To return seat to original position, slide the seat bottom back, then push the seatback up to lock it in place. The seat will lock, and you will have to use the release bar to move the seat back to the original position. REAR SEATS
Center facing jump seat (2 door SuperCab) (if equipped) To open, pull inboard and down on the seat strap. To stow the seat, pull seat bottom back to the fully upright position. Do not install a child seat in the center facing jump seats as there are no child restraints recommended for use in this seating
position.
Center facing jump seat (4 door SuperCab) (if equipped) To open, pull seat assembly down, then raise seatback. To stow the seat, fold seat back down and raise seat assembly to the fully upright position.
Do not install a child seat in the center facing jump seats
as there are no child restraints recommended for use in this seating position.
66
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Booster seats must be installed only in seating positions equipped with a combination lap/shoulder belt.
SAFETY RESTRAINTS Safety restraints precautions
Always drive and ride with your seatback upright and the lap belt snug and low across the hips.
To reduce the risk of injury, make sure children sit where they can be properly restrained.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always properly wear their safety belts, even when an air bag
supplemental restraint system (SRS) is provided.
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in these areas
are more likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not allow people to ride in any area of your vehicle that is not equipped with seats and safety belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and using a safety belt properly.
In a rollover crash, an unbelted person is significantly more likely to die than a person wearing a safety belt.
Each seating position in your vehicle has a specific safety belt assembly which is made up of one buckle and one tongue that
are designed to be used as a pair. 1) Use the shoulder belt on the outside shoulder only. Never wear the shoulder belt under the arm. 2) Never swing the safety belt around your neck over the inside shoulder. 3) Never use a single belt for more than one person.
67
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
On four-door SuperCab vehicles, do not open the rear door when the rear safety belt is still buckled.
Combination lap and shoulder belts 1. Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle (the buckle closest to the direction the tongue is coming from) until you hear a snap and feel it latch. Make sure the tongue is securely fastened in the buckle.
2. To unfasten, push the release button and remove the tongue from the buckle.
The front outboard safety restraints in the vehicle are combination lap and shoulder belts. The front passenger outboard safety belt has two types of locking modes described below:
Vehicle sensitive mode This is the normal retractor mode, which allows free shoulder belt length adjustment to your movements and locking in response to vehicle movement. For example, if the driver brakes suddenly or turns a corner sharply, or the vehicle receives an impact of approximately 5 mph (8
km/h) or more, the combination safety belts will lock to help reduce forward movement of the driver and passengers.68
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Automatic locking mode The automatic locking mode is not available on the driver safety belt. In this mode, the shoulder belt is automatically pre-locked. The belt will still retract to remove any slack in the shoulder belt. The automatic locking mode is not available on the driver safety belt. This mode should be used any time a child safety seat is installed in a passenger front seat. Refer to Safety restraints for children or Safety seats for children later in this chapter. How to use the automatic locking mode • Buckle the combination lap and
shoulder belt.
• Grasp the shoulder portion and pull downward until the entire belt is pulled out.
• Allow the belt to retract. As the belt retracts, you will hear a clicking sound. This indicates the safety belt is now in the automatic locking mode.
How to disengage the automatic locking mode Disconnect the combination lap/shoulder belt and allow it to retract completely to disengage the automatic locking mode and activate the vehicle sensitive (emergency) locking mode.
69
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
After any vehicle collision, the seat belt system at all outboard seating positions (except driver, which has no “automatic locking
retractor” feature) must be checked by an authorized dealer to verify that the “automatic locking retractor” feature for child seats is still functioning properly. In addition, all safety belts should be checked for proper function.
BELT AND RETRACTOR ASSEMBLY MUST BE REPLACED if the safety belt assembly “automatic locking retractor” feature or any other safety belt function is not operating properly when checked authorized dealer.
Failure to replace the Belt and Retractor assembly could increase the risk of injury in collisions.
Energy Management Feature • This vehicle has a safety belt system with an energy management
feature at the front outboard seating positions to help further reduce the risk of injury in the event of a head-on collision.
• This energy management system has a retractor assembly that is
designed to pay out webbing in a controlled manner. This feature is designed to help reduce the belt force acting on the occupant’s chest.
Lap belts
Adjusting the front center seat and rear center facing jump seat lap belts (if equipped) The lap belt does not adjust automatically.
The lap belt should fit snugly and as low as possible around the hips, not across the waist.
70
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Insert the tongue into the correct buckle (the buckle closest to the direction the tongue is coming from). To lengthen the belt, turn the tongue at a right angle to the belt and pull across your lap until it reaches the buckle. To tighten the belt, pull the loose end of the belt through the tongue until it fits snugly across the hips. Shorten and fasten the belt when not in use. For the rear jump seat, shorten and fold the belt into the seat when not in use.
Safety belt pretensioner Your vehicle is equipped with safety belt pretensioners at the driver and front outboard passenger seating positions. The safety belt pretensioner is a device which removes excess webbing from the safety belt system. The safety belt pretensioner uses the same crash sensor system as the front airbag supplemental restraint system (SRS). When the safety belt pretensioner deploys, webbing from the lap and shoulder belt is tightened. Refer to the Safety belt maintenance section in this chapter.
The driver and front passenger seat belt system (including retractors, buckles and height adjusters) must be replaced if the
vehicle is involved in a collision that results in deployment of front airbags and safety belt pretensioners.
Front safety belt height adjustment Your vehicle has safety belt height adjustments for the driver and front outboard passenger. Adjust the height of the shoulder belt so the belt rests across the middle of your shoulder.
71
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints • Regular Cab and 4–door Super
Cab
• 2–door SuperCab
To lower the shoulder belt height, push the button and slide the height adjuster down. To raise the height of the shoulder belt, slide the height adjuster up. Pull down on the height adjuster to make sure it is locked in place.
Position the safety belt height adjusters so that the belt rests across the middle of your shoulder. Failure to adjust the safety
belt properly could reduce the effectiveness of the seat belt and increase the risk of injury in a collision.
Safety belt extension assembly If the safety belt is too short when fully extended, there is a 8 inch (20
cm) safety belt extension assembly that can be added (part number 611C22). This assembly can be obtained from an authorized dealer. Use only extensions manufactured by the same supplier as the safety belt. Manufacturer identification is located at the end of the webbing on the label. Also, use the safety belt extension only if the safety belt is too short for you when fully extended.72
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Do not use extensions to change the fit of the shoulder belt across the torso.
Safety belt warning light and indicator chime The safety belt warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster and a chime sounds to remind the occupants to fasten their safety belts. Conditions of operation If... The driver’s safety belt is not buckled before the ignition switch is turned to the ON position... The driver’s safety belt is buckled while the indicator light is illuminated and the warning chime is sounding... The driver’s safety belt is buckled before the ignition switch is turned to the ON position...
Then... The safety belt warning light illuminates 1-2 minutes and the warning chime sounds 4-8 seconds.
The safety belt warning light and warning chime turn off.
The safety belt warning light and indicator chime remain off.
BeltMinder姞 The BeltMinder威 feature is a supplemental warning to the safety belt warning function. This feature provides additional reminders to the driver that the driver’s safety belt is unbuckled by intermittently sounding a chime and illuminating the safety belt warning lamp in the instrument cluster.
73
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Then... The BeltMinder威 feature is activated - the safety belt warning light illuminates and the warning chime sounds for 6 seconds every 30
seconds, repeating for approximately 5 minutes or until safety belt is buckled. The BeltMinder威 feature will not activate.If... The driver’s safety belt is not buckled before the vehicle has reached at least 3 mph (5
km/h) and 1-2 minutes have elapsed since the ignition switch has been turned to ON... The driver’s safety belt is buckled while the safety belt indicator light is illuminated and the safety belt warning chime is sounding... The driver’s safety belt is buckled before the ignition switch is turned to the ON position... The following are reasons most often given for not wearing safety belts (All statistics based on U.S. data): Reasons given... “Crashes are rare events”The BeltMinder威 feature will not activate.
Consider... 36700 crashes occur every day. The more we drive, the more we are exposed to “rare” events, even for good drivers. 1 in 4 of us will be seriously injured in a crash during our lifetime. 3 of 4 fatal crashes occur within 25
miles (40 km) of home. We design our safety belts to enhance comfort. If you are uncomfortable - try different positions for the safety belt upper anchorage and seatback which should be as upright as possible; this can improve comfort.“I’m not going far”
“Belts are uncomfortable”
74
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Reasons given... “I was in a hurry”
“Safety belts don’t work”
“Traffic is light”
“Belts wrinkle my clothes”
“The people I’m with don’t wear belts”
“I have an airbag”
“I’d rather be thrown clear”
Seating and Safety Restraints
Consider... Prime time for an accident. BeltMinder威 reminds us to take a few seconds to buckle up. Safety belts, when used properly, reduce risk of death to front seat occupants by 45% in cars, and by 60% in light trucks. Nearly 1 of 2 deaths occur in single-vehicle crashes, many when no other vehicles are around. Possibly, but a serious crash can do much more than wrinkle your clothes, particularly if you are unbelted. Set the example, teen deaths occur 4
times more often in vehicles with TWO or MORE people. Children and younger brothers/sisters imitate behavior they see. Airbags offer greater protection when used with safety belts. Frontal airbags are not designed to inflate in rear and side crashes or rollovers. Not a good idea. People who are ejected are 40 times more likely to DIE. Safety belts help prevent ejection, WE CAN’T “PICK OUR CRASH”.Do not sit on top of a buckled safety belt to avoid the BeltMinder威 chime. Sitting on the safety belt will increase the risk of injury in an accident. To disable (one-time) or deactivate the BeltMinder威 feature please follow the directions stated below.
75
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
One time disable Any time the safety belt is buckled and then unbuckled during an ignition ON cycle, the BeltMinder威 will be disabled for that ignition cycle only. Deactivating/activating the BeltMinder姞 feature Read Steps 1 - 9 thoroughly before proceeding with the deactivation/activation programming procedure. The BeltMinder威 feature can be deactivated/activated by performing the following procedure: Before following the procedure, ensure that the following conditions are met: • The parking brake is set. • The gearshift is in P (Park) (automatic transmission) or the neutral • The ignition switch is in the OFF position. • All vehicle doors are closed. • The driver’s safety belt is unbuckled. • The parklamps/headlamps are in OFF position (If vehicle is equipped
position (manual transmission).
with Autolamps, this will not affect the procedure).
To reduce the risk of injury, do not deactivate/activate the BeltMinder威 feature while driving the vehicle.
BeltMinder威 activation and deactivation procedure 1. Turn the ignition switch to the RUN (or ON) position. (DO NOT START THE ENGINE.) 2. Wait until the safety belt warning light turns off. (Approximately 1–2
minutes.) • Steps 3–5 must be completed within 60 seconds or the procedure willhave to be repeated.
3. At a moderate speed, buckle then unbuckle the safety belt three times, ending with the safety belt unbuckled. This can be done before or during BeltMinder威 warning activation. 4. Turn on the parklamps/headlamps, turn off the parklamps/headlamps. 5. At a moderate speed, buckle then unbuckle the safety belt three times, ending with the safety belt unbuckled.
76
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints • After Step 5 the safety belt warning light will be turned on for three
seconds.
6. Within seven seconds of the safety belt warning light turning off, at a moderate speed, buckle then unbuckle the safety belt. • This will disable BeltMinder威 if it is currently enabled, or enable
BeltMinder威 if it is currently disabled.
7. Confirmation of disabling BeltMinder威 is provided by the safety belt warning light flashing four times per second for three seconds. 8. Confirmation of enabling BeltMinder威 is provided by: • The safety belt warning light flashing four times per second for three • Followed by three seconds with the safety belt warning light off. • Once again, the safety belt warning light will flash four times per
seconds.
second for three seconds.
9. After receiving confirmation, the deactivation/activation procedure is complete.
Safety belt maintenance Inspect the safety belt systems periodically to make sure they work properly and are not damaged. Inspect the safety belts to make sure there are no nicks, tears or cuts. Replace if necessary. All safety belt assemblies, including retractors, buckles, front safety belt buckle assemblies, buckle support assemblies (slide bar-if equipped), shoulder belt height adjusters (if equipped), shoulder belt guide on seatback (if equipped), child safety seat LATCH and tether anchors, and attaching hardware, should be inspected after a collision. Ford Motor Company recommends that all safety belt assemblies in use in vehicles involved in a collision be replaced. However, if the collision was minor and an authorized dealer finds that the belts do not show damage and continue to operate properly, they do not need to be replaced. Safety belt assemblies not in use during a collision should also be inspected and replaced if either damage or improper operation is noted. The energy absorbing functions may have been activated in a collision so the restraints should be examined; if the front airbags have deployed, the pretensioners have also deployed and must be replaced — regardless of whether there was an occupant in the passenger seat or not.
77
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Failure to inspect and if necessary replace the safety belt assembly under the above conditions could result in severe
personal injuries in the event of a collision.
Refer to Interior in the Cleaning chapter.
AIRBAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS)
Important supplemental restraint system (SRS) precautions The supplemental restraint system is designed to work with the safety belt to help protect the driver and right front passenger from certain upper body injuries. Airbags DO NOT inflate slowly or gently and the risk of injury from a deploying airbag is greatest close to the trim covering the airbag module.
Never place a rear facing infant seat in the front seat
unless the passenger air bag is turned off.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always properly wear their safety belts, even when an air bag supplemental restraint system (SRS) is provided.
78
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) recommends a minimum distance of at least 25 cm (10 inches)
between an occupant’s chest and the driver air bag module.
Never place your arm over the air bag module as a deploying air bag can result in serious arm fractures or other injuries.
Steps you can take to properly position yourself away from the airbag: • Move your seat to the rear as far as you can while still reaching the • Recline the seat slightly (one or two degrees) from the upright
pedals comfortably.
position.
Do not put anything on or over the airbag module. Placing objects on or over the airbag inflation area may cause those
objects to be propelled by the airbag into your face and torso causing serious injury.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the Airbag Supplemental Restraint System or its fuses. See your authorized
dealer.
The front passenger airbag is not designed to offer protection to an occupant in the center front seating position.
Modifying or adding equipment to the front end of the vehicle (including frame, bumper, front end body structure and tow
hooks) may affect the performance of the airbag system, increasing the risk of injury. Do not modify the front end of the vehicle.
Additional equipment may affect the performance of the airbag sensors increasing the risk of injury. Please refer to the Body
Builders Layout Book for instructions about the appropriate installation of additional equipment.
79
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Children and airbags For additional important safety information, read all information on safety restraints in this guide.
Never place a rearward facing child safety restraint in front of an activated airbag. Airbags have been known to kill or injure
children in front facing child safety restraints. Whenever placing a child safety seat in a front seating position (including center if equipped), turn off the passenger side airbag switch after being certain the child is properly restrained. If using a forward facing child safety restraint in the front outboard seat, slide the seat all the way back, and turn off the passenger airbag. If using a rear facing child safety seat in the front outboard seating position, make sure the passenger airbag is turned off and slide the passenger seat all the way forward until the safety seat rests on the dashboard. See Passenger airbag on/off switch in this chapter.
Do not install a child seat in a center facing jump seat.
An airbag can kill or injure a child in a child seat. Child seats should never be placed in the front seats, unless passenger
airbag switch is turned off. See Passenger airbag on/off switch in this chapter.
Rear facing child seats should NEVER be placed in the front seats unless the passenger airbag switch is turned off.
80
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Booster seats must be installed only in seating positions equipped with a combination lap/shoulder belt.
To reduce the risk of injury, make sure children sit where they can be properly restrained.
How does the airbag supplemental restraint system work? The airbag SRS is designed to activate when the vehicle sustains sufficient longitudinal deceleration. The fact that the airbags did not inflate in a collision does not mean that something is wrong with the system. Rather, it means the forces were not of the type sufficient to cause activation. Airbags are designed to inflate in frontal and near-frontal collisions, not rollover, side-impact, or rear-impacts. The airbags inflate and deflate rapidly upon activation. After airbag deployment, it is normal to notice a smoke-like, powdery residue or smell the burnt propellant. This may consist of cornstarch, talcum powder (to lubricate the bag) or sodium compounds (e.g., baking soda) that result from the combustion process that inflates the airbag. Small amounts of sodium hydroxide may be present which may irritate the skin and eyes, but none of the residue is toxic.
81
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
While the system is designed to help reduce serious injuries, it may also cause minor abrasions, swelling or temporary hearing loss. Because airbags must inflate rapidly and with considerable force, there is the risk of death or serious injuries such as fractures, facial and eye injuries or internal injuries, particularly to occupants who are not properly restrained or are otherwise out of position at the time of airbag deployment. Thus, it is extremely important that occupants be properly restrained as far away from the airbag module as possible while maintaining vehicle control.
Several air bag system components get hot after inflation. Do not touch them after inflation.
If the air bag has deployed, the air bag will not function again and must be replaced immediately. If the air bag is not
replaced, the unrepaired area will increase the risk of injury in a collision.
airbags),
switch and diagnostic monitor (RCM)
The SRS consists of: • driver and passenger airbag modules (which include the inflators and • one or more impact and safing sensors, passenger airbag deactivation • a readiness light and tone, • and the electrical wiring which connects the components. • Safety belt pretensioners The RCM (restraints control module) monitors its own internal circuits and the supplemental airbag electrical system wiring (including the passenger airbag deactivation switch, the impact sensors, the system wiring, the airbag system readiness light, the airbag back up power and the airbag ignitors).
Determining if the system is operational The SRS uses readiness lights in the instrument cluster and the passenger airbag deactivate switch or a tone to indicate the condition of the system. Refer to the Airbag readiness section in the Instrument cluster chapter or Passenger airbag on/off switch section in this chapter. Routine maintenance of the airbag is not required.
82
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
flash or stay lit.
A difficulty with the system is indicated by one or more of the following: • The readiness lights will either • The readiness lights will not illuminate immediately after ignition is turned on.
• A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone pattern will repeat
periodically until the problem and/or light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the SRS serviced at an authorized dealer immediately. Unless serviced, the system may not function properly in the event of a collision.
Disposal of airbags and airbag equipped vehicles (including pretensioners) See your authorized dealer. Airbags MUST BE disposed of by qualified personnel.
Passenger airbag ON/OFF switch
An airbag ON/OFF switch has been installed in this vehicle. Before driving, always look at the face of the switch to be sure the switch is in the proper position in accordance with these instructions and warnings. Failure to put the switch in a proper position can increase the risk of serious injury or death in a collision.
ON
OFF
OFF
PASSENGER AIRBAG
Turning the passenger airbag off The passenger airbag on/off switch is located below the center stack of the instrument panel or in the center console.
83
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
1. Insert the ignition key, turn the switch to OFF position and hold in OFF position while removing the key. 2. When the ignition is turned to the ON position the OFF light illuminates briefly, momentarily shuts off and then turns back on. This indicates that the passenger airbag is deactivated.
ON
OFF
OFF
PASSENGER AIRBAG
If the light fails to illuminate when the passenger airbag switch is in the OFF position and the ignition switch is in the On position,
have the passenger airbag switch serviced at an authorized dealer immediately.
In order to avoid inadvertent activation of the switch, always remove the ignition key from the passenger air bag ON/OFF
switch.
Turning the passenger airbag back on The passenger airbag remains OFF until you turn it back ON. 1. Insert the ignition key and turn the switch to ON. 2. The OFF light will briefly illuminate when the ignition is turned to ON. This indicates that the passenger airbag is operational.
ON
OFF
OFF
PASSENGER AIRBAG
If the OFF light is illuminated when the passenger airbag ON/OFF switch is in the ON position and the ignition switch is
ON, have the passenger airbag ON/OFF switch serviced at an authorized dealer immediately.
84
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
The safety belts for the driver and right front passenger seating positions have been specifically designed to function together
with the airbags in certain types of crashes. When you turn OFF your airbag, you not only lose the protection of the airbag, you also may reduce the effectiveness of your safety belt system, which was designed to work with the airbag. If you are not a person who meets the requirements stated in the NHTSA/Transport Canada deactivation criteria turning OFF the airbag can increase the risk of serious injury or death in a collision.
Always use safety belts and child restraints properly. If a child in a rear facing infant seat must be transported in front, the
passenger airbag must be turned OFF. This is because the back of the infant seat is too close to the inflating airbag and the risk of a fatal injury to the infant when the airbag inflates is substantial.
The vast majority of drivers and passengers are much safer with an airbag than without. To do their job and reduce the risk of life threatening injuries, airbags must open with great force, and this force can pose a potentially deadly risk in some situations, particularly when a front seat occupant is not properly buckled up. The most effective way to reduce the risk of unnecessary airbag injuries without reducing the overall safety of the vehicle is to make sure all occupants are properly restrained in the vehicle, especially in the front seat. This provides the protection of safety belts and permits the airbags to provide the additional protection they were designed to provide. If you choose to deactivate your airbag, you are losing the very significant risk reducing benefits of the airbag and you are also reducing the effectiveness of the safety belts, because safety belts in modern vehicles are designed to work as a safety system with the airbags. Read all airbag Warning labels in the vehicle as well as the other important airbag instructions and Warnings in this Owner’s Guide. The passenger side airbag should always be ON (the airbag OFF light should not be illuminated) unless the passenger is a person who meets the requirements stated either in Category 1, 2 or 3 of the NHTSA/Transport Canada deactivation criteria which follows.
85
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
NHTSA deactivation criteria (excluding Canada) 1. Infant. An infant (less than 1 year old) must ride in the front seat because: • the vehicle has no rear seat; • the vehicle has a rear seat too small to accommodate a rear-facing • the infant has a medical condition which, according to the infant’s
infant seat; or
physician, makes it necessary for the infant to ride in the front so that the driver can constantly monitor the child’s condition.
2. Child age 1 to 12. A child age 1 to 12 must ride in the front seat because: • the vehicle has no rear seat; • although children ages 1 to 12 ride in the rear seat(s) whenever possible, children ages 1 to 12 sometimes must ride in the front because no space is available in the rear seat(s) of the vehicle; or • the child has a medical condition which, according to the child’s
physician, makes it necessary for the child to ride in the front seat so that the driver can constantly monitor the child’s condition.
and
3. Medical condition. A passenger has a medical condition which, according to his or her physician: • causes the passenger airbag to pose a special risk for the passenger; • makes the potential harm from the passenger airbag in a crash greater than the potential harm from turning OFF the airbag and allowing the passenger, even if belted, to hit the dashboard or windshield in a crash.
This vehicle has special energy management safety belts for the driver and right front passenger. These particular belts are
specifically designed to work with airbags to help reduce the risk of injury in a collision. The energy management safety belt is designed to give or release additional belt webbing in some accidents to reduce concentration of force on an occupant’s chest and reduce the risk of certain bone fractures and injuries to underlying organs. In a crash, if the airbag is turned OFF, this energy management safety belt might permit the person wearing the belt to move forward enough to incur a serious or fatal injury. The more severe the crash, and the heavier the occupant, the greater the risk. Be sure the airbag is turned ON for any person who does not qualify under the NHTSA deactivation criteria.
86
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Transport Canada deactivation criteria (Canada Only) 1. Infant: An infant (less than 1 year old) must ride in the front seat because: • the vehicle has no rear seat; • the rear seat in the vehicle cannot accommodate a rear-facing infant • the infant has a medical condition which, according to the infant’s
seat; or
physician, makes it necessary for the infant to ride in the front seat so that the driver can monitor the infant’s condition.
2. Child age 12 or under: A child age 12 or under must ride in the front seat because: • the vehicle has no rear seat; • although children age 12 and under ride in the rear seat whenever
possible, children age 12 and under have no option but to sometimes ride in the front seat because rear seat space is insufficient; or • the child has a medical condition that, according to the child’s
physician, makes it necessary for the child to ride in the front seat so that the driver can monitor the child’s condition.
3. Medical condition: A passenger has a medical condition that, according to his or her physician: • poses a special risk for the passenger if the airbag deploys; and • makes the potential harm from the passenger airbag deployment greater than the potential harm from turning OFF the airbag and experiencing a crash without the protection offered by the airbag.
This vehicle has special energy management safety belts for the driver and right front passenger. These particular belts are
specifically designed to work with airbags to help reduce the risk of injury in a collision. The energy management safety belt is designed to give or release additional belt webbing in some accidents to reduce concentration of force on an occupant’s chest and reduce the risk of certain bone fractures and injuries to underlying organs. In a crash, if the airbag is turned OFF, this energy management safety belt might permit the person wearing the belt to move forward enough to incur a serious or fatal injury. The more severe the crash, and the heavier the occupant, the greater the risk. Be sure the airbag is turned ON for any person who does not qualify under the Transport Canada deactivation criteria.
87
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
SAFETY RESTRAINTS FOR CHILDREN See the following sections for directions on how to properly use safety restraints for children. Also see Airbag supplemental restraint system (SRS) in this chapter for special instructions about using airbags.
Important child restraint precautions You are required by law to use safety restraints for children in the U.S. and Canada. If small children ride in your vehicle (generally children who are four years old or younger and who weigh 40 lb. [18 kg] or less), you must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Many states require that children use approved booster seats until they are eight years old. Check your local and state or provincial laws for specific requirements regarding the safety of children in your vehicle.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the vehicle is moving. The passenger cannot protect the child from
injury in a collision.
Always follow the instructions and warnings that come with any infant or child restraint you might use.
Do not install a child seat in a center facing jump seat.
Children and safety belts If the child is the proper size, restrain the child in a safety seat. Children who are too large for child safety seats (as specified by your child safety seat manufacturer) should always wear safety belts. Follow all the important safety restraint and airbag precautions that apply to adult passengers in your vehicle. If the shoulder belt portion of a combination lap and shoulder belt can be positioned so it does not cross or rest in front of the child’s face or neck, the child should wear the lap and shoulder belt. Moving the child closer to the center of the vehicle may help provide a good shoulder belt fit.
Do not leave children, unreliable adults, or pets unattended in your vehicle.
88
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Child booster seats Children outgrow a typical convertible or toddler seat when they weigh 40 lb. (18 kg) and are around 4 years of age. Although the lap/shoulder belt will provide some protection, these children are still too small for lap/shoulder belts to fit properly, which could increase the risk of serious injury in a crash. To improve the fit of both the lap and shoulder belt on children who have outgrown child safety seats, Ford Motor Company recommends use of a belt-positioning booster. Booster seats position a child so that safety belts fit better. They lift the child up so that the lap belt rests low across the hips and the knees bend comfortably. Booster seats may also make the shoulder belt fit better and more comfortably. Try to keep the belt near the middle of the shoulder. When children should use booster seats Children need to use booster seats from the time they outgrow the toddler seat until they are big enough for the vehicle seat and lap/shoulder belt to fit properly. Generally this is when they weigh about 80 lb. (36 kg) (about 8 to 12 years old). Booster seats should be used until you can answer YES to ALL of these questions: • Can the child sit all the way back against the vehicle seat back with knees bent comfortably at the edge of the seat without slouching?
• Does the lap belt rest low across the hips? • Is the shoulder belt centered on the shoulder and chest? • Can the child stay seated like this for the whole trip?
89
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Types of booster seats There are two types of belt-positioning booster seats: • Those that are backless.
If your backless booster seat has a removable shield, remove the shield and use the lap/shoulder belt. If a seating position has a low seat back and no head restraint, a backless booster seat may place your child’s head (top of ear level) above the top of the seat. In this case, move the backless booster to another seating position with a higher seat back and lap/shoulder belts.
• Those with a high back.
If, with a backless booster seat, you cannot find a seating position that adequately supports your child’s head, a high back booster seat would be a better choice.
Either type can be used at any seating position equipped with lap/shoulder belts if your child is over 40 lb. (18 kg).
90
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Children and booster seats vary widely in size and shape. Choose a booster that keeps the lap belt low and snug across the hips, never up across the stomach, and lets you adjust the shoulder belt to cross the chest and rest snugly near the center of the shoulder. The drawings below compare the ideal fit (center) to a shoulder belt uncomfortably close to the neck and a shoulder belt that could slip off the shoulder.
If the booster seat slides on the vehicle seat, placing a rubberized mesh sold as shelf or carpet liner under the booster seat may improve this condition. The importance of shoulder belts Using a booster without a shoulder belt increases the risk of a child’s head hitting a hard surface in a collision. For this reason, you should never use a booster seat with a lap belt only. It is best to use a booster seat with lap/shoulder belts in the back seat- the safest place for children to ride.
Move a child to a different seating location if the shoulder belt does not stay positioned on the shoulder during use.
Follow all instructions provided by the manufacturer of the booster seat.
Never put the shoulder belt under a child’s arm or behind the back because it eliminates the protection for the upper part of
the body and may increase the risk of injury or death in a collision.
91
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Never use pillows, books, or towels to boost a child. They can slide around and increase the likelihood of injury or death in a
collision.
SAFETY SEATS FOR CHILDREN
Child and infant or child safety seats Use a safety seat that is recommended for the size and weight of the child. Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or collision. When installing a child safety seat: • Review and follow the information
presented in the airbag supplemental restraint system (SRS) section in this chapter. • Use the correct safety belt buckle for that seating position (the buckle closest to the direction the tongue is coming from).
• Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle until you hear a snap and feel it latch. Make sure the tongue is securely fastened in the buckle. • Keep the buckle release button pointing up and away from the safety seat, with the tongue between the child seat and the release button, to prevent accidental unbuckling. • Place seat back in upright position. • Put the safety belt in the automatic locking mode. Refer to Automatic
locking mode (passenger side front and outboard rear seating positions) (if equipped) section in this chapter.
• LATCH lower anchors are recommended for use by children up to 22
kg (48 pounds) in a child restraint. Top tether anchors can be used for children up to 27 kg (60 pounds) in a child restraint, and to provide upper torso restraint for children up to 36 kg (80 pounds) using an upper torso harness and a belt-positioning booster.92
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Ford recommends the use of a child safety seat having a top tether strap. Install the child safety seat in a seating position with LATCH and tether anchors. For more information on top tether straps and anchors, refer to Attaching safety seats with tether straps in this chapter. For more information of LATCH anchors refer to Attaching safety seats with LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) attachments in this chapter.
Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions included with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or collision.
Installing child safety seats with combination lap and shoulder belts 1. Position the child safety seat in a seat with a combination lap and shoulder belt.
An airbag can kill or injure a child in a child seat. Child seats should NEVER be placed in the front seats, unless the passenger
airbag switch is turned off, See Passenger airbag on/off switch.
Rear facing child seats should NEVER be placed in the front seats unless the passenger airbag switch is turned off.
93
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
2. Pull down on the shoulder belt and then grasp the shoulder belt and lap belt together.
3. While holding the shoulder and lap belt portions together, route the tongue through the child seat according to the child seat manufacturer’s instructions. Be sure the belt webbing is not twisted.
4. Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle (the buckle closest to the direction the tongue is coming from) for that seating position until you hear and feel the latch engage. Make sure the tongue is latched securely by pulling on it.
94
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
5. To put the retractor in the automatic locking mode, grasp the shoulder portion of the belt and pull downward until all of the belt is extracted and a click is heard.
6. Allow the belt to retract. The belt will click as it retracts to indicate it is in the automatic locking mode. 7. Pull the lap belt portion across the child seat toward the buckle and pull up on the shoulder belt while pushing down with knee on the child seat.
8. Allow the safety belt to retract to remove any slack in the belt. 9. Before placing the child in the seat, forcibly tilt the seat forward and back to make sure the seat is securely held in place. To check this, grab the seat at the belt path and attempt to move it side to side and forward. There should be no more than one inch of movement for proper installation. 10. Try to pull the belt out of the retractor to make sure the retractor is in the automatic locking mode (you should not be able to pull more belt out). If the retractor is not locked, unbuckle the belt and repeat Steps 2
through 9. Check to make sure the child seat is properly secured before each use.95
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Attaching child safety seats with tether straps Most new forward-facing child safety seats include a tether strap which goes over the back of the seat and hooks to an anchoring point. Tether straps are available as an accessory for many older safety seats. Contact the manufacturer of your child seat for information about ordering a tether strap. The tether anchors in your vehicle are located on the back of the front seat cushion. The tether strap anchors in your vehicle are in the following positions (shown from top view): • Bucket seats
• 60/40 seats
Attach the tether strap only to the appropriate tether anchor as shown. The tether strap may not work properly if attached
somewhere other than the correct tether anchor.
1. Position the child safety seat on the front seat cushion. 2. Route the child safety seat tether strap over the back of the seat.
96
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
3. Locate the correct anchor for the selected seating position. The tether anchor is located on the rear lower portion of the passenger seat.
4. Clip the tether strap to the anchor.
97
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Center seating location
When installing a child safety seat in the front center position, route the tether strap over the center arm rest and clip it to the center anchor.
If the tether strap is clipped incorrectly, the child safety seat may not be retained properly in the event of a collision.
5. Install the child safety seat tightly using the safety belt. Follow the instructions in this chapter. 6. Tighten the child safety seat tether strap according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
If the safety seat is not anchored properly, the risk of a child being injured in a collision greatly increases.
98
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Attaching safety seats with LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) attachments for child seat anchors Some child safety seats have two rigid or webbing mounted attachments that connect to two anchors at certain seating positions in your vehicle. This type of child seat eliminates the need to use safety belts to attach the child seat. For forward-facing child seats, the tether strap must also be attached to the proper tether anchor. See Attaching safety seats with tether straps in this chapter. Your vehicle may be equipped with LATCH anchors for child seat installation at the following seating positions:
• Bucket seats
• 60/40 seats
Never attach two LATCH child safety seats to the same anchor. In a crash, one anchor may not be strong enough to hold two
child safety seat attachments and may break, causing serious injury or death.
99
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
The lower anchors for child seat installation are located at the rear section of the front passenger seat between the cushion and seat back. The LATCH anchors are below the locator symbols on the seat back. Two plastic LATCH guides may be obtained at no charge from an authorized dealer (part number 1W4Z-54613F16–AA). They snap onto the LATCH lower anchor in the vehicle to help attach a child seat with rigid LATCH attachments. It will hold the seat foam away and expose the anchor making attachment of the child seat easier.
Follow the child seat manufacturer’s instructions to properly install a child seat with LATCH attachments.
Attach LATCH lower attachments of the child seat only to the anchors shown.
If you install a child seat with rigid LATCH attachments, do not tighten the tether strap enough to lift the child seat off the vehicle seat cushion when the child is seated in it. Keep the tether strap just snug without lifting the front of the child seat. Keeping the child seat just touching the vehicle seat gives the best protection in a severe crash. Each time you use the safety seat, check that the seat is properly attached to the lower anchors and tether anchor. Try to tilt the child seat from side to side. Also try to tug the seat forward. Check to see if the anchors hold the seat in place.
If the safety seat is not anchored properly, the risk of a child being injured in a crash greatly increases.
100
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
NOTICE TO UTILITY VEHICLE AND TRUCK OWNERS Utility vehicles and trucks handle differently than passenger cars in the various driving conditions that are encountered on streets, highways and off-road. Utility vehicles and trucks are not designed for cornering at speeds as high as passenger cars any more than low-slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily under off-road conditions.
Utility vehicles have a significantly higher rollover rate than other types of vehicles. To reduce the risk of serious injury or
death from a rollover or other crash you must: • Avoid sharp turns and abrupt maneuvers; • Drive at safe speeds for the conditions; • Keep tires properly inflated; • Never overload or improperly load your vehicle; and • Make sure every passenger is properly restrained.
In a rollover crash, an unbelted person is significantly more likely to die than a person wearing a seat belt. All occupants must
wear safety belts and children/infants must use appropriate restraints to minimize the risk of injury or ejection.
Study your Owner’s Guide and any supplements for specific information about equipment features, instructions for safe driving and additional precautions to reduce the risk of an accident or serious injury.
VEHICLE CHARACTERISTICS
4WD and AWD Systems (if equipped) A vehicle equipped with AWD or 4WD (when selected) has the ability to use all four wheels to power itself. This increases traction which may enable you to safely drive over terrain and road conditions that a conventional two-wheel drive vehicle cannot.
101
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Power is supplied to all four wheels through a transfer case or power transfer unit. 4WD vehicles allow you to select different drive modes as necessary. Information on transfer case operation and shifting procedures can be found in the Driving chapter. Information on transfer case maintenance can be found in the Maintenance and Specifications chapter. You should become thoroughly familiar with this information before you operate your vehicle. On some 4WD models, the initial shift from two-wheel drive to 4WD while the vehicle is moving can cause a momentary clunk and ratcheting sound. These sounds are normal as the front drivetrain comes up to speed and is not cause for concern.
Do not become overconfident in the ability of 4WD and AWD vehicles. Although a 4WD or AWD vehicle may accelerate better
than two-wheel drive vehicle in low traction situations, it won’t stop any faster than two-wheel drive vehicles. Always drive at a safe speed.
How your vehicle differs from other vehicles SUV and trucks can differ from some other vehicles in a few noticeable ways. Your vehicle may be: • Higher – to allow higher load carrying capacity and to allow it to travel over rough terrain without getting hung up or damaging underbody components. • Shorter – to give it the capability
to approach inclines and drive over the crest of a hill without getting hung up or damaging underbody components. All other things held equal, a shorter wheelbase may make your vehicle quicker to respond to steering inputs than a vehicle with a longer wheelbase.
102
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
• Narrower — to provide greater maneuverability in tight spaces, particularly in off-road use.
As a result of the above dimensional differences, SUV’s and trucks often will have a higher center of gravity and a greater difference in center of gravity between the loaded and unloaded condition. These differences that make your vehicle so versatile also make it handle differently than an ordinary passenger car.
INFORMATION ABOUT UNIFORM TIRE QUALITY GRADING New vehicles are fitted with tires that have a rating on them called Tire Quality Grades. The Quality grades can be found where applicable on the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and maximum section width. For example: • Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature A These Tire Quality Grades are determined by standards that the United States Department of Transportation has set. Tire Quality Grades apply to new pneumatic tires for use on passenger cars. They do not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with nominal rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches or limited production tires as defined in Title 49 Code of Federal Regulations Part 575.104(c)(2). U.S. Department of Transportation-Tire quality grades: The U.S. Department of Transportation requires Ford Motor Company to give you the following information about tire grades exactly as the government has written it.
103
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Treadwear The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one-half (1 1/2) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices, and differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction AA A B C The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B, and C. The grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking traction tests, and does not include
acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature A B C The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
TIRES Tires are designed to give many thousands of miles of service, but they must be maintained in order to get the maximum benefit from them.
104
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
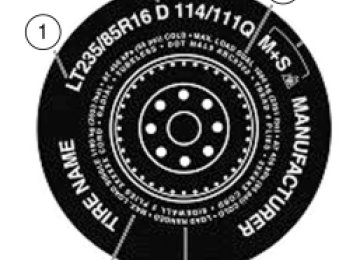
Glossary of tire terminology • Tire label: A label showing the OE (Original Equipment) tire sizes, recommended inflation pressure and the maximum weight the vehicle can carry.
• Tire Identification Number (TIN): A number on the sidewall of each tire providing information about the tire brand and manufacturing plant, tire size and date of manufacture. Also referred to as DOT code.
• Inflation pressure: A measure of the amount of air in a tire. • Standard load: A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a maximum load at 35 psi [37 psi (2.5 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tire’s load carrying capability.
• Extra load: A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a heavier maximum load at 41 psi [43 psi (2.9 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tire’s load carrying capability.
• kPa: Kilopascal, a metric unit of air pressure. • PSI: Pounds per square inch, a standard unit of air pressure. • Cold inflation pressure: The tire pressure when the vehicle has been stationary and out of direct sunlight for an hour or more and prior to the vehicle being driven for 1 mile (1.6 km).
• Recommended inflation pressure: The cold inflation pressure found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label or Tire Label located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. • B-pillar: The structural member at the side of the vehicle behind the • Bead area of the tire: Area of the tire next to the rim. • Sidewall of the tire: Area between the bead area and the tread. • Tread area of the tire: Area of the perimeter of the tire that • Rim: The metal support (wheel) for a tire or a tire and tube assembly
contacts the road when mounted on the vehicle.
front door.
upon which the tire beads are seated.
INFLATING YOUR TIRES Safe operation of your vehicle requires that your tires are properly inflated. Remember that a tire can lose up to half of its air pressure without appearing flat.
105
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Every day before you drive, check your tires. If one looks lower than the others, use a tire gauge to check pressure of all tires and adjust if required. At least once a month and before long trips, inspect each tire and check the tire pressure with a tire gauge (including spare, if equipped). Inflate all tires to the inflation pressure recommended by Ford Motor Company. Use a tire gauge to check the tire inflation pressure, including the spare (if equipped), at least monthly and before long trips. You are strongly urged to buy a reliable tire pressure gauge, as automatic service station gauges may be inaccurate. Ford recommends the use of a digital or dial type tire pressure gauge rather than a stick type tire pressure gauge. Use the recommended cold inflation pressure for optimum tire performance and wear. Under-inflation or over-inflation may cause uneven treadwear patterns.
Under-inflation is the most common cause of tire failures and may result in severe tire cracking, tread separation or ⬙blowout⬙,
with unexpected loss of vehicle control and increased risk of injury. Under-inflation increases sidewall flexing and rolling resistance, resulting in heat buildup and internal damage to the tire. It also may result in unnecessary tire stress, irregular wear, loss of vehicle control and accidents. A tire can lose up to half of its air pressure and not appear to be flat!
Always inflate your tires to the Ford recommended inflation pressure even if it is less than the maximum inflation pressure information found on the tire. The Ford recommended tire inflation pressure is found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label or Tire Label which is located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. Failure to follow the tire pressure recommendations can cause uneven treadwear patterns and adversely affect the way your vehicle handles. Maximum Permissible Inflation Pressure is the tire manufacturer’s maximum permissible pressure and/or the pressure at which the maximum load can be carried by the tire. This pressure is normally higher than the manufacturer’s recommended cold inflation pressure
106
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
which can be found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label or Tire Label which is located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. The cold inflation pressure should never be set lower than the recommended pressure on the Safety Compliance Certification Label or Tire Label. When weather temperature changes occur, tire inflation pressures also change. A 10° F (6° C) temperature drop can cause a corresponding drop of 1 psi (7 kPa) in inflation pressure. Check your tire pressures frequently and adjust them to the proper pressure which can be found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label or Tire Label. If you are checking tire pressure when the tire is hot, (i.e. driven more than 1 mile [1.6 km]), never “bleed” or reduce air pressure. The tires are hot from driving and it is normal for pressures to increase above recommended cold pressures. A hot tire at or below recommended cold inflation pressure could be significantly under-inflated. To check the pressure in your tire(s): 1. Make sure the tires are cool, meaning they are not hot from driving even a mile. Note: If you have to drive a distance to get air for your tire(s), check and record the tire pressure first and add the appropriate air pressure when you get to the pump. It is normal for tires to heat up and the air pressure inside to go up as you drive. Never “bleed” or reduce air pressure when tires are hot. 2. Remove the cap from the valve on one tire, then firmly press the tire gauge onto the valve and measure the pressure. 3. Add enough air to reach the recommended air pressure Note: If you overfill the tire, release air by pushing on the metal stem in the center of the valve. Then recheck the pressure with your tire gauge. 4. Replace the valve cap. 5. Repeat this procedure for each tire, including the spare. Note: Some spare tires operate at a higher inflation pressure than the other tires. For T-type/mini-spare tires (see T-Type/Mini-Spare Tire Information section for description): Store and maintain at 60psi (4.15
bars). For Full Size and Dissimilar spare tires (see Dissimilar Spare Tire/Wheel Information section for description): Store and maintain at the higher of the front and rear inflation pressure as shown on the Tire Label. 6. Visually inspect the tires to make sure there are no nails or other objects embedded that could poke a hole in the tire and cause an air leak.107
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
7. Check the sidewalls to make sure there are no gouges, cuts or bulges.
TIRE CARE
Inspecting your tires Periodically inspect the tire treads for uneven or excessive wear and remove objects such as stones, nails or glass that may be wedged in the tread grooves. Check for holes or cuts that may permit air leakage from the tire and make necessary repairs. Also inspect the tire sidewalls for cracking, cuts, bruises and other signs of damage or excessive wear. If internal damage to the tire is suspected, have the tire demounted and inspected in case it needs to be repaired or replaced. For your safety, tires that are damaged or show signs of excessive wear should not be used because they are more likely to blow out or fail. Improper or inadequate vehicle maintenance can cause tires to wear abnormally. Inspect all your tires, including the spare, frequently, and replace them if one or more of the following conditions exist:
Tire wear When the tread is worn down to 1/16th of an inch (2 mm), tires must be replaced to help prevent your vehicle from skidding and hydroplaning. Built-in treadwear indicators, or “wear bars”, which look like narrow strips of smooth rubber across the tread will appear on the tire when the tread is worn down to 1/16th of an inch (2 mm). When the tire tread wears down to the same height as these “wear bars”, the tire is worn out and must be replaced.
Damage Periodically inspect the tire treads and sidewalls for damage (such as bulges in the tread or sidewalls, cracks in the tread groove and separation in the tread or sidewall). If damage is observed or suspected have the tire inspected by a tire professional. Tires can be damaged during off-road use, so inspection after off-road use is also recommended.
108
2006 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Age Tires degrade over time, even when they are not being used. It is
recommended that tires generally be replaced after 6 years of normal service. Heat caused by hot climates or frequent high loading conditions can accelerate the aging process. You should replace the spare tire when you replace the other road tires due to the aging of the spare tire.
U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number (TIN) Both U.S. and Canada Federal regulations require tire manufacturers to place standardized information on the sidewall of all tires. This information identifies and describes the fundamental characteristics of the tire and also provides a U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number for safety standard certification and in case of a recall. This begins with the letters “DOT” and indicates that the tire meets all federal standards. The next two numbers or letters are the plant code designating where it was manufactured, the next two are the tire size code and the last four numbers represent the week and year the tire was built. For example, the numbers 317 mean the 31st week of 1997. After 2000 the numbers go to four digits. For example, 2501 means the 25th week of 2001. The numbers in between are identification codes used for traceability. This information is used to contact customers if a tire defect requires a recall.
Tire Replacement Requirements Your vehicle is equipped with tires designed to provide a safe ride and handling capability.
Only use replacement tires and wheels that are the same size and type (such as P-metric versus LT-metric or all-season versus
all-terrain) as those originally provided by Ford. Use of any tire or wheel not recommended by Ford can affect the safety and performance of your vehicle, which could result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. Additionally the use of non-recommended tires and wheels could cause steering, suspension, axle or transfer case/power transfer unit failure. If