- 2006 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2016 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2008 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2012 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2004 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2000 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 1998 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2005 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2015 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2010 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2011 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 1997 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2013 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 1996 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2009 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 1999 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2007 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- 2014 Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Ford Mustang Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or collision.
Rear-facing child seats or infant carriers should never be placed in the front seats.
Installing child safety seats with combination lap and shoulder belts
Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat. NEVER place a rear-facing child seat in front of an active air bag. If you must
use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move the seat all the way back.
1. Position the child safety seat in a seat with a combination lap and shoulder belt.
Children 12 and under should be properly restrained in the rear seat whenever possible.
110
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
2. Pull down on the shoulder belt and then grasp the shoulder belt and lap belt together.
3. While holding the shoulder and lap belt portions together, route the tongue through the child seat according to the child seat manufacturer’s instructions. Be sure the belt webbing is not twisted.
4. Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle (the buckle closest to the direction the tongue is coming from) for that seating position until you hear a snap and feel the latch engage. Make sure the tongue is latched securely by pulling on it.
111
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
5. To put the retractor in the automatic locking mode, grasp the shoulder portion of the belt and pull downward until all of the belt is extracted and a click is heard.
6. Allow the belt to retract. The belt will click as it retracts to indicate it is in the automatic locking mode. 7. Pull the lap belt portion across the child seat toward the buckle and pull up on the shoulder belt while pushing down with your knee on the child seat.
8. Allow the safety belt to retract to remove any slack in the belt. 9. Before placing the child in the seat, forcibly move the seat forward and back to make sure the seat is securely held in place. To check this, grab the seat at the belt path and attempt to move it side to side and forward. There should be no more than one inch of movement for proper installation.
10. Try to pull the belt out of the retractor to make sure the retractor is in the automatic locking mode (you should not be able to pull more belt out). If the retractor is not locked, unbuckle the belt and repeat Steps 2
through 9. Check to make sure the child seat is properly secured before each use.112
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Attaching child safety seats with tether straps Most new forward-facing child safety seats include a tether strap which goes over the back of the seat and hooks to an anchoring point. Tether straps are available as an accessory for many older safety seats. Contact the manufacturer of your child seat for information about ordering a tether strap. The rear seats of your vehicle are equipped with built-in tether strap anchors located behind the seats and below the rear window behind the speakers (coupe) or rearward of the seatback in the convertible top sling (convertible). The tether anchors in your vehicle are either located under a cover marked with the child tether anchor symbol (shown with title) or are under a tag marked with the child tether anchor symbol in the convertible top sling. The tether strap anchors in your vehicle are in the following positions (shown from top view):
Attach the tether strap only to the appropriate tether
anchor as shown. The tether strap may not work properly if attached somewhere other than the correct tether anchor.
1. Position the child safety seat on the seat cushion. 2. Route the child safety seat tether strap over the back of the seat. For vehicles with adjustable head restraints, route the tether strap under the head restraint and between the head restraint posts, otherwise route the tether strap over the top of the seatback. 3. Locate the correct anchor for the selected seating position as shown previously.
113
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
For Coupe only: 4. Open the tether anchor covers.
5. Clip the tether strap to the anchor as shown.
For Convertible only: The tether anchors on the convertible are located rearward of the seatback in the convertible top sling. Note: For easier access, attach the tether with the convertible top up.
114
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Note: The attachments for the convertible boot located on the back of the head restraints are not tether anchors.
115
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
4. Access tether anchors located behind the seatback under the vinyl tag marked with the child tether anchor symbol.
5. Clip the tether strap to the anchor as shown.
If the tether strap is clipped incorrectly, the child safety seat may not be retained properly in the event of a collision.
6. Install the child safety seat tightly using the LATCH anchors or safety belts. Follow the instructions in this chapter. 7. Tighten the child safety seat tether strap according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
116
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
If the safety seat is not anchored properly, the risk of a child being injured in a collision greatly increases.
Attaching safety seats with LATCH (Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children) attachments Some child safety seats have two rigid or web mounted attachments that connect to two anchors at certain seating positions in your vehicle. This type of child seat eliminates the need to use safety belts to attach the child seat. For forward-facing child seats, the upper tether strap must also be attached to the proper tether anchor. See Attaching safety seats with tether straps in this chapter. Your vehicle has LATCH anchors for child seat installation at the seating positions marked with the child seat symbol.
The center of the rear seat is NOT designed as a seating position. The LATCH anchors were not designed to be used with a child seat in the center position and there is no tether anchor available at the center. Attempted use of the center as a seating position will increase the risk of injury or death in the event of a collision.
Never attach two LATCH child safety seats to the same anchor. In a crash, one anchor may not be strong enough to hold two
child safety seat attachments and may break, causing serious injury or death.
117
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Seating and Safety Restraints
Locator symbols on the seat cushion indicate the seat has LATCH anchors. The LATCH anchors are located behind the slits in the seat cushion.
Follow the child seat manufacturer’s instructions to properly install a child seat with LATCH attachments.
Attach LATCH lower attachments of the child seat only to the anchors shown.
If you install a child seat with rigid LATCH attachments, do not tighten the tether strap enough to lift the child seat off the vehicle seat cushion when the child is seated in it. Keep the tether strap just snug without lifting the front of the child seat. Keeping the child seat just touching the vehicle seat gives the best protection in a severe crash. Each time you use the safety seat, check that the seat is properly attached to the lower anchors and tether anchor. Try to tilt the child seat from side to side. Also try to tug the seat forward. Check to see if the anchors hold the seat in place.
If the safety seat is not anchored properly, the risk of a child being injured in a crash greatly increases.
118
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
INFORMATION ABOUT UNIFORM TIRE QUALITY GRADING New vehicles are fitted with tires that have a rating on them called Tire Quality Grades. The Quality grades can be found where applicable on the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and maximum section width. For example: • Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature A These Tire Quality Grades are determined by standards that the United States Department of Transportation has set. Tire Quality Grades apply to new pneumatic tires for use on passenger cars. They do not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with nominal rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches or limited production tires as defined in Title 49 Code of Federal Regulations Part 575.104(c)(2). U.S. Department of Transportation-Tire quality grades: The U.S. Department of Transportation requires Ford Motor Company to give you the following information about tire grades exactly as the government has written it.
Treadwear The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one-half (1 1/2) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices, and differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction AA A B C The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B, and C. The grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
119
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking traction tests, and does not include
acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature A B C The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
TIRES Tires are designed to give many thousands of miles of service, but they must be maintained in order to get the maximum benefit from them.
Glossary of tire terminology • Tire label: A label showing the OE (Original Equipment) tire sizes, recommended inflation pressure and the maximum weight the vehicle can carry.
• Tire Identification Number (TIN): A number on the sidewall of
each tire providing information about the tire brand and manufacturing plant, tire size and date of manufacture.
• Inflation pressure: A measure of the amount of air in a tire. • Standard load: A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a maximum load at 35 psi [37 psi (2.5 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tire’s load carrying capability.
• Extra load: A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a heavier maximum load at 41 psi [43 psi (2.9 bar) for Metric tires].
120
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tire’s load carrying capability.
• kPa: Kilopascal, a metric unit of air pressure. • PSI: Pounds per square inch, a standard unit of air pressure. • Cold inflation pressure: The tire pressure when the vehicle has been stationary and out of direct sunlight for an hour or more and prior to the vehicle being driven for 1 mile (1.6 km).
front door.
• Recommended inflation pressure: The cold inflation pressure found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. • B-pillar: The structural member at the side of the vehicle behind the • Bead area of the tire: Area of the tire next to the rim. • Sidewall of the tire: Area between the bead area and the tread. • Tread area of the tire: Area of the perimeter of the tire that • Rim: The metal support (wheel) for a tire or a tire and tube assembly
contacts the road when mounted on the vehicle.
upon which the tire beads are seated.
INSPECTING AND INFLATING YOUR TIRES Safe operation of your vehicle requires that your tires are properly inflated. Remember that a tire can lose up to half of its air pressure without appearing flat. Every day before you drive, check your tires. If one looks lower than the others, use a tire gauge to check pressure of all tires, and adjust if required. At least once a month and before long trips, inspect each tire and check the tire pressure with a tire gauge (including spare, if equipped). Inflate all tires to the inflation pressure recommended by Ford Motor Company.
121
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Inspecting your tires Periodically inspect the tire treads for uneven or excessive wear and remove stones, nails, glass or other objects that may be wedged in the tread grooves. Check for holes or cuts that may permit air leakage from the tire and make necessary repairs. Also inspect the tire sidewalls for cuts, bruises and other damage. If internal damage to the tire is suspected, have the tire demounted and inspected in case it needs to be repaired or replaced. For your safety, tires that are damaged should not be used because they are more likely to blow out or fail. Tires can be damaged during off-road use, so inspection after off-road use is also recommended.
Inflating your tires Use a tire gauge to check the tire inflation pressure, including the spare (if equipped), at least monthly and before long trips. You are strongly urged to buy a reliable tire pressure gauge, as automatic service station gauges may be inaccurate. Ford Motor Company recommends the use of a digital or dial-type tire pressure gauge rather than a stick-type tire pressure gauge. Use the recommended cold inflation pressure for optimum tire performance and wear. Under-inflation or over-inflation may cause uneven treadwear patterns.
Under-inflation is the most common cause of tire failures and may result in severe tire cracking, tread separation or ⬙blowout⬙,
with unexpected loss of vehicle control and increased risk of injury. Under-inflation increases sidewall flexing and rolling resistance, resulting in heat buildup and internal damage to the tire. It also may result in unnecessary tire stress, irregular wear, loss of vehicle control and accidents. A tire can lose up to half of its air pressure and not appear to be flat!
Always inflate your tires to the Ford recommended inflation pressure even if it is less than the maximum inflation pressure information found on the tire. The Ford recommended tire inflation pressure is found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label which is located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. Failure to follow the tire pressure recommendations can cause uneven treadwear patterns and adversely affect the way your vehicle handles.
122
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Maximum Permissible Inflation Pressure is the tire manufactures’ maximum permissible pressure and/or the pressure at which the maximum load can be carried by the tire. This pressure is normally higher than the manufacturer’s recommended cold inflation pressure which can be found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label which is located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. The cold inflation pressure should never be set lower than the recommended pressure on the Safety Compliance Certification Label. When weather temperature changes occur, tire inflation pressures also change. A 10° F (6° C) temperature drop can cause a corresponding drop of 1 psi (7 kPa) in inflation pressure. Check your tire pressures frequently and adjust them to the proper pressure which can be found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label. If you are checking tire pressure when the tire is hot, (i.e. driven more than 1 mile [1.6 km]), never “bleed” or reduce air pressure. The tires are hot from driving and it is normal for pressures to increase above recommended cold pressures. A hot tire at or below recommended cold inflation pressure could be significantly under-inflated. To check the pressure in your tire(s): 1. Make sure the tires are cool, meaning they are not hot from driving even a mile. Note: If you have to drive a distance to get air for your tire(s), check and record the tire pressure first and add the appropriate air pressure when you get to the pump. It is normal for tires to heat up and the air pressure inside to go up as you drive. Never “bleed” or reduce air pressure when tires are hot. 2. Remove the cap from the valve on one tire, then firmly press the tire gauge onto the valve and measure the pressure with the tire gauge. 3. Add enough air to reach the recommended air pressure. Note: If you overfill the tire, release air by pushing on the metal stem in the center of the valve. Then recheck the pressure with your tire gauge. 4. Replace the valve cap. 5. Repeat this procedure for each tire, including the spare. Note: Some spare tires require higher inflation pressure than the other tires. Check the Tire Label on the B pillar or the edge of the driver’s door for the recommended spare tire pressure. 6. Visually inspect the tires to make sure there are no nails or other objects embedded that could poke a hole in the tire and cause an air leak. 7. Check the sidewalls to make sure there are no gouges, cuts or bulges.
123
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
TIRE REPLACEMENT REQUIREMENTS Your vehicle is equipped with tires designed to provide a safe ride and handling capability.
Only use replacement tires and wheels that are the same size and type (such as P-metric versus LT-metric or all-season versus
all-terrain) as those originally provided by Ford. Use of any tire or wheel not recommended by Ford can affect the safety and performance of your vehicle, which could result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. Additionally the use of non-recommended tires and wheels could cause steering, suspension, axle or transfer case/power transfer unit failure. If you have questions regarding tire replacement, see an authorized dealer.
Make sure all tires and wheels on the vehicle are of the same size, type, tread design, brand, load-carrying capacity and speed rating because it can affect the safety and performance of your vehicle, which could result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. Important: Remember to replace the spare tire when you replace the road tires on your vehicle. Even if it has never been used, the spare tire should be replaced because tires degrade over time. Important: Remember to replace the wheel air valves when the road tires are replaced on your vehicle.
CHANGING THE TIRES If you get a flat tire while driving: • do not brake heavily. • gradually decrease the vehicle’s speed. • hold the steering wheel firmly. • slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
The use of tire sealants is not recommended and may damage your tires.
124
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Safety Compliance Label
Temporary Emergency Spare Tire Information Your vehicle may be equipped with a temporary emergency spare tire. This tire may be a T-type/mini-spare tire which will have the words “Temporary Use Only” molded into the tire sidewall or it may be a full size dissimilar spare tire/wheel that is different in brand, size or appearance from the road tire, which will be identified with a “Caution” label on the wheel. Both of these spare tires are considered “temporary”. Replace these temporary emergency spare tires on the vehicle with a tire of the same size, speed rating and load carrying capacity as the other road tires as soon as possible. When driving with the temporary emergency spare tire do not: • Exceed 50 mph (80 km/h) • Exceed 2000 miles (3200 km) • Load the vehicle beyond maximum vehicle load rating listed on the • Tow a trailer • Use snow chains • Use more than one temporary emergency spare tire • Use commercial car washing equipment • Try to repair the temporary emergency spare tire Use of a temporary emergency spare tire at any one wheel location can lead to impairment of the following: • Handling, stability and braking performance • Comfort and noise • Ground clearance and parking at curbs • Winter weather driving capability • Wet weather driving capability How to change a flat tire
To help prevent the vehicle from moving when you change a tire, be sure the parking brake is set, then block (in both directions)
the wheel that is diagonally opposite (other side and end of the vehicle) to the tire being changed.
125
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
If the vehicle slips off the jack, you or someone else could be seriously injured.
Do not attempt to change a tire on the side of the vehicle close to moving traffic. Pull far enough off the road to avoid the
danger of being hit when operating the jack or changing the wheel.
Before changing the tire: 1. Park on a level surface. 2. Activate the hazard flashers. 3. Place the gearshift lever in P (Park) (automatic transmission) or R (Reverse) (manual transmission). 4. Set the parking brake. 5. Turn off the ignition. To change the tire: Note: Passengers should not remain in the vehicle when the vehicle is being jacked. 1. Block both the front and rear of the wheel diagonally opposite the flat tire. For example, if the left front tire is flat, block the right rear wheel.
126
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
2. Remove the lug wrench, spare tire and jack.
3. Remove the center ornament (if equipped) from the wheel. Loosen each wheel lug nut one-half turn counterclockwise but do not remove them until the wheel is raised off the ground.
4. Put the jack in the jack notch next to the tire you are changing. Turn the jack handle clockwise until the wheel is completely off the ground.
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
127
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Never use the rear differential as a jacking point.
To lessen the risk of personal injury, do not put any part of your body under the vehicle while changing a tire. Do not start the engine when your vehicle is on the jack. The jack is only meant for changing the tire.
5. Remove the lug nuts with the lug wrench. 6. Replace the flat tire with the spare tire, making sure the valve stem is facing outward. Reinstall lug nuts until the wheel is snug against the hub. Do not fully tighten the lug nuts until the wheel has been lowered. If you are using the temporary tire, the lug nut washers will not appear to be flush with the rim. This is normal only when using the temporary spare tire. 7. Lower the wheel by turning the jack handle counterclockwise. 8. Remove the jack and fully tighten the lug nuts in the order shown. Refer to Wheel lug nut torque specifications later in this chapter for the proper lug nut torque specification. 9. Put flat tire, wheel ornament (if equipped), jack and lug wrench away. Make sure jack is fastened so it does not rattle when you drive. 10. Unblock the wheels.
128
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
WHEEL LUG NUT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS Retighten the lug nuts to the specified torque at 500 miles (800 km) after any wheel disturbance (tire rotation, changing a flat tire, wheel removal, etc.).
Bolt size
Wheel lug nut torque*
1⁄2 x 20
* Torque specifications are for nut and bolt threads free of dirt and rust. Use only Ford recommended replacement fasteners.lb.ft. 100
N•m 135
When a wheel is installed, always remove any corrosion, dirt or foreign materials present on the mounting surfaces of the wheel
or the surface of the wheel hub, brake drum or brake disc that contacts the wheel. Ensure that any fasteners that attach the rotor to the hub are secured so they do not interfere with the mounting surfaces of the wheel. Installing wheels without correct metal-to-metal contact at the wheel mounting surfaces can cause the wheel nuts to loosen and the wheel to come off while the vehicle is in motion, resulting in loss of control.
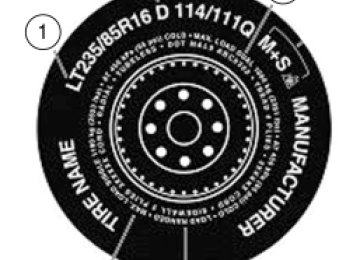
INFORMATION CONTAINED ON THE TIRE SIDEWALL Federal law requires tire manufacturers to place standardized information on the sidewall of all tires. This information identifies and describes the fundamental characteristics of the tire and also provides a U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number for safety standard certification and in case of a recall.
129
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Information on “P” type tires P215/65R15 95H is an example of a tire size, load index and speed rating. The definitions of these items are listed below. (Note that the tire size, load index and speed rating for your vehicle may be different from this example.) 1. P: Indicates a tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA), that may be used for service on cars, SUVs, minivans and light trucks. Note: If your tire size does not begin with a letter this may mean it is designated by either ETRTO (European Tire and Rim Technical Organization) or JATMA (Japan Tire Manufacturing Association). 2. 215: Indicates the nominal width of the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire. 3. 65: Indicates the aspect ratio which gives the tire’s ratio of height to width. 4. R: Indicates a “radial” type tire. 5. 15: Indicates the wheel or rim diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel diameter. 6. 95: Indicates the tire’s load index. It is an index that relates to how much weight a tire can carry. You may find this information in your Owner’s Guide. If not, contact a local tire dealer. Note: You may not find this information on all tires because it is not required by federal law. 7. H: Indicates the tire’s speed rating. The speed rating denotes the speed at which a tire is designed to be driven for extended periods of time under a standard condition of load and inflation pressure. The tires on your vehicle may operate at different conditions for load and inflation pressure. These speed ratings may need to be adjusted for the difference in conditions. The ratings range from 81 mph (130 km/h) to 186 mph (299 km/h). These ratings are listed in the following chart.
130
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Note: You may not find this information on all tires because it is not required by federal law.
Letter rating
Speed rating - mph (km/h)
81 mph (130 km/h) 87 mph (140 km/h) 99 mph (159 km/h) 106 mph (171 km/h) 112 mph (180 km/h) 118 mph (190 km/h) 124 mph (200 km/h) 130 mph (210 km/h) 149 mph (240 km/h) 168 mph (270 km/h) 186 mph (299 km/h) Note: For tires with a maximum speed capability over 149 mph (240 km/h), tire manufacturers sometimes use the letters ZR. For those with a maximum speed capability over 186 mph (299 km/h), tire manufacturers always use the letters ZR. 8. U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number (TIN): This begins with the letters “DOT” and indicates that the tire meets all federal standards. The next two numbers or letters are the plant code designating where it was manufactured, the next two are the tire size code and the last four numbers represent the week and year the tire was built. For example, the numbers 317 mean the 31st week of 1997. After 2000 the numbers go to four digits. For example, 2501 means the 25th week of 2001. The numbers in between are identification codes used for traceability. This information is used to contact customers if a tire defect requires a recall. 9. M+S or M/S: Mud and Snow, or AT: All Terrain, or AS: All Season. 10. Tire Ply Composition and Material Used: Indicates the number of plies or the number of layers of rubber-coated fabric in the tire tread and sidewall. Tire manufacturers also must indicate the ply materials in the tire and the sidewall, which include steel, nylon, polyester, and others. 11. Maximum Load: Indicates the maximum load in kilograms and pounds that can be carried by the tire. Refer to the Safety Compliance Certification Label, which is located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door, for the correct tire pressure for your vehicle.
131
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
12. Treadwear, Traction and Temperature Grades • Treadwear: The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the
wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150
would wear one and one-half (11⁄2) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. • Traction: The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B,and C. The grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
• Temperature: The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel.
13. Maximum Permissible Inflation Pressure: Indicates the tire manufacturers’ maximum permissible pressure and/or the pressure at which the maximum load can be carried by the tire. This pressure is normally higher than the manufacturer’s recommended cold inflation pressure which can be found on the Safety Compliance Certification Label which is located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. The cold inflation pressure should never be set lower than the recommended pressure on the vehicle label. The tire suppliers may have additional markings, notes or warnings such as standard load, radial tubeless, etc.
132
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Additional information contained on the tire sidewall for “LT” type tires “LT” type tires have some additional information beyond those of “P” type tires; these differences are described below: 1. LT: Indicates a tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA), that is intended for service on light trucks. 2. Load Range/Load Inflation Limits: Indicates the tire’s load-carrying capabilities and its inflation limits. 3. Maximum Load Dual lb. (kg) at psi (kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load and tire pressure when the tire is used as a dual; defined as four tires on the rear axle (a total of six or more tires on the vehicle). 4. Maximum Load Single lb. (kg) at psi (kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load and tire pressure when the tire is used as a single; defined as two tires (total) on the rear axle.
133
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Information on “T” type tires “T” type tires have some additional information beyond those of “P” type tires; these differences are described below: T145/80D16 is an example of a tire size. Note: The temporary tire size for your vehicle may be different from this example. 1. T: Indicates a type of tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA), that is intended for temporary service on cars, SUVs, minivans and light trucks. 2. 145: Indicates the nominal width of the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire. 3. 80: Indicates the aspect ratio which gives the tire’s ratio of height to width. Numbers of 70 or lower indicate a short sidewall. 4. D: Indicates a “diagonal” type tire. R: Indicates a “radial” type tire. 5. 16: Indicates the wheel or rim diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel diameter. Location of the tire label You will find a Tire Label containing tire inflation pressure by tire size and other important information located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. Refer to the payload description and graphic in the Vehicle loading — with and without a trailer section. TIRE CARE Improper or inadequate vehicle maintenance can also cause tires to wear abnormally. Here are some of the important maintenance items: Tire wear Measure and inspect the tire tread on all your tires periodically. Advanced and unusual tire wear can reduce the ability of tread to grip
134
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
the road in adverse (wet, snowy, etc.) conditions. Visually check your tires for uneven wear, looking for high and low areas or unusually smooth areas. Also check for signs of tire damage. When the tread is worn down to 1/16th of an inch (2 mm), tires must be replaced to prevent your vehicle from skidding and hydroplaning. Built-in treadwear indicators, or “wear bars”, which look like narrow strips of smooth rubber across the tread will appear on the tire when the tread is worn down to 1/16th of an inch (2 mm). When the tire tread wears down to the same height as these “wear bars”, the tire is worn out and should be replaced. Inspect your tires frequently for any of the following conditions and replace them if one or more of the following conditions exist: • Fabric showing through the tire • Bulges in the tread or sidewalls • Cracks or cuts on the sidewalls • Cracks in the tread groove • Impact damage resulting from use • Separation in the tread • Separation in the sidewall • Severe abrasion on the sidewall If your vehicle has a leak in the exhaust system, a road tire or the spare tire may be exposed to hot exhaust temperatures requiring the tire to be replaced.
rubber
Safety practices Driving habits have a great deal to do with your tire mileage and safety. • Observe posted speed limits • Avoid fast starts, stops and turns • Avoid potholes and objects on the road • Do not run over curbs or hit the tire against a curb when parking
135
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
If your vehicle is stuck in snow, mud, sand, etc., do not rapidly spin the tires; spinning the tires can tear the tire and cause an
explosion. A tire can explode in as little as three to five seconds.
Never spin the tires in excess of the 35 mph (55 km/h) point indicated on the speedometer.
Highway hazards No matter how carefully you drive there’s always the possibility that you may eventually have a flat tire on the highway. Drive slowly to the closest safe area out of traffic. This may further damage the flat tire, but your safety is more important. If you feel a sudden vibration or ride disturbance while driving, or you suspect your tire or vehicle has been damaged, immediately reduce your speed. Drive with caution until you can safely pull off the road. Stop and inspect the tires for damage. If a tire is under-inflated or damaged, deflate it, remove wheel and replace it with your spare tire and wheel. If you cannot detect a cause, have the vehicle towed to the nearest repair facility or tire dealer to have the vehicle inspected.
Tire and wheel alignment A bad jolt from hitting a curb or pothole can cause the front end of your vehicle to become misaligned or cause damage to your tires. If your vehicle seems to pull to one side when you’re driving, the wheels may be out of alignment. Have an authorized dealer check the wheel alignment periodically. Wheel misalignment in the front or the rear can cause uneven and rapid treadwear of your tires and should be corrected by an authorized dealer. Front wheel drive (FWD) vehicles and those with an independent rear suspension (if equipped) may require alignment of all four wheels. The tires should also be balanced periodically. An unbalanced tire and wheel assembly may result in irregular tire wear.
Tire rotation Rotating your tires at the recommended interval (as indicated in the scheduled maintenance information that comes with your vehicle) will help your tires wear more evenly, providing better tire performance and longer tire life. Unless otherwise specified, rotate the tires approximately every 5,000 miles (8,000 km).
136
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
• Front Wheel Drive (FWD)
vehicles (front tires at top of diagram)
• Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) vehicles/Four Wheel Drive (4WD)/ All Wheel Drive (AWD) vehicles (front tires at top of diagram)
137
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Sometimes irregular tire wear can be corrected by rotating the tires. Note: If your tires show uneven wear ask an authorized dealer to check for and correct any wheel misalignment, tire imbalance or mechanical problem involved before tire rotation. Note: Your vehicle may be equipped with a dissimilar spare tire/wheel. A dissimilar spare tire/wheel is defined as a spare tire and/or wheel that is different in brand, size or appearance from the road tires and wheels. If you have a dissimilar spare tire/wheel it is intended for temporary use only and should not be used in a tire rotation. Note: After having your tires rotated, inflation pressure must be checked and adjusted to the vehicle requirements.
SNOW TIRES AND CHAINS
Driving too fast for conditions creates the possibility of loss of vehicle control. Driving at very high speeds for extended periods
of time may result in damage to vehicle components.
Snow tires must be the same size and grade as the tires you currently have on your vehicle.
If your vehicle has P215/65R16 or P235/55R17 tires, they have all weather treads to provide traction in rain or snow. However, in some climates, you may need to use snow tires and chains. Use chains on the tires only in an emergency or if the law requires them. Follow these guidelines when using snow tires and chains: • Chains may damage aluminum wheels. • Use only SAE Class S chains with P215/65R16 tires on the rear of the • Do not use tire chains with size P235/55R17 or P255/45R18 tires. Use of SAE Class S chains or other chain types may damage your vehicle. • Install chains securely, verifying that the chains do not touch any • Drive cautiously. If you hear the chains rub or bang against your
wiring, brake lines or fuel lines.
vehicle only.
vehicle, stop and re-tighten the chains. If this does not work, remove the chains to prevent damage to your vehicle.
• If possible, avoid fully loading your vehicle. • Remove the tire chains when they are no longer needed. Do not use
tire chains on dry roads.
138
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
• The suspension insulation and bumpers will help prevent vehicle damage. Do not remove these components from your vehicle when using snow tires and chains.
VEHICLE LOADING – WITH AND WITHOUT A TRAILER This section will guide you in the proper loading of your vehicle and/or trailer, to keep your loaded vehicle weight within its design rating capability, with or without a trailer. Properly loading your vehicle will provide maximum return of vehicle design performance. Before loading your vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms for determining your vehicle’s weight ratings, with or without a trailer, from the vehicle’s Safety Compliance Certification Label: Base Curb Weight – is the weight of the vehicle including a full tank of fuel and all standard equipment. It does not include passengers, cargo, or optional equipment. Vehicle Curb Weight – is the weight of your new vehicle when you picked it up from your authorized dealer plus any aftermarket equipment.
Payload – is the combined weight of cargo and passengers that the vehicle is carrying. The maximum payload for your vehicle can be found on the Tire Label on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door (vehicles exported outside the US and Canada may not have a Tire Label). Look for “THE COMBINED WEIGHT OF OCCUPANTS AND CARGO SHOULD NEVER EXCEED XXX kg OR XXX lb.” for maximum payload. The payload listed on the Tire Label is the maximum payload for the vehicle as built by the assembly plant. If any aftermarket or authorized-dealer installed equipment has been installed on the vehicle, the weight of the equipment must be subtracted from the payload listed on the Tire Label in order to determine the new payload.
139
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
The appropriate loading capacity of your vehicle can be limited either by volume capacity (how much space is available) or by payload capacity (how much weight the vehicle should carry). Once you have reached the maximum payload of your vehicle, do not add more cargo, even if there is space available. Overloading or improperly loading your vehicle can contribute to loss of vehicle control and vehicle rollover.
Example only:
140
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Cargo Weight – includes all weight added to the Base Curb Weight, including cargo and optional equipment. When towing, trailer tongue load or king pin weight is also part of cargo weight. GAW (Gross Axle Weight) – is the total weight placed on each axle (front and rear) – including vehicle curb weight and all payload. GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating) – is the maximum allowable weight that can be carried by a single axle (front or rear). These numbers are shown on the Safety Compliance Certification Label located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. The total load on each axle must never exceed its GAWR.
Exceeding the Safety Compliance Certification Label axle weight rating limits could result in substandard vehicle handling or
performance, engine, transmission and/or structural damage, serious damage to the vehicle, loss of control and personal injury.
Note: For trailer towing information refer to Trailer towing found in this chapter or the RV and Trailer Towing Guide provided by your authorized dealer.
141
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight) – is the Vehicle Curb Weight + cargo + passengers. GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating) – is the maximum allowable weight of the fully loaded vehicle (including all options, equipment, passengers and cargo). The GVWR is shown on the Safety Compliance Certification Label located on the B-Pillar or the edge of the driver’s door. The GVW must never exceed the GVWR.
Exceeding the Safety Compliance Certification Label vehicle weight rating limits could result in substandard vehicle handling or performance, engine, transmission and/or structural damage, serious damage to the vehicle, loss of control and personal injury.
142
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
GCW (Gross Combined Weight) – is the weight of the loaded vehicle (GVW) plus the weight of the fully loaded trailer. GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating) – is the maximum allowable weight of the vehicle and the loaded trailer – including all cargo and passengers – that the vehicle can handle without risking damage. (Important: The towing vehicles’ braking system is rated for operation at GVWR, not at GCWR. Separate functional brakes should be used for safe control of towed vehicles and for trailers where the GCW of the towing vehicle plus the trailer exceed the GVWR of the towing vehicle. The GCW must never exceed the GCWR. Maximum Loaded Trailer Weight – is the highest possible weight of a fully loaded trailer the vehicle can tow. It assumes a vehicle with only mandatory options, no cargo (internal or external), a tongue load of 10–15% (conventional trailer) or king pin weight of 15–25% (fifth wheel trailer), and driver only (150 lb. [68 kg]). Consult your authorized dealer (or the RV and Trailer Towing Guide provided by your authorized dealer) for more detailed information.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the Safety Compliance Certification Label.
Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities than the originals because they may lower the vehicle’s GVWR and GAWR limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the originals do not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations.
Exceeding any vehicle weight rating limitation could result in serious damage to the vehicle and/or personal injury.
Steps for determining the correct load limit: 1. Locate the statement “The combined weight of occupants and cargo should never exceed XXX kg or XXX lbs.” on your vehicle’s placard.
143
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
2. Determine the combined weight of the driver and passengers that will be riding in your vehicle. 3. Subtract the combined weight of the driver and passengers from XXX kg or XXX lbs. 4. The resulting figure equals the available amount of cargo and luggage load capacity. For example, if the “XXX” amount equals 1,400 lbs. and there will be five 150 lb. passengers in your vehicle, the amount of available cargo and luggage load capacity is 650 lbs. (1400–750 (5 x 150) = 650 lb.). In metric units (635–340 (5 x 68) = 295 kg.) 5. Determine the combined weight of luggage and cargo being loaded on the vehicle. That weight may not safely exceed the available cargo and luggage load capacity calculated in Step 4. 6. If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, load from your trailer will be transferred to your vehicle. Consult this manual to determine how this reduces the available cargo and luggage load capacity of your vehicle. The following gives you a few examples on how to calculate the available amount of cargo and luggage load capacity: • Another example for your vehicle with 1400 lb. (635 kg) of cargo and luggage capacity. You decide to go golfing. Is there enough load capacity to carry you, 4 of your friends and all the golf bags? You and four friends average 220 lb. (99 kg) each and the golf bags weigh approximately 30 lb. (13.5 kg) each. The calculation would be: 1400 – (5 x 220) – (5 x 30) = 1400 – 1100 – 150 = 150 lb. Yes, you have enough load capacity in your vehicle to transport four friends and your golf bags. In metric units, the calculation would be: 635 kg — (5 x 99 kg) — (5 x 13.5 kg) = 635 — 495 — 67.5 = 72.5 kg. • A final example for your vehicle with 1400 lb. (635 kg) of cargo and luggage capacity. You and one of your friends decide to pick up cement from the local home improvement store to finish that patio you have been planning for the past 2 years. Measuring the inside of the vehicle with the rear seat folded down, you have room for 12-100 lb. (45 kg) bags of cement. Do you have enough load capacity to transport the cement to your home? If you and your friend each weigh 220 lb. (99 kg), the calculation would be: 1400 – (2 x 220) – (12 x 100) = 1400 – 440 – 1200 = – 240 lb. No, you do not have enough cargo capacity to carry that much weight. In metric units, the calculation would be: 635 kg — (2 x 99 kg) — (12 x 45 kg) = 635 — 198 — 540 = —103 kg. You will need to reduce the load weight by at least 240 lb. (104 kg). If you remove 3-100 lb. (45 kg) cement bags, then the load calculation would be:
144
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
1400 – (2 x 220) – (9 x 100) = 1400 – 440 – 900 = 60 lb. Now you have the load capacity to transport the cement and your friend home. . In metric units, the calculation would be: 635 kg — (2 x 99 kg) — (9 x 45 kg) = 635 — 198 — 405 = 32 kg.
The above calculations also assume that the loads are positioned in your vehicle in a manner that does not overload the Front or the Rear Gross Axle Weight Rating specified for your vehicle on the Safety Compliance Certification Label found on the edge of the driver’s door.
TRAILER TOWING Your vehicle is capable of towing a trailer up to 1,000 lb. (454 kg) gross trailer weight with a maximum tongue load of 100 lb. (45 kg). Do not tow a trailer until your vehicle has been driven at least 500 miles (800 km). Towing a trailer places an additional load on your vehicle’s engine, transmission, brakes, tires and suspension. Inspect these components carefully after towing.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the certification label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer weight exceeds the limit of the vehicle and could result in
engine damage, transmission damage, structural damage, loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover and personal injury.
Preparing to tow Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer and make sure it is properly attached to your vehicle. See your authorized dealer or a reliable trailer dealer if you require assistance.
Hitches Do not use hitches that clamp onto the vehicle bumper. Use a load carrying hitch. You must distribute the load in your trailer so that 10–15% of the total weight of the trailer is on the tongue.
Safety chains Always connect the trailer’s safety chains to the frame or hook retainers of the vehicle hitch. To connect the trailer’s safety chains, cross the chains under the trailer tongue and allow slack for turning corners.
145
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
If you use a rental trailer, follow the instructions that the rental agency gives to you. Do not attach safety chains to the bumper. Trailer brakes Electric brakes and manual, automatic or surge-type trailer brakes are safe if installed properly and adjusted to the manufacturer’s specifications. The trailer brakes must meet local and Federal regulations.
Do not connect a trailer’s hydraulic brake system directly to your vehicle’s brake system. Your vehicle may not have enough
braking power and your chances of having a collision greatly increase.
The braking system of the tow vehicle is rated for operation at the GVWR not GCWR. Trailer lamps Trailer lamps are required on most towed vehicles. Make sure all running lights, brake lights, turn signals and hazard lights are working. Do not splice into the vehicle lamp wiring for trailer lamps. Your vehicle uses an advanced electronic module to control and monitor your vehicle lamps. Splicing into the wiring or attaching wiring to the vehicle bulb. may DISABLE the rear vehicle lamps or cause them not to function properly. See your authorized dealer for proper instructions and equipment for hooking up trailer lamps. Driving while you tow When towing a trailer: • Turn off the speed control. The speed control may shut off automatically when you are towing on long, steep grades. • Consult your local motor vehicle speed regulations for towing a trailer. • Shift out of D (Overdrive) into D (Overdrive cancelled) or a lower gear (3, 2, or 1) when towing up or down steep hills. This will eliminate excessive downshifting and upshifting for optimum fuel economy and transmission cooling. • Anticipate stops and brake gradually. Servicing after towing If you tow a trailer for long distances, your vehicle will require more frequent service intervals. Refer to your Scheduled Maintenance Guide for more information.
146
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Tires, Wheels and Loading
Trailer towing tips • Practice turning, stopping and backing up before starting on a trip to get the feel of the vehicle trailer combination. When turning, make wider turns so the trailer wheels will clear curbs and other obstacles.
• Allow more distance for stopping with a trailer attached. • The trailer tongue weight should be 10–15% of the loaded trailer • After you have traveled 50 miles (80 km), thoroughly check your • To aid in engine/transmission cooling and A/C efficiency during hot weather while stopped in traffic, place the gearshift lever in P (Park) (automatic transmission) or N (Neutral) (manual transmissions). • Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. If you must
hitch, electrical connections and trailer wheel lug nuts.
weight.
park on a grade, place wheel chocks under the trailer’s wheels.
RECREATIONAL TOWING (ALL WHEELS ON THE GROUND) Follow these guidelines for your specific powertrain combination to tow your vehicle with all four wheels on the ground (such as behind a recreational vehicle). These guidelines are designed to ensure that your transmission is not damaged due to insufficient lubrication. All Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) vehicles: This applies to all cars and 4x2 trucks/sport utilities with rear wheel drive capability. • Place the transmission in N (Neutral) • Maximum speed is 35 mph (56 km/h) • Maximum distance is 50 miles (80 km) If a distance of 50 miles (80 km) or a speed of 35 mph (56 km/h) must be exceeded, you must disconnect the driveshaft. Ford Motor Company recommends the driveshaft be removed/installed only by a qualified technician at an authorized dealer. See your authorized dealer for driveshaft removal/installation. Improper removal/installation of the driveshaft can cause transmission fluid loss, damage to the driveshaft and internal transmission components.
147
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
STARTING
Positions of the ignition 1. OFF/LOCK, locks the steering wheel, automatic transmission gearshift lever and allows key removal. Note: The ignition key cannot be removed from the ignition unless the gearshift lever is securely latched in P (Park). 2. ACCESSORY, allows the electrical accessories such as the radio to operate while the engine is not running. 3. ON, all electrical circuits operational. Warning lights illuminated. Key position when driving. 4. START, cranks the engine. Release the key as soon as the engine starts.
Preparing to start your vehicle Engine starting is controlled by the powertrain control system. This system meets all Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment standard requirements regulating the impulse electrical field strength of radio noise. When starting a fuel-injected engine, don’t press the accelerator before or during starting. Only use the accelerator when you have difficulty starting the engine. For more information on starting the vehicle, refer to Starting the engine in this chapter.
Extended idling at high engine speeds can produce very high temperatures in the engine and exhaust system, creating the risk
of fire or other damage.
Do not park, idle, or drive your vehicle in dry grass or other dry ground cover. The emission system heats up the engine
compartment and exhaust system, which can start a fire.
148
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
Do not start your vehicle in a closed garage or in other enclosed areas. Exhaust fumes can be toxic. Always open the garage door before you start the engine. See Guarding against exhaust fumes in this chapter for more instructions.
If you smell exhaust fumes inside your vehicle, have your dealer inspect your vehicle immediately. Do not drive if you smell
exhaust fumes.
Important safety precautions A computer system controls the engine’s idle revolutions per minute (RPM). When the engine starts, the idle RPM runs higher than normal in order to warm the engine. If the engine idle speed does not slow down automatically, have the vehicle checked. Do not allow the vehicle to idle for more than 10 minutes at the higher engine RPM. Before starting the vehicle: 1. Make sure all vehicle occupants have buckled their safety belts. For more information on safety belts and their proper usage, refer to the Seating and Safety Restraints chapter. 2. Make sure the headlamps and vehicle accessories are off. If starting a vehicle with an automatic transmission:
149
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving • Make sure the gearshift is in P
(Park).
• Make sure the parking brake is
set.
If starting a vehicle with a manual transmission: • Make sure the parking brake is • Push the clutch pedal to the floor
set.
150
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
3. Turn the key to 3 (ON) without turning the key to 4 (START).
Driving
Make sure the corresponding lights illuminate or illuminate briefly. If a light fails to illuminate, have the vehicle serviced. • If the driver’s safety belt is fastened, the
light may not illuminate.
151
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
Starting the engine 1. Turn the key to 3 (ON) without turning the key to 4 (START). If there is difficulty in turning the key, rotate the steering wheel until the key turns freely. 2. Turn the key to 4 (START), then release the key as soon as the engine starts.
Note: If the engine does not start within five seconds on the first try, turn the key to OFF, wait 10 seconds and try again. If the engine still fails to start, press and hold the accelerator to the floor and try again; this will allow the engine to crank with the fuel shut off in case the engine is flooded with fuel. Using the engine block heater (if equipped) An engine block heater warms the engine coolant which aids in starting and heater/defroster performance. Use of an engine block heater is strongly recommended if you live in a region where temperatures reach -10°F (-23°C) or below. For best results, plug the heater in at least three hours before starting the vehicle. The heater can be plugged in the night before starting the vehicle.
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, do not use your heater with ungrounded electrical systems or two-pronged (cheater)
adapters.
Guarding against exhaust fumes Carbon monoxide is present in exhaust fumes. Take precautions to avoid its dangerous effects.
If you smell exhaust fumes inside your vehicle, have your dealer inspect your vehicle immediately. Do not drive if you smell
exhaust fumes.
Important ventilating information If the engine is idling while the vehicle is stopped for a long period of time, open the windows at least one inch (2.5 cm) or adjust the heating or air conditioning to bring in fresh air.
152
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
BRAKES Occasional brake noise is normal. If a metal-to-metal, continuous grinding or continuous squeal sound is present, the brake linings may be worn-out and should be inspected by an authorized dealer. If the vehicle has continuous vibration or shudder in the steering wheel while braking, the vehicle should be inspected by an authorized dealer. Refer to Brake system warning light in the Instrument Cluster chapter for information on the brake system warning light.
BRAKE
Four-wheel anti-lock brake system (ABS) (if equipped) Your vehicle may be equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). This system helps you maintain steering control during emergency stops by keeping the brakes from locking. Noise from the ABS pump motor and brake pedal pulsation may be observed during ABS braking; any pulsation or mechanical noise you may feel or hear is normal.
ABS warning lamp The ABS lamp in the instrument cluster momentarily illuminates when the ignition is turned on. If the light does not illuminate during start up, remains on or flashes, the ABS may be disabled and may need to be serviced. Even when the ABS is disabled, normal braking is still effective. (If your BRAKE warning lamp illuminates with the parking brake released, have your brake system serviced immediately.)
ABS
BRAKE
Using ABS When hard braking is required, apply continuous force on the brake pedal; do not pump the brake pedal since this will reduce the effectiveness of the ABS and will increase your vehicle’s stopping distance. The ABS will be activated immediately, allowing you to retain full steering control during hard braking and on slippery surfaces. However, the ABS does not decrease stopping distance.
153
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
Brake Assist (if equipped) The Brake Assist system provides full braking force during panic braking situations. It detects a rapid application of the brake pedal and maximizes the amount of brake booster assist, helping the driver to achieve maximum braking pressure. Once a panic brake application is detected, the system will remain activated as long as the brake pedal is depressed. The system is deactivated by releasing the brake pedal. When the system activates, the brake pedal will travel with very little effort; this is normal.
Parking brake To set the parking brake (1), pull the parking brake handle up as far as possible.
The BRAKE warning lamp will illuminate and will remain illuminated until the parking brake is released.
BRAKE
To release, press and hold the button (2), pull the handle up slightly, then push the handle down.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure that the gearshift is securely latched in P (Park) (automatic
transmission) or in 1 (First) (manual transmission).
If the parking brake is fully released, but the brake warning lamp remains illuminated, the brakes may not be working properly.
See your authorized dealer as soon as possible.
STEERING To prevent damage to the power steering system: • Never hold the steering wheel at its furthest turning points (until it
stops) for more than a few seconds when the engine is running.
154
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving • Do not operate the vehicle with a low power steering pump reservoir
fluid level (below the MIN mark on the reservoir).
If the power steering system breaks down (or if the engine is turned off), you can steer the vehicle manually, but it takes more effort. If the steering wanders or pulls, check for: • an improperly inflated tire • uneven tire wear • loose or worn suspension components • loose or worn steering components • improper steering alignment A high crown in the road or high crosswinds may also make the steering seem to wander/pull.
TRACTION CONTROL姟 (IF EQUIPPED) Your vehicle may be equipped with a Traction Control娂 system. This system helps you maintain the stability and steerability of your vehicle, especially on slippery road surfaces such as snow- or ice-covered roads and gravel roads. The system operates by detecting and controlling wheel spin. The system borrows many of the electronic and mechanical elements already present in the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS). Wheel-speed sensors allow excess rear wheel spin to be detected by the Traction Control娂 portion of the ABS computer. Any excessive wheel spin is controlled by automatically applying and releasing the rear brakes in conjunction with engine torque reductions. The Traction Control娂 system will allow your vehicle to make better use of available traction on slippery surfaces while you are trying to accelerate or while your foot is on the accelerator pedal. The system is a driver aid which makes your vehicle easier to handle primarily on snow and ice covered roads. During Traction Control娂 operation, the traction control active light will illuminate. If your vehicle is equipped with a message center, a message will display during Traction Control娂 operation. You may hear an electric motor type of sound coming from the engine compartment and the engine will not “rev-up” when you push further on the accelerator. This is normal system behavior and should be no reason for concern.
155
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
The Traction Control娂 switch, located above the radio, illuminates when the system is off. The Traction Control娂 system will automatically turn on every time the ignition is turned OFF and ON. If you should become stuck in snow or ice or on a very slippery road surface, try switching the Traction Control娂 system off. This may allow excess wheel spin to “dig” the vehicle out and enable a successful “rocking” maneuver. The traction control on/off status is shown by an indicator lamp on the traction control switch. If the system is off, the indicator will be illuminated. If a system fault is detected, the traction control active light will illuminate, the Traction Control娂 button will also illuminate and will not turn the system on or off and your vehicle should be serviced by an authorized dealer.
Aggressive driving in any road conditions can cause you to lose control of your vehicle increasing the risk of severe personal injury or property damage. The occurrence of a Traction Control娂 event is an indication that at least some of the tires have exceeded their ability to grip the road; this may lead to an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. If you experience a severe road event, SLOW DOWN.
TRACTION-LOK姟 AXLE (IF EQUIPPED) This axle provides added traction on slippery surfaces, particularly when one wheel is on a poor traction surface. Under normal conditions, the Traction-Lok娂 axle functions like a standard rear axle. Extended use of other than the manufacturer’s specified size tires on a Traction-Lok娂 rear axle could result in a permanent reduction in effectiveness. This loss of effectiveness does not affect normal driving and should not be noticeable to the driver.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
Brake-shift interlock This vehicle is equipped with a brake-shift interlock feature that prevents the gearshift lever from being moved from P (Park) when the ignition is in the ON position unless the brake pedal is depressed.
156
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
If you cannot move the gearshift lever out of P (Park) with ignition in the ON position and the brake pedal depressed: 1. Apply the parking brake, turn ignition key to LOCK, then remove the key. 2. Using a flat head screwdriver, remove the plastic cover. 3. Insert the ignition key and push it straight down to release the interlock.
4. Apply the parking brake, then shift to N (Neutral). 5. Start the vehicle. If it is necessary to use the above procedure to move the gearshift lever, it is possible that a fuse has blown or the vehicle’s brakelamps are not operating properly. Refer to Fuses and relays in the Roadside Emergencies chapter.
Do not drive your vehicle until you verify that the brakelamps are working.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is latched in P (Park). Turn the ignition to the LOCK position and
remove the key whenever you leave your vehicle.
If the parking brake is fully released, but the brake warning lamp remains illuminated, the brakes may not be working properly.
See your authorized dealer.
157
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
Understanding the gearshift positions of the 5–speed automatic transmission
This vehicle is equipped with an adaptive Transmission Shift Strategy. Adaptive Shift Strategy offers the optimal transmission operation and shift quality. When the vehicle’s battery has been disconnected for any type of service or repair, the transmission will need to relearn the normal shift strategy parameters, much like having to reset your radio stations when your vehicle battery has been disconnected. The Adaptive Transmission Strategy allows the transmission to relearn these operating parameters. This learning process could take several transmission upshifts and downshifts; during this learning process, slightly firmer shifts may occur. After this learning process, normal shift feel and shift scheduling will resume. P (Park) This position locks the transmission and prevents the rear wheels from turning. To put your vehicle in gear: • Start the engine • Depress the brake pedal • Move the gearshift lever into the desired gear
158
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
To put your vehicle in P (Park): • Come to a complete stop • Move the gearshift lever and securely latch it in P (Park)
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is latched in P (Park). Turn the ignition to the LOCK position and
remove the key whenever you leave your vehicle.
R (Reverse) With the gearshift lever in R (Reverse), the vehicle will move backward. Always come to a complete stop before shifting into and out of R (Reverse). N (Neutral) With the gearshift lever in N (Neutral), the vehicle can be started and is free to roll. Hold the brake pedal down while in this position. D (Drive) with Overdrive The normal driving position for the best fuel economy. Transmission operates in gears one through five. D (Drive) without Overdrive D (Drive) with Overdrive can be deactivated by pressing the transmission control switch on the right side of the shift handle.
• This position allows for all forward gears except Overdrive. • O/D OFF lamp is illuminated.
O/D OFF
• Provides engine braking. • Use when driving conditions cause excessive shifting from O/D to other gears. Examples: city traffic, hilly terrain, heavy loads, trailer towing and when engine braking is required. • To return to Overdrive mode, press the transmission control switch.
The O/D OFF lamp will not be illuminated.
159
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving • Overdrive mode is automatically returned each time the key is turned
off.
3 (Third) This position allows for third gear only. • Provides engine braking. • To return to D (Drive) without Overdrive, move the transmission shift • Selecting 3 (Third) at higher speeds will cause the transmission to
lever into the D (Drive) position.
downshift to third gear at the appropriate vehicle speed.
2 (Second) This position allows for second gear only. • Provides engine braking. • Use to start-up on slippery roads. • To return to D (Drive) without Overdrive or 3 (Third), move the transmission shift lever into the D (Drive) or 3 (Third) position. • Selecting 2 (Second) at higher speeds will cause the transmission to
downshift to second gear at the appropriate vehicle speed.
1 (First) This position allows for first gear only. • Provides maximum engine braking. • Will not downshift into first gear at high speeds; will cause the
transmission to downshift to a lower gear, then allows for first gear when the vehicle reaches slower speeds.
Forced downshifts • Allowed in Overdrive or Drive. • Depress the accelerator to the floor. • Allows transmission to select an appropriate gear. If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow, it may be rocked out by shifting between forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts in a steady pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear. Do not rock the vehicle if the engine is not at normal operating temperature or damage to the transmission may occur. Do not rock the vehicle for more than a minute or damage to the transmission and tires may occur, or the engine may overheat.
160
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
MANUAL TRANSMISSION OPERATION (IF EQUIPPED)
Driving
Using the clutch The manual transmission has a starter interlock that prevents cranking the engine unless the clutch pedal is fully depressed. To start the vehicle: 1. Make sure the parking brake is fully set. 2. Press the clutch pedal to the floor, then put the gearshift lever in the neutral position. 3. Start the engine, then press the brake pedal and release the parking brake. 4. Move the gearshift lever to 1st gear, then slowly release the clutch pedal while slowly pressing on the accelerator. During each shift, the clutch pedal must be fully depressed to the floor. Failure to fully depress the clutch pedal to the floor may cause increased shift efforts, prematurely wear transmission components or damage the transmission. Make sure the floor mat is properly positioned so it doesn’t interfere with the full extension of the clutch pedal. Do not drive with your foot resting on the clutch pedal or use the clutch pedal to hold your vehicle at a standstill while waiting on a hill. These actions will reduce the life of the clutch.
Recommended shift speeds Do not downshift into 1 (First) when your vehicle is moving faster than 15 mph (24 km/h). This will damage the clutch.
161
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
Upshift according to the following chart:
Upshifts when accelerating (recommended for best fuel
1 - 2
2 - 3
3 - 4
4 - 5economy) Shift from:
11 mph (18 km/h) 19 mph (31 km/h) 30 mph (48 km/h) 40 mph (64 km/h)
Reverse 1. Make sure that your vehicle is at a complete stop before you shift into R (Reverse). Failure to do so may damage the transmission. 2. Move the gearshift lever into the neutral position and wait at least three seconds before shifting into R (Reverse). • The gearshift lever can only be moved into R (Reverse) by moving it from left of 3 (Third) and 4 (Fourth) before shifting into R (Reverse). This is a lockout feature that protects the transmission from accidentally being shifted into R (Reverse) from 5 (Overdrive).
Parking your vehicle 1. Apply the brake and shift into the neutral position. 2. Fully apply the parking brake, then shift into 1 (First). 3. Turn the ignition off.
Do not park your vehicle in Neutral, it may move unexpectedly and injure someone. Use 1 (First) gear and set the parking brake
fully.
162
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Driving
DRIVING THROUGH WATER Do not drive quickly through standing water, especially if the depth is unknown. Traction or brake capability may be limited and if the ignition system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your engine’s air intake and severely damage your engine. If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the hubs (for trucks) or the bottom of the wheel rims (for cars). Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Driving through deep water where the transmission vent tube is submerged may allow water into the transmission and cause internal transmission damage. Have the fluid checked and, if water is found, replace the fluid.
163
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Roadside Emergencies
GETTING ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE To fully assist you should you have a vehicle concern, Ford Motor Company offers a complimentary roadside assistance program. This program is separate from the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. The service is available: • 24–hours, seven days a week • for the New Vehicle Limited Warranty period of three years or 36,000 miles (60,000 km), whichever occurs first on Ford and Mercury vehicles, and four years or 50,000 miles (80,000 km) on Lincoln vehicles.
inflation kit)
Roadside assistance will cover: • a flat tire change with a good spare (except Ford GT which has a tire • battery jump start • lock-out assistance (key replacement cost is the customer’s • fuel delivery (2.0 gallons [7.5L], maximum two occurrences within • towing of your disabled vehicle to the nearest authorized dealer, or
12 month period)
responsibility)
your selling authorized dealer if within 35 miles (56.3 km) of the nearest authorized dealer (one tow per disablement). Even non-warranty related tows, like accidents, are covered (some exclusions apply, such as impound towing or repossession).
Canadian customers refer to your Owner Information Guide for information on: • coverage period • exact fuel amounts • towing of your disabled vehicle • emergency travel expense reimbursement • travel planning benefits USING ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE Complete the roadside assistance identification card and place it in your wallet for quick reference. In the United States, this card is found in the Owner Guide portfolio in the glove compartment. In Canada, the card is found in the Owner Information Guide in the glove compartment. U.S. Ford or Mercury vehicle customers who require roadside assistance, call 1–800–241–3673; Lincoln vehicle customers call 1–800–521–4140.
164
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Roadside Emergencies
Canadian customers who require roadside assistance, call 1–800–665–2006. If you need to arrange roadside assistance for yourself, Ford Motor Company will reimburse a reasonable amount. To obtain reimbursement information, U.S. Ford or Mercury vehicles customers call 1-800-241-3673; Lincoln vehicle customers call 1–800–521–4140. Canadian customers who need to obtain reimbursement information, call 1–800–665–2006.
ROADSIDE COVERAGE BEYOND BASIC WARRANTY In the United States, you may purchase additional roadside assistance coverage beyond this period through the Ford Auto Club by contacting your authorized dealer. Similarly in Canada, for uninterrupted Roadside Assistance coverage, you may purchase extended coverage prior to your Basic Warranty’s Roadside Assistance expiring. For more information and enrollment, contact 1–877–294–2582 or visit our website at www.ford.ca.
HAZARD FLASHER CONTROL The hazard flasher is located on the instrument panel by the radio. The hazard flashers will operate when the ignition is in any position or if the key is not in the ignition. Push in the flasher control and all front and rear direction signals will flash. Press the flasher control again to turn them off. Use it when your vehicle is disabled and is creating a safety hazard for other motorists. Note: With extended use, the flasher may run down your battery.
FUEL PUMP SHUT-OFF SWITCH FUEL RESET This device stops the electric fuel pump from sending fuel to the engine when your vehicle has had a substantial jolt. After an accident, if the engine cranks but does not start, this switch may have been activated.
165
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Roadside Emergencies
The fuel pump shut-off switch is located in the driver’s footwell, by the hood release To reset the switch: 1. Turn the ignition OFF. 2. Check the fuel system for leaks. 3. If no leaks are apparent, reset the switch by pushing in on the reset button. 4. Turn the ignition ON. 5. Wait a few seconds and return the key to OFF. 6. Make another check for leaks.
FUSES AND RELAYS
Fuses If electrical components in the vehicle are not working, a fuse may have blown. Blown fuses are identified by a broken wire within the fuse. Check the appropriate fuses before replacing any electrical components. Note: Always replace a fuse with one that has the specified amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can cause severe wire damage and could start a fire. Standard fuse amperage rating and color
15
COLOR
Standard
fuses
Grey Violet Pink Tan
Maxi fuses
— — — —
Mini fuses
Grey Violet Pink Tan
Cartridge
maxi fuses
Fuse link cartridge
— — — —
— — — —
Fuse rating
2A 3A 4A 5A
166
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Roadside Emergencies
COLOR
Standard
fuses
Maxi fuses
Brown
Red Blue Yellow Natural Green
— — — — —
— — —
Yellow
—
Green Orange
Red Blue Tan
Natural
Cartridge
maxi fuses
— — — Blue — Pink Green Red — — —
Fuse link cartridge
— — — Blue — Pink Green Red Yellow Brown Black
Fuse rating
7.5A 10A 15A 20A 25A 30A 40A 50A 60A 70A 80A
Mini fuses
Brown
Red Blue Yellow Natural Green
— — — — —
Passenger compartment fuse panel The fuse panel is located in the lower passenger side area behind the kick panel. Remove the trim panel cover and the fuse cover to access the fuses. To remove a fuse use the fuse puller tool provided on the fuse panel cover.
167
2005 05+ Mustang (197) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA (fus)
Roadside Emergencies
The fuses are coded as follows:
Fuse/Relay Location
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1718
19
20
21