- 2011 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2004 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 1997 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2007 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2008 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2005 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2006 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2009 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 1998 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2001 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 1999 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2003 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2010 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- 2002 Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Ford Ranger Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
Maintenance and Specifications
Filling the tank The advertised fuel capacity of the fuel tank on your vehicle is equal to the rated refill capacity of the fuel tank as listed in the Refill capacities section of this chapter. The advertised capacity is the amount of the indicated capacity and the empty reserve combined. Indicated capacity is the difference in the amount of fuel in a full tank and a tank when the fuel gauge indicates empty. Empty reserve is the small amount of fuel remaining in the fuel tank after the fuel gauge indicates empty. The amount of usable fuel in the empty reserve varies and should not be relied upon to increase driving range. When refueling your vehicle after the fuel gauge indicates empty, you might not be able to refuel the full amount of the advertised capacity of the fuel tank due to the empty reserve still present in the tank. For consistent results when filling the fuel tank: • Turn the engine/ignition switch to the off position prior to refueling, • Use the same filling rate setting (low — medium — high) each time • Allow no more than 2 automatic click-offs when filling. • Always use fuel with the recommended octane rating. • Use a known quality gasoline, preferably a national brand. • Use the same side of the same pump and have the vehicle facing the • Have the vehicle loading and distribution the same every time. Your results will be most accurate if your filling method is consistent.
an error in the reading will result if the engine is left running.
same direction each time you fill up.
the tank is filled.
Calculating fuel economy 1. Fill the fuel tank completely and record the initial odometer reading (in kilometers or miles). 2. Each time you fill the tank, record the amount of fuel added (in liters or gallons). 3. After at least three to five tank fill-ups, fill the fuel tank and record the current odometer reading. 4. Subtract your initial odometer reading from the current odometer reading.
202
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
5. Follow one of the simple calculations in order to determine fuel economy:
Calculation 1: Multiply liters used by 100, then divide by total kilometers traveled. Calculation 2: Divide total miles traveled by total gallons used.
Keep a record for at least one month and record the type of driving (city or highway). This will provide an accurate estimate of the vehicle’s fuel economy under current driving conditions. Additionally, keeping records during summer and winter will show how temperature impacts fuel economy. In general, lower temperatures give lower fuel economy.
fuel.
economy.
Driving style — good driving and fuel economy habits Give consideration to the lists that follow and you may be able to change a number of variables and improve your fuel economy. Habits • Smooth, moderate operation can yield up to 10% savings in fuel. • Steady speeds without stopping will usually give the best fuel • Idling for long periods of time (greater than one minute) may waste • Anticipate stopping; slowing down may eliminate the need to stop. • Sudden or hard accelerations may reduce fuel economy. • Slow down gradually. • Driving at reasonable speeds (traveling at 88 km/h [55 mph] uses 15% • Revving the engine before turning it off may reduce fuel economy. • Using the air conditioner or defroster may reduce fuel economy. • You may want to turn off the speed control in hilly terrain if unnecessary shifting between third and fourth gear occurs. Unnecessary shifting of this type could result in reduced fuel economy.
less fuel than traveling at 105 km/h [65 mph]).
reduce fuel economy.
• Warming up a vehicle on cold mornings is not required and may • Resting your foot on the brake pedal while driving may reduce fuel • Combine errands and minimize stop-and-go driving.
economy.
203
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Maintenance • Keep tires properly inflated and use only recommended size. • Operating a vehicle with the wheels out of alignment will reduce fuel • Use recommended engine oil. Refer to Lubricant specifications in • Perform all regularly scheduled maintenance items. Follow the
this chapter.
economy.
recommended maintenance schedule and owner maintenance checks found in your vehicle scheduled maintenance guide.
at any speed.
Conditions • Heavily loading a vehicle or towing a trailer may reduce fuel economy • Carrying unnecessary weight may reduce fuel economy (approximately • Adding certain accessories to your vehicle (for example bug
0.4 km/L [1 mpg] is lost for every 180 kg [400 lb] of weight carried).
driving on hilly terrain.
deflectors, rollbars/light bars, running boards, ski/luggage racks) may reduce fuel economy.
12–16 km (8–10 miles) of driving.
cruise gear and with steady pressure on the gas pedal.
• Using fuel blended with alcohol may lower fuel economy. • Fuel economy may decrease with lower temperatures during the first • Driving on flat terrain offers improved fuel economy as compared to • Transmissions give their best fuel economy when operated in the top • Four-wheel-drive operation (if equipped) is less fuel efficient than • Close windows for high speed driving. EPA window sticker Every new vehicle should have the EPA window sticker. Contact your dealer if the window sticker is not supplied with your vehicle. The EPA window sticker should be your guide for the fuel economy comparisons with other vehicles. It is important to note the box in the lower left corner of the window sticker. These numbers represent the Range of L/100 km (MPG) expected on the vehicle under optimum conditions. Your fuel economy may vary depending upon the method of operation and conditions.
two-wheel-drive operation.
204
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM Your vehicle is equipped with various emission control components and a catalytic converter which will enable your vehicle to comply with applicable exhaust emission standards. To make sure that the catalytic converter and other emission control components continue to work properly: • Use only the specified fuel listed. • Avoid running out of fuel. • Do not turn off the ignition while your vehicle is moving, especially at • Have the items listed in your Scheduled Maintenance Guide
high speeds.
performed according to the specified schedule.
The scheduled maintenance items listed in the Scheduled Maintenance Guide are essential to the life and performance of your vehicle and to its emissions system. If other than Ford, Motorcraft or Ford-authorized parts are used for maintenance replacements or for service of components affecting emission control, such non-Ford parts should be equivalent to genuine Ford Motor Company parts in performance and durability.
Do not park, idle, or drive your vehicle in dry grass or other dry ground cover. The emission system heats up the engine
compartment and exhaust system, which can start a fire.
Illumination of the “Check Engine” light, charging system warning light or the temperature warning light, fluid leaks, strange odors, smoke or loss of engine power, could indicate that the emission control system is not working properly.
Exhaust leaks may result in entry of harmful and potentially lethal fumes into the passenger compartment.
Do not make any unauthorized changes to your vehicle or engine. By law, vehicle owners and anyone who manufactures, repairs, services, sells, leases, trades vehicles, or supervises a fleet of vehicles are not permitted to intentionally remove an emission control device or prevent it from working. Information about your vehicle’s emission system is on the Vehicle Emission Control Information Decal located on or near the engine. This decal identifies engine displacement and gives some tune up specifications.
205
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Please consult your Warranty Guide for complete emission warranty information.
On board diagnostics (OBD-II) Your vehicle is equipped with a computer that monitors the engine’s emission control system. This system is commonly known as the On Board Diagnostics System (OBD-II). This OBD-II system protects the environment by ensuring that your vehicle continues to meet government emission standards. The OBD-II system also assists the service technician in properly servicing your vehicle. When the Check engine light illuminates, the OBD-II system has detected a malfunction. Temporary malfunctions may cause your Check engine light to illuminate. Examples are: 1. The vehicle has run out of fuel. (The engine may misfire or run poorly.) 2. Poor fuel quality or water in the fuel. 3. The fuel cap may not have been securely tightened. In which case, the fuel filler cap light will also be illuminated. These temporary malfunctions can be corrected by filling the fuel tank with good quality fuel and/or properly tightening the fuel cap. After three driving cycles without these or any other temporary malfunctions present, the Check engine light should turn off. (A driving cycle consists of a cold engine startup followed by mixed city/highway driving.) No additional vehicle service is required. If the Check engine light remains on, have your vehicle serviced at the first available opportunity.
Readiness for Inspection/Maintenance (I/M) testing In some localities, it may be a legal requirement to pass an I/M test of the on-board diagnostics system. If your Check engine/Service engine soon light is on, refer to the description in the Warning lights and chimes section of the Instrument Cluster chapter. Your vehicle may not pass the I/M test with the Check engine/Service engine soon light on. If the vehicle’s powertrain system or its battery has just been serviced, the on-board diagnostics system is reset to a “not ready for I/M test” condition. To ready the on-board diagnostics system for I/M testing, a minimum of 30 minutes of city and highway driving is necessary as described below: • First, at least 10 minutes of driving on an expressway or highway. 206
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications • Next, at least 20 minutes driving in stop-and-go, city-type traffic with
at least four idle periods.
Allow the vehicle to sit for at least eight hours without starting the engine. Then, start the engine and complete the above driving cycle. The engine must warm up to its normal operating temperature. Once started, do not turn off the engine until the above driving cycle is complete.
CHECKING AND ADDING POWER STEERING FLUID • 2.3L I4 engine
• 3.0L V6 engine
207
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications • 4.0L V6 engine
D O NOT E R FILL
O V
RI
FLUID ERSTEE
POW
Check the power steering fluid. Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the service interval schedules. If adding fluid is necessary, use only MERCON威 ATF. 1. Start the engine and let it run until it reaches normal operating temperature (the engine coolant temperature gauge indicator will be near the center of the normal area between H and C). 2. While the engine idles, turn the steering wheel left and right several times. 3. Turn the engine off. 4. If your vehicle is equipped with a 3.0L V6 engine, check the fluid level on the dipstick. It should be within the FULL HOT range. Do not add fluid if the level is within this range. 5. If your vehicle is equipped with a 4.0L SOHC V6 or 2.3L I4
engine, check the fluid level in the reservoir. It should be between the MIN and MAX lines. Do not add fluid if the level is within this range. 6. If the fluid is low, add fluid in small amounts, continuously checking the level until it reaches the FULL HOT range. Be sure to put the dipstick back in the reservoir.208
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR The fluid level will drop slowly as the brakes wear, and will rise when the brake components are replaced. Fluid levels below the “MAX” line that do not trigger the brake system warning lamp are within the normal operating range, there is no need to add fluid. If the fluid levels are outside of the normal operating range, the performance of your brake system could be compromised, seek service from your dealer immediately.
MAX
CLUTCH FLUID (IF EQUIPPED) Check the fluid level. Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the service interval schedules. During normal operation, the fluid level in the clutch reservoir should remain constant. If the fluid level drops, refill the fluid level to the step in the reservoir. Use only a DOT 3 brake fluid designed to meet Ford specification ESA-M6C25–A. Refer to Lubricant Specifications in this chapter.
Brake fluid is toxic. If brake fluid contacts the eyes, flush eyes with running water for 15 minutes. Seek medical attention if
irritation persists. If taken internally, drink water and induce vomiting. Seek medical attention immediately.
209
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
1. Clean the reservoir cap before removal to prevent dirt and water from entering the reservoir. 2. Remove cap and rubber diaphragm from reservoir. 3. Add fluid until the level reaches the step in the reservoir. 4. Reinstall rubber diaphragm and cap onto reservoir.
TRANSMISSION FLUID
and change intervals.
Checking automatic transmission fluid • Refer to your Scheduled Maintenance Guide for scheduled check • Transmission does not consume fluid. • Check fluid when transmission is not operating properly or if you see • Fluid level must be checked at normal operating temperature, 30 km
a leak.
(20 miles) of driving. To check and add fluid: 1. Drive the vehicle 30 km (20 miles) to reach normal operating temperatures. 2. If driven in hot weather, city traffic, pulling a trailer, allow transmission to cool for 30 minutes before checking. 3. Engage parking brake, start engine. 4. Put your foot on the brake pedal and move the gearshift lever slowly through all of the gear ranges. 5. Shift to P (Park) and leave the engine running. 6. Remove the dipstick, wipe clean with a dry lint free rag. 7. Install and fully seat the dipstick into the filler tube.
210
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
8. Remove the dipstick and inspect the fluid level. Level should be in the cross-hatched area.
9. If necessary, add fluid in 250ml (1/2 pint) increments through the filler tube until the level is correct at normal operating temperatures. Refer to the Lubricant specifications section in this chapter for the correct fluid type. The use of any other non-approved fluid may cause internal transmission damage. 10. Fluid can be checked at ambient temperatures between 10–30°C (50–95°F). DO NOT ADD fluid until the transmission is at normal operating temperatures or the transmission will be overfilled. Low fluid level Do not drive the vehicle if the fluid level is at or below the bottom of the dipstick.
High fluid level Fluid levels above the safe range may cause overheating, shift and/or engagement concerns and internal transmission damage. If an overfill condition occurs, excess fluid should be removed by a qualified technician.
211
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Checking and adding manual transmission fluid (if equipped) 1. Clean the filler plug. 2. Remove the filler plug and inspect the fluid level.
3. Fluid level should be at the bottom of the opening. 4. Add enough fluid through the filler opening so that the fluid level is at the bottom of the opening. 5. Install and tighten the fill plug securely.
Use only fluid that meets Ford specifications. Refer to Lubricant specifications in this chapter.
212
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Checking and adding transfer case fluid (if equipped) 1. Clean the filler plug. 2. Remove the filler plug and inspect the fluid level.
3. Add only enough fluid through the filler opening so that the fluid level is at the bottom of the opening.
Use only fluid that meets Ford specifications. Refer to Lubricant specifications in this chapter.
DRIVELINE UNIVERSAL JOINT AND SLIP YOKE Your vehicle may be equipped with universal joints that require lubrication. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for maintenance intervals. If the original universal joints are replaced with universal joints equipped with grease fittings, lubrication will also be necessary.
213
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
AIR FILTER MAINTENANCE Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the appropriate intervals for changing the air filter element. When changing the air filter element, use only the Motorcraft air filter element listed. Refer to Motorcraft part numbers in this chapter. Note: Do not start your engine with the air cleaner removed and do not remove it while the engine is running.
CHANGING THE AIR FILTER ELEMENT 1. Loosen the clamp that secures the air inlet tube to the engine air filter cover and disconnect the tube from the cover (for V6 only). 2. Release the clamps that secure the air filter housing cover. 3. Carefully separate the two halves of the air filter housing.
4. Remove the air filter element from the air filter housing. 5. Wipe the air filter housing and cover clean to remove any dirt or debris and to ensure good sealing. 6. Install a new air filter element. Be careful not to crimp the filter element edges between the air filter housing and cover. This could cause filter damage and allow unfiltered air to enter the engine if not properly seated.
7. Replace the air filter housing cover and secure the clamps. 8. Replace the air inlet tube and secure the clamp.
214
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Note: Failure to use the correct air filter element may result in severe engine damage. The customer warranty may be voided for any damage to the engine if the correct air filter element is not used.
INFORMATION ABOUT UNIFORM TIRE QUALITY GRADING New vehicles are fitted with tires that have a rating on them called Tire Quality Grades. The Quality grades can be found where applicable on the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and maximum section width. For example: • Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature A These Tire Quality Grades are determined by standards that the United States Department of Transportation has set. Tire Quality Grades apply to new pneumatic tires for use on passenger cars. They do not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with nominal rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches or limited production tires as defined in Title 49 Code of Federal Regulations Part 575.104(c)(2). U.S. Department of Transportation-Tire quality grades: The U.S. Department of Transportation requires Ford to give you the following information about tire grades exactly as the government has written it.
Treadwear The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one-half (1 1/2) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices, and differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction AA A B C The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B, and C. The grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
215
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking traction tests, and does not include
acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature A B C The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded. Excessive speed,
underinflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
TIRES Tires are designed to give many thousands of miles of service, but they must be maintained in order to get the maximum benefit from them.
Glossary of tire terminology • Tire label: A label showing the OE (Original Equipment) tire sizes, recommended inflation pressure and the maximum weight the vehicle can carry.
• Tire Identification Number (TIN): A number on the sidewall of
each tire providing information about the tire brand and manufacturing plant, tire size and date of manufacture.
• Inflation pressure: A measure of the amount of air in a tire. • Standard load: A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a maximum load at 35 psi [37 psi (2.5 bar) for Metric tires]. Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tires load carrying capability. • Extra load: A class of P-metric or Metric tires designed to carry a heavier maximum load at 41 psi [43 psi (2.9 bar) for Metric tires].
216
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Increasing the inflation pressure beyond this pressure will not increase the tires load carrying capability.
• kPa: Kilopascal, a metric unit of air pressure. • PSI: Pounds per square inch, a standard unit of air pressure. • B-pillar: The structural member at the side of the vehicle behind the • Bead area of the tire: Area of the tire next to the rim. • Sidewall of the tire: Area between the bead area and the tread. • Tread area of the tire: Area of the perimeter of the tire that • Rim: The metal support (wheel) for a tire or a tire and tube assembly
contacts the road when mounted on the vehicle.
front door.
upon which the tire beads are seated.
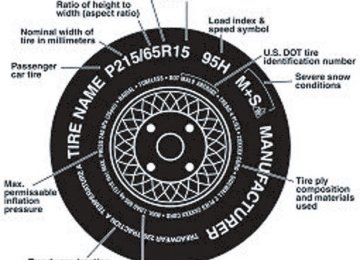
INFORMATION CONTAINED ON THE TIRE SIDEWALL Federal law requires tire manufacturer’s to place standardized information on the sidewall of all tires. This information identifies and describes the fundamental characteristics of the tire and also provides a U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number for safety standard certification and in case of a recall. Information on “P” type tires P215/65R15 95H is an example of a tire size, load index and speed rating. The definitions of these items are listed below. (Note that the tire size, load index and speed rating for your vehicle may be different than this example.) 1. P: Indicates a tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA), that may be used for service on cars, SUVs, minivans and light trucks. Note: If your tire size does not begin with a letter this may mean it is designated by either ETRTO (European Tire and Rim Technical Organization) or JATMA (Japan Tire Manufacturing Association). 2. 215: Indicates the nominal width of the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire.
217
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
3. 65: Indicates the aspect ratio which gives the tire’s ratio of height to width. 4. R: Indicates a “radial” type tire. 5. 15: Indicates the wheel or rim diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel diameter. 6. 95: Indicates the tire’s load index. It is an index that relates to how much weight a tire can carry. You may find this information in your owner’s guide. If not, contact a local tire dealer. Note: You may not find this information on all tires because it is not required by federal law. 7. H: Indicates the tire’s speed rating. The speed rating denotes the speed at which a tire is designed to be driven for extended periods of time under a standard condition of load and inflation pressure. The tires on your vehicle may operate at different conditions for load and inflation pressure. These speed ratings may need to be adjusted for the difference in conditions. The ratings range from 99 mph (159 km/h) to 186 mph (299 km/h). These ratings are listed in the following chart. Note: You may not find this information on all tires because it is not required by federal law.
Letter rating
Speed rating - mph (km/h)
99 mph (159 km/h) 106 mph (171 km/h) 112 mph (180 km/h) 118 mph (190 km/h) 124 mph (200 km/h) 130 mph (210 km/h) 149 mph (240 km/h) 168 mph (270 km/h) 186 mph (299 km/h)
Note: For tires with a maximum speed capability over 149 mph (240
km/h), tire manufacturers sometimes use the letters ZR. For those with a maximum speed capability over 186 mph (299 km/h), tire manufacturers always use the letters ZR.218
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
8. U.S. DOT Tire Identification Number (TIN): This begins with the letters “DOT” and indicates that the tire meets all federal standards. The next two numbers or letters are the plant code where it was manufactured, the next two are the tire size code and the last four numbers represent the week and year the tire was built. For example, the numbers 317 mean the 31st week of 1997. After 2000 the numbers go to four digits. For example, 2501 means the 25th week of 2001. The numbers in between are identification codes used for traceability. This information is used to contact customers if a tire defect requires a recall. 9. M+S or M/S: Mud and Snow. or AT: All Terrain. or AS: All Season. 10. Tire Ply Composition and Material Used: Indicates the number of plies or the number of layers of rubber-coated fabric in the tire tread and sidewall. Tire manufacturers also must indicate the ply materials in the tire and the sidewall, which include steel, nylon, polyester, and others. 11. Maximum Load: Indicates the maximum load in kilograms and pounds that can be carried by the tire. Refer to the tire label or the safety certification label, located on the B-Pillar or the driver’s door, for the correct tire pressure for your vehicle 12. Treadwear, Traction and Temperature Grades • Treadwear: The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the
wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150
would wear one and one-half (11⁄2) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. • Traction: The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B,and C. The grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
• Temperature: The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel.
219
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
13. Maximum Permissible Inflation Pressure: Tire manufacturer’s maximum permissible pressure and/or the pressure at which the maximum load can be carried by the tire. This pressure is normally higher than the manufacturer’s recommended cold inflation pressure which can be found on either the tire label or certification label which is located on the structure by the trailing edge of the driver’s door or the edge of the driver’s door. The cold inflation pressure should never be set lower than the recommended pressure on the vehicle label. The tire suppliers may have additional markings, notes or warnings such as standard load, radial tubeless, etc.
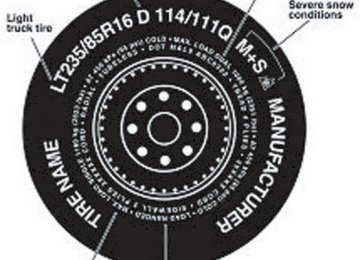
Additional information contained on the tire sidewall for “LT” type tires “LT” type tires have some additional information than those of “P” type tires; these differences are described below: 1. LT: Indicates a tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA), that is intended for service on light trucks. 2. Load Range/Load Inflation Limits: Indicates the tires load-carrying capabilities and its inflation limits. 3. Maximum Load Dual lbs. (kg) at psi (kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load and tire pressure when the tire is used as a dual; a dual is defined as when four tires are put on the rear axle (a total of six or more tires on the vehicle). 4. Maximum Load Single lbs. (kg) at psi (kPa) cold: Indicates the maximum load and tire pressure when the tire is used as a single; a single is defined as when two tires (total) are put on the rear axle.
220
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Information on “T” type tires T145/80D16 is an example of a tire size. Note: The temporary tire size for your vehicle may be different than this example. 1. T: Indicates a type of tire, designated by the Tire and Rim Association (T&RA), that is intended for temporary service on cars, SUVs, minivans and light trucks. 2. 145: Indicates the nominal width of the tire in millimeters from sidewall edge to sidewall edge. In general, the larger the number, the wider the tire. 3. 80: Indicates the aspect ratio which gives the tires ratio of height to width. Numbers of 70 or lower indicate a short sidewall. 4. D: Indicates a “diagonal” type tire. R: Indicates a “radial” type tire. 5. 16: Indicates the wheel or rim diameter in inches. If you change your wheel size, you will have to purchase new tires to match the new wheel diameter.
Location of the tire label You will find a tire label containing tire inflation pressure by tire size and other important information located on the B-Pillar or the driver’s door.
TIRE CARE Improper or inadequate vehicle maintenance can also cause tires to wear abnormally. Here are some of the important maintenance items:
Inflating your tires Use a tire gauge to check the tire inflation pressure, including the spare, at least monthly and before long trips. You are strongly urged to buy a reliable tire pressure gauge, as automatic service station gauges may be inaccurate. Ford recommends the use of a digital or dial type tire pressure gauge rather than a stick type tire pressure gauge.
221
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Use the recommended cold inflation pressure for optimum tire performance and wear. Under-inflation or over-inflation may cause uneven treadwear patterns.
Under-inflation is the most common cause of tire failures and may result in severe tire cracking, tread separation or ⬙blowout⬙,
with unexpected loss of vehicle control and increased risk of injury. Under-inflation increases sidewall flexing and rolling resistance, resulting in heat buildup and internal damage to the tire. It also may result in unnecessary tire stress, irregular wear, loss of vehicle control and accidents. A tire can lose up to half of its air pressure and not appear to be flat!
When weather temperature changes occur, tire inflation pressures also change. A 10° F (6° C) temperature change can cause a corresponding drop of 1 psi (7 kPa) in inflation pressure. Check your tire pressures frequently and adjust them to the proper pressure which can be found on the tire label or certification label. If you are checking tire pressure when the tire is hot, (i.e. driven more than 1 mile [1.6 km]), never “bleed” or reduce air pressure. The tires are hot from driving and it is normal for pressures to increase above recommended cold pressures. A hot tire at or below recommended cold inflation pressure could be significantly under-inflated. To check the pressure in your tire(s): 1. Make sure the tires are cool, meaning they are not hot from driving even a mile. Note: If you have to drive a distance to get air for your tire(s), check and record the tire pressure first and add the appropriate air pressure when you get to the pump. It is normal for tires to heat up and the air pressure inside to go up as you drive. Never “bleed” or reduce air pressure when tires are hot. 2. Remove the cap from the valve on one tire, then firmly press the tire gauge onto the valve and measure the pressure. 3. Add enough air to reach the recommended air pressure Note: If you overfill the tire, release air by pushing on the metal stem in the center of the valve. Then recheck the pressure with your tire gauge. 4. Replace the valve cap. 5. Repeat this procedure for each tire, including the spare. Note: Some spare tires require higher inflation pressure than the other tires. Check the tire label on the B pillar or the driver’s door for the recommended spare tire pressure.
222
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
6. Visually inspect the tires to make sure there are no nails or other objects embedded that could poke a hole in the tire and cause an air leak. 7. Check the sidewalls to make sure there are no gouges, cuts or bulges.
Tire and wheel alignment A bad jolt from hitting a curb or pothole can cause the front end of your vehicle to become misaligned or damage to your tires. If your vehicle seems to pull to one side when you’re driving, the wheels may be out of alignment. Have a qualified technician at a Ford or Lincoln/Mercury dealer check the wheel alignment periodically. Wheel misalignment in the front or the rear can cause uneven and rapid treadwear of your tires and should be corrected by a qualified technician at a Ford or Lincoln/Mercury dealer. Front wheel drive (FWD) vehicles, and those with an independent rear suspension require alignment of all four wheels. The tires should also be balanced periodically. An unbalanced tire and wheel assembly may result in irregular tire wear.
Tire rotation Rotating your tires at the recommended interval (as indicated in the Scheduled Maintenance Guide that comes with your vehicle) will help your tires wear more evenly providing better tire performance and longer tire life. Unless otherwise specified, rotate the tires approximately every 5,000 miles (8,000 km).
223
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications • Front Wheel Drive (FWD)
vehicles (front tires at top of diagram)
• Rear Wheel Drive (RWD)
vehicles/Four Wheel Drive (4WD) vehicles (front tires at top of diagram)
224
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Sometimes irregular tire wear can be corrected by rotating the tires. Note: If your tires show uneven wear ask a qualified technician at a Ford or Lincoln/Mercury dealership to check for and correct any wheel misalignment, tire imbalance or mechanical problem involved before tire rotation. Note: Your vehicle may be equipped with a dissimilar spare tire/wheel. A dissimilar spare tire/wheel is defined as a spare tire and/or wheel that is different in brand, size or appearance from the road tires and wheels. If you have a dissimilar spare tire/wheel it is intended for temporary use only and should not be used in a tire rotation. Note: After having your tires rotated, inflation pressure must be checked and adjusted to the vehicle requirements.
Tire wear Measure and inspect the tire tread on all your tires periodically. Advanced and unusual tire wear can reduce the ability of tread to grip the road in adverse (wet, snowy, etc.) conditions. Visually check your tires for uneven wear, looking for high and low areas or unusually smooth areas. Also check for signs of tire damage. When the tread is worn down to 1/16th of an inch (2 mm), tires must be replaced to prevent your vehicle from skidding and hydroplaning. Built-in treadwear indicators, or “wear bars”, which look like narrow strips of smooth rubber across the tread will appear on the tire when the tread is worn down to 1/16th of an inch (2 mm). When you see these “wear bars”, the tire is worn out and should be replaced. Inspect your tires frequently for any of the following conditions and replace them if one or more of the following conditions exist: • Fabric showing through the tire rubber • Bulges in the tread or sidewalls • Cracks or cuts on the sidewalls • Cracks in the tread groove • Impact damage resulting from use • Separation in the tread • Separation in the sidewall
225
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications • Severe abrasion on the sidewall If your vehicle has a leak in the exhaust system, a road tire or the spare tire may be exposed to hot exhaust temperatures requiring the tire to be replaced.
Tire Replacement Requirements Your vehicle is equipped with tires designed to provide safe ride and handling capability.
Only use replacement tires and wheels that are the same size and type (such as P-metric versus LT-metric or all-season versus
all-terrain) as those originally provided by Ford. Use of any tire or wheel not recommended by Ford can affect the safety and performance of your vehicle, which could result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. Additionally the use of non-recommended tires and wheels could cause steering, suspension, axle or transfer case/power transfer unit failure. If you have questions regarding tire replacement, see an authorized Ford or Lincoln/Mercury dealer.
Make sure all tires and wheels on the vehicle are of the same size, type, tread design, brand, load-carrying capacity and speed rating because it can affect the safety and performance of your vehicle, which could result in an increased risk of loss of vehicle control, vehicle rollover, personal injury and death. You should replace the spare tire when you replace the other road tires due to the aging of the spare tire.
Safety practices Driving habits have a great deal to do with your tire mileage and safety. • Observe posted speed limits • Avoid fast starts, stops and turns • Avoid potholes and objects on the road • Do not run over curbs or hit the tire against a curb when parking If your vehicle is stuck in snow, mud, sand, etc., do not rapidly spin the tires; spinning the tires can tear the tire and cause an explosion. A tire can explode in as little as three to five seconds.
226
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Tire explosions can cause death, personal injury or property damage. Do not allow anyone to stand near, directly ahead or
behind the spinning tire.
Never spin the tires in excess of the 35 mph (55 km/h) point indicated on the speedometer.
Highway hazards No matter how carefully you drive there’s always the possibility that you may eventually have a flat tire on the highway. Drive slowly to the closest safe area out of traffic. This may further damage the flat tire, but your safety is more important. If you feel a sudden vibration or ride disturbance while driving, or you suspect your tire or vehicle has been damaged, immediately reduce your speed. Drive with caution until you can safely pull off the road. Stop and inspect the tires for damage. If a tire is under-inflated or damaged, deflate it, remove wheel and replace it with your spare tire and wheel. If you cannot detect a cause, have the vehicle towed to the nearest repair facility or tire dealer to have the vehicle inspected.
SNOW TIRES AND CHAINS
Driving too fast for conditions creates the possibility of loss of vehicle control. Driving at very high speeds for extended periods
of time may result in damage to vehicle components.
Snow tires must be the same size and grade as the tires you currently have on your vehicle.
The tires on your vehicle have all weather treads to provide traction in rain and snow. However, in some climates, you may need to use snow tires and chains. If you need to use snow tires and chains, it is recommended that steel wheels are used of the same size and specifications as those originally installed. Follow these guidelines when using snow tires and chains: • Do not use tire chains on aluminum wheels. Chains may chip the • Use only SAE Class S chains.
wheels.
227
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
2.3L I4
engine FA-1658Maintenance and Specifications • Install chains securely, verifying that the chains do not touch any • Drive cautiously. If you hear the chains rub or bang against your
wiring, brake lines or fuel lines.
vehicle, stop and re-tighten the chains. If this does not work, remove the chains to prevent damage to your vehicle.
• If possible, avoid fully loading your vehicle. • Remove the tire chains when they are no longer needed. Do not use • The suspension insulation and bumpers will help prevent vehicle damage. Do not remove these components from your vehicle when using snow tires and chains.
tire chains on dry roads.
MOTORCRAFT PART NUMBERS Component
3.0L V6 engine
4.0L V6 engine
FA-1658
FA-1658
FG-1080
BXT-59
FL-820SFG-1080
BXT-59
FL-400SFG-1080
BXT-59
FL-400SAir filter element Fuel filter Battery Oil filter PCV valve Spark plugs 1The PCV valve is a critical emission component. It is one of the items listed in the Scheduled Maintenance Guide and is essential to the life and performance of your vehicle and to its emissions system. For PCV valve replacement, see your dealer or a qualified service technician. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the appropriate intervals for changing the PCV valve. Replace the PCV valve with one that meets Ford material and design specifications for your vehicle, such as a Motorcraft or equivalent replacement part. The customer warranty may be void for any damage to the emissions system if such a PCV valve is not used. 2For spark plug replacement, see your dealer or a qualified service technician. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the appropriate intervals for changing the spark plugs.
228
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Replace the spark plugs with ones that meet Ford material and design specifications for your vehicle, such as Motorcraft or equivalent replacement parts. The customer warranty may be void for any damage to the engine if such spark plugs are not used. Refer to Vehicle Emissions Control Information (VECI) decal for spark plug gap information.
REFILL CAPACITIES Fluid
Engine oil (includes filter change)7
Brake fluid and Clutch fluid
Power steering fluid
Ford Part Name Motorcraft SAE 5W- 20 Premium Synthetic Blend Motor Oil (US) Motorcraft SAE 5W-20 Super Premium Motor Oil (Canada) Motorcraft SAE 5W- 30 Super Premium Motor Oil Motorcraft High Performance DOT 3 Motor Vehicle Brake Fluid Motorcraft MERCON威 ATF
Application
Capacity
2.3L engine
3.0L V6 engine
4.0L V6 engine
3.8L (4.0
quarts)4.3L (4.5
quarts)4.7L (5.0
quarts)All
Fill to line or step (for clutch) on reservoir
3.0L engine
2.3L and 4.0L engine
Fill to FULL HOT line on dipstick Fill to MAX line on the reservoir
229
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Fluid
Transmission fluid 1
Ford Part Name Motorcraft MERCON威 ATF Motorcraft MERCON威V ATF
Engine coolant 4 Motorcraft
Premium Gold Engine Coolant (yellow-colored)
Application
Capacity
5-speed manual
4x2 vehicles with automatic and 2.3L I4
engine 4x2 vehicles with automatic and 3.0L or 4.0L engines 4x4 vehicles with automatic and 3.0L or 4.0L 2.3 L I4 engine with manual transmission 2.3L I4 engine with automatic transmission 3.0L V6 engine with manual transmission 3.0L V6 engine with automatic transmission 4.0L V6 engine with manual transmission 4.0L V6 engine with automatic transmission2.65L (2.8
quarts) 3
9.4L (9.9
quarts) 29.5L (10.0
quarts)29.8L (10.3
quarts) 210.0L (10.5
quarts)9.7L (10.2
quarts)14.3L (15.1
quarts)14.0L (14.8
quarts)13.0L (13.7
quarts)12.5L (13.2
quarts)230
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Fluid
Fuel tank
Ford Part Name N/A
Transfer case Fluid Front axle lubricant
Rear axle lubricant5, 6
Rear axle lubricant (FX4
Level II only)6Windshield washer fluid
Motorcraft MERCON威 ATF Motorcraft SAE 80W-90
Premium Rear Axle Lubricant Motorcraft SAE 80W-90
Premium Rear Axle Lubricant Motorcraft SAE 75W-140
Synthetic Rear Axle Lubricant Motorcraft Premium Windshield Washer ConcentrateApplication
Capacity
Regular cab (Short wheel base) Regular cab (Long wheel base) SuperCab
4x4 Vehicles
4x4 Vehicles
64.4L (17
gallons)76.8L (20.3
gallons)73.8L (19.5
gallons) 1.2L (1.25
quarts) 1.7L (3.6 pints)All (except FX4
Level II)2.4-2.5L (5.0-5.3
pints)FX4 Level II only
2.5-2.6L (5.25-5.5 pints)
All
2.6L (2.75
quarts)1Ensure the correct automatic transmission fluid is used. Transmission fluid requirements are indicated on the dipstick or on the dipstick handle. MERCON威 and MERCON威 V are not interchangeable. DO NOT mix MERCON威 and MERCON威V. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide to determine the correct service interval.
231
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
2Indicates only approximate dry-fill capacity. Some applications may vary based on cooler size and if equipped with an in-tank cooler. The amount of transmission fluid and fluid level should be set by the indication on the dipstick’s normal operating range. 3Service refill capacity for the manual transmission is determined by filling the transmission to the bottom of the filler hole with the vehicle on a level surface. 4Add the coolant type originally equipped in your vehicle. 5Traction-Lok axles use 2.2–2.4L (4.75–5.0 pints) of rear axle lubricant. 6Add 118 ml (4 oz.) of Additive Friction Modifier XL–3 or equivalent meeting Ford specification EST-M2C118–A for complete refill of Traction-Lok axles. Service refill capacities are determined by filling the rear axle 6 mm to 14 mm (1/4 inch to 9/16 inch) below the bottom of the filler hole. 7Use of synthetic or synthetic blend motor oil is not mandatory. Engine oil need only meet the requirements of Ford specification WSS-M2C153–H and the API Certification mark.
LUBRICANT SPECIFICATIONS
Ford part number
Ford specification
XY-80W90-QL
WSP-M2C197-A
XY-80W90-QL
WSP-M2C197-A
XY-75W140–QL
WSL-M2C192–A
Ford part name or equivalent Motorcraft SAE 80W-90
Premium Rear Axle Lubricant Motorcraft SAE 80W-90
Premium Rear Axle Lubricant1
Motorcraft SAE 75W-140
Synthetic Rear Axle Lubricant1Item
Front axle (4X4)
Rear axle
Rear axle (FX4
Level II only)232
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Ford part number
PM-1
Ford specification
ESA-M6C25-A and DOT 3
XL-6
ESR-M13P4-A
VC-7-A (U.S., except CA and OR), VC-7-B (CA and OR only) XO-5W20-QSP (US) CXO-5W20–LSP12
(Canada)WSS-M97B51-A1
WSS-M2C153-H and API Certification Mark
XO-5W30-QSP
XG-4 or XL-5
WSS-M2C205–A and API Certification Mark
ESB-M1C159-A or ESB-M1C93-B
233
Item
Brake fluid and clutch fluid (if equipped)
Ford part name or equivalent Motorcraft High Performance DOT 3 Motor Vehicle Brake Fluid Silicone Door weather strips Lubricant Engine coolant Motorcraft
Premium Gold Engine Coolant (yellow-colored) 2.3L and 3.0L engines Motorcraft SAE 5W-20 Premium Synthetic Blend Motor Oil (US) Motorcraft SAE 5W-20 Super Premium Motor Oil (Canada) 4.0L engines Motorcraft SAE 5W-30 Super Premium Motor Oil Multi-Purpose Grease
Engine oil
Hinges, door checks, latches, striker plates, fuel filler door hinge and seat tracks
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Item
Transmission /steering/parking brake linkages and pivots, brake and clutch pedal shaft, clutch pilot bearing and. input shaft spline (manual transmission) Power steering fluid, transfer case fluid (4X4) and transmission fluid (manual) Automatic transmission (5R44E and 5R55E)
Windshield washer fluid
Ford part number
Ford specification
XG-1-C or XG-1-K ESA-M1C75-B
Ford part name or equivalent Motorcraft Premium Long-Life Grease
Motorcraft MERCON威 ATF
XT-2-QDX
MERCON威
XT-5-QM
MERCON威V
ZC-32–A
WSB-M8B16–A2
Motorcraft MERCON威V ATF 2
Motorcraft Premium Windshield Washer Concentrate
1Add 118 ml (4 oz.) of Additive Friction Modifier XL-3 or equivalent meeting Ford specification EST-M2C118–A for complete refill of Traction-Lok axles. 2Ensure the correct automatic transmission fluid is used. Transmission fluid requirements are indicated on the dipstick or on the dipstick handle. MERCON威 and MERCON威 V are not interchangeable. DO NOT mix MERCON威 and MERCON威 V. Refer to your Scheduled Maintenance Guide to determine the correct service interval.
234
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
2.3L I4 engine 3.0L V6 engine 4.0L V6 engine 138
87 octane 1-3-4-2182
87 octane 1-4-2-5-3-6
EDIS 9.7:1245
87 octane 1-4-2-5-3-6
EDIS 9.7:1ENGINE DATA Engine Cubic inches Required fuel Firing order Ignition system EDIS Compression ratio
9.7:1
VEHICLE DIMENSIONS Vehicle dimensions
Regular Cab Short Wheel Base (SWB) mm (in) 4787 (188.4)
Regular Cab Long Wheel Base (LWB) mm (in) 5092 (200.4)
Supercab mm (in)
5124 (201.7)
1785 (70.3)
1785 (70.3)
1785 (70.3)
1651 (65.0) / 1727 (68.0) 2831 (111.4) 1486 (58.5)
1651 (65.0) / 1727 (68.0) 2983 (117.4) 1486 (58.5)
1651 (65.0) / 1727 (68.0) 3192 (125.7) 1485 (58.5)
1455 (57.3)
1455 (57.3)
1455 (57.3)
(1) Overall length (2) Overall width (3) Overall height 4x2/4x4
(4) Wheelbase (5) Track - Front (5) Track - Rear235
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
236
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
IDENTIFYING YOUR VEHICLE
Certification label The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Regulations require that a Certification label be affixed to a vehicle and prescribe where the Certification label may be located. The Certification label is located on the structure by the trailing edge of the driver’s door or the edge of the driver’s door.
237
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Maintenance and Specifications
Vehicle identification number (VIN) The vehicle identification number is attached to a metal tag and is located on the driver side instrument panel. (Please note that in the graphic XXXX is representative of your vehicle identification number.)
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Engine number The engine number (the last eight numbers of the vehicle identification number) is stamped on the engine block, transmission, frame and transfer case (if equipped). TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE CODE DESIGNATIONS
You can find a transmission/transaxle code on the vehicle certification label which is located on the door pillar. The following table tells you which transmission or transaxle each code represents.
238
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
TRUCK APPLICATION: Code
PASSENGER CAR APPLICATION: Code
Maintenance and Specifications
Transmission Description Manual transmission Manual 5–speed (AKK)) Manual 5–speed overdrive (Close ratio) Manual 5–speed overdrive (Dana ZF) Manual 6–speed ZF Automatic transmission Automatic 4–speed overdrive (CD4E) Automatic 4–speed overdrive (4R70W) Automatic 4–speed overdrive (4R44E) Automatic 4–speed overdrive (4R100) Automatic 5–speed overdrive (5R55E) Electric One speed electric Automatic 5–speed overdrive (5R44E) Automatic 5–speed overdrive (5R55S)
Transmission/Transaxle Description Front wheel drive manual transaxle 5–speed overdrive (MTX75) 5–speed overdrive (M5) Front wheel drive automatic transaxle 4–speed overdrive (4F27E) 4–speed overdrive (4FE) 3–speed (Mazda) 4–speed overdrive (AX4S) 4–speed overdrive (4F20E) 4–speed overdrive (4F50N) 4–speed overdrive (CD4E) Rear wheel drive manual transaxle 5–speed (Mazda M5) Rear wheel drive automatic transmission 4–speed overdrive (4R70W) 5–speed overdrive (5R55N)
239
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Accessories
GENUINE FORD ACCESSORIES FOR YOUR VEHICLE A wide selection of Genuine Ford Accessories are available for your vehicle through your local authorized Ford or Ford of Canada dealer. These quality accessories have been specifically engineered to fulfill your automotive needs; they are custom designed to complement the style and aerodynamic appearance of your vehicle. In addition, each accessory is made from high quality materials and meets or exceeds Ford’s rigorous engineering and safety specifications. Ford Motor Company will repair or replace any properly dealer-installed Genuine Ford Accessory found to be defective in factory-supplied materials or workmanship during the warranty period, as well as any component damaged by the defective accessory. The accessory will be warranted for whichever provides you the greatest benefit: • 12 months or 12,000 miles (20,000 km) (whichever occurs first), or • the remainder of your new vehicle limited warranty. This means that Genuine Ford Accessories purchased along with your new vehicle and installed by the dealer are covered for the full length of your New Vehicle’s Limited Warranty — 3 years or 36,000 miles (60,000
km) (whichever occurs first). Contact your dealer for details and a copy of the warranty. Not all accessories are available for all models. The following is a list of several Genuine Ford Accessory products for your vehicle. Not all accessories are available for all models. For a complete listing of the accessories that are available for your vehicle, please contact your dealer or visit our online store at: www.fordaccessoriesstore.com.Exterior style Bug shields Deflectors Exterior trim Fender flares Front end covers Grille inserts Headlamps, taillamps, fog lights and Daytime Running Lamps (DRLs) Running boards Sliding rear windows - manual and power
240
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Accessories
Splash guards Step bars Tonneau covers Truck caps Wheels
Interior style Cell phone holders Consoles Electrochromatic compass/temperature interior mirrors Floor mats Interior trim kits Leather wrapped steering wheels Scuff plates Speed control
Lifestyle Bedliners and bedmats Bed tents Bike racks Cargo organization and management Diamond plate accessories Engine block heaters and blankets Rear seat entertainment systems Toolboxes Towing mirrors TracRac and accessories Trailer hitches, wiring harnesses and accessories
241
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Accessories
Peace of mind Airbag anti-theft locks First aid and safety kits Full vehicle covers Locking gas cap Navigation systems Remote start Vehicle security systems For maximum vehicle performance, keep the following information in mind when adding accessories or equipment to your vehicle: • When adding accessories, equipment, passengers and luggage to your vehicle, do not exceed the total weight capacity of the vehicle or of the front or rear axle (GVWR or GAWR as indicated on the Safety Compliance Certification label). Consult your dealer for specific weight information. • The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and Canadian Radio Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) regulate the use of mobile communications systems — such as two-way radios, telephones and theft alarms - that are equipped with radio transmitters. Any such equipment installed in your vehicle should comply with FCC or CRTC regulations and should be installed only by a qualified service technician.
• Mobile communications systems may harm the operation of your
vehicle, particularly if they are not properly designed for automotive use.
242
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Index
Air bag supplemental restraint system ....................................73–74
and child safety seats ..............75
description ................................74
disposal ......................................79
driver air bag ............................77
indicator light ...........................78
operation ...................................77
passenger air bag .....................77
passenger deactivation switch ........................................79
Air cleaner filter ...............214, 228
Ambulance packages ....................7
Antifreeze (see Engine coolant) ................191
Anti-lock brake system (see Brakes) ..............................101
Audio system (see Radio) ..........16–17, 20, 24, 27
Automatic transmission ............103driving an automatic overdrive .................................104
fluid, refill capacities ..............229
fluid, specification ..................235
Auxiliary power point .................46
Axlelubricant specifications ..232, 235
refill capacities ........................229
traction lok ..............................102Battery .......................................188
acid, treating emergencies .....188
jumping a disabled battery ....154
maintenance-free ....................188
replacement, specifications ...228
servicing ..................................1882004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Index
Bed extender ..............................51
BeltMinder ...................................69
Brakes ........................................100
anti-lock ...................................101
anti-lock brake system (ABS) warning light ...........................101
fluid, checking and adding ....209
fluid, refill capacities ..............229
fluid, specifications .........232, 235
lubricant specifications ..232, 235
parking ....................................101
shift interlock ..........................103
Bulbs ............................................40Calculating load ........................122
Capacities for refilling fluids ....229
Cargo area shade ........................51
Cargo net .....................................51
Cell phone use ............................50
Certification Label ....................237
Changing a tire .........................146
Child safety restraints ................84
child safety belts ......................84
Child safety seats ........................86
attaching with tether straps ....90
in front seat ..............................88
in rear seat ................................88Cleaning your vehicle
engine compartment ..............171
instrument panel ....................173
interior .....................................174
plastic parts ............................173
safety belts ..............................174
washing ....................................170
waxing .....................................170
wheels ......................................171243
Index
wiper blades ............................173
Daytime running lamps (see Lamps) ................................36
Dipstickengine oil .................................182
Doors
lubricant specifications ..........232
Driveline universal joint and slip yoke ....................................213
Driving under special conditions ..................108, 112, 114
sand .........................................113
snow and ice ...........................115
through water .................114, 118Emergencies, roadside
jump-starting ..........................154
Emergency Flashers .................135
Emission control system ..........205
Engine ........................................235
cleaning ...................................171
coolant .....................................191
fail-safe coolant ......................196
idle speed control ...................188
lubrication specifications ..................232, 235
refill capacities ........................229
service points ..................178–180
starting after a collision .........135
Engine block heater .................100
Engine oil ..................................182
checking and adding ..............182
dipstick ....................................182
filter, specifications ........187, 228
recommendations ...................187
refill capacities ........................229Clock adjust
AM/FM Stereo ...........................16
AM/FM stereo CD .....................18
AM/FM stereo tape/CD/MP3 ....21
CD-MP3 .....................................28
Premium AM/FM stereo CD6/MP3 ...................................24
Clutch fluid ..........................................209
operation while driving ..........106
recommended shift speeds ....107
Console ........................................50
Coolant checking and adding ..............191
refill capacities ................195, 229
specifications ..................232, 235
Cruise control (see Speed control) ....................48
Customer Assistance ................134
Ford accessories for your vehicle .....................................175
Ford Extended Service Plan ..........................................163
Getting assistance outside the U.S. and Canada .....................167
Getting roadside assistance ...134
Getting the service you need .........................................161
Ordering additional owner’s literature .................................168
The Dispute Settlement Board .......................................163
Utilizing the Mediation/Arbitration Program ...................................166244
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Index
Gauges .........................................14
GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating)calculating ...............................122
GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating)
calculating ...............................122
Hazard flashers .........................135
Headlamps ...................................36
aiming ........................................37
bulb specifications ....................40
daytime running lights .............36
flash to pass ..............................37
high beam .................................37
replacing bulbs .........................41
turning on and off ....................36Heating
heating and air conditioning system .................................33–34
Hood ..........................................177Ignition .................................96, 235
Infant seats (see Safety seats) ..86
Inspection/maintenance (I/M) testing ........................................206
Instrument panelcleaning ...................................173
cluster ........................................10
lighting up panel and interior .......................................37Jack ............................................146
positioning .......................146, 150245
specifications ..................232, 235
Exhaust fumes ..........................100Fail safe cooling ........................196
Fluid capacities .........................229
Foglamps .....................................36
Four-Wheel Drive vehicles .......109
driving off road .......................110
electronic shift ................109–110
indicator light .........................109
preparing to drive your vehicle .....................................103
Fuel ............................................197
calculating fuel economy .......201
cap ...........................................199
capacity ...................................229
choosing the right fuel ...........200
comparisons with EPA fuel economy estimates .................204
detergent in fuel .....................201
filling your vehicle with fuel ...........................197, 199, 202
filter, specifications ........201, 228
fuel pump shut-off switch .....135
improving fuel economy ........201
octane rating ...................200, 235
quality ......................................200
running out of fuel .................201
safety information relating to automotive fuels .....................197
Fuel pump shut-off switch .......135
Fuses ..................................136–137Gas cap (see Fuel cap) ............199
Gas mileage (see Fuel economy) .................2012004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Index
storage .....................146, 148–149
Jump-starting your vehicle ......154Keys
positions of the ignition ...........96
Motorcraft parts ................201, 228
Octane rating ............................200
Oil (see Engine oil) ..................182Lamps
bulb replacement specifications chart ..................40
daytime running light ...............36
fog lamps ...................................36
headlamps .................................36
headlamps, flash to pass ..........37
instrument panel, dimming .....37
interior lamps .....................39–40
replacing bulbs ...................40–44Lane change indicator (see Turn signal) ........................39
Lights, warning and indicator ....10
anti-lock brakes (ABS) ..........101
Load limits .................................118
Loading instructions .................122
Lubricant specifications ...232, 235
Lug nuts ....................................153
Lumbar support, seats ...............61Manual transmission .................106
fluid capacities ........................229
lubricant specifications ..........235
reverse .....................................108Mirrors
fold away ...................................48
side view mirrors (power) .......47246
Parking brake ............................101
Parts (see Motorcraft parts) ....228
Power distribution box (see Fuses) ...............................140
Power door locks ........................53
Power mirrors .............................47
Power point .................................46
Power steering ..........................102
fluid, checking and adding ....207
fluid, refill capacity ................229
fluid, specifications .........232, 235
Power Windows ...........................47
Preparing to drive your vehicle ........................................103Radio ....................16–17, 20, 24, 27
CD-MP3 .....................................28
Relays ........................................136
Remote entry system .................54
illuminated entry ......................56
locking/unlocking doors .....53–54
Roadside assistance ..................134Safety Belt Maintenance ............73
2004 Ranger (ran) Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) USA English (fus)
Index
Steering wheel
tilting .........................................46
Tilt steering wheel ......................46
Tires ...........................146, 215–216
alignment ................................223
care ..........................................221
changing ..................146, 148, 150
checking the pressure ............221
label .........................................221
replacing ..................................226
rotating ....................................223
safety practices .......................226
sidewall information ...............217
snow tires and chains ............227
spare tire .................................147
terminology .............................216
tire grades ...............................216
treadwear ........................215, 225
Towing .......................................122
recreational towing .................132