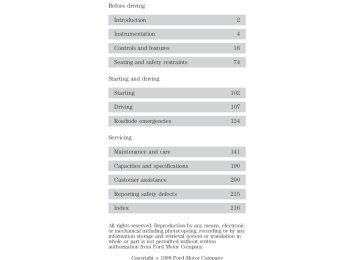
- 2008 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2010 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2011 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1999 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2004 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2009 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2005 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2015 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1996 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2016 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2014 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2007 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2006 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1998 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2013 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2000 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1997 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2012 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
The fuses are coded as follows.
Fuse/Relay Location
Fuse Amp
Rating
Description
10
11
— 5A 10A
10A
5A
15A
10A
5A
10A 20A
5A
Not Used Instrument Illumination Left Low Beam Headlamp Right Low Beam Headlamp Instrument Cluster, Shift Lock Actuator, Rear Defrost TR Sensor, Reverse Lamps, DRL, A/C Controls TR Sensor, Starter Relay Power Antenna, RCU, GEM ABS PCM Relay, Ignition Coil, PATS, Radio Instrument Cluster
127
Roadside emergencies
Fuse/Relay Location
Fuse Amp
Rating
Description
5A
5A
5A
10A
— 30A 5A 15A 5A 20A 5A
5A 5A 10A
15A 10A 15A
15A
15A
Instrument Cluster, Autolamps, Transmission Control Switch, ICP, GEM Electronic Crash Unit (ECU), Blower Motor, EATC Semi-Active Ride Control Module Multifunction Switch (Turn Signal) Not Used Front Wiper/Washer Headlamp Switch Rear Wiper/Washer ICP, RAP, Phone, GEM Cigar Lighter Power Mirrors, Power Antenna, Luggage Compartment Lamp, Autolamp GEM, RAP, PATS ICP, RCC, Speedometer Data Link Connector (DLC) Luggage Compartment Battery Saver Relay Speed Control, Brake Lamp Multifunction Switch, (Hazard) High Beams, Daytime Running Lamps, Instrument Cluster
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2223
24
2526
27
2829
30
128
Roadside emergencies
Fuse/Relay Location
Fuse Amp
Rating
Description
31
32
3334
3536
37
3839
— 10A 5A
— —
— — —
—
Not Used ICP, Heated Mirrors Power Windows, Lock Illumination Battery Saver Relay Driver Door Unlock Relay Rear Defroster Relay Interior Lamp Relay One Touch Window Down Relay Accessory Delay Relay
Power distribution box The power distribution box is located in the engine compartment. The power distribution box contains high-current fuses that protect your vehicle’s main electrical systems from overloads.
Always disconnect the battery before servicing high current fuses.
Always replace the cover to the Power Distribution Box before reconnecting the
battery or refilling fluid reservoirs.
129
Roadside emergencies
If the battery has been disconnected and reconnected, refer to the Battery section of the Maintenance and Care chapter.
The high-current fuses are coded as follows.
Fuse Amp
Rating 40A** 30A** 40A**
30A C.B.
40A**
—
40A**
30A**
40A**
20A** 40A** 20A**
Description
Fuse Junction Panel PCM Relay Ignition Switch, Starter Relay Accessory Delay Relay, Power Seat Ignition Switch Not Used Rear Window Defrost Relay Thermactor Air ByPass Solenoid, EAM Solid State Relay High Speed Cooling Fan Relay, Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Fuel Pump Relay Blower Motor Relay Semi-Active Ride Control Module
Fuse/Relay Location
10
11
12130
Roadside emergencies
Fuse Amp
Rating 40A**
—
15A*
10A*
20A*
30A* 15A*
15A*
—
30A*
— — —
30A* 10A* 15A*
— — —
— — —
Description
Anti-Lock Brake Module Not Used Daytime Running Lamps (DRL) Module Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Rear Control Unit, CD Changer Anti-Lock Brake Module Horn Relay, Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Headlamp Switch, Autolamp Park Relay Not Used Autolamps Relay, Multifunction Switch, Headlamp Switch Blower Motor Relay Starter Relay A/C Clutch Relay Generator A/C Clutch Relay Heated Oxygen Sensors, Canister Vent Fuel Pump Relay PCM Relay Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay PCM Diode A/C Clutch Diode Not Used
Fuse/Relay Location
13
14
1516
17
18
1920
21
2223
24
25
26
27
2829
30
3132
33
34* Mini Fuses ** Maxi Fuses
131
Roadside emergencies
Relays Relays are located in the power distribution box and should be replaced by qualified technicians.
CHANGING THE TIRES If you get a flat tire while driving, do not apply the brake heavily. Instead, gradually decrease your speed. Hold the steering wheel firmly and slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
Temporary spare tire information The temporary spare tire for your vehicle is labeled as such. It is smaller than a regular tire and is designed for emergency use only.
If you use the temporary spare tire continuously or do not follow these
precautions, the tire could fail, causing you to lose control of the vehicle, possibly injuring yourself or others.
circumstances
rating listed on the Safety Compliance Label
When driving with the temporary spare tire do not: † exceed 80 km/h (50 mph) under any † load the vehicle beyond maximum vehicle load † tow a trailer † use tire chains † drive through an automatic car wash, because of † try to repair the temporary spare tire or remove it † use the wheel for any other type of vehicle Tire change procedure 1. Park on a level surface, activate hazard flashers and set parking brake.
the vehicle’s reduced ground clearance
from its wheel
132
Roadside emergencies
When one of the front wheels is off the ground, the transaxle alone will not prevent
the vehicle from moving or slipping off the jack, even if the vehicle is in P (Park).
To prevent the vehicle from moving when you change a tire, be sure the parking brake
is set, then block (in both directions) the wheel that is diagonally opposite (other side and end of the vehicle) to the tire being changed.
If the vehicle slips off the jack, you or someone else could be seriously injured.
2. Place gearshift lever in P (Park), turn engine OFF, block the diagonally opposite wheel, then remove the spare tire, jack and lug wrench. † In the sedan, these are located in the trunk cargo area storage compartment.
† In the wagon, they are stored in the left side rear trim panel for the temporary spare and in the floor cargo area storage compartment for the full size spare.
133
Roadside emergencies
3. Remove the center ornament or wheel cover from the wheel with the tapered end of the wheel nut wrench that came with your vehicle. Insert and twist the handle, then pry against the wheel. 4. Loosen each wheel lug nut one-half turn counterclockwise but do not remove them until the wheel is raised off the ground.
5. Put the jack in the jack notch next to the door of the tire you are changing. Turn the jack handle clockwise until the wheel is completely off the ground. 6. Remove the lug nuts with the lug wrench. 7. Replace the flat tire with the spare tire, making sure the valve stem is facing outward. Reinstall lug nuts until the wheel is snug against the hub. Do not fully tighten the lug nuts until the wheel has been lowered. 8. Lower the wheel by turning the jack handle counterclockwise. 9. Remove the jack and fully tighten the lug nuts in the order shown.
134
Roadside emergencies
10. Return the flat tire, jack and lug wrench to their proper storage locations. Make sure the jack is fastened so it does not rattle when you drive. 11. Unblock the wheels.
JUMP STARTING YOUR VEHICLE
The gases around the battery can explode if exposed to flames, sparks, or lit cigarettes.
An explosion could result in injury or vehicle damage.
Do not push start your vehicle. You could damage the catalytic converter.
Batteries contain sulfuric acid which can burn skin, eyes, and clothing, if contacted.
Do not attempt to push start your vehicle. Automatic transmissions do not have push-start capability.
Preparing your vehicle 1. Use only a 12–volt supply to start your vehicle. 2. Do not disconnect the battery of the disabled vehicle as this could damage the vehicle’s electrical system. 3. Park the booster vehicle close to the hood of the disabled vehicle making sure the two vehicles do
135
Roadside emergencies
not touch. Set the parking brake on both vehicles and stay clear of the engine cooling fan and other moving parts. 4. Check all battery terminals and remove any excessive corrosion before you attach the battery cables. Ensure that vent caps are tight and level. 5. Turn the heater fan on in both vehicles to protect any electrical surges. Turn all other accessories off.
Connecting the jumper cables, 3.0L Vulcan, 3.0L Duratec and 3.4L SHO engines
+–
+–
1. Connect the positive (+) booster cable to the positive (+) terminal of the discharged battery. Note: In the illustrations, lightning bolts are used to designate the assisting (boosting) battery.
+–
+–
2. Connect the other end of the positive (+) cable to the positive (+) terminal of the assisting battery.
136
Roadside emergencies
+–
+–
3. Connect the negative (-) cable to the negative (-) terminal of the assisting battery.
+–
+–
4. Make the final connection of the negative (-) cable. For the 3.0L Vulcan and 3.4L SHO, make the connection to an exposed metal part of the stalled vehicle’s engine, away from the battery and the carburetor/fuel injection system. For the 3.0L Duratec, make the connection to the hood latch of the disabled engine, away from the battery and the carburetor/fuel injection system. The preferred locations of an exposed metal part (to ground the circuit) are the alternator mounting brackets or an engine lifting eye. Do not use fuel lines, engine rocker covers or the intake manifold as grounding points.
Do not connect the end of the second cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery to be jumped. A spark may cause an explosion of the gases that surround the battery.
137
Roadside emergencies
5. Be sure that the cables are clear of fan blades, belts and other moving parts of both engines.
Jump starting 1. Start the engine of the booster vehicle and run the engine at moderately increased speed. 2. Start the engine of the disabled vehicle. 3. Once the disabled vehicle has been started, run both engines for an additional three minutes before disconnecting the jumper cables.
Removing the jumper cables, 3.0L Vulcan, 3.0L Duratec and 3.4L SHO engines
+–
+–
Remove the jumper cables in the reverse order that they were connected. 1. Remove the jumper cable. For the 3.0L Vulcan and 3.4L SHO, remove the jumper cable from the ground metal surface. For the 3.0L Duratec, remove the jumper cable from the hood latch.
+–
+–
2. Remove the jumper cable on the negative (-) connection of the booster vehicle’s battery.
138
Roadside emergencies
+–
+–
3. Remove the jumper cable from the positive (+) terminal of the booster vehicle’s battery.
+–
+–
4. Remove the jumper cable from the positive (+) terminal of the disabled vehicle’s battery. After the disabled vehicle has been started and the jumper cables removed, allow it to idle for several minutes so the engine computer can relearn its idle conditions.
139
Roadside emergencies
WRECKER TOWING
If you need to have your vehicle towed, contact a professional towing service or, if you are a member, your roadside assistance center. It is recommended that your vehicle be towed with a wheel lift or flatbed equipment. Do not tow with a slingbelt. Ford Motor Company has not approved a slingbelt towing procedure. If your vehicle is to be towed from the rear using wheel lift equipment, the front wheels (drive wheels) must be placed on a dolly to prevent damage to the transaxle. Ford Motor Company provides a towing manual for all authorized tow truck operators. Have your tow truck operator refer to this manual for proper hook-up and towing procedures for your vehicle.
140
Maintenance and care
SERVICE RECOMMENDATIONS To help you service your vehicle: † We highlight do-it-yourself items in the engine † We provide a Scheduled Maintenance Guide which
compartment for easy location.
makes tracking routine service easy.
If your vehicle requires professional service, your dealership can provide necessary parts and service. Check your “Warranty Guide” to find out which parts and services are covered. Use only recommended fuels, lubricants, fluids and service parts conforming to specifications. Motorcraft parts are designed and built to provide the best performance in your vehicle.
PRECAUTIONS WHEN SERVICING YOUR VEHICLE Be especially careful when inspecting or servicing your vehicle. † Do not work on a hot engine. † When the engine is running, keep loose clothing, † Do not work on a vehicle with the engine running
jewelry or long hair away from moving parts.
in an enclosed space, unless you are sure you have enough ventilation. † Keep all lit cigarettes, open flames and other lit
material away from the battery and all fuel related parts.
If you disconnect the battery, the engine must “relearn” its idle conditions before your vehicle will drive properly, as explained in the Battery section in this chapter.
Working with the engine off 1. Set the parking brake, and ensure the gearshift is securely latched in park. 2. Turn off the engine and remove the key.
141
Maintenance and care
3. Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving unexpectedly.
Working with the engine on 1. Set the parking brake and ensure the gearshift is securely latched in P (Park). 2. Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving unexpectedly.
Do not start your engine with the air cleaner removed and do not remove it while the
engine is running.
OPENING THE HOOD 1. Inside the vehicle, pull the hood release handle located under the bottom of the instrument panel. 2. Go to the front of the vehicle and release the auxiliary latch that is located under the front center of the hood. 3. Lift the hood until the lift cylinders hold it open.
BRAKE
H O O D
142
Maintenance and care
IDENTIFYING COMPONENTS IN THE ENGINE COMPARTMENT
3.0L V6 Vulcan engine
1. Automatic transmission fluid dipstick 2. Brake fluid reservoir 3. Air filter assembly 4. Battery 5. Engine oil filler cap 6. Engine oil dipstick 7. Power steering fluid reservoir 8. Engine coolant reservoir 9. Windshield washer fluid reservoir
143
3
Maintenance and care
3.0L DOHC V6 Duratec engine
1. Automatic transmission fluid dipstick 2. Brake fluid reservoir 3. Air filter assembly 4. Battery 5. Engine oil filler cap 6. Engine oil dipstick 7. Engine coolant reservoir 8. Windshield washer fluid reservoir 9. Power steering fluid reservoir
144
Maintenance and care
3.4L-32V V8 SHO engine
V8 32 VALVE
1. Automatic transmission fluid dipstick 2. Brake fluid reservoir 3. Air filter assembly 4. Battery 5. Engine oil dipstick 6. Engine oil filler cap 7. Engine coolant reservoir 8. Windshield washer fluid reservoir 9. Power steering fluid reservoir
ENGINE OIL
Checking the engine oil Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the appropriate intervals for checking the engine oil . 1. Make sure the vehicle is on level ground. 2. Turn the engine off and wait a few minutes for the oil to drain into the oil pan.
145
Maintenance and care
3. Set the parking brake and ensure the gearshift is securely latched in P. 4. Open the hood. Protect yourself from engine heat. 5. Locate and carefully remove the engine oil indicator (dipstick).
ADD 1 QT
MIN
FULL
MAX
6. Wipe the indicator clean. Insert the indicator fully, then remove it again. † If the oil level is between the ADD and FULL marks or between the MIN and MAX marks (depending on application), the oil level is acceptable. DO NOT ADD OIL.
† If the oil level is below the ADD or MIN mark, add enough oil to raise the level within the ADD-FULL or within the MIN-MAX range.
† Oil levels above the F in FULL or above the MAX mark, may cause engine damage. Some oil must be removed from the engine by a service technician.
7. Put the indicator back in and ensure it is fully seated.
146
Maintenance and care
Adding engine oil 1. Check the engine oil. For instructions, refer to Checking the engine oil in this chapter. 2. If the engine oil level is not within the normal range, add only certified engine oil of the recommended viscosity. Remove the engine oil filler cap and use a funnel to pour the engine oil into the opening. 3. Recheck the engine oil level. Make sure the oil level is not above the F in FULL mark on the engine oil level indicator (dipstick). 4. Install the indicator and ensure it is fully seated. 5. Fully install the engine oil filler cap by turning the filler cap clockwise until three clicks can be heard. To avoid possible oil loss, DO NOT operate the vehicle with the engine oil level indicator and/or the engine oil filler cap removed.
Engine oil and filter recommendations Look for this Certification Trademark.
Use SAE 5W-30 motor oil certified for gasoline engines by the American Petroleum Institute (API). Motor oil displaying the API Certification Trademark will meet all requirements for your vehicle’s engine. Ford oil specification is WSS-M2C153-G. Do not use supplemental engine oil additives, oil treatments or engine treatments. They are unnecessary and could, under certain conditions, lead to engine damage which is not covered by your warranty.
147
Maintenance and care
Change your engine oil and filter according to the appropriate schedule listed in the Scheduled Maintenance Guide. Ford production and aftermarket (Motorcraft) oil filters are designed for added engine protection and long life. If a replacement oil filter is used that does not meet Ford material and design specifications, startup engine noises or knock may be experienced. It is recommended you use the appropriate Motorcraft oil filter (or another brand meeting Ford specifications) for your engine application.
BRAKE FLUID
Checking and adding brake fluid Brake fluid should be checked and refilled as needed. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the service interval schedules: 1. Clean the reservoir cap before removal to prevent dirt or water from entering the reservoir. 2. Visually inspect the fluid level. 3. If necessary, add brake fluid until the level reaches MAX. Do not fill above this line. 4. Use only a DOT 3 brake fluid certified to meet Ford specifications. Refer to Lubricant specifications in the Capacities and specifications chapter.
MAX
Brake fluid is toxic.
148
Maintenance and care
If you use a brake fluid that is not DOT 3, you will cause permanent damage to your
brakes.
Do not let the reservoir for the master cylinder run dry. This may cause the brakes
to fail.
WINDSHIELD WASHER FLUID
Checking and adding washer fluid Check the washer fluid whenever you stop for fuel. The reservoir is highlighted with a
symbol.
If the level is low, add enough fluid to fill the reservoir. In very cold weather, do not fill the reservoir all the way.
Do not put engine coolant in the container for the windshield washer fluid.
149
Maintenance and care
Checking and adding washer fluid for the liftgate (if equipped) The opening for the reservoir is located on the passenger side under the tail lamp. Refill this reservoir with the same fluid you use for your windshield.
ENGINE COOLANT Check the level of the engine coolant in the reservoir. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for service interval schedules. Be sure to read and understand Precautions when servicing your vehicle in this chapter.
If the engine coolant has not been checked at the recommended interval, the engine coolant reservoir may become empty. If this occurs, add engine coolant to the reservoir. For more information on engine coolant maintenance, refer to Adding engine coolant in this chapter. Automotive fluids are not interchangeable; do not use engine coolant, antifreeze or windshield washer fluid outside of its specified function and vehicle location.
150
Maintenance and care
Adding engine coolant
Do not put engine coolant in the reservoir for the windshield washer fluid.
Use only Ford Premium Engine Coolant E2FZ-19549–AA (in Oregon, F5FZ-19549–CC, in Canada, Motorcraft CXC-10) or a premium engine coolant that meets Ford specification ESE-M97B44–A. † DO NOT USE Ford Extended Life Engine Coolant F6AZ-19544–AA (orange in color). † DO NOT USE a DEX-COOLt engine coolant or an equivalent engine coolant that meets Ford specification WSS-M97B44–D. † DO NOT USE alcohol or methanol antifreeze or any engine coolants mixed with alcohol or methanol antifreeze. † DO NOT USE supplemental coolant additives
in your vehicle. These additives may harm your engine’s cooling system.
† DO NOT MIX recycled coolant and
conventional coolant together in your vehicle. Mixing of engine coolants may harm your engine’s cooling system.
† The use of an improper coolant may harm engine and cooling system components and may void the warranty of your vehicle’s engine cooling system.
† Use only the type of coolant with which your
vehicle was originally equipped. If you are unsure which type of coolant your vehicle requires, contact your local dealer.
If sprayed on the windshield, engine coolant could make it difficult to see through the windshield. When the engine is cool, add a 50/50 mixture of engine coolant and distilled water to the engine coolant reservoir.
151
Maintenance and care
Plain water may be added in an emergency, but you must replace it with a 50/50 mixture of coolant and distilled water as soon as possible. Check the coolant level in the coolant reservoir the next few times you drive the vehicle. If necessary, add enough of a 50/50 mixture of coolant and distilled water to bring the liquid level into the cold fill range on the reservoir.
Never remove the coolant reservoir cap while the engine is running or hot.
If you must remove the coolant reservoir cap, follow these steps to avoid personal injury: 1. Before you remove the cap, turn the engine off and let it cool. 2. When the engine is cool, wrap a thick cloth around the cap. Slowly turn cap counterclockwise until pressure begins to release. 3. Step back while the pressure releases. 4. When you are sure that all the pressure has been released, use the cloth to turn it counterclockwise and remove the cap. Change your engine coolant according to the appropriate schedule listed in the Scheduled Maintenance Guide. Recycled engine coolant Ford Motor Company recommends that Ford and Lincoln-Mercury dealers use recycled engine coolant produced by Ford-approved processes. Not all coolant recycling processes produce coolant which meets Ford specification ESE-M97B44–A, and use of such coolant may harm engine and cooling system components.
Always dispose of used automotive fluids in a responsible manner. Follow your community’s
regulations and standards for recycling and disposing of automotive fluids.
152
Maintenance and care
Coolant refill capacity To find out how much fluid your vehicle’s cooling system can hold, refer to Refill capacities in the Capacities and specifications chapter. Have your dealer check the engine cooling system for leaks if you have to add more than 1.0 liter (1.0 quart) of engine coolant per month.
Severe winter climate If you drive in extremely cold climates (less than –36°C [–34°F]), it may be necessary to increase the coolant concentration above 50%. Refer to the chart on the coolant container to ensure the coolant concentration in your vehicle is such that the coolant will not freeze at the temperature level in which you drive during winter months. Never increase the coolant concentration above 60%. Increased engine coolant concentrations above 60% will decrease the freeze protection characteristics of the engine coolant. Vehicles driven year-round in non-extreme climates should use a 50/50 mixture of engine coolant and distilled water for optimum freeze protection.
CHECKING AND ADDING POWER STEERING FLUID Check the power steering fluid. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the service interval schedules. If adding fluid is necessary, use only MERCONt ATF.
1. Start the engine and let it run until it reaches normal operating temperature (the engine coolant
153
Maintenance and care
temperature gauge indicator will be near the center of the normal area between H and C). 2. While the engine idles, turn the steering wheel left and right several times. 3. Turn the engine off. Perform steps 4 and 5 following the procedure for your engine.
3.0L V6 Vulcan engine 4. Check the fluid level on the dipstick. It should be between the arrows in the FULL HOT range. Do not add fluid if the level is within this range.
O T
F U L L H
5. If the fluid is low, add fluid in small amounts, continuously checking the level until it reaches the FULL HOT range. Be sure to put the dipstick back in the reservoir.
3.0L Duratec engine and 3.4L SHO engine 4. Check the fluid level in the reservoir. It should be between the MIN and MAX lines. Do not add fluid if the level is within this range.
M A X M I N
5. If the fluid is low, add fluid in small amounts, continuously checking the level until it reaches the range between the MIN and MAX lines. Be sure to put the cap back on the reservoir.
154
Maintenance and care
TRANSMISSION FLUID
Checking automatic transmission fluid Refer to your Scheduled Maintenance Guide for scheduled intervals for fluid checks and changes. Your transaxle does not consume fluid. However, the fluid level should be checked if the transaxle is not working properly, i.e., if the transaxle slips or shifts slowly or if you notice some sign of fluid leakage. Automatic transmission fluid expands when warmed. To obtain an accurate fluid check, drive the vehicle until it is warmed up (approximately 30 km [20 miles]). If your vehicle has been operated for an extended period at high speeds, in city traffic during hot weather or pulling a trailer, the vehicle should be turned off for about 30 minutes to allow fluid to cool before checking. 1. Drive the vehicle 30 km (20 miles) or until it reaches normal operating temperature. 2. Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. 3. With the parking brake engaged and your foot on the brake pedal, start the engine and move the gearshift lever through all of the gear ranges. Allow sufficient time for each gear to engage. 4. Latch the gearshift lever in P (Park) and leave the engine running. 5. Remove the dipstick, wiping it clean with a clean, dry lint free rag. 6. Install the dipstick making sure it is fully seated in the filler tube. 7. Remove the dipstick and inspect the fluid level. The fluid should be in the designated areas for normal operating temperature.
155
Maintenance and care
DON’T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCH AREA--CHECH WHEN HOT-IDLING
DON’T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCH AREA--CHECH WHEN HOT-IDLING
Lowfluidlevel Do not drive the vehicle if the fluid level is at the bottom of the dipstick and the outside temperatures are above 10°C (50°F). Correctfluidlevel The transmission fluid should be checked at normal operating temperatures 66°C-77°C (150°F-170°F) on a level surface. The normal operating temperature can be reached after approximately 30 km (20
miles) of driving. The transmission fluid should be in this range if at normal operating temperature (66°C-77°C [150°F-170°F]). Highfluidlevel Fluid levels above the safe range may result in transaxle failure. An overfill condition of transmission fluid may cause shift and/or engagement concerns and/or possible damage. High fluid levels can be caused by an overheating condition. Adjustingautomatictransmissionfluidlevels Before adding any fluid, make sure the correct type is used. The type of fluid used is normally indicated on the dipstick and/or dipstick handle and also in the Lubricant specifications section in the Capacities and specifications chapter. Use of a non-approved automatic transmission fluid may cause internal transaxle component damage. If necessary, add fluid in 250 mL (1/2 pint) increments through the filler tube until the level is correct.DON’T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCH AREA--CHECH WHEN HOT-IDLING
156
Maintenance and care
If an overfill occurs, excess fluid should be removed by a qualified technician. An overfill condition of transmission fluid may cause shift and/or engagement concerns and/or possible damage.
DON’T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCH AREA--CHECH WHEN HOT-IDLING
BATTERY Your vehicle is equipped with a Motorcraft maintenance-free battery which normally does not require additional water during its life of service. However, for severe usage or in high temperature climates, check the battery electrolyte level. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the service interval schedules. Keep the electrolyte level in each cell up to the “level indicator”. Do not overfill the battery cells. If the electrolyte level in the battery is low, you can add plain tap water to the battery, as long as you do not use hard water (water with a high mineral or alkali content). If possible, however, try to only fill the battery cells with distilled water. If the battery needs water often, have the charging system checked. If your battery has a cover/shield, make sure it is reinstalled after the battery has been cleaned or replaced. For longer, trouble-free operation, keep the top of the battery clean and dry. Also, make certain the battery cables are always tightly fastened to the battery terminals.
157
Maintenance and care
If you see any corrosion on the battery or terminals, remove the cables from the terminals and clean with a wire brush. You can neutralize the acid with a solution of baking soda and water.
Batteries normally produce explosive gases which can cause personal injury. Therefore, do not allow flames, sparks or lighted substances to come near the battery. When working near the battery, always shield your face and protect your eyes. Always provide proper ventilation.
When lifting a plastic-cased battery, excessive pressure on the end walls could
cause acid to flow through the vent caps, resulting in personal injury and/or damage to the vehicle or battery. Lift the battery with a battery carrier or with your hands on opposite corners.
Keep batteries out of reach of children. Batteries contain sulfuric acid. Avoid contact with skin, eyes or clothing. Shield your eyes when working near the battery to protect against possible splashing of acid solution. In case of acid contact with skin or eyes, flush immediately with water for a minimum of 15 minutes and get prompt medical attention. If acid is swallowed, call a physician immediately.
Because your vehicle’s engine is electronically controlled by a computer, some control conditions are maintained by power from the battery. When the battery is disconnected or a new battery is installed, the engine must relearn its idle and fuel trim strategy for optimum driveability and performance. To begin this process: 1. Set your parking brake.
158
Maintenance and care
2. Put the gearshift in P (Park), turn off all accessories and start the engine. 3. Let the engine idle for at least one minute. 4. The relearning process will automatically complete as you drive the vehicle. † The vehicle may need to be driven 16 km (10
miles) or more to relearn the idle and fuel trim strategy. † If you do not allow the engine to relearn its idle trim, the idle quality of your vehicle may be adversely affected until the idle trim is eventually relearned.If the battery has been disconnected or a new battery has been installed, the clock and the preset radio stations must be reset once the battery is reconnected. † Always dispose of automotive batteries in a responsible manner. Follow your local authorized standards for disposal. Call your local authorized recycling center to find out more about recycling automotive batteries.
RECYCLE
WINDSHIELD WIPER BLADES Check the wiper blades at least twice a year or when they seem less effective. Substances such as tree sap and some hot wax treatments used by commercial car washes reduce the effectiveness of wiper blades.
Checking the wiper blades If the wiper blades do not wipe properly, clean both the windshield and wiper blades using undiluted windshield wiper solution or a mild detergent. Rinse thoroughly with clean water. To avoid damaging the
159
Maintenance and care
blades, do not use fuel, kerosene, paint thinner or other solvents.
Changing the wiper blades To replace the wiper blades: 1. Pull the wiper arm away from the windshield and lock into the service position. 2. Turn the blade at an angle from the wiper arm. Push the lock pin manually to release the blade and pull the wiper blade down toward the windshield to remove it from the arm. 3. Attach the new wiper to the wiper arm and press it into place until a click is heard.
INFORMATION ABOUT TIRE QUALITY GRADES New vehicles are fitted with tires that have their Tire Quality Grade (described below) molded into the tire’s sidewall. These Tire Quality Grades are determined by standards that the United States Department of Transportation has set. Tire Quality Grades apply to new pneumatic tires for use on passenger cars. They do not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with nominal rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches or limited production tires as defined in Title 49 Code of Federal Regulations Part 575.104(c)(2).
160
Maintenance and care
U.S. Department of Transportation-Tire quality grades: The U.S. Department of Transportation requires Ford to give you the following information about tire grades exactly as the government has written it.
Treadwear The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and one-half (1 1/2) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices, and differences in road characteristics and climate.
Traction AA A B C The traction grades, from highest to lowest are AA, A, B, and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking traction
tests, and does not include acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature A B C The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive
161
Maintenance and care
temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated
and not overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
SERVICING YOUR TIRES
Checking the tire pressure † Use an accurate tire pressure gauge. † Check the tire pressure when tires are cold, after the vehicle has been parked for at least one hour or has been driven less than 5 km (3 miles).
† Adjust tire pressure to recommended
specifications found on the Certification Label.
Improperly inflated tires can affect vehicle handling and can fail suddenly, possibly
resulting in loss of vehicle control.
Tire rotation Because your vehicle’s tires perform different jobs, they often wear differently. To make sure your tires wear evenly and last longer, rotate them as indicated in the Scheduled Maintenance Guide. If you notice that the tires wear unevenly, have them checked.
162
Maintenance and care
† Four tire rotation
Replacing the tires Replace the tires when the wear band is visible through the tire treads.
When replacing full size tires, never mix radial bias-belted, or bias-type tires. Use
only the tire sizes that are listed on the Certification Label. Make sure that all tires are the same size, speed rating, and load-carrying capacity. Use only the tire combinations recommended on the label. If you do not follow these precautions, your vehicle may not drive properly and safely.
Make sure that all replacement tires are of the same size, type, load-carrying capacity
and tread design (e.g., “All Terrain”, etc.), as originally offered by Ford.
163
Maintenance and care
Failure to follow these precautions may adversely affect the handling of the vehicle
and make it easier for the driver to lose control and roll over.
Tires that are larger or smaller than your vehicle’s original tires may also affect the accuracy of your speedometer.
SNOW TIRES AND CHAINS
Snow tires must be the same size and grade as the tires you currently have on your
vehicle.
The tires on your vehicle have all weather treads to provide traction in rain and snow. However, in some climates, you may need to use snow tires and chains. If you need to use snow tires and chains, it is recommended that steel wheels are used of the same size and specifications as those originally installed. Follow these guidelines when using snow tires and chains: † Use only SAE Class S chains. † Install chains securely, verifying that the chains do not touch any wiring, brake lines or fuel lines. † Drive cautiously. If you hear the chains rub or bang against your vehicle, stop and re-tighten the chains. If this does not work, remove the chains to prevent damage to your vehicle.
† If possible, avoid fully loading your vehicle. † Do not use tire chains if your vehicle is equipped † Remove the tire chains when they are no longer
with P225/55ZR16 or P215/6OR16 tires.
needed. Do not use tire chains on dry roads.
164
Maintenance and care † The suspension insulation and bumpers will help prevent vehicle damage. Do not remove these components from your vehicle when using snow tires and chains.
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT AUTOMOTIVE FUELS
Important safety precautions
Do not overfill the fuel tank. The pressure in an overfilled tank may cause leakage and
lead to fuel spray and fire.
The fuel system may be under pressure. If the fuel filler cap is venting vapor or if you
hear a hissing sound, wait until it stops before completely removing the fuel filler cap. Otherwise, fuel may spray out and injure you or others.
If you do not use the proper fuel filler cap, excessive pressure or vacuum in the fuel
tank may damage the fuel system or cause the fuel system to work improperly in a collision, which may result in possible personal injury.
Automotive fuels can cause serious injury or death if misused or mishandled.
165
Maintenance and care
Observe the following guidelines when handling automotive fuel: † Extinguish all
smoking materials and any open flames before fueling your vehicle. † Always turn off the
vehicle before fueling.
† Automotive fuels can be harmful or fatal if
swallowed. Fuel such as gasoline is highly toxic and if swallowed can cause death or permanent injury. If fuel is swallowed, call a physician immediately, even if no symptoms are immediately apparent. The toxic effects of fuel may not be visible for hours.
† Avoid inhaling fuel vapors. Inhaling too much fuel vapor of any kind can lead to eye and respiratory tract irritation. In severe cases, excessive or prolonged breathing of fuel vapor can cause serious illness and permanent injury.
† Avoid getting fuel liquid in your eyes. If fuel is splashed in the eyes, remove contact lenses (if worn), flush with water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention. Failure to seek proper medical attention could lead to permanent injury. † Fuels can also be harmful if absorbed through the skin. If fuel is splashed on the skin and/or clothing, promptly remove contaminated clothing and wash skin thoroughly with soap and water. Repeated or prolonged skin contact with fuel liquid or vapor causes skin irritation.
† Be particularly careful if you are taking
“Antabuse” or other forms of disulfiram for the treatment of alcoholism. Breathing gasoline vapors, or skin contact could cause an adverse reaction. In sensitive individuals, serious personal injury or sickness may result. If fuel is splashed
166
Maintenance and care
on the skin, promptly wash skin thoroughly with soap and water. Consult a physician immediately if you experience an adverse reaction.
When refueling always shut the engine off and never allow sparks or open flames near the filler neck. Never smoke while refueling. Fuel vapor is extremely hazardous under certain conditions. Care should be taken to avoid inhaling excess fumes.
The flow of fuel through a fuel pump nozzle can produce static electricity, which can
cause a fire if fuel is pumped into an ungrounded fuel container.
Use the following guidelines to avoid static build-up when filling an ungrounded fuel container: † Place approved fuel container on the ground. † DO NOT fill a fuel container while it is in the † Keep the fuel pump nozzle in contact with the † DO NOT use a device that would hold the fuel
fuel container while filling.
vehicle.
pump handle in the fill position.
Fuel Filler Cap Your fuel tank filler cap has an indexed design with a 1/8 turn on/off feature. When fueling your vehicle: 1. Turn the engine off. 2. Carefully turn the filler cap counterclockwise 1/8
of a turn until it stops. 3. Pull to remove the cap from the fuel filler pipe. 4. To install the cap, align the tabs on the cap with the notches on the filler pipe.167
Maintenance and care
5. Turn the filler cap clockwise 1/8 of a turn until it stops. If the “Service Engine Soon/Check Engine” indicator comes on and stays on when you start the engine, the fuel filler cap may not be properly installed. Turn off the engine, remove the fuel filler cap, align the cap properly and reinstall it. If you must replace the fuel filler cap, replace it with a fuel filler cap that is designed for your vehicle. The customer warranty may be void for any damage to the fuel tank or fuel system if the correct genuine Ford or Motorcraft fuel filler cap is not used.
The fuel system may be under pressure. If the fuel filler cap is venting vapor or if you
hear a hissing sound, wait until it stops before completely removing the fuel filler cap. Otherwise, fuel may spray out and injure you or others.
If you do not use the proper fuel filler cap, excessive pressure or vacuum in the fuel
tank may damage the fuel system or cause the fuel system to work improperly in a collision, which may result in possible personal injury.
Choosing the right fuel Use only UNLEADED FUEL. The use of leaded fuel is prohibited by law and could damage your vehicle. Do not use fuel containing methanol. It can damage critical fuel system components. Your vehicle was not designed to use fuel or fuel additives with metallic compounds, including manganese-based compounds containing MMT. Repairs to correct the effects of using a fuel for which your vehicle was not designed may not be covered by your warranty.
168
Maintenance and care
87(R+M)/2 METHOD
Octane recommendations 3.0LV6Vulcanand3.0LDOHCV6Duratec engines Your vehicle is designed to use “Regular” unleaded gasoline with an (R+M)/2 octane rating of 87. We do not recommend the use of gasolines labeled as “Regular” that are sold with octane ratings of 86 or lower in high altitude areas. Do not be concerned if your engine sometimes knocks lightly. However, if it knocks heavily under most driving conditions while you are using fuel with the recommended octane rating, see your dealer or a qualified service technician to prevent any engine damage. 3.4L-32VV8SHOengine Your vehicle is designed to use “Premium” gasoline with an (R+M)/2
octane rating of 91 or higher for optimum performance. The use of gasolines with lower octane ratings may degrade performance. We do not recommend the use of gasolines labeled as “Premium” in high altitude areas that are sold with octane ratings of less than 91. Do not be concerned if your engine sometimes knocks lightly. However, if it knocks heavily under most driving conditions while you are using fuel with the recommended octane rating, see your dealer or a qualified service technician to prevent any engine damage.91(R+M)/2 METHOD
169
Maintenance and care
Fuel quality If you are experiencing starting, rough idle or hesitation driveability problems during a cold start, try a different brand of gasoline. “Premium” unleaded gasoline should not be used (particularly in the United States) if “Regular” unleaded gasoline is recommended because it may cause these problems to become more pronounced. If the problems persist, see your dealer or a qualified service technician. It should not be necessary to add any aftermarket products to your fuel tank if you continue to use a high quality fuel.
Cleaner air Ford approves the use of gasolines to improve air quality, including reformulated gasolines that contain oxygenates up to 10% ethanol or 15% MTBE.
Running out of fuel Avoid running out fuel because this situation may have an adverse affect on powertrain components. If you have run out of fuel: † You may need to crank the engine several times after refueling before the system starts to pump the fuel from the tank to the engine. † Your “Service Engine Soon” indicator may come on. For more information on the “Service Engine Soon” indicator, refer to the Instrumentation chapter.
Fuel Filter For fuel filter replacement, see your dealer or a qualified service technician. Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for the appropriate intervals for changing the fuel filter. Replace the fuel filter with an authorized Motorcraft part. The customer warranty may be void for any damage to the fuel system if an authorized Motorcraft fuel filter is not used.
170
Maintenance and care
ESSENTIALS OF GOOD FUEL ECONOMY
Measuring techniques Your best source of information about actual fuel economy is you, the driver. You must gather information as accurately and consistently as possible. Fuel expense, frequency of fillups or fuel gauge readings are NOT accurate as a measure of fuel economy. We do not recommend taking fuel economy measurements during the first 1 600 km (1 000 miles) of driving (engine break-in period). You will get a more accurate measurement after 3 000 km–5 000 km (2 000 miles-3 000 miles).
Filling the tank The advertised fuel capacity of the fuel tank on your vehicle is equal to the rated refill capacity of the fuel tank as listed in the Refill Capacities chart in this “Owner Guide”. The advertised capacity is the amount of the Indicated Capacity and the Empty Reserve combined. Indicated Capacity is the difference in the amount of fuel in a full tank and a tank when the fuel gauge indicates empty. Empty Reserve is the small amount of usable fuel remaining in the fuel tank after the fuel gauge indicates empty. The amount of Empty Reserve varies and should not be relied upon to increase driving range. When refueling your vehicle after the fuel gauge indicates empty, you might not be able to refuel the full amount of the advertised capacity of the fuel tank due to the empty reserve still present in the tank. For consistent results when filling the fuel tank: † Use the same filling rate setting (low — medium † Allow three automatic click-offs when filling. † Always use fuel with the recommended octane
— high) each time the tank is filled.
rating.
171
national brand.
Maintenance and care † Use a known quality gasoline, preferably a † Use the same side of the same pump and have the vehicle facing the same direction each time you fill up.
† Have the vehicle loading and distribution the
same every time.
Your results will be most accurate if your filling method is consistent.
Calculating fuel economy 1. Fill the fuel tank completely and record the initial odometer reading (in kilometers or miles). 2. Each time you fill the tank, record the amount of fuel added (in liters or gallons). 3. After at least three to five tank fill-ups, fill the fuel tank and record the current odometer reading. 4. Subtract your initial odometer reading from the current odometer reading. 5. Follow one of the simple calculations in order to determine fuel economy: Multiply liters used by 100, then divide by total kilometers traveled. Divide total miles traveled by total gallons used. Keep a record for at least one month and record the type of driving (city or highway). This will provide an accurate estimate of the vehicle’s fuel economy under current driving conditions. Additionally, keeping records during summer and winter will show how temperature impacts fuel economy. In general, lower temperatures give lower fuel economy.
172
Maintenance and care
savings in fuel.
Driving style — good driving and fuel economy habits Give consideration to the lists that follow and you may be able to change a number of variables and improve your fuel economy. Habits † Smooth, moderate operation can yield up to 10% † Steady speeds without stopping will usually give † Idling for long periods of time (greater than one † Anticipate stopping; slowing down may eliminate † Sudden or hard accelerations may reduce fuel † Slow down gradually. † Driving at reasonable speeds (traveling at 88 km/h
minute) may waste fuel.
the best fuel economy.
the need to stop.
economy.
fuel economy.
reduce fuel economy.
[55 mph] uses 15% less fuel than traveling at 105 km/h [65 mph]). † Revving the engine before turning it off may † Using the air conditioner or defroster may reduce † Using speed control (if equipped) may improve fuel economy. Speed control can help maintain a constant speed and reduce speed changes. You may want to turn off the speed control in hilly terrain as unnecessary shifting between third and fourth gears may occur and could result in reduced fuel economy.