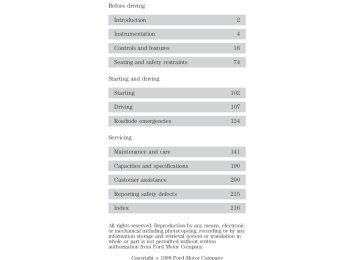
- 2008 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2010 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2011 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1999 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2004 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2009 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2005 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2015 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1996 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2016 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2014 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2007 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2006 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1998 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2013 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2000 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 1997 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- 2012 Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Ford Taurus Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
pull across your lap until it reaches the buckle. To tighten the belt, pull the loose end of the belt through the tongue until it fits snugly across the hips.
84
Seating and safety restraints
Shorten and fasten the belt when not in use.
Safety belts for rear-facing occupants (wagon only)
Never use child safety seats in the third seat of a wagon.
Your vehicle is equipped with safety belts containing an adjust tongue at the rear-facing seating positions. When the adjust tongue of the lap/shoulder combination seat belt is latched into the buckle, the tongue will allow the lap portion to become shorter, but locks the webbing in place to restrict it from becoming longer. Before you reach and latch a combination lap and shoulder belt having an adjust tongue into the buckle, you may have to lengthen the lap belt portion of it. To lengthen the lap belt, pull some webbing out of the shoulder belt retractor. While holding the webbing below the tongue, grasp the tongue so that it is parallel to the webbing and slide the tongue upward. Provide enough length so that the tongue can reach the buckle. To fasten the belt, pull the combination lap and shoulder belt from the retractor so that the shoulder belt portion of the safety belt crosses your shoulder and chest. Be sure the belt is not twisted. If the belt is twisted, remove the twist. Insert the tongue into the proper buckle for your seating position until you hear a snap and feel it latch. Make sure the tongue is securely fastened to the buckle by pulling on the tongue.
85
Seating and safety restraints
The lap belts should fit snugly and as low as possible around the hips, not around the
waist.
Front and rear seat occupants, including pregnant women, should wear safety belts
for optimum protection in an accident.
Each seating position in your vehicle has a specific safety belt assembly which is made
up of one buckle and one tongue that are designed to be used as a pair. 1) Use the shoulder belt on the outside shoulder only. Never wear the shoulder belt under the arm. 2) Never swing the safety belt around your neck over the inside shoulder. 3) Never use a single belt for more than one person.
Due to folding rear seats, sometimes the buckles and tongues toward the center of the vehicle may be hidden by the rear edge of the seat cushion. Pull them out so they will be accessible. While you are fastened in the seat belt, the shoulder belt adjusts to your movement. However, if you brake hard, turn hard or your vehicle receives an impact of 8 km/h (5 mph) or more, the safety belt will become locked and help reduce your forward movement. To unfasten the belt, push the red release button on the end of the buckle. This allows the tongue to unlatch from the buckle. While the belt retracts, guide the tongue to its original position to prevent it from striking you or the vehicle.
Safety belt extension assembly If the safety belt assembly is too short, even when fully extended, 20 cm (8 inches) can be added to the safety belt assembly by adding a safety belt
86
Seating and safety restraints
extension assembly (part number 611C22). Safety belt extension assemblies can be obtained from your dealer at no cost. Use only extensions manufactured by the same supplier as the safety belt. Manufacturer identification is located at the end of the webbing on the label. Also, use the safety belt extension only if the safety belt is too short for you when fully extended. Do not use extensions to change the fit of the shoulder belt across the torso.
Safety belt warning light and indicator chime The seat belt warning light illuminates in the instrument cluster and a chime sounds to remind the occupants to fasten their safety belts.
Conditions of operation If... The driver’s safety belt is not buckled before the ignition switch is turned to the ON position...
The driver’s safety belt is buckled while the indicator light is illuminated and the warning chime is sounding... The driver’s safety belt is buckled before the ignition switch is turned to the ON position...
Then... The safety belt warning light illuminates for one to two minutes and the warning chime sounds for four to eight seconds. The safety belt warning light and warning chime turn off.
The safety belt warning light and indicator chime remain off.
87
Seating and safety restraints
Safety belt maintenance Inspect the safety belt systems periodically to make sure they work properly and are not damaged. Inspect the safety belts to make sure there are no nicks, wears or cuts, replacing if necessary. All safety belt assemblies, including retractors, buckles, front seat belt buckle assemblies, buckle support assemblies (slide bar-if equipped), shoulder belt height adjusters (if equipped), child safety seat tether bracket assemblies (if equipped), and attaching hardware, should be inspected after a collision. Ford recommends that all safety belt assemblies used in vehicles involved in a collision be replaced. However, if the collision was minor and a qualified technician finds that the belts do not show damage and continue to operate properly, they do not need to be replaced. Safety belt assemblies not in use during a collision should also be inspected and replaced if either damage or improper operation is noted.
Failure to inspect and if necessary replace the safety belt assembly under the above
conditions could result in severe personal injuries in the event of a collision.
Refer to Cleaning and maintaining the safety belts in the Maintenance and care section.
AIR BAG SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS)
50
60
70
–
0 0 0 0
100
60
0 0 0 0 0
140
80
90
100
RPMx1000
180
110
km/h
120
MPH
R N D 2 1
O/D OFF
PREMIUM UNLEADED FUEL RECOMMENDED
REAR LAMP OUT
ABS
CRUISE
BRAKE
FM 12
AMC BLAM
FM
ST
RF
VOL
PUSH-ON
SEEK
EJECT
BASS
REW FF
SCAN
TUNE
TAPE SIDE
TAPE
TREB
BAL
FADE
R-DEF
LO
OFF
VENT
A/C MAX A/C
HI
FUEL DOOR>
SERVICE ENGINE SOON
LOW
COOLANT
THEFT
40
30
20
10
20
88
Seating and safety restraints
Important supplemental restraint system (SRS) precautions The supplemental restraint system is designed to work with the safety belt to help protect the driver and right front passenger from certain upper body injuries. Air bags DO NOT inflate slowly or gently and the risk of injury from a deploying air bag is greatest close to the trim covering the air bag module.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always properly wear their
safety belts, even when an air bag SRS is provided.
Always transport children 12 years old and under in the back seat and always properly
use appropriate child restraints.
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) recommends a
minimum distance of at least 25 cm (ten [10] inches) between an occupant’s chest and the driver air bag module.
Never place your arm over the air bag module as a deploying air bag can result in
serious arm fractures or other injuries.
Steps you can take to properly position yourself away from the airbag:
89
Seating and safety restraints † Move your seat to the rear as far as you can while † Recline the seat slightly (one or two degrees)
still reaching the pedals comfortably.
from the upright position.
Do not put anything on or over the air bag module. Placing objects on or over the air bag inflation area may cause those objects to be propelled by the air bag into your face and torso causing serious injury.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the Air Bag Supplemental Restraint System
or its fuses. See your Ford or Lincoln-Mercury dealer.
Children and air bags For additional important safety information, read all information on safety restraints in this guide. Children must always be properly restrained. Accident statistics suggest that children are safer when properly restrained in the rear seating positions than in the front seating position. Failure to follow these instructions may increase the risk of injury in a collision.
90
Seating and safety restraints
Air bags can kill or injure a child in a child seat. NEVER place a rear-facing child seat
in front of an active air bag. If you must use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move the seat all the way back.
How does the air bag supplemental restraint system work? The air bag SRS is designed to activate when the vehicle sustains longitudinal deceleration sufficient to cause the sensors to close an electrical circuit that initiates air bag inflation. The fact that the air bags did not inflate in a collision does not mean that something is wrong with the system. Rather, it means the forces were not of the type sufficient to cause activation. Air bags are designed to inflate in frontal and near-frontal collisions, not rollover, side-impact, or rear-impacts unless the collision causes sufficient longitudinal deceleration. The air bags inflate and deflate rapidly upon activation. After air bag deployment, it is normal to notice a smoke-like, powdery residue or smell the burnt propellant. This may consist of cornstarch, talcum powder (to lubricate the bag) or sodium compounds (e.g., baking soda) that result from the combustion process that inflates the air bag. Small
91
Seating and safety restraints
amounts of sodium hydroxide may be present which may irritate the skin and eyes, but none of the residue is toxic. While the system is designed to help reduce serious injuries, contact with a deploying air bag may also cause abrasions, swelling or temporary hearing loss. Because air bags must inflate rapidly and with considerable force, there is the risk of death or serious injuries such as fractures, facial and eye injuries or internal injuries, particularly to occupants who are not properly restrained or are otherwise out of position at the time of air bag deployment. Thus, it is extremely important that occupants be properly restrained as far away from the air bag module as possible while maintaining vehicle control.
Several air bag system components get hot after inflation. Do not touch them after
inflation.
If the air bag is deployed, the air bag will not function again and must be replaced
immediately. If the air bag is not replaced, the unrepaired area will increase the risk of injury in a collision.
include the inflators and air bags),
The SRS consists of: † driver and passenger air bag modules (which † one or more impact and safing sensors, † a readiness light and tone † and the electrical wiring which connects the
components.
The diagnostic module monitors its own internal circuits and the supplemental air bag electrical system warning (including the impact sensors), the system wiring, the air bag system readiness light, the air bag back up power and the air bag ignitors.
92
Seating and safety restraints
Determining if the system is operational The SRS uses a readiness light in the instrument cluster or a tone to indicate the condition of the system. Refer to the Air bag readiness section in the Instrumentation chapter. Routine maintenance of the air bag is not required. A difficulty with the system is indicated by one or more of the following: † The readiness light will either flash or stay lit. † The readiness light
will not illuminate immediately after ignition is turned on. † A series of five beeps will be heard. The tone
pattern will repeat periodically until the problem and light are repaired.
If any of these things happen, even intermittently, have the SRS serviced at your dealership or by a qualified technician immediately. Unless serviced, the system may not function properly in the event of a collision.
Disposal of air bags and air bag equipped vehicles (including pretensioners) For disposal of air bags or air bag equipped vehicles, see your local dealership or qualified technician. Air bags MUST BE disposed of by qualified personnel.
SAFETY RESTRAINTS FOR CHILDREN See the following sections for directions on how to properly use safety restraints for children. Also see Air Bag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) in this chapter for special instructions about using air bags.
93
Seating and safety restraints
Important child restraint precautions You are required by law to use safety restraints for children in the U.S. and Canada. If small children ride in your vehicle (generally children who are four years old or younger and who weigh 18 kg [40 lbs] or less), you must put them in safety seats made especially for children. Check your local and state or provincial laws for specific requirements regarding the safety of children in your vehicle.
Never let a passenger hold a child on his or her lap while the vehicle is moving. The
passenger cannot protect the child from injury in a collision.
Always follow the instructions and warnings that come with any infant or child restraint you might use. When possible, always place children under age 12
in the rear seat of your vehicle. Accident statistics suggest that children are safer when properly restrained in the rear seating positions than in the front seating position.Children and safety belts If the child is the proper size, restrain the child in a safety seat. Children who are too large for child safety seats (as specified by your child safety seat manufacturer) should always wear safety belts. Follow all the important safety restraint and air bag precautions that apply to adult passengers in your vehicle. If the shoulder belt portion of a combination lap and shoulder belt can be positioned so it does not cross or rest in front of the child’s face or neck, the child should wear the lap and shoulder belt. Moving the child closer to the center of the vehicle may help provide a good shoulder belt fit.
94
Seating and safety restraints
Do not leave children, unreliable adults, or pets unattended in your vehicle.
To improve the fit of lap and shoulder belts on children who have outgrown child safety seats, Ford recommends use of a belt-positioning booster seat that is labelled as conforming to all Federal motor vehicle safety standards. Belt-positioning booster seats raise the child and provide a shorter, firmer seating cushion that encourages safer seating posture and better fit of lap and shoulder belts on the child. A belt-positioning booster should be used if the shoulder belt rests in front of the child’s face or neck, or if the lap belt does not fit snugly on both thighs, or if the thighs are too short to let the child sit all the way back on the seat cushion when the lower legs hang over the edge of the seat cushion. You may wish to discuss the special needs of your child with your pediatrician.
SAFETY SEATS FOR CHILDREN
95
Seating and safety restraints
Child and infant or child safety seats Use a safety seat that is recommended for the size and weight of the child. Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or collision. When installing a child safety seat: † Review and follow
the information presented in the Air Bag Supplemental Restraint System section in this chapter. † Use the correct † Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle until
safety belt buckle for that seating position.
you hear a snap and feel it latch. Make sure the tongue is securely fastened in the buckle. † Keep the buckle release button pointing up and away from the safety seat, with the tongue between the child seat and the release button, to prevent accidental unbuckling.
† Place seat back in upright position. † Put the safety belt in the automatic locking mode.
Refer to Automatic locking mode.
Ford recommends the use of a child safety seat having a top tether strap. Install the child safety seat in a seating position which is capable of providing a tether anchorage. For more information on top tether straps, refer to Attaching safety seats with tether straps.
96
Seating and safety restraints
Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions included with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden stop or collision.
Installing child safety seats in combination lap and shoulder belt seating positions 1. Position the child safety seat in a seat with a combination lap and shoulder belt.
An air bag can kill or injure a child in a child seat. If you must use a forward-facing child seat in the front seat, move seat all the way back.
Children 12 and under should be properly restrained in the rear seat whenever
possible.
2. Pull down on the shoulder belt and then grasp the shoulder belt and lap belt together.
97
Seating and safety restraints
3. While holding the shoulder and lap belt portions together, route the tongue through the child seat according to the child seat manufacturer’s instructions. Be sure the belt webbing is not twisted. 4. Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle (the buckle closest to the direction the tongue is coming from) for that seating position until you hear a snap and feel the latch engage. Make sure the tongue is latched securely by pulling on it. 5. To put the retractor in the automatic locking mode, grasp the shoulder portion of the belt and pull downward until all of the belt is extracted and a click is heard. 6. Allow the belt to retract. The belt will click as it retracts to indicate it is in the automatic locking mode. 7. Pull the lap belt portion across the child seat toward the buckle and pull up on the shoulder belt while pushing down with your knee on the child seat.
98
Seating and safety restraints
8. Allow the safety belt to retract to remove any slack in the belt. 9. Before placing the child in the seat, forcibly tilt the seat forward and back to make sure the seat is securely held in place. 10. Try to pull the belt out of the retractor to make sure the retractor is in the automatic locking mode (you should not be able to pull more belt out). If the retractor is not locked, unbuckle the belt and repeat steps two through nine. Check to make sure the child seat is properly secured before each use.
Installing child safety seats in the lap belt seating positions 1. Lengthen the lap belt. To lengthen the belt, hold the tongue so that its bottom is perpendicular to the direction of webbing while sliding the tongue up the webbing. 2. Place the child safety seat in the center seating position. 3. Route the tongue and webbing through the child seat according to the child seat manufacturer’s instructions. 4. Insert the belt tongue into the proper buckle for the center seating position until you hear a snap and feel it latch. Make sure the tongue is securely fastened to the buckle by pulling on tongue. 5. Push down on the child seat while pulling on the loose end of the lap belt webbing to tighten the belt. 6. Before placing the child into the child seat, forcibly tilt the child seat from side to side and in forward direction to make sure that the seat is held
99
Seating and safety restraints
securely in place. If the child seat moves excessively, repeat steps 5 through 6, or properly install the child seat in a different position.
Attaching safety seats with tether straps Some manufacturers make safety seats that include a tether strap that goes over the back of the vehicle seat and attaches to an anchoring point. Other manufacturers offer the tether strap as an accessory. Contact the manufacturer of your child safety seat for information about ordering a tether strap.
Tether anchorage hardware Attachment holes (at each rear outboard seating position) have been provided in your vehicle to attach anchor hardware, if desired. Tether anchorage hardware kits (part number 613D74) including instructions, may be obtained at no charge from any Ford or Lincoln-Mercury dealer. All vehicles built for sale in Canada include a tether anchor hardware kit. Be sure to follow the child safety seat manufacturer’s instructions.
Tighten the anchor according to specifications. Otherwise, the safety seat
may not be properly secured and the child may be injured in a sudden stop or collision.
If you have a station wagon, tether anchors are already installed for each of the second row seating positions. 1. Behind the second seat, find the plastic snap-on covers for the floor anchors.
100
Seating and safety restraints
2. Use a screwdriver or coin to snap the covers off the anchor in a rearward and upward direction. Remove the covers completely.
3. Snap the tether strap hook onto the U-shaped tether anchor.
101
Starting
PREPARING TO START YOUR VEHICLE Engine starting is controlled by the ignition system. This system meets all Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment standard requirements regulating the impulse electrical field strength of radio noise. When starting a fuel-injected engine, avoid pressing the accelerator before or during starting. Only use the accelerator when you have difficulty starting the engine. For more information on starting the vehicle, refer to Starting the engine in this chapter.
Extended idling at high engine speeds can produce very high temperatures in the
engine and exhaust system, creating the risk of fire or other damage.
Do not park, idle, or drive your vehicle in dry grass or other dry ground cover. The
emission system heats up the engine compartment and exhaust system, which can start a fire.
Do not start your vehicle in a closed garage or in other enclosed areas. Exhaust fumes can be toxic. Always open the garage door before you start the engine. See Guarding against exhaust fumes in this chapter for more instructions.
If you smell exhaust fumes inside your vehicle, have your dealer inspect your
vehicle immediately. Do not drive if you smell exhaust fumes.
102
Starting
Important safety precautions A computer system controls the engine’s idle revolutions per minute (RPM). When the engine starts, the idle RPM runs faster to warm the engine. If the engine idle speed does not slow down automatically, have the vehicle checked. Do not allow the vehicle to idle for more than ten minutes at the higher engine RPM. Before starting the vehicle: 1. Make sure all vehicle occupants have buckled their safety belts. For more information on safety belts and their proper usage, refer to the Seating and safety restraints chapter. 2. Make sure the headlamps and vehicle accessories are off. 3. Make sure the parking brake is set.
4. Make sure the gearshift is in P (Park).
P R N D D 1
5. Turn the key to 4
(ON) without turning the key to 5 (START).103
Starting
FUEL DOOR>
40
30
20
10
20
50
60
70
–
0 0 0 0
100
60
0 0 0 0 0
140
80
90
100
180
110
SERVICE ENGINE SOON
LOW
COOLANT
THEFT
MPH
km/h R N D 2 1
120
RPMx1000
UNLEADED FUEL ONLY
ABS
CRUISE
O/D OFF
BRAKE
Make sure the corresponding lights illuminate briefly. If a light fails to illuminate, have the vehicle serviced. † If the driver’s safety belt is fastened, the
light
may not illuminate.
STARTING THE ENGINE 1. Turn the key to 5
(START) without pressing the accelerator pedal and release as soon as the engine starts. The key will return to 4 (ON).2. If the temperature is above –12° C (10° F) and the engine does not start within five seconds on the first try, turn the key to OFF, wait ten seconds and try again. 3. If the temperature is below -12°C (10°F) and the engine does not start in fifteen seconds on the first try, turn the key OFF and wait ten seconds and try again. If the engine does not start in two attempts, depress the accelerator and start the engine while holding the accelerator down to the floor. Release the accelerator when the engine starts. 4. After idling for a few seconds, apply the brake and release the parking brake.
104
Starting
Using the engine block heater (if equipped) An engine block heater warms the engine coolant, which improves starting, warms up the engine faster and allows the heater-defroster system to respond quickly. Use of an engine block heater is strongly recommended if you live in a region where temperatures reach -23°C (-10°F) or below. For best results, plug the heater in at least three hours before starting the vehicle. Using the heater for longer than three hours will not harm the engine, so the heater can be plugged in the night before starting the vehicle.
To prevent electrical shock, do not use your heater with ungrounded electrical systems
or two-pronged (cheater) adapters.
Guarding against exhaust fumes Although odorless and colorless, carbon monoxide is present in exhaust fumes. Take precautions to avoid its dangerous effects.
If you ever smell exhaust fumes of any kind inside your vehicle, have your dealer inspect
and fix your vehicle immediately. Do not drive if you smell exhaust fumes. These fumes are harmful and could kill you.
Have the exhaust and body ventilation systems checked whenever: † the vehicle is raised for service. † the sound of the exhaust system changes. † the vehicle has been damaged in a collision.
105
Starting
Engine exhaust, some of its constituents, and certain vehicle components contain or
emit chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer, and birth defects or other reproductive harm.
Important ventilating information If the engine is idling while the vehicle is stopped in an open area for long periods of time, open the windows at least 2.5 cm (one inch). Adjust the heating or air conditioning (if equipped) to bring in fresh air. Improve vehicle ventilation by keeping all air inlet vents clear of snow, leaves and other debris.
106
Driving
BRAKES Your service brakes are self-adjusting. Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for scheduled maintenance. Occasional brake noise is normal and often does not indicate a performance concern with the vehicle’s brake system. In normal operation, automotive brake systems may emit occasional or intermittent squeal or groan noises when the brakes are applied. Such noises are usually heard during the first few brake applications in the morning; however, they may be heard at any time while braking and can be aggravated by environmental conditions such as cold, heat, moisture, road dust, salt or mud. If a “metal-to-metal”, “continuous grinding” or “continuous squeal” sound is present while braking, the brake linings may be worn-out and should be inspected by a qualified service technician.
Anti-lock brake system (ABS) (if equipped) On vehicles equipped with an anti-lock braking system (ABS), a noise from the hydraulic pump motor and pulsation in the pedal may be observed during ABS braking events. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise while braking under panic conditions or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or snowy roads is normal and indicates proper functioning of the vehicle’s anti-lock brake system. The ABS performs a self-check at 17 km/h (10 mph) after you start the engine and begin to drive away. A brief mechanical noise may be heard during this test. This is normal. If a malfunction is found, the ABS warning light will come on. If the vehicle has continuous vibration or shudder in the steering wheel while braking, the vehicle should be inspected by a qualified service technician.
107
Driving
The ABS operates by detecting the onset of wheel lockup during brake applications and compensating for this tendency. The wheels are prevented from locking even when the brakes are firmly applied. The accompanying illustration depicts the advantage of an ABS equipped vehicle (on bottom) to a non-ABS equipped vehicle (on top) during hard braking with loss of front braking traction.
ABS warning lamp The ABS warning lamp in the instrument cluster momentarily illuminates when the ignition is turned on and the engine is off. If the light does not illuminate momentarily at start up, remains on or continues to flash, the ABS needs to be serviced. With the ABS light on, the anti-lock brake system is disabled and normal braking is still effective unless the brake warning light also remains illuminated with parking brake released. (If your brake warning lamp illuminates, have your vehicle serviced immediately).
BRAKE
Using ABS † In an emergency or when maximum efficiency from the ABS is required, apply continuous full force on the brake. The ABS will be activated immediately, thus allowing you to retain full steering control of your vehicle and, providing there is sufficient space, will enable you to avoid obstacles and bring the vehicle to a controlled stop.
† The Anti-Lock system does not decrease the time
necessary to apply the brakes or always reduce
108
Driving
stopping distance. Always leave enough room between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you to stop. † We recommend that you familiarize yourself with this braking technique. However, avoid taking any unnecessary risks.
Parking brake Apply the parking brake whenever the vehicle is parked. To set the parking brake, press the parking brake pedal down until the pedal stops.
The BRAKE warning lamp in the instrument cluster illuminates and remains illuminated (when the ignition is turned ON) until the parking brake is released.
BRAKE
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure that the gearshift is securely latched in
P (Park).
The parking brake is not recommended to stop a moving vehicle. However, if the normal brakes fail, the parking brake can be used to stop your vehicle in an emergency. Since the parking brake applies only the rear brakes, the vehicle’s stopping distance will increase greatly and the handling of your vehicle will be adversely affected.
109
Driving
Pull the release lever to release the brake. Driving with the parking brake on will cause the brakes to wear out quickly and reduce fuel economy.
STEERING Your vehicle is equipped with power steering. Power steering uses energy from the engine to help steer the vehicle. To prevent damage to the power steering pump: † Never hold the steering wheel to the extreme right or the extreme left for more than a few seconds when the engine is running. † Do not operate the vehicle with a low power
steering pump fluid level.
If the power steering system breaks down (or if the engine is turned off), you can steer the vehicle manually, but it takes more effort. If the steering wanders or pulls, the condition could be caused by any of the following: † underinflated tire(s) on any wheel(s) † high crown in center of road † high crosswinds † wheels out of alignment † loose or worn components in steering linkage
110
Driving
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE OPERATION
Brake-shift interlock This vehicle is equipped with a brake-shift interlock feature that prevents the gearshift from being moved from P (Park) unless the brake pedal is depressed. If you cannot move the gearshift out of P (Park) with the brake pedal depressed: 1. Apply the parking brake, turn ignition key to LOCK, then remove the key. 2. Insert the key and turn it to OFF. Apply the brake pedal and shift to N (Neutral). 3. Start the vehicle. If it is necessary to use the above procedure to move the gearshift, it is possible that a fuse has blown or the vehicle’s brakelamps are not operating properly. Refer to Fuses and relays in the Roadside emergencies chapter.
Do not drive your vehicle until you verify that the brakelamps are working.
If your vehicle gets stuck in mud or snow it may be rocked out by shifting from forward and reverse gears, stopping between shifts, in a steady pattern. Press lightly on the accelerator in each gear. Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes. The transmission and tires may be damaged or the engine may overheat.
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is latched in P (Park). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave your vehicle.
111
Driving
If the parking brake is fully released, but the brake warning lamp remains illuminated, the
brakes may not be working properly. See your dealer or a qualified service technician.
Driving with an automatic overdrive transaxle Your automatic transaxle electronically controls the shift feel by using an adaptive learning strategy. This feature is designed to optimize shift smoothness. It is normal for your transaxle to shift firmly during the first few hundred kilometers (miles) of operation until the adaptive strategy has been learned. The adaptive learning strategy is maintained by power from the battery. When the battery is disconnected or a new battery is installed, the transaxle must relearn its adaptive strategy. Optimal shifting will resume within a few hundred kilometers (miles) of operation. Your automatic overdrive transaxle provides fully automatic operation in (Overdrive) either or D (Drive). Driving with the shift selector in the best fuel economy for normal driving conditions. For manual control start in 1 (First) and then shift manually. If your vehicle is equipped with a console mounted gearshift, you must press the thumb button on the side of the gearshift to move the gearshift from P (Park).
(Overdrive) gives
112
Driving
To put your vehicle in gear, start the engine, depress the brake pedal, then move gearshift out of P (Park).
Hold the brake pedal down while you move the gearshift lever from P (Park) to another position. If you do not hold the brake pedal down, your vehicle may move unexpectedly and injure someone.
Understanding gearshift positions P(Park) Always come to a complete stop before shifting into P (Park). Make sure the gearshift is securely latched in P (Park). This locks the transaxle and prevent the front wheels from rotating.
P R N D D 1
Always set the parking brake fully and make sure the gearshift is latched in P (Park). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave your vehicle.
113
P R N D D 1
P R N D D 1
P R N D D 1
Driving
R(Reverse) With the gearshift in R (Reverse), the vehicle will move backward. You should always come to a complete stop before shifting into and out of R (Reverse).
N(Neutral) With the gearshift in the N (Neutral) position, the vehicle can be started and is free to roll. Hold the brake pedal down while in this position.
(Overdrive)
(Overdrive)
The position is the normal driving position for an automatic overdrive transaxle. It works the same way as D (Drive) but shifts to a fourth gear — an overdrive gear — when your vehicle cruises at a constant speed for any length of time. This
114
Driving
fourth gear will increase your fuel economy when you travel at cruising speeds. Overdrive may not be appropriate for certain terrains. If the transaxle shifts back and forth between third and fourth gears while you are driving hilly roads or if your vehicle requires additional power for climbing hills, shift into D (Drive). WhentouseD(Drive) The D (Drive) position eliminates the needless shifting back and forth between third and fourth gears that your vehicle may do when driving on hilly terrain. It also gives more engine braking than overdrive to slow your vehicle on downgrades.
P R N D D 1
P R N D D 1
1(First) Use 1 (First) for when added engine braking is desired when descending steep hills. The automatic transaxle will shift to the proper gear to ascend any grade without any need to shift to 1 (First).
Do not go faster than 61 km/h (38 mph) when in this gear. You can upshift from 1 (First) to overdrive at any time.
115
Driving
When parking, do not use the gearshift in place of the parking brake. Always set the
parking brake fully and make sure that the gearshift is securely latched in Park (P). Turn off the ignition whenever you leave your vehicle. Never leave your vehicle unattended while it is running. If you do not take these precautions, your vehicle may move unexpectedly and injure someone.
VEHICLE LOADING Before loading a vehicle, familiarize yourself with the following terms: † Base Curb Weight: Weight of the vehicle including any standard equipment, fluids, lubricants, etc. It does not include passengers or aftermarket equipment. † Payload: Combined maximum allowable weight of
cargo, passengers and optional equipment. The payload equals the gross vehicle weight rating minus base curb weight.
† GVW (Gross Vehicle Weight): Base curb weight plus payload weight. The GVW is not a limit or a specification.
† GVWR (Gross Vehicle Weight Rating): Maximum total weight of the base vehicle, passengers, optional equipment and cargo. The GVWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety Compliance Label on the driver’s door pillar. † GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating): Carrying capacity for each axle system. The GAWR is specific to each vehicle and is listed on the Safety Compliance Label on the driver’s door pillar. † GCW (Gross Combined Weight): The combined weight of the towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the trailer.
116
Driving
† GCWR (Gross Combined Weight Rating): Maximum combined weight of towing vehicle (including passengers and cargo) and the trailer. The GCWR indicates the maximum loaded weight that the vehicle is designed to tow.
† Maximum Trailer Weight Rating: Maximum
weight of a trailer the vehicle is permitted to tow. The maximum trailer weight rating is determined by subtracting the vehicle curb weight for each engine/transmission combination, any required option weight for trailer towing and the weight of the driver from the GCWR for the towing vehicle. † Maximum Trailer Weight: maximum weight of a
trailer the loaded vehicle (including passengers and cargo) is permitted to tow. It is determined by subtracting the weight of the loaded trailer towing vehicle from the GCWR for the towing vehicle. † Trailer Weight Range: Specified weight range that the trailer must fall within that ranges from zero to the maximum trailer weight rating.
Remember to figure in the tongue load of your loaded trailer when figuring the total weight.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the certification label.
Do not use replacement tires with lower load carrying capacities than the originals because they may lower the vehicle’s GVWR and GAWR limitations. Replacement tires with a higher limit than the originals do not increase the GVWR and GAWR limitations. The Certification Label, found on the inside pillar of the driver’s door, lists several important vehicle weight rating limitations. Before adding any additional equipment, refer to these limitations. If you are adding weight to the front of your vehicle, (potentially including weight added to the cab), the
117
Driving
weight added should not exceed the Front Axle Reserve Capacity (FARC). Additional frontal weight may be added to the front axle reserve capacity provided you limit your payload in other ways (i.e. restrict the number of passengers or amount of cargo carried). You may add equipment throughout your vehicle if the total weight added is equal to or less than the Total Axle Reserve Capacity (TARC) weight. You should NEVER exceed the Total Axle Reserve Capacity. Always ensure that the weight of passengers, cargo and equipment being carried is within the weight limitations that have been established for your vehicle including both Gross Vehicle Weight and Front and Rear Gross Axle Weight Rating limits. Under no circumstance should these limitations be exceeded. Exceeding any vehicle weight rating limitation could result in serious damage to the vehicle and/or personal injury.
DRIVING THROUGH WATER Do not drive quickly through standing water, especially if the depth is unknown. Traction or brake capability may be limited and if the ignition system gets wet, your engine may stall. Water may also enter your engine’s air intake and severely damage your engine. If driving through deep or standing water is unavoidable, proceed very slowly. Never drive through water that is higher than the bottom of the hubs. Once through the water, always try the brakes. Wet brakes do not stop the vehicle as effectively as dry brakes. Drying can be improved by moving your vehicle slowly while applying light pressure on the brake pedal. Driving through deep water where the transmission is submerged may allow water into the transmission and cause internal transmission damage.
118
Driving
TRAILER TOWING Your vehicle is classified as a light duty towing vehicle. The amount of weight you can safely tow depends on the type of engine you have in your vehicle. Your vehicle does not come from the factory fully equipped to tow. No towing packages are available through Ford or Mercury/Lincoln dealers. Do not tow a trailer until your vehicle has been driven at least 800 km (500 miles). If towing with a station wagon, inflate the rear tires to 35 psi. Towing a trailer places an additional load on your vehicle’s engine, transaxle, brakes, tires and suspension. Inspect these components carefully after towing. In order to identify your vehicle’s engine, refer to Identifying components in the engine compartment in the Maintenance and Care chapter. The amount of weight that you can tow depends on the type of engine in your vehicle. See the following charts:
Model
Sedan
Wagon
Max Trailer Wt.-kg (lbs.)
Luggage Load-kg (lbs.)
3.0L 2-Valve Vulcan Engine Passenger Load-#/kg (lbs.) 5/340 (750) 0
4/270 (600) 70 (150) 2/135 (300) 70 (150) 2/135 (300) 0
4/270 (600) 0
2/135 (300) 70 (150) 2/135 (300) 0365 (800) 365 (800) 500 (1 100) 565 (1 250) 365 (800) 430 (950) 500 (1 100)
The above chart is based on the specified vehicle at a maximum GCW (Vehicle weight + Trailer weight) equal to 2 245 kg (4 950 lbs.).
119
Driving
3.0L 4-Valve Duratec Engine and SHO engine Model Max Trailer Wt.-kg (lbs.)
Sedan
Wagon
Luggage Load-kg (lbs.)
Passenger Load-#/kg (lbs.) 5/340 (750) 0
2/135 (300) 70 (150) 2/135 (300) 0
5/340 (750) 70 (150) 2/135 (300) 70 (150) 2/135 (300) 0590 (1 300) 725 (1 600) 795 (1750) 455 (1 000) 660 (1 450) 725 (1 600)
The above chart is based on the specified vehicle at a maximum GCW (Vehicle weight + Trailer weight) equal to 2 470 kg (5 450 lbs.).
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the certification label.
Towing trailers beyond the maximum recommended gross trailer weight exceeds the limit of the vehicle and could result in engine damage, transaxle damage, structural damage, loss of control, and personal injury.
Preparing to tow Use the proper equipment for towing a trailer, and make sure it is properly attached to your vehicle. See your dealer or a reliable trailer dealer if you require assistance. Hitches Do not use hitches that clamp onto the vehicle bumper. Use a load carrying hitch. You must distribute the load in your trailer so that 10% of the total weight of the trailer is on the tongue.
120
Driving
Safetychains Always connect the trailer’s safety chains to the vehicle. To connect the trailer’s safety chains, cross the chains under the trailer tongue and allow slack for turning corners. If you use a rental trailer, follow the instructions that the rental agency gives to you. Do not attach safety chains to the bumper. Trailerbrakes Electric brakes and manual, automatic or surge-type brakes are safe if installed properly and adjusted to the manufacturer’s specifications. The trailer brakes must meet local and Federal regulations.
Do not connect a trailer’s hydraulic brake system directly to your vehicle’s brake
system. Your vehicle may not have enough braking power and your chances of having a collision greatly increase.
The braking system of the tow vehicle is rated for operation at the GVWR not GCWR. Trailerlamps Trailer lamps are required on most towed vehicles. Make sure your trailer lamps conform to local and Federal regulations. See your dealer or trailer rental agency for proper instructions and equipment for hooking up trailer lamps.
Driving while you tow Do not drive faster than 88 km/h (55 mph) when towing a trailer. Do not drive faster than 72 km/h (45 mph) with any weight on the trailer while towing on a hot day or in hilly country. Speed control may shut off if you are towing on long, steep grades.
121
Driving
When towing a trailer: † Use D (Drive) or a lower gear when towing up or
down steep hills. This will eliminate excessive downshifting and upshifting for optimum fuel economy and transaxle cooling.
† Anticipate stops and brake gradually. Servicingaftertowing If you tow a trailer for long distances, your vehicle will require more frequent service intervals. Refer to your maintenance guide and or service guide for more information.
Trailer towing tips † Practice turning, stopping and backing up in an area before starting on a trip to get the feel of the vehicle trailer combination. When turning, make wider turns so the trailer wheels will clear curbs and other obstacles. † Allow more distance for stopping with a trailer † The trailer tongue weight should be 10% of the † After you have traveled 80 km (50 miles),
loaded trailer weight.
attached.
thoroughly check your hitch, electrical connections and trailer wheel lug nuts.
† When stopped in traffic for long periods of time in hot weather, place the gearshift in P (Park) and increase idle speed. This aids engine cooling and air conditioner efficiency. † Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. If you must park on a grade, place wheel chocks under the trailer’s wheels.
Towing your vehicle behind another vehicle At times, you may want to tow your vehicle behind another vehicle, such as a recreational vehicle, car or a truck.
122
Driving
Before you have your vehicle towed: † Release the parking brake. † Turn the key in the ignition to OFF. † Move the gearshift to N (Neutral). † Unlock the steering wheel. Do not tow your vehicle at a speed faster than 56 km/h (35 mph) or for a distance greater than 80
km (50 miles), unless the drive wheels are placed on dollies.Never use a tow bar that attaches to the bumper when you tow your vehicle. This
could damage the bumper and cause an accident.
LUGGAGE RACK (IF EQUIPPED) The rear crossbar can be adjusted to fit the item being carried. The front crossbar does not move. Do not load more than 44 kg (100 lbs.) on the luggage rack. To adjust cross-bar position: 1. Loosen the thumbwheel at both ends of the cross-bar. 2. Slide the cross-bar to the desired location. 3. Tighten the thumbwheel at both ends of the cross-bar. Use adjustable tie down loops to secure the load.
123
Roadside emergencies
HAZARD FLASHER Use only in an emergency to warn traffic of vehicle breakdown, approaching danger, etc. The hazard flashers can be operated when the ignition is off. † The hazard lights control is located on top of the steering column.
† Depress hazard lights control to activate all hazard flashers simultaneously.
† Depress control again to turn the flashers off. RESETTING THE FUEL PUMP SHUT-OFF SWITCH After a collision, if the engine cranks but does not start, the fuel pump shut-off switch may have been activated. The shut-off switch is a device intended to stop the electric fuel pump when your vehicle has been involved in a substantial jolt. If your vehicle is a sedan, the fuel pump shut-off switch is located on the right side of the trunk behind the trunk liner.
124
Roadside emergencies
If your vehicle is a wagon, the fuel pump shut-off switch is located behind the service panel on the right side of the cargo area.
Use the following procedure to reset the fuel pump shut-off switch. 1. Turn the ignition to the OFF position. 2. Check the fuel system for leaks. 3. If no fuel leak is apparent, reset the fuel pump shut-off switch by pushing in on the reset button. 4. Turn the ignition to the ON position. Pause for a few seconds and return the key to the OFF position. 5. Make a further check for leaks in the fuel system.
FUSES AND RELAYS
Fuses If electrical components in the vehicle are not working, a fuse may have blown. Blown fuses are identified by a broken wire within the fuse. Check the appropriate fuses before replacing any electrical components.
15
Always replace a fuse with one that has the specified amperage rating. Using a fuse with
a higher amperage rating can cause severe wire damage and could start a fire.
125
Roadside emergencies
Standardfuseamperageratingandcolor
COLOR
Fuse Rat- ing
Mini Fuses
Stan- dard Fuses
Maxi Fuses
Car- tridge Maxi Fuses
Fuse Link Car- tridge
Red Blue
— — — — — — —
Grey Violet Pink Tan
Grey Violet Pink Tan
— — — — — — — Blue — Pink
Red Blue Yellow Yellow Yellow
2A 3A 4A 5A 7.5A Brown Brown 10A 15A 20A 25A Natural Natural — 30A 40A 50A 60A 70A 80A
— — — — — — — Blue — Pink — Orange Green Green Red Red — Yellow — — — — Brown Black — Natural —
Green Green Green
Red Blue Tan
— — — — —
Passenger compartment fuse panel The fuse panel is located below and to the left of the steering wheel by the brake pedal. Remove the panel cover to access the fuses. To remove a fuse use the fuse puller tool provided on the fuse panel cover.
126
Roadside emergencies