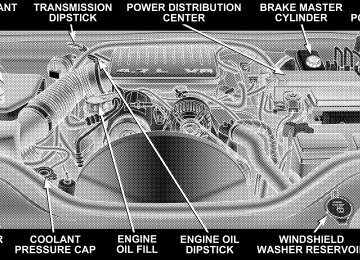
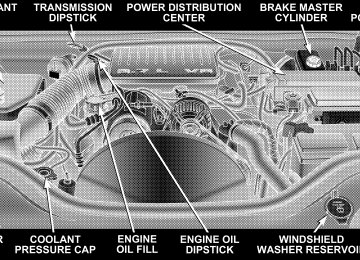
- 2009 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2005 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2013 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2008 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2006 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2004 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2007 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2011 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2012 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- 2010 Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Jeep Grand Cherokee Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
1-5
236 STARTING AND OPERATING
left “D(-)” and hold it there. The transmission will shift to the range from which the vehicle can best be slowed down. Overdrive Operation The overdrive automatic transmission contains an elec- tronically controlled fourth and fifth speed (Overdrive). The transmission will automatically shift from 3rd gear to Overdrive if the following conditions are present: • the transmission selector is in D (Drive); • the engine coolant has reached normal operating tem- • vehicle speed is above approximately 30 mph (48
• the “TOW/HAUL” button has not been activated; • transmission has reached normal operating tempera-perature;
km/h);
ture.
If the vehicle is started in extremely cold tem- NOTE: peratures, the transmission may not shift into Overdrive and will automatically select the most desirable gear for operation at this temperature. Normal operation will resume when the transmission fluid temperature has risen to a suitable level. Refer also to the Note under torque converter clutch, later in this section. If the transmission temperature gets extremely hot, the transmission will automatically select the most desirable gear for operation at this temperature. If the transmission temperature becomes hot enough, the “TRANSMISSION OVER TEMP” message may display and the transmis- sion may downshift out of Overdrive until the transmis- sion cools down. After cooldown, the transmission will resume normal operation. In high ambient temperatures with sustained high engine speed and load, an upshift followed shortly thereafter by
a downshift may occur. This is a normal part of the overheat protection strategy when operating in the “Tow/Haul” mode. The transmission will downshift from Overdrive to the most desirable gear if the accelerator pedal is fully depressed at vehicle speeds above approximately 35 mph (56 km/h). When To Use “TOW/HAUL” Mode — If Equipped When driving in hilly areas, towing a trailer, carrying a heavy load, etc., and frequent transmission shifting oc- curs, press the “TOW/HAUL” button. This will improve performance and reduce the potential for transmission overheating or failure due to excessive shifting. When operating in “TOW/HAUL” mode, the transmission will shift to 3rd gear and 4th will be enabled under steady cruise conditions.
STARTING AND OPERATING 237
Tow/Haul Button
The “TOW/HAUL” light will illuminate in the instru- ment cluster to indicate when the switch has been activated. Pressing the switch a second time restores normal operation. If the “TOW/HAUL” mode is desired, the switch must be pressed each time the engine is started.
238 STARTING AND OPERATING
Torque Converter Clutch A feature designed to improve fuel economy is included in all automatic transmissions. A clutch within the torque converter engages automatically at a calibrated speed at light throttle. It engages at higher speeds under heavier acceleration. This may result in a slightly different feeling or response during normal operation in high gear. When the vehicle speed drops below a calibrated speed, or during acceleration, clutch automatically and smoothly disengages. The feature is operational in Over- drive and in Drive. NOTE: The torque converter clutch will not engage until the transmission fluid and engine coolant are warm [usually after 1-3 miles (1.6 - 4.8 km) of driving]. Because the engine speed is higher when the torque converter clutch is not engaged, it may seem as if the transmission is not shifting into Overdrive when cold. This is normal. Manually shifting between 3 (third gear) and 4 (fourth
the
gear) positions (using the ERS shift control) will demon- strate that the transmission is able to shift into and out of Overdrive. If the vehicle has not been driven in several NOTE: days, the first few seconds of operation after shifting the transmission into gear may seem sluggish. This is due to the fluid partially draining from the torque converter into the transmission. This condition is normal and will not cause damage to the transmission. The torque converter will refill within five seconds of shifting from Park into any other gear position. Rocking the Vehicle If the vehicle becomes stuck in snow, sand, or mud, it can often be moved by a rocking motion. Move the gear selector rhythmically between D (Drive) and R (Reverse), while applying slight pressure to the accelerator.
NOTE: The Electronic Stability Program (ESP) and Traction Control (if equipped) should be turned OFF before attempting to rock the vehicle. Refer to Section 3 of this manual. The least amount of accelerator pedal pressure to main- tain the rocking motion without spinning the wheels or racing the engine is most effective. Racing the engine or spinning the wheels, due to the frustration of not freeing the vehicle, may lead to transmission overheating and failure. Allow the engine to idle with the transmission selector in N (Neutral) for at least one minute after every five rocking-motion cycles. This will minimize overheat- ing and reduce the risk of transmission failure during prolonged efforts to free a stuck vehicle.
STARTING AND OPERATING 239
CAUTION!
When “rocking” a stuck vehicle by moving between “First” and R (Reverse), do not spin the wheels faster than 15 mph (24 km/h), or drivetrain damage may result.
FOUR-WHEEL DRIVE OPERATION
case which provides
Quadra-Trac I姞 Operating Instructions/Precautions — If Equipped The Quadra-Trac I威 is a single speed (HI range only) transfer full-time 4–wheel drive. No driver interaction is required. This transfer case divides engine torque almost evenly with 48
percent of engine torque to the front axle and 52 percent of engine torque to the rear axle. The Brake Traction Control System (BTC), which combines standard ABSconvenient
240 STARTING AND OPERATING
and Traction Control, provides resistance to any wheel that is slipping to allow additional torque transfer to wheels with traction. NOTE: The Quadra-Trac I威 system is not appropriate for conditions where LOW range is recommended. Refer to “Off-Road Driving Tips” in this section. Quadra-Trac II姞 Operating Instructions/Precautions — If Equipped The Quadra-Trac II威 transfer case is fully automatic in the normal driving 4 HI mode. The Quadra-Trac II威 transfer case provides three mode positions — four wheel drive high range, neutral, and four wheel drive low range. This transfer case is fully automatic in the 4 HI mode. This transfer case divides engine torque almost evenly with 48 percent of engine torque to the front axle and 52
percent of engine torque to the rear axle. When speed differences are increased between the front and rear driveshafts, the transfer case can transmit up to 100 percent of available engine torque to the front or rear drive shafts. When additional traction is required, the 4 LOW position can be used to lock the front and rear driveshafts together and force the front and rear wheels to rotate at the same speed. The 4 LOW position is intended for loose, slippery road surfaces only. Driving in the 4 LOW position on dry hard surfaced roads may cause increased tire wear and damage to driveline components. When operating your vehicle in 4 LOW, the engine speed is approximately three times that of the 4 HI position at a given road speed. Take care not to overspeed the engine and do not exceed 25 mph (40 km/h). Proper operation of four wheel drive vehicles depends on tires of equal size, type, and circumference on each wheel. Any difference will adversely affect shifting and cause damage to the transfer case.
Because four wheel drive provides improved traction, there is a tendency to exceed safe turning and stopping speeds. Do not go faster than road conditions permit.
WARNING!
You or others could be injured if you leave the vehicle unattended with the transfer case in the N (Neutral) position without first fully engaging the parking brake. The transfer case N (Neutral) position disengages both the front and rear driveshafts from the powertrain and will allow the vehicle to move regardless of the transmission position. The parking brake should always be applied when the driver is not in the vehicle.
STARTING AND OPERATING 241
Shift Positions
For additional information on the appropriate use of each transfer case mode position, see the information below: 4 HI Four Wheel Drive High Range — All roads surfaces such as ice, snow, gravel, sand, and dry hard pavement. N (Neutral) Neutral — Disengages both the front and rear driveshafts from the powertrain. To be used for flat towing behind another vehicle. Refer to “Recreational Towing” in Sec- tion 5 of this manual. 4 LOW Four Wheel Drive Low Range — Low speed 4 wheel drive. Locks the front and rear driveshafts together. Forces the front and rear wheels to rotate at the same
242 STARTING AND OPERATING
speed. Additional traction and maximum pulling power for loose, slippery road surfaces only. Do not exceed 25
mph (40 km/h). Shifting Procedures4 HI to 4 LOW With the vehicle at speeds of 0 to 3 mph (0 to 5 km/h), key ON or engine running, shift the transmission into N (Neutral), and raise the transfer case T-handle. “The 4WD LOW Indicator Lamp” in the instrument cluster will begin to flash and remain on solid when the shift is complete. Release the T-handle. If shift conditions/interlocks are not met, or a NOTE: transfer case motor temperature protection condition exists, a “CHECK SHIFT PROCEDURES” message will flash from the EVIC (Electronic Vehicle Information Cen- ter). Refer to “Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)” in Section 4 of this manual.
Shifter T-Handle
4 LOW to 4 HI With the vehicle at speeds of 0 to 3 mph (0 to 5 km/h), key ON or engine running, shift the transmission into N (Neutral), and raise the transfer case T-handle. The “4WD
LOW Indicator Lamp” in the instrument cluster will flash and go out when the shift is complete. Release the T-handle. If shift conditions/interlocks are not met, or a NOTE: transfer case motor temperature protection condition exists, a “CHECK SHIFT PROCEDURES” message will flash from the EVIC (Electronic Vehicle Information Cen- ter). Refer to “Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)” in Section 4 of this manual. NOTE: Shifting into or out of 4WD LOW is possible with the vehicle completely stopped, however difficulty may occur due to the mating clutch teeth not being properly aligned. Several attempts may be required for clutch teeth alignment and shift completion to occur. The preferred method is with the vehicle rolling 0 to 3 mph (0
to 5 km/h). If the vehicle is moving faster than 3 mph (5
km/h), the transfer case will not allow the shift.STARTING AND OPERATING 243
Neutral (N) Shift Procedure 1. Key ON, engine off. 2. Vehicle stopped, with foot on brake. 3. Place transmission in N (Neutral). 4. Hold down N (Neutral) “pin” switch (with a pen, etc.) for 4 seconds until the LED lamp by the switch starts to blink indicating shift in progress. Lamp will stop blinking (stay on solid) when Neutral shift is complete. A “4WD SYSTEM IN NEUTRAL” message will display on the EVIC (Electronic Vehicle Information Center). Refer to “Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)” in Sec- tion 4 of this manual. 5. Repeat Steps 1– 4 to shift out of Neutral. If shift conditions/interlocks are not met, a NOTE: “CHECK SHIFT PROCEDURES” message will flash from
244 STARTING AND OPERATING
the EVIC (Electronic Vehicle Information Center). Refer to “Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)” in Section 4 of this manual. Quadra-Drive姞 System — If Equipped The optional Quadra-Drive威 System features three torque transfer couplings. The couplings include ELSD (Electronic Limited Slip Differential) front and rear axles and Quadra-Trac II威 transfer case. The optional ELSD axles are fully automatic and require no driver input to operate. Under normal driving conditions the units func- tion as standard axles balancing torque evenly between left and right wheels. With a traction difference between left and right wheels the coupling will sense a speed difference. As one wheel begins to spin faster than the other, torque will automatically transfer from the wheel that has less traction to the wheel that has traction. While the transfer case and axle couplings differ in design, their
operation is similar. Follow the Quadra-Trac II威 transfer case shifting information, preceding this section, for shifting this system.
PARKING BRAKE To set the parking brake, pull the lever up as firmly as possible. When the parking brake is applied with the ignition ON, the “Brake Warning Light” in the instru- ment cluster will light. NOTE: The instrument cluster “Brake Warning Light” indicates only that the parking brake is applied. It does not indicate the degree of brake application.
STARTING AND OPERATING 245
When parking on a hill, it is important to set the parking brake before placing the gear selector in P (Park), other- wise the load on the transmission locking mechanism may make it difficult to move the selector out of P (Park). The parking brake should always be applied when the driver is not in the vehicle.
WARNING!
• Leaving children unattended in a vehicle is dan- gerous for a number of reasons. A child or others could be injured. Children should be warned not to touch the parking brake or the gear selector lever. Don’t leave the keys in the ignition. A child could operate power windows, other controls, or move the vehicle. • Do not leave children or animals inside parked vehicles in hot weather. Interior heat build up may cause serious injury or death.
Parking Brake
Before leaving the vehicle parked on a hill, you must make sure the parking brake is fully applied and place the gear selector in the P (Park) position. Make certain the transfer case is in gear. Failure to do so may cause the vehicle to roll and cause damage or injury.
246 STARTING AND OPERATING
To release the parking brake, pull up slightly, press the center button, then lower the lever completely. Be sure the parking brake is fully disengaged before driving. Failure to do so can lead to brake failure. NOTE: Parking brake adjustment and maintenance should be performed by your authorized dealer.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) is designed to aid the driver in maintaining vehicle control under adverse braking conditions. The system operates with a separate computer to modulate hydraulic pressure to prevent wheel lock-up and help avoid skidding on slippery surfaces. All vehicle wheels and tires must be the same size and type and tires must be properly inflated to produce accurate signals for the computer.
WARNING!
Significant over or under inflation of tires, or mixing sizes of tires or wheels on the vehicle can lead to loss of braking effectiveness.
The Anti-Lock Brake System conducts a low-speed self- test at about 12 mph (20 km/h). If you have your foot lightly on the brake while this test is occurring you may feel slight pedal movement. The movement can be more apparent on ice and snow. This is normal. The Anti-Lock Brake System pump motor runs during the self-test at 12 mph (20 km/h) and during an ABS stop. The pump motor makes a low humming noise during operation, which is normal.
WARNING!
WARNING!
STARTING AND OPERATING 247
Pumping of the Anti-Lock Brakes will diminish their effectiveness and may lead to an accident. Pumping makes the stopping distance longer. Just press firmly on your brake pedal when you need to slow down or stop.
• The Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) cannot pre- vent the natural laws of physics from acting on the vehicle, nor can it increase braking or steering efficiency beyond that afforded by the condition of the vehicle brakes and tires or the traction afforded.
• The ABS cannot prevent accidents,
including those resulting from excessive speed in turns, following another vehicle too closely, or hydro- planing. Only a safe, attentive, and skillful driver can prevent accidents. • The capabilities of an ABS equipped vehicle must never be exploited in a reckless or dangerous manner which could jeopardize the user’s safety or the safety of others.
248 STARTING AND OPERATING
CAUTION!
The Anti-Lock Brake System is subject to possible detrimental effects of electronic interference caused by improperly installed after-market radios or tele- phones.
NOTE: During severe braking conditions, a pulsing sensation may occur and a clicking noise will be heard. This is normal, the Anti-Lock Brake System is functioning.
indicating that
WARNING!
To use your brakes and accelerator more safely, follow these tips:
• Do not “ride” the brakes by resting your foot on the pedal. This could overheat the brakes and result in longer stopping dis- unpredictable braking action, tances, or brake damage. • When descending mountains or hills, repeated brak- ing can cause brake fade with loss of braking control. Avoid repeated heavy braking by downshifting the transmission or locking out overdrive whenever pos- sible. • Engines may idle at higher speeds during warm-up, which could cause rear wheels to spin and result in loss of vehicle control. Be especially careful while driving on slippery roads, in close-quarter maneuver- ing, parking or stopping. • Do not drive too fast for road conditions, especially when roads are wet or slushy. A wedge of water can
build up between the tire tread and the road. This hydroplaning action can cause loss of traction, braking ability, and control. • After going through deep water or a car wash, brakes may become wet, resulting in decreased performance and unpredictable braking action. Dry the brakes by gentle, intermittent pedal action while driving at very slow speeds.
VARI-LOK REAR AXLE — IF EQUIPPED The optional Vari-Lok axle is fully automatic and requires no driver input to operate. Under normal driving condi- tions the unit functions as a standard axle balancing torque evenly between left and right wheels. With a traction difference between left and right wheels the coupling will sense a speed difference. As one wheel begins to spin faster than the other, torque will automati- cally transfer from the wheel that has less traction to the wheel that has traction.
STARTING AND OPERATING 249
ON-ROAD DRIVING TIPS Utility vehicles have higher ground clearance and a narrower track to make them capable of performing in a wide variety of off-road applications. Specific design characteristics give them a higher center of gravity than ordinary cars. An advantage of the higher ground clearance is a better view of the road, allowing you to anticipate problems. They are not designed for cornering at the same speeds as conventional 2-wheel drive vehicles any more than low- slung sports cars are designed to perform satisfactorily in off-road conditions. If at all possible, avoid sharp turns or abrupt maneuvers. As with other vehicles of this type, failure to operate this vehicle correctly may result in loss of control or vehicle rollover.
250 STARTING AND OPERATING
OFF-ROAD DRIVING TIPS
NOTE: Prior to off-road driving, remove the front air dam to prevent damage. The front air dam is attached to the lower front fascia with quarter turn fasteners, and can be removed by hand. When To Use 4WD LOW Range — If Equipped When off-road driving, shift to 4WD LOW for additional traction. This range should be limited to extreme situa- tions such as deep snow, mud, or sand where additional low speed pulling power is needed. Vehicle speeds in excess of 25 mph (40 km/h) should be avoided when in 4WD LOW range. Driving Through Water Although your vehicle is capable of driving through water, there are a number of precautions that must be considered before entering the water:
CAUTION!
When driving through water, do not exceed 5 mph (8
km/h). Always check water depth before entering as a precaution, and check all fluids afterward. Driving through water may cause damage that may not be covered by the new vehicle limited warranty.Driving through water more than a few inches deep will require extra caution to ensure safety and prevent dam- age to your vehicle. If you must drive through water, try to determine the depth and the bottom condition (and location of any obstacles) prior to entering. Proceed with caution and maintain a steady controlled speed less than 5 mph (8 km/h) in deep water to minimize wave effects. Flowing Water If the water is swift flowing and rising (as in storm run-off) avoid crossing until the water level recedes
and/or the flow rate is reduced. If you must cross flowing water avoid depths in excess of 9 inches. The flowing water can erode the streambed causing your vehicle to sink into deeper water. Determine exit point(s) that are downstream of your entry point to allow for drifting. Standing Water Avoid driving in standing water deeper than 20 inches, and reduce speed appropriately to minimize wave ef- fects. Maximum speed in 20 inches of water is less than 5
mph (8 km/h). Maintenance After driving through deep water, inspect your vehicle fluids and lubricants (engine oil, transmission oil, axle, transfer case) to assure the fluids have not been contami- nated. Contaminated fluid (milky, foamy in appearance) should be flushed/changed as soon as possible to pre- vent component damage.STARTING AND OPERATING 251
Driving In Snow, Mud and Sand In heavy snow, when pulling a load, or for additional control at slower speeds, shift the transmission to a low gear and shift the transfer case to 4WD LOW if necessary. Refer to “Four-Wheel Drive Operation” in this section. Do not shift to a lower gear than necessary to maintain headway. Over-revving the engine can spin the wheels and traction will be lost. Avoid abrupt downshifts on icy or slippery roads, be- cause engine braking may cause skidding and loss of control. Hill Climbing
NOTE: Before attempting to climb a hill, determine the conditions at the crest and/or on the other side. Before climbing a steep hill, shift the transmission to a lower gear and shift the transfer case to 4WD LOW. Use first gear and 4WD LOW for very steep hills.
252 STARTING AND OPERATING
If you stall or begin to lose headway while climbing a steep hill, allow your vehicle to come to a stop and immediately apply the brakes. Restart the engine and shift to R (Reverse). Back slowly down the hill allowing the compression braking of the engine to help regulate your speed. If the brakes are required to control vehicle speed, apply them lightly and avoid locking or skidding the tires.
WARNING!
If the engine stalls or you lose headway or cannot make it to the top of a steep hill or grade, never attempt to turn around. To do so may result in tipping and rolling the vehicle. Always back care- fully straight down a hill in R (Reverse) gear. Never back down a hill in N (Neutral) using only the brake.
Remember, never drive diagonally across a hill-always drive straight up or down. If the wheels start to slip as you approach the crest of a hill, ease off the accelerator and maintain headway by turning the front wheels slowly. This may provide a fresh “bite” into the surface and will usually provide traction to complete the climb. Traction Downhill Shift the transmission into a low gear and the transfer case to 4WD LOW range. Let the vehicle go slowly down the hill with all four wheels turning against engine compression drag. This will permit you to control the vehicle speed and direction. When descending mountains or hills, repeated braking can cause brake fade with loss of braking control. Avoid repeated heavy braking by downshifting the transmis- sion whenever possible.
After Driving Off-Road Off-road operation puts more stress on your vehicle than does most on-road driving. After going off-road it is always a good idea to check for damage. That way you can get any problems taken care of right away and have your vehicle ready when you need it. • Completely inspect the underbody of your vehicle. Check tires, body structure, steering, suspension, and exhaust system for damage. • Check threaded fasteners for looseness, particularly on the chassis, drivetrain components, steering, and sus- pension. Retighten them, if required, and torque to the values specified in the Service Manual. • Check for accumulations of plants or brush. These things could be a fire hazard. They might hide damage to fuel lines, brake hoses, axle pinion seals, and propeller shafts.
STARTING AND OPERATING 253
• After extended operation in mud, sand, water, or similar dirty conditions, have brake rotors, wheels, brake linings, and axle yokes inspected and cleaned as soon as possible.
WARNING!
Abrasive material in any part of the brakes may cause excessive wear or unpredictable braking. You might not have full braking power when you need it to prevent an accident. If you have been operating your vehicle in dirty conditions, get your brakes checked and cleaned as necessary. • If you experience unusual vibration after driving in mud, slush or similar conditions, check the wheels for impacted material. Impacted material can cause a wheel imbalance and freeing the wheels of it will correct the situation.
254 STARTING AND OPERATING
MULTI DISPLACEMENT SYSTEM (MDS) - 5.7L Engine Only This feature offers improved fuel economy by shutting off four of the engine’s eight cylinders during light load and cruise conditions. The system is automatic with no driver inputs or additional driving skills required. NOTE: This system must be reset if the vehicle battery is disconnected. See your authorized dealer for service.
TIRE SAFETY INFORMATION
Tire Markings
NOTE: • P(Passenger)-Metric tire sizing is based on U.S. design standards. P-Metric tires have the letter “P” molded into the sidewall preceding the size designation. Ex- ample: P215/65R15 95H.
• European Metric tire sizing is based on European design standards. Tires designed to this standard have the tire size molded into the sidewall beginning with the section width. The letter ⬙P⬙ is absent from this tire size designation. Example: 215/65R15 96H • LT(Light Truck)-Metric tire sizing is based on U.S. design standards. The size designation for LT-Metric tires is the same as for P-Metric tires except for the letters “LT” that are molded into the sidewall preced- ing the size designation. Example: LT235/85R16.
STARTING AND OPERATING 255
• Temporary Spare tires are high pressure compact spares designed for temporary emergency use only. Tires designed to this standard have the letter “T” molded into the sidewall preceding the size designa- tion. Example: T145/80D18 103M. • High Flotation tire sizing is based on U.S. design standards and begins with the tire diameter molded into the sidewall. Example: 31x10.5 R15 LT.
256 STARTING AND OPERATING
Tire Sizing Chart
Size Designation:
EXAMPLE:
P = Passenger car tire size based on U.S. design standards ⴖ....blank....ⴖ = Passenger car tire based on European design standards LT = Light Truck tire based on U.S. design standards T = Temporary Spare tire 31 = Overall Diameter in Inches (in) 215 = Section Width in Milimeters (mm) 65 = Aspect Ratio in Percent (%)
—Ratio of section height to section width of tire.
10.5 = Section Width in Inches (in) R = Construction Code
—⬙R⬙ means Radial Construction. —⬙D⬙ means Diagonal or Bias Construction.
15 = Rim Diameter in Inches (in)
STARTING AND OPERATING 257
Service Description:
95 = Load Index
EXAMPLE:
—A numerical code associated with the maximum load a tire can carry.
H = Speed Symbol
—A symbol indicating the range of speeds at which a tire can carry a load corresponding to its load index under certain operating conditions. —The maximum speed corresponding to the Speed Symbol should only be achieved un- der specified operating conditions. (ie. tire pressure, vehicle loading, road conditions and posted speed limits).
Load Identification:
ⴖ....blank....ⴖ = Absence of any text on sidewall of the tire indicates a Standard Load (SL) Tire Extra Load (XL) = Extra Load (or Reinforced) Tire Light Load = Light Load Tire C,D,E = Load range associated with the maximum load a tire can carry at a specified pressure
Maximum Load — Maximum Load indicates the maximum load this tire is designed to carry. Maximum Pressure — Maximum Pressure indicates the maximum permissible cold tire inflation pressure for this tire.
258 STARTING AND OPERATING
Tire Identification Number (TIN) The TIN may be found on one or both sides of the tire however the date code may only be on one side. Tires with white sidewalls will have the full TIN including date code located on the white sidewall side of the tire.
Look for the TIN on the outboard side of black sidewall tires as mounted on the vehicle. If the TIN is not found on the outboard side then you will find it on the inboard side of the tire.
DOT = Department of Transportation
—This symbol certifies that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation tire safety standards, and is approved for highway use.
EXAMPLE:
DOT MA L9 ABCD 0301
MA = Code representing the tire manufacturing location.(2 digits) L9 = Code representing the tire size.(2 digits) ABCD = Code used by tire manufacturer.(1 to 4 digits) 03 = Number representing the week in which the tire was manufactured.(2 digits)
—03 means the 3rd week.
01 = Number representing the year in which the tire was manufactured.(2 digits)
—01 means the year 2001. —Prior to July 2000, tire manufacturers were only required to have 1 number to represent the year in which the tire was manufactured. Example: 031 could represent the 3rd week of 1981 or 1991.
Tire Loading and Tire Pressure
Tire Placard Location NOTE: The proper cold tire inflation pressure for pas- senger cars is listed on either the face of the driver’s door or the driver’s side “B” pillar. For vehicles other than passenger cars, the cold tire inflation pressures are listed on either the shutface of the driver’s door, the “B” pillar, the Certification Label or in the Tire Inflation Pressures brochure in the glove compartment.
STARTING AND OPERATING 259
Tire Placard Location
260 STARTING AND OPERATING
Tire and Loading Information Placard
Tire and Loading Information
This placard tells you important information about the: 1) number of people that can be carried in the vehicle 2) the total weight your vehicle can carry 3) the tire size designed for your vehicle 4) the cold tire inflation pressures for the front, rear and spare tires.
Loading The vehicle maximum load on the tire must not exceed the load carrying capacity of the tire on your vehicle. You will not exceed the tire’s load carrying capacity if you adhere to the loading conditions, tire size and cold tire inflation pressures specified on the Tire and Loading Information placard and the Vehicle Loading section of this manual. NOTE: Under a maximum loaded vehicle condition, gross axle weight ratings (GAWR’s) for the front and rear axles must not be exceeded. For further information on GAWR’s, vehicle loading and trailer towing, see the Vehicle Loading section of this manual. To determine the maximum loading conditions of your vehicle, locate the statement “The combined weight of occupants and cargo should never exceed XXX kg or XXX lbs.” on the Tire and Loading Information placard. The
combined weight of occupants, cargo/luggage and trailer tongue weight (if applicable) should never exceed the weight referenced here. Steps for Determining Correct Load Limit 1. Locate the statement “The combined weight of occu- pants and cargo should never exceed XXX pounds” on your vehicle’s placard. 2. Determine the combined weight of the driver and passengers that will be riding in your vehicle. 3. Subtract the combined weight of the driver and pas- sengers from XXX kilograms or XXX pounds. 4. The resulting figure equals the available amount of cargo and luggage load capacity. For example, if “XXX” amount equals 1400 lbs. and there will be five 150 lb. passengers in your vehicle, the amount of available cargo and luggage load capacity is 650 lb. (since 5 x 150 = 750, and 1400 – 750 = 650 lb.)
STARTING AND OPERATING 261
5. Determine the combined weight of luggage and cargo being loaded on the vehicle. That weight may not safely exceed the available cargo and luggage load capacity calculated in step 4. 6. If your vehicle will be towing a trailer, load from your trailer will be transferred to your vehicle. Consult this manual to determine how this reduces the available cargo and luggage load capacity of your vehicle. NOTE: The following table shows examples on how to calculate total load, cargo/luggage and towing capacities of your vehicle with varying seating configurations and number and size of occupants. This table is for illustra- tion purposes only and may not be accurate for the seating and load carry capacity of your vehicle. NOTE: For the following example the combined weight of occupants and cargo should never exceed 865 lbs. (392
Kg).262 STARTING AND OPERATING
WARNING!
1. Safety—
STARTING AND OPERATING 263
Overloading of your tires is dangerous. Overloading can cause tire failure, affect vehicle handling, and increase your stopping distance. Use tires of the recommended load capacity for your vehicle. Never overload them.
TIRES — GENERAL INFORMATION Proper tire inflation pressure is essential to the safe and satisfactory operation of your vehicle. Three primary areas are affected by improper tire pressure:
WARNING!
Improperly inflated tires are dangerous and can cause accidents. • Under inflation increases tire flexing and can result in tire failure. • Over inflation reduces a tire’s ability to cushion shock. Objects on the road and chuck holes can cause damage that results in tire failure. • Unequal tire pressures can cause steering prob- lems. You could lose control of your vehicle. • Overinflated or under inflated tires can affect vehicle handling and can fail suddenly, resulting in loss of vehicle control. Always drive with each tire properly inflated.
264 STARTING AND OPERATING
2. Economy— Improper inflation pressures can cause uneven wear patterns to develop across the tire tread. These abnormal wear patterns will reduce tread life resulting in a need for earlier tire replacement. Under inflation also increases tire rolling resistance and results in higher fuel consump- tion. 3. Ride Comfort and Vehicle Stability— Proper tire inflation contributes to a comfortable ride. Over inflation produces a jarring and uncomfortable ride. Both under inflation and over inflation affect the stability of the vehicle and can produce a feeling of sluggish response or over responsiveness in the steering. Unequal tire pressures can cause erratic and unpredict- able steering response. Unequal tire pressure from side to side may cause the vehicle to drift left or right.
Tire Inflation Pressures The proper cold tire inflation pressure is listed on either the face of the driver’s door, or the driver’s side “B” pillar.
Tire Placard Location
The “Cold Inflation Pressure” of each tire should be checked and adjusted at least once every month. Check
more often if subject to a wide range of outdoor tempera- tures, as tire pressures vary with temperature changes. Inflation pressures specified on the label are always “Cold Inflation Pressure.” Cold inflation pressure is defined as the tire pressure after the vehicle has been idle for at least 3 hours, or driven less than a mile after a 3
hour period. The cold inflation pressure of each tire should be set according to the manufacturers recom- mended pressure, and must not exceed the maximum values molded into the tire sidewall. Tire pressures may increase from 13 to 40 kPa (2 to 6 psi) [0.138 to 0.414 bar] during operation. DO NOT reduce this normal pressure buildup.STARTING AND OPERATING 265
High Speed Operation
WARNING!
High speed driving with your vehicle under load is dangerous. The added strain on your tires could cause them to fail. You could have a serious accident. Don’t drive a vehicle loaded to maximum capacity at continuous speeds above 75 mph (120 km/h).
The manufacturer advocates driving at safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed limits or condi- tions are such that the vehicle can be driven at high speeds, correct tire inflation pressure is very important.
266 STARTING AND OPERATING
Radial-Ply Tires
WARNING!
Tire Spinning When stuck in mud, sand, snow, or ice conditions, do not spin your vehicle’s wheels above 35 mph (55 km/h).
Combining radial ply tires with other types of tires on your vehicle will cause your vehicle to handle poorly. The instability could cause an accident. Al- ways use radial tires in sets of four. Never combine them with other types of tires.
Cuts and punctures in radial tires are repairable only in the tread area because of sidewall flexing. Consult your dealer for radial tire repairs.
WARNING!
Fast spinning tires can be dangerous. Forces gener- ated by excessive wheel speeds may cause tire dam- age or failure. A tire could explode and injure someone. Do not spin your vehicle’s wheels faster than 35 mph (55 km/h) when you are stuck, and do not let anyone near a spinning wheel no matter what the speed.
Tread Wear Indicators These indicators are narrow strips 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) thick and are found in the tread pattern grooves. When the tread pattern is worn down to these treadwear indicators, the tires should be replaced.
STARTING AND OPERATING 267
Replacement Tires The tires on your new vehicle provide a balance of many characteristics. They should be inspected regularly for wear and correct inflation pressure. The manufacturer strongly recommends that you use tires equivalent to the originals in quality and performance when replacement is needed (see section on tread wear indicators). Failure to use equivalent replacement tires may adversely affect the safety, handling, ride and fuel economy of your vehicle. We recommend that you contact your original equipment tire dealer on any questions you may have on tire specifications or capability.
Overloading your vehicle, long trips in very hot weather, and driving on bad roads may result in greater wear.
268 STARTING AND OPERATING
WARNING!
• Do not use a tire, wheel size or rating other than that specified for your vehicle. Some combinations of un- approved tires and wheels may change suspension dimensions and performance characteristics, resulting in changes to steering, handling, and braking of your vehicle. This can cause unpredictable handling and stress to steering and suspension components. You could lose control and have an accident resulting in serious injury or death. Use only the tire and wheel sizes with load ratings approved for your vehicle. • Never use a tire smaller than the minimum tire size listed on your vehicle’s tire label. Using a smaller tire could result in tire overloading and failure. You could lose control and have an accident. • Failure to equip your vehicle with tires having adequate speed capability can result in sudden tire failure and loss of vehicle control. • Overloading your tires is dangerous. Overloading can cause tire failure. Use tires of the recommended load capacity for your vehicle - never overload them.
CAUTION!
Replacing original tires with tires of a different size may result in false speedometer and odometer read- ings. Check with your dealer before replacing tires with a different size.
Alignment and Balance The suspension components of your vehicle should be inspected and aligned when needed, to obtain maximum tire tread life. Poor suspension alignment may result in: • reduced tread life; • uneven tire wear, such as feathering and one-sided • vehicle pull to the right or to the left.
wear;
Tires may also cause the vehicle to pull left or right. Alignment will not correct this problem. See your dealer for proper diagnosis of the problem. Improper alignment will not normally cause vehicle vibration, which may be a result of tire and wheel out-of-balance. Proper balancing will reduce vibration and avoid tire cupping and spotty wear.
TIRE PRESSURE MONITOR SYSTEM
Tire Pressure Monitoring — Base System The Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPM) system uses wireless technology with wheel rim mounted electronic sensors to monitor tire pressure levels. Sensors, mounted to each wheel as part of the valve stem, transmit tire pressure readings to the Receiver Module. It is particularly important, for you to check the NOTE: tire pressure in all of your tires regularly and to maintain the proper pressure.
STARTING AND OPERATING 269
The “Tire Pressure Monitoring Indicator Lamp” will illuminate in the instrument cluster, and an audible chime will be activated when one or more tire pressures is low. The “Tire Pressure Monitoring Indicator Lamp” will flash on and off for ten seconds when a system fault is detected. The flash cycle will repeat every ten minutes or until the fault condition is removed and reset. The Tire Pressure Monitoring System consists of the following components: • Receiver Module • 5 Wheel Sensors (including Full Size Spare Tire) • Amber Colored Tire Pressure Monitoring Indicator
Lamp
The system will consist of tire pressure monitoring sensors attached to each wheel through the valve stem mounting hole, a central receiver module and an amber
270 STARTING AND OPERATING
colored Indicator Lamp. A sensor is located in the spare wheel if the vehicle is equipped with a matching full size spare wheel and tire assembly. NOTE: For vehicles with optional wheel/tire sizes and significantly different tire placard pressures, the placard pressure value and the low-pressure threshold value is re-programmable at your authorized dealer to accommo- date the customer selected wheel/tire combinations rec- ommended by DaimlerChrysler Corporation.
CAUTION!
The TPM system has been optimized for the original equipment tires and wheels. TPM system pressures have been established for the tire size equipped on your vehicle. Undesirable system operation or sen- sor damage may result when using replacement equipment that is not of the same size, type, and/or style. After-market wheels can cause sensor damage. Do not use tire sealant from a can, or balance beads if your vehicle is equipped with a TPM system, as damage to the sensors may result.
CAUTION!
After inspecting or adjusting the tire pressure al- ways reinstall the valve stem cap. This will prevent moisture and dirt from entering the valve stem, which could damage the wheel rim sensor.
pressure condition.
NOTE: • The TPM system can inform the driver of a low tire • The TPM system is not intended to replace normal tire care and maintenance, nor to provide warning of a tire failure or condition. • The TPM system should not be used as a tire pressure
gauge while adjusting your tire pressure.
STARTING AND OPERATING 271
Tire Pressure Monitoring — Premium System The Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPM) system uses wireless technology with wheel rim mounted electronic sensors to monitor tire pressure levels. Sensors mounted to each wheel as part of the valve stem transmit tire pressure readings to the Receiver Module. The wheel sensors monitor tire pressure, and status for all four active road tires and the spare tire. The spare tire pressure is monitored, but not displayed. It is particularly important, for you to check the NOTE: tire pressure in all of your tires regularly and to maintain the proper pressure.
The “Tire Pressure Monitoring Indicator Lamp” will illuminate in the instrument cluster, and an audible chime will be activated when one or more tire pressures is low. The “Tire Pressure Monitoring Indicator Lamp” will flash on and off for ten seconds
272 STARTING AND OPERATING
when a system fault is detected. The flash cycle will repeat every ten minutes or until the fault condition is removed and reset. The Tire Pressure Monitoring System consists of the following components: • Receiver Module • 5 Wheel Sensors (including Full Size Spare Tire) • 4 Wheel Sensor Trigger Modules • Tire Pressure Monitoring System Display Messages in • Amber Colored Tire Pressure Monitoring Indicator
the EVIC
Lamp
The system consists of tire pressure monitoring sensors attached to each wheel through the valve stem mounting hole, a central receiver module, Wheel Sensor Trigger Modules mounted in three of the four wheel wells,
various Tire Pressure Monitoring System Display Mes- sages in the EVIC, and an amber colored Indicator Lamp. A sensor shall be installed in the spare wheel if the vehicle is equipped with a matching full size spare wheel and tire assembly. NOTE: For vehicles with optional wheel/tire sizes and significantly different tire placard pressures, the placard pressure value and the low-pressure threshold value is re-programmable at your authorized dealer to accommo- date the customer selected wheel/tire combinations rec- ommended by DaimlerChrysler Corporation. The following ⬙warnings⬙ will cause a text message to be displayed, an audible chime to sound and the “Tire Pressure Indicator Lamp” to illuminate. The audible chime will occur once every ignition cycle for each ⬙warning⬙ detected. The “Tire Pressure Indicator Lamp”
STARTING AND OPERATING 273
Inspect all tires for proper inflation pressure, once the proper tire pressure has been set, the TPM system warning will reset automatically when the vehicle has been driven for at least 2 minutes at or above 15 mph (24
km/h). CHECK TPM SYSTEM See your authorized dealer when this message appears in the EVIC. This message indicates that a system fault condition has been detected.will illuminate continuously (solid) and shall remain illuminated until the warning condition is removed/ reset. NOTE: The Indicator Lamp will only illuminate for the four active road tires. A low spare tire pressure will not cause the Indicator Lamp to illuminate When the appropriate conditions exist, the Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) displays the following messages. LEFT FRONT, LEFT REAR, RIGHT FRONT, RIGHT REAR, SPARE LOW PRESSURE One or more of these messages will be displayed in the EVIC if a low tire pressure condition exists in one or more tires.
274 STARTING AND OPERATING
CAUTION!
CAUTION!
The TPM system has been optimized for the original equipment tires and wheels. TPM system pressures have been established for the tire size equipped on your vehicle. Undesirable system operation or sen- sor damage may result when using replacement equipment that is not of the same size, type, and/or style. After-market wheels can cause sensor damage. Do not use tire sealant from a can, or balance beads if your vehicle is equipped with a TPM system, as damage to the sensors may result.
After inspecting or adjusting the tire pressure al- ways reinstall the valve stem cap. This will prevent moisture and dirt from entering the valve stem, which could damage the wheel rim sensor.
pressure condition.
NOTE: • The TPM system can inform the driver of a low tire • The TPM system is not intended to replace normal tire care and maintenance, nor to provide warning of a tire failure or condition. • The TPM system should not be used as a tire pressure
gauge while adjusting your tire pressure.
General Information This device complies with part 15 of the FCC rules and RSS 210 of Industry Canada. Operation is subject to the following conditions: • This device may not cause harmful interference. • This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired op- eration.
The tire pressure sensors are covered under one of the following licenses:
United States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . KR5S120123
Canada . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2671-S120123STARTING AND OPERATING 275
TIRE CHAINS Certain models have sufficient tire-to-body clearance to allow use of tire chains. Install chains on rear tires only. Follow these recommendations to guard against damage and excessive tire and chain wear: • Do not install tire chains or traction devices on ve- hicles with larger than P235/65R17 size tires. Tires larger than this may not provide sufficient body clearance with chains or other traction devices. • Use SAE class “S” tire chains or traction devices only. • Follow tire chain manufacturer’s instructions for • Install chains snugly and tighten after 1/2 mile (1 km) • Do not exceed 35 mph (56 km/h), unless otherwise • Drive cautiously, avoiding large bumps, potholes and
specified by the chain manufacturer.
mounting chains.
of driving.
extreme driving maneuvers.
NOTE: The Premium Tire Pressure Monitor System will automatically locate the pressure values displayed in the correct vehicle position following a tire rotation. The suggested rotation method is the “forward-cross” shown in the following diagram.
276 STARTING AND OPERATING
TIRE ROTATION RECOMMENDATIONS Tires on the front and rear axles of vehicles operate at different loads and perform different steering, handling, and braking functions. For these reasons, they wear at unequal rates, and develop irregular wear patterns. These effects can be reduced by timely rotation of tires. The benefits of rotation are especially worthwhile with aggressive tread designs such as those on On/Off Road type tires. Rotation will increase tread life, help to main- tain mud, snow, and wet traction levels, and contribute to a smooth, quiet ride. Follow the recommended tire rotation frequency for your type of driving found in the “Maintenance Schedules” Section of this manual. More frequent rotation is permis- sible if desired. The reasons for any rapid or unusual wear should be corrected prior to rotation being per- formed.
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
3.7/4.7L Engines (If Equipped)
All engines (except 5.7L engines) are de- signed to meet all emissions regulations and provide excellent fuel economy and performance when using high quality un- leaded “regular” gasoline having an oc- tane rating of 87. The use of premium gasoline is not recommended. Under normal conditions, the use of premium gasoline will not provide a benefit over high quality regular gasolines, and in some circum- stances may result in poorer performance. 5.7L Engines (If Equipped)
The 5.7L engine is designed to meet all emissions regulations and provide satisfac- tory fuel economy and performance when
STARTING AND OPERATING 277
using high quality unleaded gasoline having an octane range of 87 to 89. The manufacturer recommends the use of 89 octane for optimum performance. The use of premium gasoline is not recommended. Under normal conditions, the use of premium gasoline will not provide a benefit over high quality regular and mid-grade gaso- lines, and in some circumstances may result in poorer performance. Light spark knock at low engine speeds is not harmful to your engine. However, continued heavy spark knock at high speeds can cause damage and immediate service is required. Poor quality gasoline can cause problems such as hard starting, stalling and hesitations. If you experience these symptoms, try another brand of gasoline before consid- ering service for the vehicle.
278 STARTING AND OPERATING
Over 40 auto manufacturer’s world wide have issued and endorsed consistent gasoline specifications (the World- wide Fuel Charter, WWFC) to define fuel properties necessary to deliver enhanced emissions, performance, and durability for your vehicle. The manufacturer recom- mends the use of gasoline that meets the WWFC speci- fications if they are available. Reformulated Gasoline Many areas of the country require the use of cleaner burning gasoline referred to as Reformulated Gasoline. Reformulated gasoline contains oxygenates, and is spe- cifically blended to reduce vehicle emissions and im- prove air quality. The manufacturer strongly supports the use of reformu- lated gasoline. Properly blended reformulated gasoline will provide excellent performance and durability for the engine and fuel system components.
Gasoline/Oxygenate Blends Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with oxy- genates such as 10% ethanol, MTBE, and ETBE. Oxygen- ates are required in some areas of the country during the winter months to reduce carbon monoxide emissions. Fuels blended with these oxygenates may be used in your vehicle.
CAUTION!
DO NOT use gasoline containing METHANOL. Gasoline containing methanol may damage critical fuel system components.
MMT In Gasoline MMT is a manganese containing metallic additive that is blended into some gasoline to increase octane. Gasoline blended with MMT provides no performance advantage beyond gasoline of the same octane number without MMT. Gasoline blended with MMT reduces spark plug life and reduces emission system performance in some vehicles. The manufacturer recommends that gasoline without MMT be used in your vehicle. The MMT content of gasoline may not be indicated on the gasoline pump, therefore, you should ask your gasoline retailer whether or not his/her gasoline contains MMT. It is even more important to look for gasoline without MMT in Canada because MMT can be used at levels higher than allowed in the United States. MMT is pro- hibited in Federal and California reformulated gasoline.
STARTING AND OPERATING 279
Materials Added To Fuel All gasoline sold in the United States is required to contain effective detergent additives. Use of additional detergents or other additives is not needed under normal conditions. Fuel System Cautions
CAUTION!
Follow these guidelines to maintain your vehicle’s performance: • The use of leaded gas is prohibited by Federal law. Using leaded gasoline can impair engine performance, damage the emission control system.
280 STARTING AND OPERATING
• An out-of-tune engine, or certain fuel or ignition malfunctions, can cause the catalytic converter to overheat. If you notice a pungent burning odor or some light smoke, your engine may be out of tune or malfunctioning and may require immediate service. Contact your dealer for service assistance. • The use of fuel additives which are now being sold as octane enhancers is not recommended. Most of these products contain high concentrations of methanol. Fuel system damage or vehicle performance problems resulting from the use of such fuels or additives is not the responsibility of the manufacturer.
NOTE: systems can result against you.
Intentional tampering with emissions control in civil penalties being assessed
Carbon Monoxide Warnings
WARNING!
Carbon monoxide (CO) in exhaust gases is deadly. Follow the precautions below to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning: • Do not inhale exhaust gases. They contain carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas which can kill. Never run the engine in a closed area, such as a garage, and never sit in a parked vehicle with the engine running for an extended period. If the vehicle is stopped in an open area with the engine running for more than a short period, adjust the ventilation system to force fresh, outside air into the vehicle.
• Guard against carbon monoxide with proper mainte- nance. Have the exhaust system inspected every time the vehicle is raised. Have any abnormal conditions repaired promptly. Until repaired, drive with all side windows fully open. • Keep the liftgate closed when driving your vehicle to prevent carbon monoxide and other poisonous ex- haust gases from entering the vehicle.
FUEL TANK FILLER CAP (GAS CAP) The fuel cap is located on the left side of the vehicle. If the fuel cap is lost or damaged, be sure the replacement cap is for use with this vehicle.
STARTING AND OPERATING 281
Fuel Filler Cap Location
282 STARTING AND OPERATING
CAUTION!
CAUTION!
Damage to the fuel system or emission control system could result from using an improper fuel cap (gas cap). A poorly fitting cap could let impurities into the fuel system. Also, a poorly fitting after- market cap can cause the MIL (Malfunction Indica- tor Light) to illuminate, due to fuel vapors escaping from the system. • Turn the engine off. • Rotate the fuel cap to the left to remove. • To replace the cap, insert it into the filler neck and tighten the cap about 1/4 turn until you hear one click. This is an indication that the cap is properly tightened. • Make sure that the fuel cap tether strap is not caught
under the fuel cap.
To avoid fuel spillage and overfilling, do not “top off” the fuel tank after filling.
NOTE: When the fuel nozzle “clicks” or shuts off, the fuel tank is full. Loose Fuel Filler Cap Message If the vehicle diagnostic system determines that the fuel filler cap is loose, improperly installed, or damaged, a “CHECK GAS CAP” message will be displayed in the EVIC (Electronic Vehicle Information Center). Refer to “Electronic Vehicle Information Center” in Section 4 of this manual. Tighten the fuel filler cap properly and press the odometer reset button to turn the message off. If the problem continues, the message will appear the next time the vehicle is started. Refer to “Onboard Diagnostic System — OBDII” in Section 7 of this manual for more information.
WARNING!
• Remove the fuel cap (gas cap) slowly to prevent fuel spray from the filler neck which may cause injury. • The volatility of some gasoline may cause a buildup of pressure in the fuel tank that may increase while you drive. This pressure can result in a spray of gasoline and/or vapors when the cap is removed from a hot vehicle. Removing the cap slowly allows the pressure to vent and prevents fuel spray. • Never have any smoking materials lit in or near the vehicle when the fuel cap is removed or the tank filled. • Never add fuel to the vehicle when the engine is
running.
STARTING AND OPERATING 283
WARNING!
A fire may result if gasoline is pumped into a portable container that is inside of a vehicle. You could be burned. Always place gas containers on the ground while filling.
TRAILER TOWING In this section you will find information on limits to the type of towing you can reasonably do with your vehicle. And you will find safety tips. Before towing a trailer carefully review this information to tow your load as efficiently and safely as possible. To maintain warranty coverage, follow the requirements and recommendations in this manual concerning ve- hicles used for trailer towing. Perform maintenance services as prescribed in the appro- priate “Maintenance Schedule.” Refer to Section 8 of this
284 STARTING AND OPERATING
manual. When your vehicle is used for trailer towing, never exceed the gross axle weight rating (GAWR) by the addition of: • The tongue weight of the trailer. • The weight of any other type of cargo or equipment
put in or on your vehicle.
WARNING!
Improper towing can lead to an injury accident. Follow these guidelines to make your trailer towing as safe as possible: • Be sure a trailer is loaded heavier in front, about 10% to 15% of gross trailer weight. Loads balanced over the wheels or heavier in the rear cause the trailer to sway severely side to side which will cause loss of control of
2,000 lbs (907 kg).
the vehicle and trailer. Failure to load trailers heavier in front is the cause of many trailer related accidents. • Do not interconnect the hydraulic brake system of your vehicle with that of the trailer. This could cause inadequate braking and possible personal injury. • Trailer brakes are required for trailers in excess of • Do not connect a trailer lighting system directly to the lighting system of your vehicle. Use an approved trailer wiring harness. Failure to do so could damage the vehicle electrical system and/or result in personal injury. • When hauling cargo or towing a trailer, do not over- load your vehicle or trailer. Overloading can cause a loss of control, poor performance or damage to brakes, axle, engine, transmission, steering, suspension, body structure or tires.
will not shift during travel.
• Make certain that the load is secured in the trailer and • It is recommended that any hitches installed on your vehicle be factory installed, or installed by a dealer using factory approved parts. Factory approved parts are specifically engineered with your vehicle’s perfor- mance in mind, including the possibility that it will be involved in an accident. Other hitches may not have been so engineered. Vehicle performance, including vehicle damage in an accident situation, may therefore be different. • If trailer towing is required and your vehicle is not equipped with a trailer tow package, the Mopar威 accessory towing harnesses are the only approved method to provide for trailer lights. These harnesses are designed to provide current to the trailer lights but bypass the module designed to monitor tail lights. Refer to the package instructions for details.
STARTING AND OPERATING 285
Trailer and Tongue Weight Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) means the weight of the trailer plus the weight of all cargo, consumables and equipment loaded on the trailer when in actual under- way towing condition. The best way to measure GTW is to put your fully loaded trailer on a vehicle scale. The entire weight of the trailer must be supported by the scale. Always load a trailer with 60% of the cargo weight in the front of the trailer. This places approximately 10% to 15% of the GTW on the tow hitch of your vehicle. This portion of the GTW becomes the tongue weight. Trailer sway control and equalizing hitch are required for tongue weights above 350 lbs (159 kg)., trailer weights heavier than 3,500 lbs (1 587 kg).
i.e.,
286 STARTING AND OPERATING
Trailer Tow Wiring The Trailer Tow Package includes a 4 and 7 pin wiring harness located at the rear underbody of the vehicle. NOTE: Connect trailer lighting and brakes using factory harnesses only. Do not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The electrical connections are all complete to the vehicle but you must mate the harness to a trailer connector. Refer to the following illustrations.
4–Pin Connector
STARTING AND OPERATING 287
Cooling System Tips—Trailer Towing To reduce potential for engine and transmission over- heating in high ambient conditions, take the following actions: • City Traffic When stopped, put transmission in N (Neutral) and increase engine idle speed. • Highway Driving Reduce speed. • Air Conditioning Turn off temporarily. To reduce the potential for transmission overheating, turn the “TOW/HAUL” feature on when driving in hilly areas or downshift the transmission to the next lower gear range to eliminate excessive transmission shifting. This action will also reduce the possibility of transmis- sion overheating and provide better engine braking.
7–Pin Connector
288 STARTING AND OPERATING
TRAILER CLASSIFICATIONS
Class
Max. GTW (Gross Trailer Wt.)
Frontal Area
Class I - Light Duty
Class II - Medium Duty Class III - Heavy Duty
2,000 lbs. (907 kg) 3,500 lbs. (1 587 kg) 5,000 lbs. (2 268 kg)
Class IV - Extra Heavy Duty
(See Note 1) Note 1 – Refer to the Trailer Towing Capability chart for the Max. GTW towable for a given drivetrain.
32 ft2
40 ft2
60 ft2
60 ft2Length 20 ft 20 ft 25 ft 30 ft
TRAILER TOWING CAPABILITY
Engine Model
(Gross Vehice Wt.
(Gross Combined
GVWR
Rating)
GCWR
Wt. Rating)
STARTING AND OPERATING 289
Hitch Type
Max. GTW
(Gross Trailer Wt.)
Max. Tongue Wt.
(See Note 1)
3.7L 3.7L 4.7L 4.7L 5.7L
4x2
4x4
4x2
4x4
4x48,000 lbs (3 629 kg) 5,700 lbs (2 585 kg) 5,900 lbs (2 676 kg) 8,200 lbs (3 719 kg) 6,010 lbs (2 726 kg) 11,200 lbs (5 080 kg) 6,100 lbs (2 767 kg) 11,450 lbs (5 194 kg) 6,150 lbs (2 789 kg) 12,200 lbs (5 534 kg)
Class II Class II Class IV Class IV Class IV
3,500 lbs (1 587 kg) 3,500 lbs (1 587 kg) 6,500 lbs (2 948 kg) 6,500 lbs (2 948 kg) 7,200 lbs (3 266 kg)
525 lbs (238 kg) 525 kbs (238 kg) 720 lbs (327 kg) 720 lbs (327 kg) 720 lbs (327 kg)
Note 1 – The towing vehicle payload should be reduced by the tongue load (for a dead weight hitch) to keep the rear axle loading below GAWR (Gross Axle Weight Rating) of 3,200 lbs (1 451 kg).
290 STARTING AND OPERATING
RECREATIONAL TOWING (BEHIND MOTORHOME, ETC.)
Towing – 2WD Models
Recreational towing is allowed ONLY if the driveshaft is removed. Towing with the rear wheels on the ground while the driveshaft is connected can result in severe transmission damage which is not covered under the Limited Warranty. Towing — Quadra-Trac I (Single-Speed Transfer Case) 4WD Models
Recreational towing is not allowed. This model does not have a N (Neutral) position in the transfer case.
Towing — Quadra–Trac II /Quadra–Drive II 4WD Models
CAUTION!
Internal damage to the transfer case will occur if a front or rear wheel lift is used when recreational towing.
NOTE: The transfer case must be in the N (Neutral) position, and the transmission must be in the P (Park) position for recreational towing. Shifting Into Neutral (N) Use the following procedure to prepare your vehicle for recreational towing.
CAUTION!
It is necessary to follow these steps to be certain that the transfer case is fully in N (Neutral) before recreational towing to prevent damage to internal parts.
1. Depress brake pedal. 2. Shift transmission into N (Neutral). 3. Shift transfer case lever into N (Neutral). Refer to “Four-Wheel Drive Operation” in this section. Start en- gine. 4. Shift transmission into D (Drive). 5. Release brake pedal and ensure that there is no vehicle movement.
STARTING AND OPERATING 291
6. Shut the engine OFF and place the ignition key into the unlocked OFF position. 7. Shift transmission into P (Park). 8. Apply parking brake. 9. Attach vehicle to the tow vehicle with tow bar. 10. Release parking brake.
CAUTION!
Transmission damage may occur if the transmission is shifted into P (Park) with the transfer case in N (Neutral) and the engine running. With the transfer case in N (Neutral) ensure that the engine is OFF prior to shifting the transmission into P (Park) (refer to steps 7 – 8 above).
292 STARTING AND OPERATING
Shifting Out Of Neutral (N) Use the following procedure to prepare your vehicle for normal usage. 1. Turn the ignition key to the unlocked OFF position. 2. Shift transmission into N (Neutral). 3. Shift transfer case lever to desired position. Refer to “Four-Wheel Drive Operation” in this section. 4. Shift transmission into P (Park). 5. Start the engine. 6. Shift transmission into D (Drive). NOTE: When shifting out of transfer case N (Neutral), turning the engine OFF may be required to avoid gear clash.
WARNING!
You or others could be injured if you leave the vehicle unattended with the transfer case in the N (Neutral) position without first fully engaging the parking brake. The transfer case N (Neutral) position disengages both the front and rear driveshafts from the powertrain and will allow the vehicle to move regardless of the transmission position. The parking brake should always be applied when the driver is not in the vehicle.
CAUTION!
Do not use a bumper mounted clamp-on tow bar on your vehicle. The bumper face bar will be damaged.
SNOW PLOW Snow plows, winches, and other aftermarket equipment should not be added to the front end of your vehicle. The airbag crash sensors may be affected by the change in the front end structure. The airbags could deploy unexpect- edly or could fail to deploy during a collision.
STARTING AND OPERATING 293
WARNING!
Do not add a snow plow, winches, or any other aftermarket equipment to the front of your vehicle. This could adversely affect the functioning of the airbag system and you could be injured.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
CONTENTS
䡵 Hazard Warning Flashers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
䡵 If Your Engine Overheats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
䡵 Jacking And Tire Changing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
▫ Jack Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
▫ Spare Tire Stowage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 299
▫ Spare Tire Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 299
▫ Preparations For Jacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300▫ Jacking Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
䡵 Jump Starting Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
䡵 Emergency Tow Hooks — If Equipped . . . . . . . . 305
䡵 Towing A Disabled Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
▫ 2WD Models Only . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
▫ 4WD Models Only . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306296 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
HAZARD WARNING FLASHERS Your vehicle’s hazard warning flasher is an emergency warning system. When you activate it, all front and rear directional signals will flash intermittently. Use it when your vehicle is disabled on or near the road. It warns other drivers to steer clear of you and your vehicle. This is an emergency warning system, not to be used when the vehicle is in motion.
Hazard Warning Switch
To activate the warning flasher, push down on the button on top of the steering column until it latches. To turn the warning flasher off, push down again to unlatch the button. NOTE: With extended use, the flasher may run down your battery.
IF YOUR ENGINE OVERHEATS In any of the following situations, you can reduce the potential for overheating by taking the appropriate ac- tion. • On the highways — Slow down. • In city traffic — While stopped, put transmission in N
(Neutral), but do not increase engine idle speed.
NOTE: There are steps that you can take to slow down an impending overheat condition. If your air conditioner is on, turn it off. The air conditioning system adds heat to the engine cooling system and turning off the A/C removes this heat. You can also turn the Temperature Control to maximum heat, the Mode Control to floor, and the Fan Control to High. This allows the heater core to act as a supplement to the radiator and aids in removing heat from the engine cooling system.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 297
CAUTION!
Driving with a hot cooling system could damage your vehicle. If the temperature gauge reads “H”, pull over and stop the vehicle. Idle the vehicle with the air conditioner turned off until the pointer drops back into the normal range. If the pointer remains on the “H”, and you hear continuous chimes, turn the engine off immediately, and call for service.
298 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
JACKING AND TIRE CHANGING
WARNING!
• Getting under a jacked-up vehicle is dangerous. The vehicle could slip off the jack and fall on you. You could be crushed. Never get any part of your body under a vehicle that is on a jack. If you need to get under a raised vehicle, take it to a service center where it can be raised on a lift. • The jack is designed to use as a tool for changing tires only. The jack should not be used to lift the vehicle for service purposes. The vehicle should be jacked on a firm level surface only. Avoid ice or slippery areas.
Jack Location The scissor-type jack and tire changing tools are located in a compartment behind the second row seat.
Jack Storage Location
Spare Tire Stowage The spare tire is stowed under the rear of the vehicle by means of a cable winch mechanism. To remove or stow the spare, use the jack handle to rotate the “spare tire drive” nut. The nut is located under a plastic cover at the center- rear of the cargo floor area, just inside the liftgate opening.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 299
Spare Tire Removal Fit the jack handle extension over the drive nut. Use the Lug Wrench to rotate the nut counter clockwise until the spare is on the ground with enough slack in the cable to allow to pull the tire out from under the vehicle.
CAUTION!
The winch mechanism is designed for use with the jack extension tube only. Use of an air wrench or other power tools is not recommended and can damage the winch.
When the spare is clear, tilt the retainer at the end of the cable and pull it through the center of the wheel.
Lowering/Raising Spare
300 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
Preparations For Jacking Park the vehicle on a firm level surface, avoid ice or slippery areas, set the parking brake and place the gear selector in P (Park). Turn OFF the ignition.
WARNING!
Do not attempt to change a tire on the side of the vehicle close to moving traffic. Pull far enough off the road to avoid being hit when operating the jack or changing the wheel. • Turn on the Hazard Warning Flasher.
• Block both the front and rear of the wheel diagonally oppo- site of the jacking position. For example, if changing the right front tire, block the left rear wheel. • Passengers should not remain in the vehicle when the
vehicle is being jacked.
Jacking Instructions
1. Remove the spare tire, jack, and tools from storage. 2. Loosen (but do not remove) the wheel lug nuts by turning them to the left one turn while the wheel is still on the ground.
3. Assemble the jack and jacking tools as shown. Connect jack handle driver (A) to two extensions (B), then to the lug wrench (C).
Ensure the jack is closest to the inside of the wheel when jacking on the rear axle. Do not raise the vehicle until you are sure the jack is fully engaged.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 301
4. Locate the jack as shown. For the front axle, place it under the front lower control arm as shown. For the rear axle, place it under the axle near the wheel to be changed.
Front Jacking Location
302 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
Rear Jacking Location
5. Raise the vehicle by turning the jack screw clockwise. Raise the vehicle only until the tire just clears the surface and enough clearance is obtained to install the spare tire. Minimum tire lift provides maximum stability.
WARNING!
Raising the vehicle higher than necessary can make the vehicle less stable. It could slip off the jack and hurt someone near it. Raise the vehicle only enough to remove the tire.
6. Remove the lug nuts and wheel. 7. Position the spare wheel/tire on the vehicle and install the lug nuts with the cone-shaped end toward the wheel. Lightly tighten the nuts. To avoid the risk of forcing the vehicle off the jack, do not tighten the nuts fully until the vehicle has been lowered. 8. Lower the vehicle by turning the jack screw counter clockwise, and remove the jack and wheel blocks. 9. Finish tightening the lug nuts. Push down on the wrench while tightening for increased leverage. Alternate
nuts until each nut has been tightened twice. Correct wheel nut tightness is 130 N·m (95 ft. lbs). If in doubt about the correct tightness, have them checked with a torque wrench by your authorized dealer or at a service station. 10. Lower the jack to it’s fully closed position.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 303
or damage to the wheel face. Continue winching up the tire until you hear the winch “ratchet” three times. Double check to ensure the tire is snug against the underbody of the vehicle. Damage to the winch cable may result if the vehicle is driven with the tire loose. 12. Reinstall the rubber plug into the floor of the cargo area.
WARNING!
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE
A loose tire or jack, thrown forward in a collision or hard stop could endanger the occupants of the ve- hicle. Always stow the jack parts and the spare tire in the places provided.
11. Secure the tire, jack, and tools in their proper loca- tions. NOTE: Tire should be stowed with the “beauty” side up. Storing the tire upside down may result in scratching
NOTE: Check the test indicator on top of battery for battery fluid level. If the indicator is clear, the level is low. Add water to the proper level and reinstall the vent caps before attempting to jump start the vehicle. 1. Wear eye protection and remove any metal jewelry such as watch bands or bracelets that might make an unintended electrical contact. 2. When boost is provided by a battery in another vehicle, park that vehicle within booster cable reach but
304 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
without letting the vehicles touch. Set the parking brake, place the transmission in P (Park), and turn the ignition to OFF for both vehicles. 3. Turn off the heater, radio and all unnecessary electrical loads. 4. Connect one end of a jumper cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery. Connect the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery. 5. Connect the other cable, first to the negative terminal of the booster battery and then connect the other end to a non-paint metal surface on the engine of the vehicle with the discharged battery. Make sure you have a good contact on the engine. 6. Start the engine in the vehicle which has the booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes, then start the engine in the vehicle with the discharged battery.
7. When removing the jumper cables, reverse the above sequence exactly. Be careful of the moving belts and fan. NOTE: To start the vehicle following connection of a booster battery, the Security Alarm System must first be disabled by cycling a front door key cylinder or by using the keyless entry transmitter.
WARNING!
Jump starting can be dangerous. To avoid personal injury or damage to electrical components in vehicle, observe the following warnings: • Battery fluid is a corrosive acid solution and can burn or even blind you. Don’t allow battery fluid to contact your eyes, skin, or clothing. Don’t lean over a battery
when attaching clamps. If acid splashes in eyes or on skin, flush the area immediately with large amounts of water. • Do not use a booster battery or any other booster source that has a greater than 12–volt system, i.e., do not use a 24–volt power source. • Never attempt to jump start a discharged battery that is frozen, because it could rupture or explode during jump starting. • Be sure your vehicle is not touching the jump start • Observe all Battery Warnings in Section 7 of this
vehicle.
manual, while jump starting your vehicle.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 305
WARNING!
Do not attempt to push or tow your vehicle to get it started. Unburned fuel could enter the catalytic converter and, once the engine has started, ignite and damage the converter and vehicle.
EMERGENCY TOW HOOKS — IF EQUIPPED If your vehicle is equipped with tow hooks, there will be one in the rear and two mounted on the front of the vehicle. The rear hook will be located on the driver’s side of the vehicle. NOTE: For off-road recovery, it is recommended to use both of the front tow hooks to minimize the risk of damage to the vehicle.
306 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
CAUTION!
Tow hooks are for emergency use only, to rescue a vehicle stranded off road. Do not use tow hooks for tow truck hookup or highway towing. You could damage your vehicle.
WARNING!
Stand clear of vehicles when pulling with tow hooks. Tow straps and chains may break, causing serious injury.
TOWING A DISABLED VEHICLE
2WD Models Only Provided the transmission is operable, tow only in N (Neutral) at speeds not exceeding 30 mph (48 km/h), for distances of not more than 15 miles (24 km). Towing at more than 30 mph (48 km/h) or for more than 15 miles (24 km) can cause severe transmission damage. If the transmission is not operable, or the vehicle must be towed faster than 30 mph (48 km/h) or farther than 15
miles (24 km), remove the driveshaft or tow with all four wheels OFF the ground. Acceptable methods are to tow the vehicle on a flatbed or with one end of the vehicle raised and the other end on a towing dolly. 4WD Models Only The manufacturer recommends towing with all four wheels OFF the ground. Acceptable methods are to tow the vehicle on a flatbed or with one end of the vehicle raised and the other end on a towing dolly.MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
CONTENTS
䡵 3.7L Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
䡵 4.7L Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
䡵 5.7L Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312
䡵 Onboard Diagnostic System — OBD II . . . . . . . . 313
▫ Loose Fuel Filler Cap Message . . . . . . . . . . . . 313䡵 Emissions Inspection And Maintenance
Programs
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
䡵 Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
䡵 Dealer Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316䡵 Maintenance Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
▫ Engine Oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
▫ Drive Belts - Check Condition And Tension . . . 320
▫ Spark Plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
▫ Catalytic Converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
▫ Ignition Cables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323
▫ Crankcase Emission Control System . . . . . . . . 323
▫ Fuel Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323
▫ Air Cleaner Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323308 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
▫ Maintenance-Free Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324
▫ Air Conditioner Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
▫ Power Steering Fluid Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
▫ Body Lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
▫ Windshield Wiper Blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
▫ Windshield Washers — Front And Rear . . . . . 328
▫ Exhaust System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 328
▫ Cooling System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
▫ Hoses And Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses . . . . . . . 334
▫ Brake System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
▫ Automatic Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
▫ Transfer Case . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
▫ Front/Rear Axle Fluid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340▫ Appearance Care And Protection From
䡵 Fuse Panel
Corrosion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 340
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
▫ Interior Fuses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
▫ Underhood Fuses(Power Distribution Center) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
▫ Underhood Fuses
(Integrated Power Module)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
䡵 Vehicle Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
䡵 Replacement Bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
䡵 Bulb Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
▫ Head Light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 351
▫ Front Turn Signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 353
▫ Front Fog Light . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354▫ Rear Tail, Stop, Turn Signal, And Back-Up
Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
▫ Center High Mounted Stop Light (CHMSL) . . . 356
䡵 Fluid Capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357䡵 Recommended Fluids, Lubricants And Genuine
Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
▫ Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
▫ Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 309
310 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
3.7L ENGINE
4.7L ENGINE
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 311
312 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
5.7L ENGINE
ONBOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM — OBD II Your vehicle is equipped with a sophisticated onboard diagnostic system called OBD II. This system monitors the performance of the emissions, engine, and automatic transmission control systems. When these systems are operating properly, your vehicle will provide excellent performance and fuel economy, as well as engine emis- sions well within current government regulations. If any of these systems require service, the OBD II system will turn on the “Malfunction Indicator Light.” It will also store diagnostic codes and other information to assist your service technician in making repairs. Al- though your vehicle will usually be drivable and not need towing, see your dealer for service as soon as possible.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 313
CAUTION!
• Prolonged driving with the “Malfunction Indica- tor Light” on could cause further damage to the emission control system. It could also affect fuel economy and driveability. The vehicle must be serviced before any emissions tests can be per- formed. • If the “Malfunction Indicator Light” is flashing while the engine is running, severe catalytic con- verter damage and power loss will soon occur. Immediate service is required.
Loose Fuel Filler Cap Message After fuel is added, the vehicle diagnostic system can determine if the fuel filler cap is loose, improperly installed, or damaged. A loose fuel filler cap message will be displayed in the instrument cluster. Tighten the gas
314 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
cap until a ⬙clicking⬙ sound is heard. This is an indication that the gas cap is properly tightened. Press the odometer reset button to turn the message off. If the problem persists, the message will appear the next time the vehicle is started. This might indicate a damaged cap. If the problem is detected twice in a row, the system will turn on the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL). Resolving the problem will turn the MIL light off.