- Download PDF Manual
-
California gasoline. Gasoline sold outside of California is allowed to have higher sulfur levels that may affect the performance of your vehicle’s catalytic converter. This may cause the Malfunction Indicator Light or Service Engine Soon Light to illuminate. The illumination of this light while operating on high sulfur gasoline does not necessarily mean your emission system control system is malfunctioning. The manufac- turer recommends that you try a different brand of unleaded gasoline having lower sulfur to determine if the problem is fuel related before returning your vehicle to an authorized dealer for service. If the Malfunction Indicator light or Service NOTE: Engine Soon light is flashing, immediate service is re- quired.
STARTING AND OPERATING 241
Materials Added to Fuel All gasoline sold in the United States and Canada is required to contain effective detergent additives. The use of additional detergents or other additives is not needed under normal conditions. Fuel System Cautions
CAUTION!
Follow these guidelines to maintain your vehicle’s performance: • The use of leaded gas is prohibited by Federal law. Using leaded gasoline can impair engine performance, damage the emission control system. • An out-of-tune engine, or certain fuel or ignition malfunctions, can cause the catalytic converter to overheat. If you notice a pungent burning odor or
242 STARTING AND OPERATING
some light smoke, your engine may be out of tune or malfunctioning and may require immediate service. Contact your dealer for service assistance. • When pulling a heavy load or driving a fully loaded vehicle when the humidity is low and the temperature is high, use a premium unleaded fuel to help prevent spark knock. If spark knock persists, lighten the load, or engine piston damage may result. • The use of fuel additives which are now being sold as octane enhancers is not recommended. Many of these products contain high concentrations of methanol. Fuel system damage or vehicle performance problems may result from the use of such fuels or additives and is not the responsibility of the manufacturer.
NOTE: systems can result against you.
Intentional tampering with emissions control in civil penalties being assessed
Carbon Monoxide Warnings
WARNING!
Carbon monoxide (CO) in exhaust gases is deadly. Follow the precautions below to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning: • Do not inhale exhaust gases. They contain carbon monoxide, a colorless and odorless gas which can kill. Never run the engine in a closed area, such as a garage, and never sit in a parked vehicle with the engine running for an extended period. If the vehicle is stopped in an open area with the engine running for more than a short period, adjust the ventilation system to force fresh, outside air into the vehicle. • Guard against carbon monoxide with proper mainte- nance. Have the exhaust system inspected every time
the vehicle is raised. Have any abnormal conditions repaired promptly. Until repaired, drive with all side windows fully open.
ADDING FUEL
NOTE: The fuel tank filler tube is about 2 inches (50
mm) down from the opening. If fuel is poured from a portable container, the container should have a flexible nozzle long enough to extend into the fuel filler tube.CAUTION!
To avoid fuel spillage and overfilling, do not “top off” the fuel tank after filling.
NOTE: When the fuel nozzle “clicks” or shuts off, the fuel tank is full.
STARTING AND OPERATING 243
NOTE: Tighten the gas cap until you hear a “clicking” sound. This is an indication that the gas cap is properly tightened. Make sure that the gas cap is tightened each time the vehicle is refueled.
WARNING!
A fire may result if gasoline is pumped into a portable container that is inside of a vehicle or on a truck bed. You could be burned. Always place gas containers on the ground while filling.
Fuel Filler Cap (Gas Cap)
The gas cap is behind the fuel filler door. If the gas cap is lost or damaged, be sure the replacement cap is for use with this vehicle.
244 STARTING AND OPERATING
CAUTION!
Damage to the fuel system or emission control system could result from using an improper fuel tank filler tube cap (gas cap). A poorly fitting cap could let impurities into the fuel system.
WARNING!
• Never allow any lit smoking materials near the vehicles while removing the cap or filling the tank. • Never add fuel to the vehicle when the engine is
running.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER The catalytic converter requires the use of unleaded fuel only. Leaded gasoline will destroy the effectiveness of the catalyst as an emission control device. Under normal operating conditions, the catalytic converter will not require maintenance. However, you must keep the en- gine maintained to assure proper operation and prevent possible damage. NOTE: systems can result against you.
Intentional tampering with emissions control in civil penalties being assessed
CAUTION!
Damage to the catalytic converter can result if your vehicle is not kept in proper operating condition. In the event of engine malfunction, particularly involv- ing engine misfire or other apparent loss of perfor- mance, have your vehicle serviced promptly. Contin- ued operation of your vehicle with a severe malfunction could cause the converter to overheat, resulting in possible damage to the converter and vehicle.
As with any vehicle, do not park or operate this vehicle in areas where combustible materials such as grass or leaves can come in contact with a hot exhaust system.
STARTING AND OPERATING 245
A scorching odor may be detected if you continue to run a malfunctioning engine. The odor may indicate severe and abnormal catalyst overheating. If this occurs, the vehicle should be stopped, the engine shut off and the vehicle allowed to cool. Service, including a tune-up to manufacturer’s specifications should be obtained imme- diately. To minimize the possibility of catalyst damage: • Do not shut off the engine or interrupt the ignition when the transmission is in gear and the vehicle is in motion. • Do not try to start engine by pushing or towing the • Do not idle the engine with any spark plug wires disconnected or removed, such as when diagnostic testing, or for prolonged periods during very rough idling or malfunctioning operating conditions.
vehicle.
246 STARTING AND OPERATING
VEHICLE LOADING
Certification Label As required by National Highway Traffic Safety Admin- istration Regulations, your vehicle has a certification label affixed to the driver’s side door or pillar. This label contains the month and year of manufacture, Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR), Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) front and rear, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). A Month-Day-Hour (MDH) number is included on this label and indicates the Month, Day and Hour of manufacture. The bar code that appears on the bottom of the label is your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) The GVWR is the total permissible weight of your vehicle including driver, passengers, vehicle, options and cargo. The label also specifies maximum capacities of front and
rear axle systems (GAWR). Total load must be limited so GVWR and front and rear GAWR are not exceeded. Payload The payload of a vehicle is defined as the allowable load weight a truck can carry, including the weight of the driver, all passengers, options and cargo. Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) The GAWR is the maximum permissible load on the front and rear axles. The load must be distributed in the cargo area so that the GAWR of each axle is not exceeded. Each axle GAWR is determined by the components in the system with the lowest load carrying capacity (axle, springs, tires or wheels). Heavier axles or suspension components sometimes specified by purchasers for in- creased durability does not necessarily increase the vehi- cle’s GVWR.
Tire Size The tire size on the Label represents the actual tire size on your vehicle. Replacement tires must be equal to the load capacity of this tire size. Rim Size This is the rim size that is appropriate for the tire size listed. Inflation Pressure This is the cold tire inflation pressure for your vehicle for all loading conditions up to full GAWR. Curb Weight The curb weight of a vehicle is defined as the total weight of the vehicle with all fluids, including vehicle fuel, at full capacity conditions, and with no occupants or cargo loaded into the vehicle. The front and rear curb weight values are determined by weighing your vehicle on a commercial scale before any occupants or cargo are added.
STARTING AND OPERATING 247
Loading The actual total weight and the weight of the front and rear of your vehicle at the ground can best be determined by weighing it when it is loaded and ready for operation. The entire vehicle should first be weighed on a commer- cial scale to insure that the GVWR has not been exceeded. The weight on the front and rear of the vehicle should then be determined separately to be sure that the load is properly distributed over front and rear axle. Weighing the vehicle may show that the GAWR of either the front or rear axles has been exceeded but the total load is within the specified GVWR. If so, weight must be shifted from front to rear or rear to front as appropriate until the specified weight limitations are met. Store the heavier items down low and be sure that the weight is distributed equally. Stow all loose items securely before driving.
248 STARTING AND OPERATING
Improper weight distributions can have an adverse effect on the way your vehicle steers and handles and the way the brakes operate.
CAUTION!
Do not load your vehicle any heavier than the GVWR or the maximum front and rear GAWR. If you do, parts on your vehicle can break, or it can change the way your vehicle handles. This could cause you to lose control. Also overloading can shorten the life of your vehicle.
An EXAMPLE of a loaded vehicle is shown in the following chart. Note that neither GVWR nor GAWR capabilities are exceeded. Overloading can cause poten- tial safety hazards and shorten service life.
NOTE: The weights shown in this chart are not necessarily the weights for your vehicle. Also, the amount of load added to both the front and rear axles can be computed after the vehicle has been weighed both in its ⴖcurb weightⴖ condition, and in its ⴖloaded and ready for operationⴖ condition.
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) 6500 LBS.
STARTING AND OPERATING 249
TRAILER TOWING In this section you will find safety tips and information on limits to the type of towing you can reasonably do with your vehicle. Before towing a trailer carefully re- view this information to tow your load as efficiently and safely as possible. To maintain warranty coverage, follow the requirements and recommendations in this manual concerning ve- hicles used for trailer towing. Common Towing Definitions The following trailer towing related definitions will assist you in understanding the following information: Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) The GVWR is the total allowable weight of your vehicle. This includes driver, passengers, cargo and tongue weight. The total load must be limited so that you do not exceed the GVWR.
250 STARTING AND OPERATING
Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) The gross trailer weight (GTW) is the weight of the trailer plus the weight of all cargo, consumables and equipment (permanent or temporary) loaded in or on the trailer in its ⬙loaded and ready for operation⬙ condition. The recom- mended way to measure GTW is to put your fully loaded trailer on a vehicle scale. The entire weight of the trailer must be supported by the scale. Gross Combination Weight Rating (GCWR) The gross combination weight rating (GCWR) is the total permissible weight of your vehicle and trailer when weighed in combination. (Note that GCWR ratings in- clude a 68 kg (150 lbs) allowance for the presence of a driver).
Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) The GAWR is the maximum capacity of the front and rear axles. Distribute the load over the front and rear axles evenly. Make sure that you do not exceed either front or rear GAWR.
WARNING!
It is important that you do not exceed the maximum front or rear GAWR. A dangerous driving condition can result if either rating is exceeded. You could lose control of the vehicle and have an accident.
Tongue Weight (TW) The downward force exerted on the hitch ball by the trailer. In most cases it should not be less than 10% or more than 15% of the trailer load. You must consider this as part of the load on your vehicle.
Frontal Area The maximum height and maximum width of the front of a trailer. Trailer Sway Control The trailer sway control is a telescoping link that can be installed between the hitch receiver and the trailer tongue that typically provides adjustable friction associated with the telescoping motion to dampen any unwanted trailer swaying motions while traveling. Weight-Carrying Hitch A weight-carrying hitch supports the trailer tongue weight, just as if it were luggage located at a hitch ball or some other connecting point of the truck. These kind of hitches are the most popular on the market today and they’re commonly used to tow small- and medium-sized trailers.
STARTING AND OPERATING 251
Weight-Distributing Hitch A weight-distributing hitch includes a receiver attached to the tow vehicle, plus a removable hitch head and spring bar assembly that fits into the receiver opening and hook up brackets that connect the spring bars to the trailer frame. Fifth-Wheel Hitch A special high platform with a coupling that mounts over the rear axle of the tow vehicle in the truck bed. Connects a vehicle and fifth-wheel trailer with a coupling king pin. Gooseneck Hitch The gooseneck hitch employs a pivoted coupling arm which attaches to a ball mounted in the bed of a pickup truck. The coupling arm connects to the hitch mounted over the rear axle in the truck bed.
252 STARTING AND OPERATING
Trailer Hitch Classification The rear bumper is intended to tow trailers up to 2,000
lbs (907 kg) without added equipment or alterations to the standard equipment. Your vehicle may be factory equipped for safe towing of trailers weighing over 2,000
lbs (907 kg) with the optional Trailer Tow Prep Package. See your dealer for package content. The following chart provides the industry standard for the maximum trailer weight a given trailer hitch class can tow and should be used to assist you in selecting the correct trailer hitch for your intended towing condition. Refer to “Trailer Towing Weights (Maximum Trailer Weight Ratings)” for the website address that contains the necessary information for your specific drivetrain.Trailer Hitch Classification
Class
Max. GTW (Gross Trailer
Wt.)
2,000 lbs (907 kg) 3,500 lbs (1587 kg)
Class I - Light Duty Class II - Medium Duty Class III - Heavy Duty Class IV - Extra Heavy Duty Fifth Wheel/ Gooseneck All trailer hitches should be professionally installed on your vehicle.
5,000 lbs (2268 kg) 10,000 lbs (4540 kg)
Greater than 10,000 lbs (4540
kg)
Trailer Towing Weights (Maximum Trailer Weight Ratings)
Never exceed the maximum tongue weight stamped on your bumper or trailer hitch.
STARTING AND OPERATING 253
NOTE: For additional trailer towing information (maxi- mum trailer weight ratings) refer to the following website addresses: • http:// www.dodge.com/towing. • http:// www.dodge.ca (Canada). Trailer and Tongue Weight Always load a trailer with 60% to 65% of the weight in the front of the trailer. This places 10% to 15% of the Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) on the tow hitch of your vehicle. Loads balanced over the wheels or heavier in the rear can cause the trailer to sway severely side to side which will cause loss of control of vehicle and trailer. Failure to load trailers heavier in front is the cause of many trailer accidents.
Consider the following items when computing the weight on the rear axle of the vehicle: • The tongue weight of the trailer.
254 STARTING AND OPERATING
put in or on your vehicle.
• The weight of any other type of cargo or equipment • The weight of the driver and all passengers. NOTE: Remember that everything put into or on the trailer adds to the load on your vehicle. Also, additional factory-installed options, or dealer-installed options, must be considered as part of the total load on your vehicle. Refer to the Tire and Loading Information plac- ard in the Tire Safety Information Section of this manual. Trailer sway control and a weight distributing (load equalizing) hitch are recommended for Tongue Weights (TW) above 150 lbs (68 kg) and required for Tongue Weights above 300 lbs (136 kg).
Towing Requirements To promote proper break-in of your new vehicle driv- etrain components the following guidelines are recom- mended:
CAUTION!
• Avoid towing a trailer for the first 500 miles (805
km) of vehicle operation. Doing so may damage your vehicle. • During the first 500 miles (805 km) of trailertowing, limit your speed to 50 mph (80 km/h).
Perform the maintenance listed in Section 8 of this manual. When towing a trailer, never exceed the GAWR, or GCWR, ratings.
WARNING!
Improper towing can lead to an injury accident. Follow these guidelines to make your trailer towing as safe as possible: Make certain that the load is secured in the trailer and will not shift during travel. When trailering cargo that is not fully secured, dynamic load shifts can occur that may be difficult for the driver to control. You could lose control of your vehicle and have an accident. • When hauling cargo or towing a trailer, do not over- load your vehicle or trailer. Overloading can cause a loss of control, poor performance or damage to brakes, axle, engine, transmission, steering, suspension, chas- sis structure or tires.
STARTING AND OPERATING 255
• Safety chains must always be used between your vehicle and trailer. Always connect the chains to the frame or hook retainers of the vehicle hitch. Cross the chains under the trailer tongue and allow enough slack for turning corners. • Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. When parking, apply the parking brake on the tow vehicle. Put the tow vehicle automatic transmission in P for Park. With a manual transmission, shift the transmission into reverse. And with four-wheel-drive vehicles, make sure the transfer case is not in neutral. Always, block or ⬙chock⬙ the trailer wheels.
• GCWR must not be exceeded.
256 STARTING AND OPERATING
• Total weight must be distributed between the tow vehicle and the trailer such that the following four ratings are not exceeded: 1. GVWR 2. GTW 3. GAWR 4. Tongue weight rating for the trailer hitch utilized (This requirement may limit the ability to always achieve the 10% to 15% range of tongue weight as a percentage of total trailer weight).
Towing Requirements — Tires − Do not attempt to tow a trailer while using a compact
spare tire.
− Proper tire inflation pressures are essential to the safe and satisfactory operation of your vehicle. Refer to the Tires–General Information section of this manual on Tire Pressures for proper tire inflation procedures.
− Also, check the trailer tires for proper tire inflation
pressures before trailer usage.
− Check for signs of tire wear or visible tire damage before towing a trailer. Refer to the Tires–General Information section of this manual on Tread Wear Indicators for the proper inspection procedure.
− When replacing tires refer to the Tires–General Infor- mation section of this manual on Replacement Tires for proper tire replacement procedures. Replacing tires with a higher load carrying capacity will not increase the vehicle’s GVWR and GAWR limits.
Towing Requirements — Trailer Brakes − Do not interconnect the hydraulic brake system or vacuum system of your vehicle with that of the trailer. This could cause inadequate braking and possible personal injury.
− An electronically actuated trailer brake controller is required when towing a trailer with electronically actuated brakes. When towing a trailer equipped with a hydraulic surge actuated brake system, an electronic brake controller is not required.
− Trailer brakes are recommended for trailers over 1,000
lbs (454 kg) and required for trailers in excess of 2,000
lbs (907 kg).STARTING AND OPERATING 257
CAUTION!
If the trailer weighs more than 1,000 lbs (454 kg) loaded, it should have its own brakes and they should be of adequate capacity. Failure to do this could lead to accelerated brake lining wear, higher brake pedal effort, and longer stopping distances.
258 STARTING AND OPERATING
WARNING!
Do not connect trailer brakes to your vehicle’s hy- draulic brake lines. It can overload your brake sys- tem and cause it to fail. You might not have brakes when you need them and could have an accident. Towing any trailer will increase your stopping dis- tance. When towing you should allow for additional space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you. Failure to do so could result in an accident.
Towing Requirements — Trailer Lights & Wiring Whenever you pull a trailer, regardless of the trailer size, stop lights and turn signals on the trailer are required for motoring safety. The Trailer Tow Package may include a 4 and 7 pin wiring harness. Use a factory approved trailer harness and connector.
NOTE: Do not cut or splice wiring into the vehicles wiring harness. The electrical connections are all complete to the vehicle but you must mate the harness to a trailer connector. Refer to the following illustrations.
4 - Pin Connector
STARTING AND OPERATING 259
If using a manual transmission vehicle for trailer towing, all starts must be in FIRST gear to avoid excessive clutch slippage. Towing Tips — Automatic Transmission The “D” range can be selected when towing. However, if frequent shifting occurs while in this range, the “TOW HAUL” range should be selected. NOTE: Using the “TOW HAUL” range while operating the vehicle under heavy operating conditions will im- prove performance and extend transmission life by re- ducing excessive shifting and heat build up. This action will also provide better engine braking. The automatic transmission fluid and filter should be changed if you REGULARLY tow a trailer for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation. See Schedule “B” in section 8 of this manual for transmission fluid change intervals.
7- Pin Connector
Towing Tips Before setting out on a trip, practice turning, stopping and backing the trailer in an area away from heavy traffic.
260 STARTING AND OPERATING
NOTE: Check the automatic transmission fluid level before towing. Towing Tips — Tow/Haul (If Equipped) To reduce potential for automatic transmission overheat- ing, turn the “TOW HAUL” feature ON when driving in hilly areas or shift the transmission to Drive position 2 on more severe grades. Towing Tips — Electronic Speed Control (If Equipped) − Don’t use in hilly terrain or with heavy loads. − When using the speed control, if you experience speed drops greater than 10 mph (16 km/h), disengage until you can get back to cruising speed.
− Use speed control in flat terrain and with light loads to
maximize fuel efficiency.
Towing Tips — Cooling System To reduce potential for engine and transmission over- heating, take the following actions: − City Driving When stopped for short periods of time, put transmission in neutral and increase engine idle speed. − Highway Driving Reduce speed. − Air Conditioning Turn off temporarily. − refer to Cooling System Operating information in the Maintenance section of this manual for more informa- tion.
Trailer Towing Mirrors — If Equipped These mirrors are designed with an adjustable mirror head to provide a greater vision range when towing extra-wide loads. To change position inboard or out- board, the mirror head should be rotated (flipped Out or In). A small blindspot mirror is integrated onto the main mirror surface. NOTE: rearward prior to entering an automated car wash.
Fold the 7 x 10 inch trailer towing mirrors
CAUTION!
Do not attempt to fold the 7 x 10 inch trailer towing mirrors forward. The 7 x 10 inch trailer towing mirrors are not designed to be folded forward and doing so will damage the mirrors and/or vehicle.
STARTING AND OPERATING 261
Blindspot Mirror
262 STARTING AND OPERATING
Trailer Towing Position
SNOWPLOW
Dodge SRT-10 Models
NOTE: snowplow applications.
DO NOT use Dodge SRT- 10 Models for
WARNING!
Snowplows, winches, and other aftermarket equip- ment should not be added to the front end or your vehicle. The airbag crash sensors may be affected by the change in the front end structure. The airbags could deploy unexpectedly or could fail to deploy during a collision resulting in serious injury or death.
CAUTION!
Using this vehicle for snowplow applications can cause damage to the vehicle.
WARNING!
Attaching a snowplow to this vehicle could ad- versely affect performance of the airbag system in an accident. Do not expect that the airbag will perform as described earlier in this manual
STARTING AND OPERATING 263
TRACTION When driving on wet or slushy roads, it is possible for a wedge of water to build up between the tire and road surface. This is known as hydroplaning and may cause partial or complete loss of vehicle control and stopping ability. To reduce this possibility, the following precau- tions should be observed: 1. Slow down during rainstorms or when roads are slushy. 2. Slow down if road has standing water or puddles. 3. Replace tires when tread wear indicators first become visible. 4. Keep tires properly inflated. 5. Maintain sufficient distance between your vehicle and the car in front to avoid a collision in a sudden stop.
264 STARTING AND OPERATING
EQUIPMENT IDENTIFICATION PLATE The equipment Identification Plate is located on the hood inner surface. The following information about your vehicle is dis- played on this plate: Model, Wheelbase, Vehicle Identifi- cation Number, Truck Order Number, and code numbers with descriptions of all production and special equip- ment on the truck as shipped from the factory. NOTE: Always refer to the Equipment Identification Plate When Ordering Parts.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
CONTENTS
䡵 Hazard Warning Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 266
䡵 Adding Fuel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
䡵 Jack Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268▫ Removal ▫ Reinstalling The Scissors-Type Jack And Tools
(Srt–10 Models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
䡵 Changing A Flat Tire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273▫ Removing The Spare Tire . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
▫ Tire Changing Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 274
䡵 Hoisting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
䡵 Jump-Starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 280
䡵 Freeing A Stuck Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
䡵 Towing A Disabled Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283266 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
HAZARD WARNING LIGHTS The Hazard Warning switch is mounted on the top of the steering column as shown in the illustration.
Hazard Light Warning Switch
To engage the Hazard Warning lights, depress the button on the top of the steering column. When the Hazard Warning switch is activated, all directional turn signals will flash off and on to warn oncoming traffic of an emergency. Push the button a second time to turn off the flashers. This is an emergency warning system and should not be used when the vehicle is in motion. Use it when your vehicle is disabled and is creating a safety hazard for other motorists. When you must leave the vehicle to seek assistance, the Hazard Warning lights will continue to operate even though the ignition switch is OFF. NOTE: With extended use, the Hazard Warning lights may discharge your battery.
ADDING FUEL The fuel tank filler tube has a restriction about 2 inches (50 mm) inside the opening. If using a portable fuel container, it should have a flexible nozzle long enough to reach past the restriction.
WARNING!
A fire may result if gasoline is pumped into a portable container that is in a vehicle or on a truck bed. You could be burned. Always place gas contain- ers on the ground while filling.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 267
WARNING!
Remove the gas cap slowly to prevent fuel spray from the filler neck which may cause injury. The volatility of present gasolines may cause a build up of pressure in the fuel tank that may increase while you drive. This pressure can result in a spray of gasoline and/or vapors when you remove the cap from a hot vehicle. Removing the cap slowly allows the pressure to vent and prevents fuel spray. Never allow any lit smoking materials near the vehicles while removing the cap or filling the tank. Never add fuel to the vehicle when the engine is running.
268 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
JACK LOCATION
Removal
Jack Cover
The jack and jack tools are stored under the front passenger seat. Lift the tab and slide the plactic cover forward for access.
Jack Wing Bolt
Remove the jack and tools by removing the wing bolt and sliding the assembly from under the seat.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 269
WARNING!
WARNING!
The jack is designed to use as a tool for changing tires only. The jack should not be used to lift the vehicle for service purposes, unless suitable sup- ports are placed under the vehicle as a safety mea- sure. The vehicle should be jacked on a firm level surface only. Avoid ice or slippery areas.
After using the jack and tools, always reinstall them in the original carrier and location. While driving you may experience, abrupt stopping, rapid accelera- tion, or sharp turns. A loose jack, tools, bracket or other objects in the vehicle may move around with force, resulting in serious injury.
270 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
Reinstalling The Scissors-Type Jack And Tools (SRT–10 Models)
1. Lower the jack all the way down by turning the jack turn-screw until the jack is snug. 2. Position the jack and tool bag (unrolled). Make sure the lug wrench is under the jack near the jack turn-screw.
Turn Screw and Lug
3. Fold the flap and roll the jack tool kit into a cylindrical package (in direction of arrows), and tie to the jack using the tie straps.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 271
Tying Bag to Jack with Straps
Folding Flap and Rolling Bag
272 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
4. Place the jack and tools in the storage position holding the jack by the jack turn-screw, slip the jack and tools under seat so that the bottom slot engages into the fastener on the floor and then secure to the floor pan using the wing bolt.
Jack and Tools Tied
Jack Wing Bolt
CHANGING A FLAT TIRE
Removing The Spare Tire Remove the spare tire before attempting to jack the truck. Attach the wheel wrench to the jack extension tube. Insert the tube through the access hole between the lower tailgate and the top of the bumper and into the winch mechanism tube. Rotate the wheel wrench handle coun- terclockwise until the spare tire is on the ground with enough cable slack to allow you to pull it out from under the vehicle. When the spare is clear, tilt the retainer at the end of the cable and pull it through the center of the wheel.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 273
It is recommended that you stow the flat or spare to avoid tangling the loose cable. NOTE: The winch mechanism is designed for use with the jack extension tube only. Use of an air wrench or other power tools is not recommended and can damage the winch.
274 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
Tire Changing Procedure
WARNING!
Getting under a jacked-up vehicle is dangerous. The vehicle could slip off the jack and fall on you. You could be crushed. Never get any part of your body under a vehicle that is on a jack. Never start or run the engine while the vehicle is on a jack. If you need to get under a raised vehicle, take it to a service center where it can be raised on a lift.
Do not raise this vehicle using a bumper jack. The jack is designed as a tool for changing tires on this vehicle only. It is not recommended that the jack be used for service purposes or to lift more than one wheel at a time.
Preparations Park the vehicle on a firm level surface, avoiding ice or slippery areas. Set the parking brake and place the gear selector in REVERSE (manual transmission).
WARNING!
Do not attempt to change a tire on the side of the vehicle close to moving traffic. Pull far enough off the road to avoid the danger of being hit when operating the jack or changing the wheel.
• Turn on the Hazard Warning Flasher.
• Block both the front and rear of the wheel diagonally oppo- site the jacking position. For example, front wheel is being changed, block the left rear wheel. • Passengers should not remain in the vehicle when the
the right
if
vehicle is being jacked.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 275
Instructions
WARNING!
be raised.
Carefully follow these tire changing warnings to help prevent personal injury or damage to your vehicle: • Always park on a firm, level surface as far from the edge of the roadway as possible before raising the vehicle. • Block the wheel diagonally opposite the wheel to • Apply the parking brake firmly before jacking. • Never start the engine with the vehicle on a jack. • Do not let anyone sit in the vehicle when it is on • Do not get under the vehicle when it is on a jack. • Only use the jack in the positions indicated. • If working on or near a roadway, be extremely
a jack.
careful of motor traffic.
276 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
1. Remove the spare wheel, jack, and tools from storage. 2. Using the wheel wrench, loosen, but do not remove, the wheel nuts by turning them counterclockwise one turn while the wheel is still on the ground. 3. Placement of the Jack: • When changing a front wheel, place the scissors jack under the rear portion of the lower control arm as shown below.
• Operate the jack using the jack drive tube and the wheel wrench. The tube extension, may be used, but is not required.
• When changing a rear wheel, assemble the jack drive tube to the jack and connect the drive tube to the extension tube. Place the jack under the axle between the spring and the shock absorber with the drive tubes extending to the rear.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 277
Before raising the wheel off the ground, make sure that the jack will not damage surrounding truck parts and adjust the jack position as required.
4. By rotating the wheel wrench clockwise, raise the vehicle until the wheel just clears the surface.
WARNING!
Raising the vehicle higher than necessary can make the vehicle unstable and cause an accident. It could slip off the jack and hurt someone near it. Raise the vehicle only enough to remove the tire.
5. Remove the wheel nuts and pull the wheel off. Install the spare wheel and wheel nuts. Lightly tighten the nuts. To avoid risk of forcing the vehicle off the jack, do not fully tighten the nuts until the vehicle has been lowered.
• Connect the jack tube extension and wheel wrench.
278 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
6. Using the wheel wrench, finish tightening the nuts using a crisscross pattern. Correct nut tightness is 90–110
ft. lbs. (125–150 N·m). If in doubt about the correct tightness, have them checked with a torque wrench by your dealer or at a service station.WARNING!
A loose tire or jack thrown forward in a collision or hard stop could injure someone in the vehicle. Always stow the jack parts and the extra tire and wheel in the places provided.
7. Remove wheel blocks. Do not install chrome or alu- minum wheel center caps on the spare wheel. This may result in cap damage. 8. Lower the jack to its fully closed position. Stow the replaced tire, jack, and tools as previously described.
9. Adjust the tire pressure when possible. NOTE: Do not oil wheel studs. For chrome wheels, do not substitute with chrome plated wheel nuts. Wheel Nuts All wheel nuts should be tightened occasionally to elimi- nate the possibility of wheel studs being sheared or the bolt holes in the wheels becoming elongated. This is especially important during the first few hundred miles of operation to allow the wheel nuts to become properly set. All nuts should first be firmly seated against the wheel. The nuts should then be tightened to recom- mended torque. Tighten the nuts to final torque in increments. Progress around the bolt circle, tightening the nut opposite to the nut just previously tightened until final torque is achieved. Recommended torques are shown in the following chart.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 279
HOISTING A conventional floor jack may be used at the jacking locations, refer to the graphics that show jacking loca- tions. However, a floor jack or frame hoist must never be used on any other parts or the underbody.
CAUTION!
Never use a floor jack directly under the differential housing of a loaded truck or damage to your vehicle may result.
Torque Newton Meters 125-150
Disc Wheels
Type Nut Stud Size Torque Ft. Lbs.
Cone
90-110
1/2-20
To Stow The Flat Or Spare Turn the wheel so that the valve stem is down. Slide the wheel retainer through the center of the wheel and position it properly across the wheel opening. For convenience in checking the spare tire inflation, stow with the valve stem toward the rear of the vehicle. Attach the wheel wrench to the extension tube. Rotate the winch mechanism until the wheel is drawn into place against the underside of the vehicle. Continue to rotate until you feel the winch mechanism slip or click 3 or 4
times. It cannot be overtightened. Push against the tire several times to be sure it is firmly in place.280 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
JUMP-STARTING You should not try to start your vehicle by pushing or towing. Vehicles equipped with an automatic transmis- sion cannot be started this way and pushing or towing a vehicle equipped with a manual transmission may over- heat and damage the catalytic converter. Also, there is a greater risk of an accident when a vehicle is being pushed or towed. If the vehicle has a discharged battery, booster cables may be used to obtain a start from a booster battery or the battery in another vehicle. This type of start can be dangerous if done improperly, so follow this procedure carefully.
WARNING!
Battery fluid is a corrosive acid solution; do not allow battery fluid to contact eyes, skin or clothing. Don’t lean over battery when attaching clamps or allow the clamps to touch each other. If acid splashes in eyes or on skin, flush contaminated area immedi- ately with large quantities of water. A battery generates hydrogen gas which is flam- mable and explosive. Keep flame or spark away from the vent holes. Do not use a booster battery or any other booster source that has a greater than 12 volt system, i.e. Do not use a 24 volt power source.
1. Remove all metal jewelry such as watch bands or bracelets which might make an unintended electrical contact.
2. Park the booster vehicle within cable reach but with- out letting the vehicles touch. Set the parking brake on both vehicles, place the automatic transmission in Park or the manual transmission in Neutral, and turn the ignition OFF. 3. Turn off the heater, radio, and all unnecessary electri- cal loads. 4. Connect one end of a jumper cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery. Connect the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery.
WARNING!
Do not permit vehicles to touch each other as this could establish a ground connection and personal injury could result.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 281
282 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
5. Connect the other cable, first to the negative terminal of the booster battery and then to the engine of the vehicle with the discharged battery. Make sure you have a good contact on the engine.
WARNING!
• Do not connect the cable to the negative post of the discharge battery. The resulting electrical spark could cause the battery to explode. • During cold weather when temperatures are be- low freezing point, electrolyte in a discharged battery may freeze. Do not attempt jump starting because the battery could rupture or explode. The battery temperature must be brought up above freezing point before attempting jump start.
6. Start the engine in the vehicle which has the booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes, then start the engine in the vehicle with the discharged battery. 7. When removing the jumper cables, reverse the above sequence exactly. Be careful of the moving belts and fan.
WARNING!
Any procedure other than above could result in: 1. Personal injury caused by electrolyte squirting out the battery vent; 2. Personal injury or property damage due to battery explosion; 3. Damage to charging system of booster vehicle or of immobilized vehicle.
FREEING A STUCK VEHICLE If vehicle becomes stuck in snow, sand, or mud, it can often be moved by a rocking motion. Move the gear selector rhythmically between FIRST and REVERSE, while applying slight pressure to the accelerator. In general, the least amount of accelerator pedal pressure to maintain the rocking motion without spinning the wheels or racing the engine is most effective. Racing the engine or spinning the wheels, due to the frustration of not freeing the vehicle, may lead to transmission over- heating and failure. Allow the engine to idle with the transmission selector in NEUTRAL for at least one minute after every five rocking-motion cycles. This will minimize overheating and reduce the risk of transmis- sion failure during prolonged efforts to free a stuck vehicle.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 283
TOWING A DISABLED VEHICLE Proper towing or lifting equipment is required to prevent damage to your vehicle. Use only tow bars and other equipment designed for the purpose, following equip- ment manufacturer’s instructions. Use of safety chains is mandatory. Attach a tow bar or other towing device to the main structural members of the vehicle—not to bumpers or associated brackets. State and local laws applying to vehicles under tow must be observed. Provided that the transmission is operable, tow with the transmission in Neutral and the ignition key in the OFF position along with the front wheels raised and the rear wheels on the ground. Speed must not exceed 30 mph (50
km/h) and distance must not exceed 15 miles (25 km). If the vehicle is to be towed more than 15 miles (25 km) the vehicle must be towed with the rear wheels raised and the front wheels on the ground. It may also be towed on a flatbed or with the front wheels raised and the rear wheels on a dolly.MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
CONTENTS
䡵 Engine Compartment— 8.3L . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
䡵 Onboard Diagnostic System (OBD II) . . . . . . . . . 289
䡵 Emissions Inspection And MaintenancePrograms
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
䡵 Dealer Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
䡵 Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
䡵 Maintenance Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
▫ Engine Oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
▫ Engine Oil Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296▫ Drive Belts — Check Condition And Tension . . 296
▫ Spark Plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
▫ Engine Air Cleaner Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
▫ Engine Fuel Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 297
▫ Catalytic Converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 298
▫ Crankcase Emission Control System . . . . . . . . 300
▫ Maintenance Free Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
▫ Air Conditioner . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
▫ Power Steering — Fluid Check . . . . . . . . . . . . 302286 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
▫ Front Suspension Ball Joints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
▫ Steering Linkage — Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
▫ Body Lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
▫ Windshield Wiper Blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
▫ Windshield Washers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
▫ Exhaust System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
▫ Cooling System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
▫ Hoses And Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses . . . . . . . 309
▫ Brake System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 310
▫ Clutch Hydraulic System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
▫ Clutch Linkage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 311
▫ Propeller Shaft Universal Joints . . . . . . . . . . . 312
▫ Rear Axle Fluid Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 312▫ Manual Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
▫ Automatic Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
▫ Front Wheel Bearings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
▫ Selection Of Lubricating Grease . . . . . . . . . . . 316
▫ Appearance Care And ProtectionFrom Corrosion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
䡵 Integrated Power Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
䡵 Vehicle Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 324
䡵 Replacement Light Bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
䡵 Bulb Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325▫ Headlight (Halogen)/Front Park And
Turn Lights
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
▫ Tail, Stop, Turn And Backup Lights . . . . . . . . . 329▫ Center High-Mounted Stoplight With
Cargo Light
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
▫ Cab Top Clearance Lights — If Equipped . . . . 332
▫ Tailgate ID Lights (Dual Rear Wheels) . . . . . . . 334
▫ Side Marker Lights (Dual Rear Wheels) . . . . . . 335
▫ Fog Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 287
䡵 Fluid Capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 337
䡵 Fluids, Lubricants And Genuine Parts . . . . . . . . 338
▫ Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
▫ Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339288 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
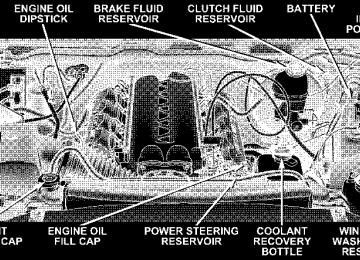
ENGINE COMPARTMENT— 8.3L
ONBOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM (OBD II) Your vehicle is equipped with a sophisticated onboard diagnostic system called OBD II. This system monitors the performance of the emissions and engine control systems. When these systems are operating properly, your vehicle will provide excellent performance and fuel economy, as well as engine emissions well within current government regulations. If any of these systems require service, the OBD II system will turn on the “Malfunction Indicator Light.” It will also store diagnostic codes and other information to assist your service technician in making repairs. Al- though your vehicle will usually be driveable and not need towing, see your dealer for service as soon as possible.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 289
CAUTION!
Prolonged driving with the “Malfunction Indicator Light” on could cause further damage to the emis- sion control system. It could also affect fuel economy and driveability. The vehicle must be serviced before any emissions tests can be performed. If the “Malfunction Indicator Light” is flashing, severe catalytic converter damage and power loss will soon occur. Immediate service is required.
EMISSIONS INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS In some localities, it may be a legal requirement to pass an inspection of your vehicle’s emissions control system. Failure to pass could prevent vehicle registration.
290 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
For states which have an I/M (Inspection and Maintenance) requirement, this check verifies the following: the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp) is functioning and is not on when the engine is running, and that the OBD (On Board Diagnostic) system is ready for testing. Normally, the OBD system will be ready. The OBD system may not be ready if your vehicle was recently serviced, if you recently had a dead battery, or a battery replacement. If the OBD system should be determined not ready for the I/M test, your vehicle may fail the test. Your vehicle has a simple ignition key actuated test which you can use prior to going to the test station. To check if your vehicle’s OBD system is ready, you must do the following: 1. Insert your ignition key into the ignition switch.
2. Turn the ignition to the ON position, but do not crank or start the engine. 3. If you crank or start the engine, you will have to start this test over. 4. As soon as you turn your key to the ON position, you will see your MIL symbol come on as part of a normal bulb check. 5. Approximately 15 seconds later, one of two things will happen:
a. The MIL light will blink for approximately 5 sec- onds and then remain on until the first engine crank or the key is turned off. This means that your vehicle’s OBD system is not ready and you should not proceed to the I/M station.
b. The MIL light will remain fully illuminated until the first engine crank or the key is turned off. This means that your vehicle’s OBD system is ready and you can proceed to the I/M station.
If your OBD system is not ready, you should see your dealer or repair facility. If your vehicle was recently serviced or had a battery failure or replacement, you may need to do nothing more than drive your vehicle as you normally would in order for your OBD system to update. A recheck with the above test routine may then indicate that the system is now ready. Regardless of whether your vehicle’s OBD system is ready or not ready, if the MIL symbol is illuminated during normal vehicle operation, you should have your vehicle serviced before going to the I/M station. The I/M station can fail your vehicle because the MIL symbol is on with the engine running.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 291
DEALER SERVICE Your dealer has the qualified service personnel, special tools and equipment to perform all service operations in an expert manner. Service manuals are available which include detailed service information for your vehicle. Refer to these manuals before attempting any procedure yourself. NOTE: systems can result against you.
Intentional tampering with emissions control in civil penalties being assessed
292 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
WARNING!
You can be badly injured working on or around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work for which you have the knowledge and the proper equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a competent mechanic.
REPLACEMENT PARTS Use of genuine Mopar威 parts for normal/scheduled maintenance and repairs is highly recommended to in- sure the designed performance. Damage or failures caused by the use of non-Mopar parts for maintenance and repairs will not be covered by the manufacturer’s warranty.
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES The pages that follow contain the required maintenance services determined by the engineers who designed your vehicle. Besides the maintenance items for which there are fixed maintenance intervals, there are other items that should operate satisfactorily without periodic maintenance. However, if a malfunction of these items does occur, it could adversely affect the engine or vehicle performance. These items should be inspected if a malfunction is observed or suspected. Engine Oil
Checking Oil Level To assure proper lubrication of your vehicle’s engine, the engine oil must be maintained at the correct level. The best time to check the engine oil level is about 5 minutes after a fully warmed up engine is shut off or before starting the engine after it has sat overnight.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level readings. Maintain the oil level between the ADD and SAFE markings on the dipstick. Adding one quart of oil when the reading is at the ADD mark will result in a SAFE reading on these engines.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 293
Change Engine Oil
CAUTION!
Overfilling or underfilling the crankcase will cause oil aeration or loss of oil pressure. This could dam- age your engine.
Road conditions as well as your kind of driving affect the interval at which your oil should be changed. Check the following to determine if any apply to you: • Day or night temperatures are below 32°F (0°C). • Stop and go driving. • Extensive engine idling. • Driving in dusty conditions • Short trips of less than 10 miles (16.2 km)
294 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
speeds during hot weather, above 32°C (90°F)
• More than 50% of your driving is at sustained high • Taxi, Police or delivery service (commercial service) • Off-road or desert operation • If equipped for and operating with E-85 (ethanol)
fuel.
If ANY of these apply to you then change your NOTE: engine oil every 3,000 miles (5 000 km) or 3 months, whichever comes first and follow schedule “B” of the ⬙Maintenance Schedules⬙ section of this manual. If none of these apply to you, then change your engine oil at every interval shown on schedule ⬙A⬙ of the ⬙Mainte- nance Schedules⬙ section of this manual. Dusty Conditions Driving through dust-laden air increases the problems of keeping abrasive materials out of the engine. Under these
conditions, special attention should be given to the engine air cleaner, the crankcase inlet air cleaner and, the crankcase ventilation system. Make sure that these units are clean at all times. This will tend to reduce to a minimum the amount of abrasive material that may enter the engine. Engine Oil Selection For best performance and maximum protection under all types of operating conditions, the manufacturer only recommends full synthetic engine oils that are API rated as SL/CF and meet the requirements of DaimlerChrysler Material Standard MS-10725. Use Mopar or an equivalent oil meeting the specification MS-10725. If you choose to operate this vehicle in a very aggres- sive driving style, the manufacturer recommends the use of a full synthetic engine oil, such as Mobil 1威 SAE 0W-40.
Engine Oil Identification (API) Symbol There is a symbol to aid you in selecting the proper engine oil.
This symbol means that the oil has been certified by the American Petroleum Institute (API). We only recommend synthetic API Certified engine oils, such as Mo- bil 1威, that meet the requirements of Material Standard MS-10725. Use Mopar or an equivalent oil meeting the specification MS-
10725. Engine Oil Viscosity Chart The proper SAE viscosity grade of engine oil should be selected based on the following recommendation and be within the operating temperature shown in the engine oil viscosity chart.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 295
Synthetic Engine Oils There are a number of engine oils being promoted as either synthetic or semi-synthetic. If you chose to use such a product, use only those oils that meet the Ameri- can Petroleum Institute (API) and SAE viscosity stan- dard. Follow the service schedule that describes your driving type.
296 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Materials Added to Engine Oil Do not add any materials (other than leak detection dyes) to engine oil. Engine oil is an engineered product and it’s performance may be impaired by supplemental addi- tives. Disposing of Used Engine Oil And Oil Filters Care should be taken in disposing of used engine oil and oil filters from your vehicle. Used oil and oil filters, indiscriminately discarded, can present a problem to the environment. Contact your dealer, service station, or governmental agency for advice on how and where used oil and oil filters can be safely discarded in your area. Engine Oil Filter The engine oil filter should be replaced at every engine oil change. Engine Oil Filter Selection The manufacturer’s engines have a full-flow type oil filter. Use a filter of this type for replacement. The quality
of replacement filters varies considerably. Only high quality filters should be used to assure most efficient service. Mopar Engine Oil Filters are a high quality oil filter and are recommended. Drive Belts — Check Condition and Tension At the mileage indicated in the maintenance schedule, all belts should be checked for condition and proper tension. Improper belt tension can cause belt slippage and failure. Belts should be inspected for evidence of cuts, cracks, or glazing, and replaced if there is indication of damage which could result in belt failure. If adjustment is re- quired, see your authorized dealer for service. Low generator belt tension can cause battery failure. A special tool is required to properly measure tension and to restore belt tension to factory specifications. Also check belt routing to make sure there is no interfer- ence between the belts and other engine components.
Spark Plugs Spark plugs must fire properly to assure engine perfor- mance and emission control. New plugs should be in- stalled at the specified mileage. The entire set should be replaced if there is any malfunction due to a faulty spark plug, malfunctioning spark plugs can damage the cata- lytic converter. For proper type of replacement spark plugs, refer to the “Vehicle Emission Control Informa- tion” label in the engine compartment. Engine Air Cleaner Filter Under normal driving conditions, replace the air filter at the intervals shown on Schedule “A”. If, however, you drive the vehicle frequently under dusty or severe con- ditions, the filter element should be inspected periodi- cally and replaced if necessary at the intervals shown on Schedule “B”.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 297
WARNING!
The air cleaner can provide a measure of protection in the case of engine backfire. Do not remove the air cleaner unless such removal is necessary for repair or maintenance. Make sure that no one is near the engine compartment before starting the vehicle with the air cleaner removed. Failure to do so can result in serious personal injury.
Engine Fuel Filter A plugged fuel filter can cause stalling, limit the speed at which a vehicle can be driven or cause hard starting. Should an excessive amount of dirt accumulate in the fuel tank, frequent filter replacement may be necessary.
298 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Catalytic Converter The catalytic converter requires the use of unleaded fuel only. Leaded gasoline will destroy the effectiveness of the catalyst as an emission control device. Under normal operating conditions, the catalytic con- verter will not require maintenance. However, it is im- portant to keep the engine properly tuned to assure proper catalyst operation and prevent possible catalyst damage.
CAUTION!
Damage to the catalytic converter can result if your vehicle is not kept in proper operating condition. In the event of engine malfunction, particularly involv- ing engine misfire or other apparent loss of perfor- mance, have your vehicle serviced promptly. Contin- ued operation of your vehicle with a severe malfunction could cause the converter to overheat, resulting in possible damage to the converter and the vehicle.
NOTE: systems can result against you.
Intentional tampering with emissions control in civil penalties being assessed
WARNING!
A hot exhaust system can start a fire if you park over materials that can burn. Such materials might be grass or leaves coming into contact with your ex- haust system. Do not park or operate your vehicle in areas where your exhaust system can contact any- thing that can burn.
In unusual situations involving grossly malfunctioning engine operation, a scorching odor may indicate severe and abnormal catalyst overheating. If this occurs, the vehicle should be stopped, the engine shut off and the vehicle allowed to cool. Thereafter, service, including a tune-up to manufacturer’s specifications, should be ob- tained immediately.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 299
To minimize the possibility of catalyst damage: • Do not shut off the engine or interrupt the ignition when the transmission is in gear and the vehicle is in motion. • Do not try to start engine by pushing or towing the • Do not idle the engine with any spark plug wires disconnected or removed, such as when diagnostic testing, or for prolonged periods during very rough idling or malfunctioning operating conditions.
vehicle.
300 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Crankcase Emission Control System Proper operation of this system depends on freedom from plugging due to deposits. As vehicle mileage builds up, the Crankcase Ventilation Valve orifice may accumu- late deposits. If a valve is not working properly, replace it with a new orifice. DO NOT ATTEMPT TO CLEAN THE OLD ORIFICE! Check the ventilation hose for indication of damage or plugging deposits. Replace if necessary. Maintenance Free Battery The top of the maintenance free battery is permanently sealed. You will never have to add water, nor is periodic maintenance required.
WARNING!
Battery fluid is a corrosive acid solution and can burn or even blind you. Don’t allow battery fluid to contact your eyes, skin or clothing. Don’t lean over a battery when attaching clamps. If acid splashes in eyes or on skin, flush the area immediately with large amounts of water. Battery gas is flammable and explosive. Keep flame or sparks away from the battery. Don’t use a booster battery or any other booster source with an output greater than 12 volts. Don’t allow cable clamps to touch each other. Battery posts, terminals and related accessories con- tain lead and lead compounds. Wash hands after handling.
CAUTION!
It is essential when replacing the cables on the battery that the positive cable is attached to the positive post and the negative cable is attached to the negative post. Battery posts are marked (+) positive and negative (-) and identified on the battery case. Also, if a “fast charger” is used while battery is in vehicle, disconnect both vehicle battery cables be- fore connecting the charger to battery. Do not use a “fast charger” to provide starting voltage.
Air Conditioner For best possible performance, your air conditioner should be checked and serviced by an Authorized Dealer at the start of each warm season. This service should include cleaning of the condenser fins and a system performance check. Drive belt tension should also be checked at this time.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 301
WARNING!
injuring
you. Other
• Use only refrigerants approved by the manufac- turer for your air conditioning system. Some un- approved refrigerants are flammable and can ex- plode, unapproved refrigerants can cause the system to fail, requiring costly repairs. • Never add air conditioning refrigerant to correct a non-cooling problem unless pressure gauges are connected to the system by a certified technician. Lack of cooling could be due to a restriction and adding refrigerant may cause a dangerous pres- sure rise and you could be injured.
302 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Refrigerant Recovery And Recycling The air conditioning system of your vehicle contains R-134a, a refrigerant that does not deplete the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere. The manufacturer recommends that air conditioning service be done by facilities using refrigerant recycling and recovery equipment that meets SAE standard J1991. Power Steering — Fluid Check Checking the power steering fluid level at a defined service interval is not required. The fluid should only be checked if a leak is suspected, abnormal noises are apparent, and/or the system is not functioning as antici- pated. Coordinate inspection efforts through a certified DaimlerChrysler Dealership.⬙
WARNING!
Fluid level should be checked on a level surface and with the engine off to prevent injury from moving parts and to insure accurate fluid level reading. Do not overfill. Use only manufacturers recommended power steering fluid.
If necessary, add fluid to restore to the proper indicated level. With a clean cloth, wipe any spilled fluid from all surfaces. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants, and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type. Front Suspension Ball Joints The ball joints and seals should be inspected whenever the vehicle is serviced for other reasons.
if the seals on the ball
The ball joints originally supplied with the vehicle are permanently lubricated at the factory and do not require service. However, joints are the joints should be replaced. Serviceable damaged, replacement ball joints are available. Front suspension ball joints should be replaced only by a qualified service technician using tools specially de- signed for this purpose. Damage to the joints and/or suspension components may result if improper replace- ment procedures are used. If seals are damaged the ball joints should be replaced to prevent leakage or contamination of the grease. Steering Linkage — Inspection Whenever the vehicle is hoisted, all steering linkage joints should be inspected for evidence of damage. If seals are damaged, parts should be replaced to prevent leakage or contamination of the grease. Lubricate the steering linkage regularly according to the “Maintenance Schedule” in this manual.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 303
Body Lubrication Locks and all body pivot points, including such items as seat tracks, doors, tailgate and hood hinges, should be lubricated periodically to assure quiet, easy operation and to protect against rust and wear. Prior to the appli- cation of any lubricant, the parts concerned should be wiped clean to remove dust and grit; after lubricating excess oil and grease should be removed. Particular attention should also be given to hood latching compo- nents to insure proper function. When performing other underhood services, the hood latch, release mechanism and safety catch should be cleaned and lubricated. The external lock cylinders should be lubricated twice a year, preferably in the fall and spring. Apply a small amount of a high quality lubricant such as Mopar威 Lock Cylinder Lubricant directly into the lock cylinder.
304 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Windshield Wiper Blades The rubber edges of the wiper blades and the windshield should be cleaned periodically with a sponge or soft cloth and a mild nonabrasive cleaner. This will remove accu- mulations of salt or road film. Operation of the wipers on dry glass for long periods may cause deterioration of the wiper blades. Always use washer fluid when using the wipers to remove salt or dirt from a dry windshield. Avoid using the wiper blades to remove frost or ice from the windshield. Keep the blade rubber out of contact with petroleum products such as engine oil, gasoline, etc. Windshield Washers The fluid reservoir is located under the hood and should be checked for fluid level at regular intervals. Fill the reservoir with windshield washer solvent only (not ra- diator antifreeze).
To prevent freeze-up of your windshield washer system in cold weather, select a solution or mixture that meets or exceeds the temperature range of your climate. This rating information can be found on most washer fluid containers.
WARNING!
Commercially available windshield washer solvents are flammable. They could ignite and burn you. Care must be exercised when filling or working around the washer solution.
After the engine has warmed, operate the defroster for a few minutes to reduce the possibility of smearing or freezing the fluid on the cold windshield. Mopar All Weather Windshield Washer Solution, used with water as directed on the container, aids cleaning action, reduces the freezing point to avoid line clogging, and is not harmful to paint or trim.
Exhaust System The best protection against carbon monoxide entry into the vehicle body is a properly maintained engine exhaust system. Whenever a change is noticed in the sound of the exhaust system, when exhaust fumes can be detected inside the vehicle, or when the underside or rear of the vehicle is damaged, have a competent mechanic inspect the com- plete exhaust system and adjacent body areas for broken, damaged, deteriorated, or mispositioned parts. Open seams or loose connections could permit exhaust fumes to seep into the passenger compartment. In addition, inspect the exhaust system each time the vehicle is raised for lubrication or oil change. Replace as required.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 305
WARNING!
Exhaust gases can injure or kill. They contain carbon monoxide (CO) which is colorless and odorless. Breathing it can make you unconscious and can eventually poison you. To avoid breathing CO, fol- low the preceding safety tips.
Exhaust System Rubber Isolator and Loop-Type Hanger — If Equipped Inspect surfaces whenever the vehicle is hoisted for rubber to metal separation or deep cracks. SLIGHT CRACKING DUE TO WEATHERING DOES NOT AD- VERSELY AFFECT PERFORMANCE. If, however, exces- sively deep localized cracks are present, or any part of the exhaust system abnormally contacts the underbody hard- ware, the isolator and/or hanger should be replaced.
306 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Cooling System
Cooling System Maintenance At the intervals shown in the Maintenance Schedules Section of the manual, the system should be drained, flushed and filled. Inspection Check engine coolant (antifreeze) protection every 12
months (before the onset of freezing weather, where applicable). If coolant is dirty or rusty in appearance, the system should be drained, flushed and refilled with fresh coolant as specified. Inspect the entire cooling system for leaks. Check the face of the radiator for any accumulation of bugs, leaves, or other foreign matter. If dirty, clean the radiator core with a garden hose. With the engine OFF, gently spray water from the back of the radiator core. Check the coolant reserve tank tube for condition and tightness or connections at the reserve tank and radiator.Check the coolant pressure cap and coolant reserve system for proper vacuum sealing. With the engine at normal operating temperature, note the level of the coolant in the coolant reserve tank. Without removing the pressure cap (with the engine off), drain a small amount of coolant from the radiator draincock. If the coolant level in the reserve tank drops, the system is sealing properly. Coolant Level The coolant reserve system provides a quick visual method of determining that the coolant level is adequate. With the engine idling, and warmed to the normal operating temperature, the level of the coolant on the overflow bottle should be between the fluid level marks. Check the coolant level whenever the hood is raised. The radiator normally remains completely full, so there is no longer a need to remove the coolant pressure cap except for checking coolant freeze point or replacement with new antifreeze coolant.
WARNING!
Never add coolant to the radiator when the engine is overheated. Do not loosen or remove pressure cap to cool an overheated engine! The coolant is under pressure and severe scalding could result.
Drain, Flush And Refill At intervals shown on the Maintenance Schedules, the system should be drained, flushed and refilled. Refer to your dealer or consult a service manual for proper procedures. Adding Coolant When adding coolant, or refilling the system, a minimum solution of 50% recommended HOAT ethylene glycol engine coolant (antifreeze) and distilled water should be used. Use higher concentrations (not to exceed 70%) if temperatures below ⫺34°F (⫺37°C) are anticipated.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 307
Use only high purity water such as distilled or deionized water when mixing the water/engine coolant solution. The use of lower quality water will reduce the amount of corrosion protection in the engine cooling system. It is the owner’s responsibility to maintain the NOTE: proper level of protection against freezing according to the temperatures occurring in the area where the vehicle is operated. NOTE: Mixing coolant types will decrease the life of the engine coolant and will require more frequent coolant changes. When additional coolant is needed to maintain the proper level, add the recommended concentration of antifreeze and water to the overflow bottle. Do not overfill.
308 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
NOTE: Failure to follow the antifreeze concentration and replacement recommendations, or failure to use antifreeze formulated to prevent corrosion of all cooling system metals, may result in radiator plugging, overheat- ing, or cooling system leaks such as in core hole plugs.
WARNING!
Never add coolant to the radiator when the engine is overheated. Do not loosen or remove pressure cap to cool an overheated engine. The coolant is under pressure and severe scalding could result.
Recommended Engine Coolant Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type.
CAUTION!
• Mixing of coolants other than specified engine coolant, may result in engine damage, and de- crease corrosion protection. If a non-HOAT cool- ant is introduced into the cooling system in an emergency, it should be replaced with the speci- fied coolant as soon as possible. • Do not use plain water alone or alcohol base engine coolant (antifreeze) products. Do not use additional rust inhibitors or antirust products, as they may not be compatible with the radiator engine coolant and may plug the radiator. • This vehicle has not been designed for use with Propylene Glycol based coolants. Use of Propy- lene Glycol based coolants is not recommended.
Disposal Of Used Engine Coolant Used ethylene glycol based engine coolant is a regulated substance requiring proper disposal. Check with your local authorities to determine the disposal rules for your community. Do not store ethylene glycol-based engine coolant in open containers or allow it to remain in puddles on the ground. Prevent ingestion by animals and children. If ingested by a child, contact a physician immediately. Clean up any ground spills immediately. Coolant Pressure Cap The coolant pressure cap must be fully tightened to prevent the loss of coolant and to insure that the coolant will return to the radiator from the coolant reserve tank. The pressure cap should be inspected and cleaned if there is any accumulation of foreign material on the sealing surfaces.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 309
WARNING!
The warning words “DO NOT OPEN HOT” on the radiator pressure cap are a safety precaution. Heat causes pressure to build up in the cooling system. To prevent scalding or injury, do not remove the pres- sure cap.
Hoses And Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses Inspect surfaces of hoses and nylon tubing for evidence of heat and mechanical damage. Hard or soft spots, brittle rubber, cracking, tears, cuts, abrasions, and exces- sive swelling indicate deterioration of the rubber. Pay particular attention to those hoses nearest to high heat sources such as the exhaust manifold. Inspect hose routing to be sure hoses do not come in contact with any heat source or moving component which may cause heat damage or mechanical wear.
310 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Insure nylon tubing in these areas has not melted or collapsed. Inspect all hose connections such as clamps and cou- plings to make sure they are secure and no leaks are present. Components should be replaced immediately if there is any evidence of wear or damage that could cause failure. Brake System
Power Disc Brakes (front and rear) Disc brakes do not require adjustment; however, several hard stops during the break-in period are recommended to seat the linings and wear off any foreign material. Brake Master Cylinder The fluid level of the master cylinder should be checked when performing under the hood service, or immedi- ately if the brake system warning lamp indicates system failure.
The brake master cylinder has a translucent plastic reservoir. On the outboard side of the reservoir, there is a “MAX” dot and an “MIN” dot. The fluid level must be kept within these two dots. Do not add fluid above the MAX mark, because leakage may occur at the cap. With disc brakes the fluid level can be expected to fall as the brake linings wear. However, an unexpected drop in fluid level may be caused by a leak and a system check should be conducted. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for the correct Fluid type.
WARNING!
Use of a brake fluid that may have a lower initial boiling point, or is unidentified as to specification, may result in sudden brake failure during hard prolonged braking. You could have an accident.
WARNING!
Overfilling the brake fluid reservoir can result in spilling brake fluid on hot engine parts and the brake fluid catching fire.
Use only brake fluid that has been in a tightly closed container to avoid contamination from foreign matter or moisture.
CAUTION!
Do not allow a petroleum-base fluid to contaminate the brake fluid. Seal damage may result.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 311
Brake Hoses Inspection should be performed whenever the brake system is serviced or at intervals specified. Inspect hy- draulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing or worn spots. If there is any evidence of cracking, scuffing, or worn spots, the hose should be replaced immediately! Eventual deterioration of the hose can take place with possible burst failure. Clutch Hydraulic System
The clutch hydraulic system is a sealed maintenance-free system. In the event of leakage or other malfunction, the system must be replaced. Clutch Linkage If the clutch pedal linkage begins to squeak or grunt, the clutch pedal pivot bushings should be lubricated. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for the correct lubricant type.
312 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Propeller Shaft Universal Joints Cross Type (No fittings) — Relubrication of this type of universal joint is not required. The seals should be inspected for external leaks or damage. If external leaks or damage is evident, the universal joint should be replaced. Rear Axle Fluid Level Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for the correct Fluid type. For normal service, periodic fluid level checks are not required. When the vehicle is serviced for other reasons the exterior surfaces of the axle assembly should be inspected. If gear oil leakage is suspected inspect the fluid level. This inspection should be made with the vehicle in a level position. The fluid level should be 3/4” ± 1/4” below the plug on DANA M60 HD/248 mm rear axles.
Drain and Refill Vehicles operated in normal service do not have regularly scheduled oil changes. If fluid has become contaminated with water or to provide the correct viscosity grade, drain and refill. Lubricant Selection Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type. NOTE: The presence of water in the gear lubricant will result in corrosion and possible failure of differential components. Operation of the vehicle in water, as may be encountered in some off-highway types of service, will require draining and refilling the axle to avoid damage.
Manual Transmission
Lubricant Selection Refer to the Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts section for correct fluid type.
CAUTION!
Using a transmission fluid other than the manufac- turer’s recommended fluid may cause deterioration in transmission shift quality. Refer to the Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts section for correct fluid type.
Fluid Level Check The fluid in the transmission should be checked when- ever other underhood services are done. Check the fluid level by removing the fill plug located on the left side of
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 313
the transmission. The fluid level should be at the bottom of the fill hole. Add fluid, if necessary, to maintain the proper level. Frequency of Fluid Change Under normal operating conditions, the fluid installed at the factory will give satisfactory lubrication for the life of the vehicle. If the vehicle is operated under severe conditions, change the fluid as specified in Maintenance Schedule B. If contaminated with water, the fluid should be changed immediately. Automatic Transmission
Fluid Level Check The fluid level should be checked when the engine is fully warmed up and the fluid in the transmission is at normal operating temperature. Operation of the trans- mission with an improper fluid level will greatly reduce the life of the transmission and of the fluid. Check the fluid level whenever the vehicle is serviced.
314 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Procedure For Checking Fluid Level To properly check the automatic transmission fluid level, the following procedure must be used: 1. The vehicle must be on level ground. 2. The engine should be running at curb idle speed for a minimum of 60 seconds. 3. Fully apply parking brake. 4. Place the gear selector briefly in each gear position ending with the lever in N (Neutral). 5. Remove the dipstick and determine if the fluid is hot or warm. Hot fluid is approximately 180°F (82°C) which is the normal operating temperature after the vehicle has been driven at least 15 miles. The fluid can not be comfortably held between the finger tips. Warm is when fluid is between 85° - 125°F (29° - 52°C).
6. Wipe the dipstick clean and reinsert until seated. Remove dipstick and note reading.
a. If the fluid is hot, the reading should be in the crosshatched area marked “OK”. b. If the fluid is warm, the reading should be between the two holes. If the fluid level indicates low, add sufficient fluid to bring to the proper level.
Fluid is added through the dipstick tube. NOTE: To prevent dirt and water from entering the transmission after checking or replenishing fluid, make certain that the dipstick cap is properly seated. Selection Of Lubricant Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for the correct lubricant type. It is important that the transmis- sion fluid be maintained at the prescribed level using the recommended fluid.
CAUTION!
Using a transmission fluid other than the manufac- turers recommended fluid may cause deterioration in transmission shift quality and/or torque converter shudder. Using a transmission fluid other than the manufacturers recommended fluid will result in more frequent fluid and filter changes. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type.
Automatic Transmission Fluid and Filter Change To obtain best performance and long life for automatic transmissions, the manufacturer recommends that you follow the maintenance schedule that applies to your type of driving (Refer to the Maintenance Schedule Section 8).
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 315
It is important that proper lubricant is used in the trans- mission. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for the correct lubricant type. A band adjustment and filter change should be made at the time of the oil change. The fluid and filter should be changed and the bands adjusted as specified in the Maintenance Schedule (Sec- tion 8). Vehicles having severe usage should follow Maintenance Schedule “B” of the Maintenance Schedule (Section 8). If the transmission is disassembled for any NOTE: reason, the fluid and filter should be changed, and the bands adjusted. Special Additives The manufacturer recommends against the addition of any additives to the transmission. Exception to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks. The use of transmission sealers should be avoided, since they may adversely affect seals.
316 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
In some instances,
Front Wheel Bearings Front wheel bearings for all Dodge Ram Trucks are sealed-for-life. They do not require greasing or seal replacement. these bearings will “purge” excess grease and the bearing will look slightly wet. This is normal. Periodic inspection for excess play is recommended. Selection of Lubricating Grease The National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI) has developed a symbol (Certification Mark) to aid the vehicle owner in the proper selection of grease for the lubrication of wheel bearings and chassis components. This symbol (an example is shown below) is located on the grease container and identifies the application and quality of the grease.
are
There two groups identified, those for wheel bearings (Letter “G”) and those for chassis (Letter “L”) lubrication. Perfor- mance categories within these groups result in dual letter for each group. The letter des- ignations shown in the ex- ample the highest quality level available and when combined as shown can be used for both wheel bearing and chassis lubrication. Use only those greases that have the NLGI symbol on the container along with the proper quality level for your application.
designations
are
Appearance Care and Protection from Corrosion
Protection of Body and Paint from Corrosion Vehicle body care requirements vary according to geo- graphic locations and usage. Chemicals that make roads passable in snow and ice, and those that are sprayed on trees and road surfaces during other seasons, are highly corrosive to the metal in your vehicle. Outside parking, which exposes your vehicle to airborne contaminants, road surfaces on which the vehicle is operated, extreme hot or cold weather and other extreme conditions will have an adverse effect on paint, metal trim, and under- body protection. The following maintenance recommendations will enable you to obtain maximum benefit from the corrosion resistance built into your vehicle. What Causes Corrosion? Corrosion is the result of deterioration or removal of paint and protective coatings from your vehicle.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 317
The most common causes are: • Road salt, dirt and moisture accumulation. • Stone and gravel impact. • Insects, tree sap and tar. • Salt in the air near seacoast localities. • Atmospheric fallout/industrial pollutants.