- 2013 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2009 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2008 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2011 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2015 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2001 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2016 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2007 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2014 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2002 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2003 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2006 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2010 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2000 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2012 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2008 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2004 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- 2005 Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Impala Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
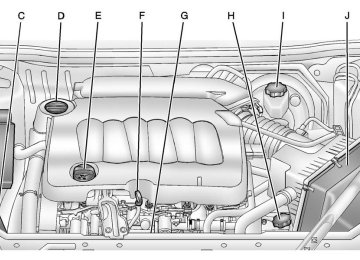
See Engine Compartment Overview on page 10‑6 for information on the location of the power steering fluid reservoir. When to Check Power Steering Fluid It is not necessary to regularly check power steering fluid unless a leak is suspected in the system or an unusual noise is heard. A fluid
loss in this system could indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and repaired. How to Check Power Steering Fluid Notice: Extremely small amounts of contamination can cause steering system damage and cause it to not work properly. Do not allow contaminants to contact the fluid side of the reservoir cap/ dipstick or to enter the reservoir. Check the level after the vehicle has been driven for at least 20 minutes so the fluid is warm. To check the power steering fluid: 1. Turn the ignition to LOCK/OFF and let the engine compartment cool down.
2. Wipe the cap and the top of the
reservoir clean.
3. Unscrew the cap and pull it
straight up.
Vehicle Care
10-17
4. Wipe the dipstick with a
clean rag.
5. Replace the cap and completely
tighten it.
6. Remove the cap again and look at the fluid level on the dipstick.
When the engine is hot, the level should be at the hot MAX level. When the engine is cold, the fluid level should be between MIN and MAX on the dipstick.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (18,1)
10-18
Vehicle Care
What to Use To determine what kind of fluid to use, see Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 11‑11. Always use the proper fluid.
Washer Fluid
What to Use When the vehicle needs windshield washer fluid, be sure to read the manufacturer's instructions before use. If operating the vehicle in an area where the temperature may fall below freezing, use a fluid that has sufficient protection against freezing. Adding Washer Fluid A WASHER FLUID LOW ADD FLUID message will be displayed on the Driver Information Center (DIC) when windshield washer fluid needs to be added to the vehicle. See Washer Fluid Messages on page 5‑35 for more information.
Open the cap with the washer symbol on it. Add washer fluid until the tank is full. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 10‑6 for more information on location. Notice
. When using concentrated
washer fluid, follow the manufacturer's instructions for adding water.
. Do not mix water with
ready-to-use washer fluid. Water can cause the solution to freeze and damage the washer fluid tank and other parts of the washer system. Also, water does not clean as well as washer fluid.
. Fill the washer fluid tank only
three-quarters full when it is very cold. This allows for fluid expansion if freezing occurs, which could damage the tank if it is completely full.
. Do not use engine coolant
(antifreeze) in the windshield washer. It can damage the windshield washer system and paint.
Brakes This vehicle has disc brakes. Disc brake pads have built-in wear indicators that make a high-pitched warning sound when the brake pads are worn and new pads are needed. The sound can come and go or be heard all the time the vehicle is moving, except when applying the brake pedal firmly.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (19,1)
{ WARNING
The brake wear warning sound means that soon the brakes will not work well. That could lead to a crash. When the brake wear warning sound is heard, have the vehicle serviced.
Notice: Continuing to drive with worn-out brake pads could result in costly brake repair. Some driving conditions or climates can cause a brake squeal when the brakes are first applied or lightly applied. This does not mean something is wrong with the brakes. Properly torqued wheel nuts are necessary to help prevent brake pulsation. When tires are rotated, inspect brake pads for wear and evenly tighten wheel nuts in the proper sequence to torque specifications in Capacities and Specifications on page 12‑2.
Brake linings should always be replaced as complete axle sets. Brake Pedal Travel See your dealer if the brake pedal does not return to normal height, or if there is a rapid increase in pedal travel. This could be a sign that brake service might be required. Brake Adjustment Every time the brakes are applied, with or without the vehicle moving, the brakes adjust for wear. Replacing Brake System Parts The braking system on a vehicle is complex. Its many parts have to be of top quality and work well together if the vehicle is to have really good braking. The vehicle was designed and tested with top-quality brake parts. When parts of the braking system are replaced, be sure to get new, approved replacement parts.
Vehicle Care
10-19
If this is not done, the brakes might not work properly. For example, installing disc brake pads that are wrong for the vehicle, can change the balance between the front and rear brakes — for the worse. The braking performance expected can change in many other ways if the wrong replacement brake parts are installed.
Brake Fluid
The brake master cylinder reservoir is filled with DOT 3 brake fluid as indicated on the reservoir cap. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 10‑6 for the location of the reservoir.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (20,1)
10-20
Vehicle Care
There are only two reasons why the brake fluid level in the reservoir might go down:
The brake fluid level goes down because of normal brake lining wear. When new linings are installed, the fluid level goes back up.
. A fluid leak in the brake
hydraulic system can also cause a low fluid level. Have the brake hydraulic system fixed, since a leak means that sooner or later the brakes will not work well.
Do not top off the brake fluid. Adding fluid does not correct a leak. If fluid is added when the linings are worn, there will be too much fluid when new brake linings are installed. Add or remove brake fluid, as necessary, only when work is done on the brake hydraulic system.
{ WARNING
If too much brake fluid is added, it can spill on the engine and burn, if the engine is hot enough. You or others could be burned, and the vehicle could be damaged. Add brake fluid only when work is done on the brake hydraulic system.
When the brake fluid falls to a low level, the brake warning light comes on. See Brake System Warning Light on page 5‑18.
What to Add Use only new DOT 3 brake fluid from a sealed container. See Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 11‑11.
Always clean the brake fluid reservoir cap and the area around the cap before removing it. This helps keep dirt from entering the reservoir.
{ WARNING
With the wrong kind of fluid in the brake hydraulic system, the brakes might not work well. This could cause a crash. Always use the proper brake fluid.
Notice
. Using the wrong fluid can
badly damage brake hydraulic system parts. For example, just a few drops of mineral-based oil, such as engine oil, in the brake hydraulic system can damage brake hydraulic system parts so badly that they will have to be replaced. Do not let someone put in the wrong kind of fluid.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (21,1)
. If brake fluid is spilled on the
vehicle's painted surfaces, the paint finish can be damaged. Be careful not to spill brake fluid on the vehicle. If you do, wash it off immediately.
Battery Refer to the replacement number shown on the original battery label when a new battery is needed. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 10‑6 for battery location.
{ WARNING
Battery posts, terminals, and related accessories contain lead and lead compounds, chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
Vehicle Storage
{ WARNING
Batteries have acid that can burn you and gas that can explode. You can be badly hurt if you are not careful. See Jump Starting on page 10‑62 for tips on working around a battery without getting hurt.
Infrequent Usage: Remove the black, negative (−) cable from the battery to keep the battery from running down. Extended Storage: Remove the black, negative (−) cable from the battery or use a battery trickle charger.
Vehicle Care
10-21
Starter Switch Check
{ WARNING When you are doing this inspection, the vehicle could move suddenly. If the vehicle moves, you or others could be injured.
1. Before starting this check, be
sure there is enough room around the vehicle.
2. Firmly apply both the parking brake and the regular brake. See Parking Brake on page 9‑27. Do not use the accelerator pedal, and be ready to turn off the engine immediately if it starts.
3. Try to start the engine in each gear. The vehicle should start only in P (Park) or N (Neutral).
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (22,1)
10-22
Vehicle Care
If the vehicle starts in any other position, contact your dealer for service.
Automatic Transmission Shift Lock Control Function Check
{ WARNING When you are doing this inspection, the vehicle could move suddenly. If the vehicle moves, you or others could be injured.
1. Before starting this check, be
sure there is enough room around the vehicle. It should be parked on a level surface.
2. Firmly apply the parking brake.
See Parking Brake on page 9‑27. Be ready to apply the regular brake immediately if the vehicle begins to move.
3. With the engine off, turn the
ignition on, but do not start the engine. Without applying the regular brake, try to move the shift lever out of P (Park) with normal effort. If the shift lever moves out of P (Park), contact your dealer for service.
Ignition Transmission Lock Check While parked, and with the parking brake set, try to turn the ignition to LOCK/OFF in each shift lever position.
The ignition should turn to LOCK/OFF only when the shift lever is in P (Park). The ignition key should come out only in LOCK/OFF.
Contact your dealer if service is required.
Park Brake and P (Park) Mechanism Check { WARNING
When you are doing this check, the vehicle could begin to move. You or others could be injured and property could be damaged. Make sure there is room in front of the vehicle in case it begins to roll. Be ready to apply the regular brake at once should the vehicle begin to move.
Park on a fairly steep hill, with the vehicle facing downhill. Keeping your foot on the regular brake, set the parking brake.
To check the parking brake's holding ability: With the engine running and the transmission in N (Neutral), slowly remove foot pressure from the regular brake pedal. Do this until the vehicle is held by the parking brake only.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (23,1)
Vehicle Care
10-23
3. With the latch open, pull the wiper blade down toward the windshield far enough to release it from the J-hooked end of the wiper arm.
4. Remove the wiper blade.
Allowing the wiper blade arm to touch the windshield when no wiper blade is installed could damage the windshield. Any damage that occurs would not be covered by the vehicle warranty. Do not allow the wiper blade to touch the windshield. 5. Reverse Steps 1 through 3 for
wiper blade replacement.
To check the P (Park) mechanism's holding ability: With the engine running, shift to P (Park). Then release the parking brake followed by the regular brake.
Contact your dealer if service is required.
Wiper Blade Replacement Windshield wiper blades should be inspected for wear or cracking. See Maintenance Schedule on page 11‑3 for more information. Replacement blades come in different types and are removed in different ways. For proper windshield wiper blade length and type, see Maintenance Replacement Parts on page 11‑12. Notice: Allowing the wiper arm to touch the windshield when no wiper blade is installed could damage the windshield. Any damage that occurs would not be
covered by your warranty. Do not allow the wiper arm to touch the windshield. To replace the windshield wiper blade: 1. Pull the wiper assembly away
from the windshield.
2. Lift up on the plastic latch in the middle of the wiper blade where the wiper arm attaches.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (24,1)
10-24
Vehicle Care
Headlamp Aiming Headlamp aim has been preset at the factory and should need no further adjustment. However, if the vehicle is damaged in a crash, the headlamp aim may be affected. Aim adjustment to the low-beam headlamps may be necessary if oncoming drivers flash their high-beam headlamps at you (for vertical aim). If the headlamps need to be re-aimed, it is recommended that the vehicle be taken to the dealer for service.
Bulb Replacement For the proper type of replacement bulbs, see Replacement Bulbs on page 10‑28. For any bulb‐changing procedure not listed in this section, contact your dealer.
Halogen Bulbs
{ WARNING
Halogen bulbs have pressurized gas inside and can burst if you drop or scratch the bulb. You or others could be injured. Be sure to read and follow the instructions on the bulb package.
Headlamps, Front Turn Signal, Sidemarker, and Parking Lamps
A. Sidemarker B. Low-Beam Headlamp C. High-Beam Headlamp D. Parking/Turn Signal Lamp
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (25,1)
To replace one of these bulbs: 1. Open the hood. See Hood on
page 10‑5.
Vehicle Care
10-25
5. Remove the round dust caps to
gain access to the bulbs.
6. Turn the old bulb
counterclockwise and remove it from the retaining ring by pulling it away from the headlamp.
3. Pull up on the plastic headlamp
retainer and remove it.
4. Pull the headlamp assembly
away from the vehicle and remove the electrical connector.
2. Remove the screw from the
headlamp assembly.
8.
7. Remove the electrical connector from the bulb by raising the lock tab and pulling the connector away from the bulb's base. Install the electrical connector to the bulb. Install the new bulb by inserting the smallest tab on the bulb base into the matching notch in the retaining ring. Turn the bulb a quarter-turn clockwise until it stops.
9.
10. Reinstall the dust caps.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (26,1)
10-26
Vehicle Care
11. Push the headlamp assembly
12. Push down on the plastic
13. Reinstall the screw from the
toward the vehicle.
headlamp retainer to reinstall it.
headlamp assembly.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (27,1)
Vehicle Care
10-27
Taillamps, Turn Signal, Sidemarker, Stoplamps, and Back-Up Lamps
To replace one of these bulbs: 1. Open the trunk. See Trunk on
page 2‑9.
2. Remove the convenience net (if equipped). Unhook the net from the upper wing nut.
A. Rear Sidemarker Lamp B. Back-up Lamp C. Stoplamp/Taillamp/Turn Signal
3. Turn the upper wing nut
counterclockwise and remove it.
5. Turn the two hex nuts
counterclockwise to remove them.
6. Pull out the taillamp assembly
and disconnect the wiring harness.
7. Turn the bulb socket
counterclockwise to remove it. 8. Pull the old bulb straight out to
4. Pull the carpet away from the
remove it.
rear of the vehicle.
9. Push the new bulb straight in
until it clicks to install it.
10. Reverse steps 1 through 7 to
reinstall.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (28,1)
10-28
Vehicle Care
License Plate Lamp To replace one of these bulbs:
1. Remove the two screws (A) from the license plate lamp assembly.
2. Pull the lamp assembly down
and turn the bulb socket counterclockwise and out of the lamp assembly.
3. Pull the old bulb straight out of
the socket. Install the new bulb.
4. 5. Reverse Steps 1 through 3 to
reinstall the license plate lamp assembly.
Replacement Bulbs
Electrical System
Exterior Lamp
Back-Up Front Parking/Turn Signal License Plate Lamp Headlamps
High-Beam Low-Beam
Sidemarker Stoplamp, Taillamp, and Turn Signal
Bulb
Number 921LL
3157NAK
194LL
H9
H11
194LL3057
For replacement bulbs not listed here, contact your dealer.
Electrical System Overload The vehicle has fuses and circuit breakers to protect against an electrical system overload. When the current electrical load is too heavy, the circuit breaker opens and closes, protecting the circuit until the current load returns to normal or the problem is fixed. This greatly reduces the chance of circuit overload and fire caused by electrical problems. Fuses and circuit breakers protect power devices in the vehicle. Replace a bad fuse with a new one of the identical size and rating. If there is a problem on the road and a fuse needs to be replaced, the same amperage fuse can be borrowed. Choose some feature of the vehicle that is not needed to use and replace it as soon as possible.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (29,1)
Vehicle Care
10-29
Fuses and Circuit Breakers The wiring circuits in the vehicle are protected from short circuits by a combination of fuses and circuit breakers. This greatly reduces the chance of fires caused by electrical problems. Look at the silver-colored band inside the fuse. If the band is broken or melted, replace the fuse. Be sure you replace a bad fuse with a new one of the identical size and rating.
Engine Compartment Fuse Block The engine compartment fuse block is located on the passenger side of the engine compartment, by the battery. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 10‑6 for more information on location. Notice: Spilling liquid on any electrical component on the vehicle may damage it. Always keep the covers on any electrical component.
Headlamp Wiring An electrical overload may cause the lamps to go on and off, or in some cases to remain off. Have the headlamp wiring checked right away if the lamps go on and off or remain off. Windshield Wipers If the wiper motor overheats due to heavy snow or ice, the windshield wipers will stop until the motor cools and will then restart. Although the circuit is protected from electrical overload, overload due to heavy snow or ice may cause wiper linkage damage. Always clear ice and heavy snow from the windshield before using the windshield wipers. If the overload is caused by an electrical problem and not snow or ice, be sure to get it fixed.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (30,1)
10-30
Vehicle Care
Fuses
Usage
A/C CMPRSR Air Conditioning
ABS MTR 1
ABS MTR 2
AIR PUMPAIR SOL
AIRBAG/ DISPLAY AUX PWR BATT 1
BATT 2
BATT 3
BATT 4BCM
The vehicle may not have all of the fuses, relays, and features shown.
Compressor Antilock Brake System (ABS) Motor 1
ABS Motor 2
Air Pump Air Injection Reactor SolenoidAirbag, Display
Auxiliary Power Battery 1
Battery 2
Battery 3
Battery 4
Body Control Module (BCM)Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (31,1)
Vehicle Care
10-31
Fuses
Usage
Fuses
Usage
Fuses
Usage
CHMSL/ BCK-UP
DISPLAY
DRL 1
DRL 2
ECM IGN
ECM/TCM
Center High-Mounted Stoplamp, Back-up Lamp Display Daytime Running Lamps 1
Daytime Running Lamps 2
Engine Control Module (ECM), Ignition ECM, Transmission Control Module (TCM)EMISSIONS 1 Emissions 1
EMISSIONS 2 Emissions 2ETC/ECM
Electronic Throttle Control, ECM
FAN 1
FAN 2FOG LAMPS
FSCM
HDLP MDL
HORN HTD MIR IGN 1
INJ 2
INT LIGHTSINT LTS/ PNL DIM
LT HI BEAM
Cooling Fan 1
Cooling Fan 2
Fog Lamps (If Equipped) Fuel System Control Module Headlamp Module Horn Heated Mirror Ignition 1
Injector 2
Interior Lamps Interior Lamps, Instrument Panel Dimmer Driver Side High-Beam HeadlampLT LO BEAM
LT PARK
LT SPOT
LT T/SIG
ONSTAR PWR DROP/ CRANK RADIO
RT HI BEAM
RT LO BEAM
Driver Side Low-Beam Headlamp Driver Side Parking Lamp Left Spot Driver Side Turn Signal Lamp OnStar Power Drop, Crank Audio System Passenger Side High-Beam Headlamp Passenger Side Low-Beam Headlamp
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (32,1)
10-32
Vehicle Care
Fuses
Usage
RT PARK
RT SPOT
RT T/SIG
RVC SEN
STRG WHL STRTR TRANS VACUUM/ PUMP WPR WSW
Passenger Side Parking Lamp Right Spot Passenger Side Turn Signal Lamp Regulated Voltage Control Sensor Steering Wheel Starter Transmission
Vacuum Pump
Wiper Windshield Wiper
Relay
A/C CMPRSR FAN 1
FAN 2
FAN 3
VAC/PUMP PWR/TRN REAR DEFOG STRTRUsage
Air Conditioning Compressor Cooling Fan 1
Cooling Fan 2
Cooling Fan 3
Vacuum Pump PowertrainRear Defogger
Starter
Instrument Panel Fuse Block
The fuse block is on the passenger side of the vehicle in the carpet molding. Remove the fuse block door to access the fuses.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (33,1)
Vehicle Care
10-33
Wheels and Tires
Tires Every new GM vehicle has high-quality tires made by a leading tire manufacturer. See the warranty manual for information regarding the tire warranty and where to get service. For additional information refer to the tire manufacturer.
Fuses
Usage
DR/LCK HTD/SEAT PWR/MIR PWR/SEAT PWR/WNDW Power Window
Door Locks Heated Seats Power Mirrors Power Seats
RAP
S/ROOF TRUNK TRUNK XM
Retained Accessory Power Sunroof Trunk Trunk Relay XM™ Radio
The vehicle may not be equipped with all of the fuses, relays, and features shown.
Fuses
Usage
AIRBAG AMP AUX CNSTR
Airbags Amplifier Auxiliary Outlets Canister
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (34,1)
10-34
Vehicle Care
{ WARNING . Poorly maintained and
improperly used tires are dangerous.
. Overloading the tires can
cause overheating as a result of too much flexing. There could be a blowout and a serious crash. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10.
. Underinflated tires pose the same danger as overloaded tires. The resulting crash could cause serious injury. Check all tires frequently to maintain the recommended pressure. Tire pressure should be checked when the tires are cold.
. Overinflated tires are more likely to be cut, punctured, or broken by a sudden
(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
impact— such as when hitting a pothole. Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
. Worn or old tires can cause a
crash. If the tread is badly worn, replace them.
. Replace any tires that have been damaged by impacts with potholes, curbs, etc.
. Improperly repaired tires can
cause a crash. Only the dealer or an authorized tire service center should repair, replace, dismount, and mount the tires.
. Do not spin the tires in
excess of 56 km/h (35 mph) on slippery surfaces such as snow, mud, ice, etc. Excessive spinning may cause the tires to explode.
Tire Sidewall Labeling Useful information about a tire is molded into its sidewall. The examples show a typical passenger vehicle tire and a compact spare tire sidewall.
Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire Example (A) Tire Size: The tire size is a combination of letters and numbers used to define a particular tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type,
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (35,1)
Vehicle Care
10-35
and service description. See the “Tire Size” illustration later in this section for more detail. (B) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria Specification): Original equipment tires designed to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines. (C) DOT (Department of Transportation): The Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. (D) Tire Identification Number (TIN): The letters and numbers following the DOT (Department of Transportation) code are the
Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture. (E) Tire Ply Material: The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread. (F) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG): Tire manufacturers are required to grade tires based on three performance factors: treadwear, traction, and temperature resistance. For more information see Uniform Tire Quality Grading on page 10‑49. (G) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit: Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load.
Compact Spare Tire Example
(A) Tire Ply Material: The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread. (B) Temporary Use Only: The compact spare tire or temporary use tire has a tread life of approximately 5 000 km (3,000 mi) and should not be driven at speeds over 105 km/h (65 mph). The compact spare tire is for emergency use when a regular road tire has lost air and
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (36,1)
10-36
Vehicle Care
gone flat. If the vehicle has a compact spare tire, see Compact Spare Tire on page 10‑61 and If a Tire Goes Flat on page 10‑53. (C) Tire Identification Number (TIN): The letters and numbers following the DOT (Department of Transportation) code are the Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture. (D) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit: Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load.
(E) Tire Inflation: The temporary use tire or compact spare tire should be inflated to 420 kPa (60 psi). For more information on tire pressure and inflation see Tire Pressure on page 10‑40. (F) Tire Size: A combination of letters and numbers define a tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type, and service description. The letter T as the first character in the tire size means the tire is for temporary use only. (G) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria Specification): Original equipment tires designed to GM's specific tire performance criteria have a TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall. GM's TPC specifications meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines.
Tire Designations
Tire Size The following is an example of a typical passenger vehicle tire size.
(A) Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire: The United States version of a metric tire sizing system. The letter P as the first character in the tire size means a passenger vehicle tire engineered to standards set by the U.S. Tire and Rim Association. (B) Tire Width: The three‐digit number indicates the tire section width in millimeters from sidewall to sidewall.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (37,1)
(C) Aspect Ratio: A two‐digit number that indicates the tire height‐to‐width measurements. For example, if the tire size aspect ratio is 60, as shown in item C of the illustration, it would mean that the tire's sidewall is 60 percent as high as it is wide. (D) Construction Code: A letter code is used to indicate the type of ply construction in the tire. The letter R means radial ply construction; the letter D means diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter B means belted‐bias ply construction. (E) Rim Diameter: Diameter of the wheel in inches. (F) Service Description: These characters represent the load index and speed rating of the tire. The load index represents the load carrying capacity a tire
is certified to carry. The speed rating is the maximum speed a tire is certified to carry a load.
Tire Terminology and Definitions Air Pressure: The amount of air inside the tire pressing outward on each square inch of the tire. Air pressure is expressed in kPa (kilopascal) or psi (pounds per square inch). Accessory Weight: The combined weight of optional accessories. Some examples of optional accessories are automatic transmission, power steering, power brakes, power windows, power seats, and air conditioning. Aspect Ratio: The relationship of a tire's height to its width.
Vehicle Care
10-37
Belt: A rubber coated layer of cords that is located between the plies and the tread. Cords may be made from steel or other reinforcing materials. Bead: The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped by steel cords that hold the tire onto the rim. Bias Ply Tire: A pneumatic tire in which the plies are laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread. Cold Tire Pressure: The amount of air pressure in a tire, measured in kPa (kilopascal) or psi (pounds per square inch) before a tire has built up heat from driving. See Tire Pressure on page 10‑40.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (38,1)
10-38
Vehicle Care
Curb Weight: The weight of a motor vehicle with standard and optional equipment including the maximum capacity of fuel, oil, and coolant, but without passengers and cargo. DOT Markings: A code molded into the sidewall of a tire signifying that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. The DOT code includes the Tire Identification Number (TIN), an alphanumeric designator which can also identify the tire manufacturer, production plant, brand, and date of production. GVWR: Gross Vehicle Weight Rating. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10.
GAWR FRT: Gross Axle Weight Rating for the front axle. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. GAWR RR: Gross Axle Weight Rating for the rear axle. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. Intended Outboard Sidewall: The side of an asymmetrical tire, that must always face outward when mounted on a vehicle. Kilopascal (kPa): The metric unit for air pressure. Light Truck (LT‐Metric) Tire: A tire used on light duty trucks and some multipurpose passenger vehicles. Load Index: An assigned number ranging from 1 to 279
that corresponds to the load carrying capacity of a tire.Maximum Inflation Pressure: The maximum air pressure to which a cold tire can be inflated. The maximum air pressure is molded onto the sidewall. Maximum Load Rating: The load rating for a tire at the maximum permissible inflation pressure for that tire. Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight: The sum of curb weight, accessory weight, vehicle capacity weight, and production options weight. Normal Occupant Weight: The number of occupants a vehicle is designed to seat multiplied by 68 kg (150 lbs). See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. Occupant Distribution: Designated seating positions. Outward Facing Sidewall: The side of an asymmetrical tire that has a particular side that faces
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (39,1)
outward when mounted on a vehicle. The side of the tire that contains a whitewall, bears white lettering, or bears manufacturer, brand, and/or model name molding that is higher or deeper than the same moldings on the other sidewall of the tire. Passenger (P-Metric) Tire: A tire used on passenger cars and some light duty trucks and multipurpose vehicles. Recommended Inflation Pressure: Vehicle manufacturer's recommended tire inflation pressure as shown on the tire placard. See Tire Pressure on page 10‑40 and Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10.
Radial Ply Tire: A pneumatic tire in which the ply cords that extend to the beads are laid at 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread. Rim: A metal support for a tire and upon which the tire beads are seated. Sidewall: The portion of a tire between the tread and the bead. Speed Rating: An alphanumeric code assigned to a tire indicating the maximum speed at which a tire can operate. Traction: The friction between the tire and the road surface. The amount of grip provided. Tread: The portion of a tire that comes into contact with the road.
Vehicle Care
10-39
Treadwear Indicators: Narrow bands, sometimes called wear bars, that show across the tread of a tire when only 1.6 mm (1/16 in) of tread remains. See When It Is Time for New Tires on page 10‑47. UTQGS (Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards): A tire information system that provides consumers with ratings for a tire's traction, temperature, and treadwear. Ratings are determined by tire manufacturers using government testing procedures. The ratings are molded into the sidewall of the tire. See Uniform Tire Quality Grading on page 10‑49.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (40,1)
10-40
Vehicle Care
Vehicle Capacity Weight: The number of designated seating positions multiplied by 68 kg (150 lbs) plus the rated cargo load. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire: Load on an individual tire due to curb weight, accessory weight, occupant weight, and cargo weight. Vehicle Placard: A label permanently attached to a vehicle showing the vehicle capacity weight and the original equipment tire size and recommended inflation pressure. See “Tire and Loading Information Label” under Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10.
Tire Pressure Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to operate effectively. Notice: Neither tire underinflation nor overinflation is good. Underinflated tires, or tires that do not have enough air, can result in:
. Tire overloading and
overheating which could lead to a blowout.
. Premature or
irregular wear. . Poor handling. . Reduced fuel economy.
Overinflated tires, or tires that have too much air, can result in:
. Unusual wear. . Poor handling.
. Rough ride. . Needless damage from
road hazards.
The Tire and Loading Information label on the vehicle indicates the original equipment tires and the correct cold tire inflation pressures. The recommended pressure is the minimum air pressure needed to support the vehicle's maximum load carrying capacity. For additional information regarding how much weight the vehicle can carry, and an example of the Tire and Loading Information label, see Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. How the vehicle is loaded affects vehicle handling and ride comfort. Never load the vehicle with more weight than it was designed to carry.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (41,1)
When to Check Check the tires once a month or more. Do not forget the compact spare tire, if the vehicle has one. The cold compact spare should be at 420 kPa (60 psi). For additional information regarding the compact spare tire, see Compact Spare Tire on page 10‑61.
How to Check Use a good quality pocket-type gauge to check tire pressure. Proper tire inflation cannot be determined by looking at the tire. Check the tire inflation pressure when the tires are cold, meaning the vehicle has not been driven for at least three hours or no more than 1.6 km (1 mi).
Remove the valve cap from the tire valve stem. Press the tire gauge firmly onto the valve to get a pressure measurement. If the cold tire inflation pressure matches the recommended pressure on the Tire and Loading Information label, no further adjustment is necessary. If the inflation pressure is low, add air until the recommended pressure is reached. If the inflation pressure is high, press on the metal stem in the center of the tire valve to release air. Recheck the tire pressure with the tire gauge. Return the valve caps on the valve stems to prevent leaks and keep out dirt and moisture.
Vehicle Care
10-41
Tire Pressure Monitor System The Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPMS) uses radio and sensor technology to check tire pressure levels. The TPMS sensors monitor the air pressure in your tires and transmit tire pressure readings to a receiver located in the vehicle. Each tire, including the spare (if provided), should be checked monthly when cold and inflated to the inflation pressure recommended by the vehicle manufacturer on the vehicle placard or tire inflation pressure label. (If your vehicle has tires of a different size than the size indicated on the vehicle placard or tire inflation pressure label, you should determine the proper tire inflation pressure for those tires.)
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (42,1)
10-42
Vehicle Care
As an added safety feature, your vehicle has been equipped with a tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) that illuminates a low tire pressure telltale when one or more of your tires is significantly under‐inflated. Accordingly, when the low tire pressure telltale illuminates, you should stop and check your tires as soon as possible, and inflate them to the proper pressure. Driving on a significantly under‐inflated tire causes the tire to overheat and can lead to tire failure. Under‐inflation also reduces fuel efficiency and tire tread life, and may affect the vehicle's handling and stopping ability. Please note that the TPMS is not a substitute for proper tire maintenance, and it is the driver's responsibility to maintain correct tire
pressure, even if under‐inflation has not reached the level to trigger illumination of the TPMS low tire pressure telltale. Your vehicle has also been equipped with a TPMS malfunction indicator to indicate when the system is not operating properly. The TPMS malfunction indicator is combined with the low tire pressure telltale. When the system detects a malfunction, the telltale will flash for approximately one minute and then remain continuously illuminated. This sequence will continue upon subsequent vehicle start‐ups as long as the malfunction exists. When the malfunction indicator is illuminated, the system may not be able to detect or signal low tire pressure as intended. TPMS malfunctions may occur for a variety
of reasons, including the installation of replacement or alternate tires or wheels on the vehicle that prevent the TPMS from functioning properly. Always check the TPMS malfunction telltale after replacing one or more tires or wheels on your vehicle to ensure that the replacement or alternate tires and wheels allow the TPMS to continue to function properly. See Tire Pressure Monitor Operation on page 10‑43 for additional information. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Rules and with Industry Canada Standards See Radio Frequency Statement on page 13‑15 for information regarding Part 15 of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Rules and with Industry Canada Standards RSS-GEN/210/220/310.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (43,1)
Tire Pressure Monitor Operation This vehicle may have a Tire Pressure Monitor System (TPMS). The TPMS is designed to warn the driver when a low tire pressure condition exists. TPMS sensors are mounted onto each tire and wheel assembly, excluding the spare tire and wheel assembly. The TPMS sensors monitor the air pressure in the tires and transmit the tire pressure readings to a receiver located in the vehicle.
When a low tire pressure condition is detected, the TPMS illuminates the low tire pressure warning light located on the instrument cluster.
If the warning light comes on, stop as soon as possible and inflate the tires to the recommended pressure shown on the Tire and Loading Information label. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. A message to check the pressure in a specific tire displays in the Driver Information Center (DIC). The low tire pressure warning light and the DIC warning message come on at each ignition cycle until the tires are inflated to the correct inflation pressure. Using the DIC, tire pressure levels can be viewed. For additional information and details about the DIC operation and displays, see Driver Information Center (DIC) on page 5‑23 and Tire Messages on page 5‑33. The low tire pressure warning light may come on in cool weather when the vehicle is first started, and then turn off as the vehicle is driven. This could be an early indicator that the air pressure is getting low and needs to be inflated to the proper pressure.
Vehicle Care
10-43
A Tire and Loading Information label shows the size of the original equipment tires and the correct inflation pressure for the tires when they are cold. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10, for an example of the Tire and Loading Information label and its location. Also see Tire Pressure on page 10‑40. The TPMS can warn about a low tire pressure condition but it does not replace normal tire maintenance. See Tire Inspection on page 10‑45, Tire Rotation on page 10‑46, and Tires on page 10‑33. Notice: Tire sealant materials are not all the same. A non-approved tire sealant could damage the TPMS sensors. TPMS sensor damage caused by using an incorrect tire sealant is not covered by the vehicle warranty. Always use only the GM-approved tire sealant available through your dealer or included in the vehicle.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (44,1)
10-44
Vehicle Care
TPMS Malfunction Light and Message The TPMS will not function properly if one or more of the TPMS sensors are missing or inoperable. When the system detects a malfunction, the low tire pressure warning light flashes for about one minute and then stays on for the remainder of the ignition cycle. A DIC warning message also displays. The malfunction light and DIC warning message come on at each ignition cycle until the problem is corrected. Some of the conditions that can cause these to come on are: . One of the road tires has been
replaced with the spare tire. The spare tire does not have a TPMS sensor. The malfunction light and the DIC message should go off after the road tire is replaced and the sensor matching process is performed successfully. See “TPMS Sensor Matching Process” later in this section.
The TPMS sensor matching process was not done or not completed successfully after rotating the tires. The malfunction light and the DIC message should go off after successfully completing the sensor matching process. See “TPMS Sensor Matching Process” later in this section.
. One or more TPMS sensors are
missing or damaged. The malfunction light and the DIC message should go off when the TPMS sensors are installed and the sensor matching process is performed successfully. See your dealer for service.
. Replacement tires or wheels do not match the original equipment tires or wheels. Tires and wheels other than those recommended could prevent the TPMS from functioning properly. See Buying New Tires on page 10‑48.
. Operating electronic devices or being near facilities using radio wave frequencies similar to the TPMS could cause the TPMS sensors to malfunction.
If the TPMS is not functioning properly, it cannot detect or signal a low tire condition. See your dealer for service if the TPMS malfunction light and DIC message come on and stay on. TPMS Sensor Matching Process Each TPMS sensor has a unique identification code. The identification code needs to be matched to a new tire/wheel position after rotating the vehicle’s tires or replacing one or more of the TPMS sensors. Also, the TPMS sensor matching process should be performed after replacing a spare tire with a road tire containing the TPMS sensor. The malfunction light and the DIC message should go off at the next ignition cycle. The sensors are matched to the tire/wheel positions,
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (45,1)
using a TPMS relearn tool, in the following order: driver side front tire, passenger side front tire, passenger side rear tire, and driver side rear. See your dealer for service or to purchase a relearn tool. There are two minutes to match the first tire/wheel position, and five minutes overall to match all four tire/wheel positions. If it takes longer, the matching process stops and must be restarted. The TPMS sensor matching process is: 1. Set the parking brake. 2. Turn the ignition to ON/RUN with
the engine off.
3. Press the Remote Keyless Entry
(RKE) transmitter's Q and " buttons at the same time for approximately five seconds. The horn sounds twice to signal the receiver is in relearn mode and the TIRE LEARNING ACTIVE message displays on the DIC screen.
4. Start with the driver side
front tire.
5. Place the relearn tool against
the tire sidewall, near the valve stem. Then press the button to activate the TPMS sensor. A horn chirp confirms that the sensor identification code has been matched to this tire and wheel position.
6. Proceed to the passenger side
front tire, and repeat the procedure in Step 5.
7. Proceed to the passenger side
rear tire, and repeat the procedure in Step 5.
8. Proceed to the driver side rear
tire, and repeat the procedure in Step 5. The horn sounds two times to indicate the sensor identification code has been matched to the driver side rear tire, and the TPMS sensor matching process is no longer active. The TIRE LEARNING ACTIVE message on the DIC display screen goes off.
Vehicle Care
10-45
9. Turn the ignition to LOCK/OFF. 10. Set all four tires to the
recommended air pressure level as indicated on the Tire and Loading Information label.
Tire Inspection We recommend that the tires, including the spare tire, if the vehicle has one, be inspected for signs of wear or damage at least once a month. Replace the tire if: . The indicators at three or
more places around the tire can be seen.
. There is cord or fabric
showing through the tire's rubber.
. The tread or sidewall is
cracked, cut, or snagged deep enough to show cord or fabric.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (46,1)
10-46
Vehicle Care
. The tire has a bump, bulge,
or split.
. The tire has a puncture, cut, or other damage that cannot be repaired well because of the size or location of the damage.
Tire Rotation Tires should be rotated every 12 000 km (7,500 mi). See Maintenance Schedule on page 11‑3. Tires are rotated to achieve a uniform wear for all tires. The first rotation is the most important. Any time unusual wear is noticed, rotate the tires as soon as possible and check the wheel alignment. Also check for damaged tires or wheels.
See When It Is Time for New Tires on page 10‑47 and Wheel Replacement on page 10‑51.
Use this rotation pattern when rotating the tires. Do not include the compact spare tire in the tire rotation. Adjust the front and rear tires to the recommended inflation pressure on the Tire and Loading Information label after the tires have been rotated.
See Tire Pressure on page 10‑40 and Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10. Reset the Tire Pressure Monitor System. See Tire Pressure Monitor Operation on page 10‑43. Check that all wheel nuts are properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque” under Capacities and Specifications on page 12‑2.
{ WARNING
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose after time. The wheel could come off and cause an accident. When changing a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
(Continued)
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (47,1)
WARNING (Continued)
In an emergency, a cloth or a paper towel can be used; however, use a scraper or wire brush later to remove all rust or dirt.
Lightly coat the center of the wheel hub with wheel bearing grease after a wheel change or tire rotation to prevent corrosion or rust build-up. Do not get grease on the flat wheel mounting surface or on the wheel nuts or bolts.
When It Is Time for New Tires Factors such as maintenance, temperatures, driving speeds, vehicle loading, and road conditions affect the wear rate of the tires.
Treadwear indicators are one way to tell when it is time for new tires. Treadwear indicators appear when the tires have only 1.6 mm (1/16 in) or less of tread remaining. See Tire Inspection on page 10‑45 and Tire Rotation on page 10‑46 for more information. The rubber in tires ages over time. This also applies for the spare tire, if the vehicle has one, even if it is never used. Multiple conditions including temperatures, loading
Vehicle Care
10-47
conditions, and inflation pressure maintenance affect how fast aging takes place. Tires will typically need to be replaced due to wear before they may need to be replaced due to age. Consult the tire manufacturer for more information on when tires should be replaced. Vehicle Storage Tires age when stored normally mounted on a parked vehicle. Park a vehicle that will be stored for at least a month in a cool, dry, clean area away from direct sunlight to slow aging. This area should be free of grease, gasoline, or other substances that can deteriorate rubber. Parking for an extended period can cause flat spots on the tires that may result in vibrations while driving. When storing a vehicle for at least a month, remove the tires or raise the vehicle to reduce the weight from the tires.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (48,1)
10-48
Vehicle Care
Buying New Tires GM has developed and matched specific tires for the vehicle. The original equipment tires installed were designed to meet General Motors Tire Performance Criteria Specification (TPC Spec) system rating. When replacement tires are needed, GM strongly recommends buying tires with the same TPC Spec rating. GM's exclusive TPC Spec system considers over a dozen critical specifications that impact the overall performance of the vehicle, including brake system performance, ride and handling, traction control, and tire pressure monitoring performance. GM's TPC Spec number is molded onto the tire's sidewall near the tire size.
If the tires have an all‐season tread design, the TPC Spec number will be followed by MS for mud and snow. See Tire Sidewall Labeling on page 10‑34
for additional information. GM recommends replacing all the tires at the same time. Uniform tread depth on all tires will help to maintain the performance of the vehicle. Braking and handling performance may be adversely affected if all the tires are not replaced at the same time. See Tire Inspection on page 10‑45
and Tire Rotation on page 10‑46
for information on proper tire rotation.{ WARNING
Tires could explode during improper service. Attempting to mount or dismount a tire could cause injury or death. Only your dealer or authorized tire service center should mount or dismount the tires.
{ WARNING
Mixing tires of different sizes, brands, or types may cause loss of control of the vehicle, resulting in a crash or other vehicle damage. Use the correct size, brand, and type of tires on all wheels.
Chevrolet Impala Owner Manual - 2012
Black plate (49,1)
{ WARNING
Using bias-ply tires on the vehicle may cause the wheel rim flanges to develop cracks after many miles of driving. A tire and/or wheel could fail suddenly and cause a crash. Use only radial-ply tires with the wheels on the vehicle.
If the vehicle tires must be replaced with a tire that does not have a TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size, load range, speed rating, and construction (radial) as the original tires. Vehicles that have a tire pressure monitoring system could give an inaccurate low‐pressure warning if non‐TPC Spec rated tires are installed. See Tire Pressure Monitor System on page 10‑41.
The Tire and Loading Information label indicates the original equipment tires on the vehicle. See Vehicle Load Limits on page 9‑10 for the label location and more information about the Tire and Loading Information label.
Different Size Tires and Wheels If wheels or tires are installed that are a different size than the original equipment wheels and tires, vehicle performance, including its braking, ride and handling characteristics, stability, and resistance to rollover may be affected. If the vehicle has electronic systems such as antilock brakes, rollover airbags, traction control, and electronic stability control, the performance of these systems can also be affected.
Vehicle Care
10-49
{ WARNING