- Download PDF Manual
-
E-85 is a mixture of approximately 85% fuel ethanol and 15% unleaded gasoline.
WARNING!
Ethanol vapors are extremely flammable and could cause serious personal injury. Never have any smok- ing materials lit in or near the vehicle when remov- ing the fuel filler tube cap (gas cap) or filling the tank. Do not use E-85 as a cleaning agent and never use it near an open flame.
Fuel Requirements Your vehicle will operate on both unleaded gasoline with an octane rating of 87, or E-85 fuel, or any mixture of these two.
For best results, a refueling pattern that alternates be- tween E-85 and unleaded gasoline should be avoided. When you do switch fuels, it is recommended that • you do not switch when the fuel gauge indicates less • you do not add less than 5 gallons when refueling • you operate the vehicle immediately after refueling for
than 1/4 full
a period of at least 5 minutes
Observing these precautions will avoid possible hard starting and/or significant deterioration in drivability during warm up. NOTE: When the ambient temperature is above 90°F, you may experience hard starting and rough idle follow- ing start up even if the above recommendations are followed.
STARTING AND OPERATING 325
Selection Of Engine Oil For Flexible Fuel Vehicles (E-85) and Gasoline Vehicles Whether operating the vehicle on an E-85 ethanol fuel or unleaded gasoline the engine oil requirements are the same. Refer to the “Maintenance Procedures” section of this manual for the proper quality and viscosity engine oil. Starting The characteristics of E-85 fuel make it unsuitable for use when ambient temperatures fall below 0°F. In the range of 0°F to 32°F, you may experience an increase in the time it takes for your engine to start, and a deterioration in drivability (sags and/or hesitations) until the engine is fully warmed up.
326 STARTING AND OPERATING
Cruising Range Because E-85 fuel contains less energy per gallon than gasoline, you will experience an increase in fuel con- sumption. You can expect your MPG and your driving range to decrease by about 30% compared to gasoline operation. Replacement Parts Many components in your Flexible Fuel Vehicle (FFV) are designed to be compatible with ethanol. Always be sure that your vehicle is serviced with correct ethanol com- patible parts.
CAUTION!
Replacing fuel system components with non-ethanol compatible components can damage your vehicle.
Maintenance If you operate the vehicle using E-85 fuel, follow Sched- ule B in the maintenance schedule section of this manual.
CAUTION!
Do not use ethanol mixture greater than 85% in your vehicle. It will cause difficulty in cold starting and may affect driveability.
VEHICLE LOADING The load carrying capacity of your vehicle is shown in the charts that follow. This information should be used for passenger and luggage loading as indicated. If the seatbacks are folded for carrying cargo, do not exceed the specified GVWR and GAWR.
Vehicle Certification Label Your vehicle has a certification label attached to the rear of the driver’s door. The label contains the following information: • Name of manufacturer • Month and year of manufacture • Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) • Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) front • Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) rear • Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) • Type of Vehicle • Month Day and Hour of Manufacture (MDH) The bar code allows a computer scanner to read the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).
STARTING AND OPERATING 327
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) The GVWR is the total allowable weight of your vehicle. This includes driver, passengers, and cargo. The total load must be limited so that you do not exceed the GVWR. Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) The GAWR is the maximum capacity of the front and rear axles. Distribute the load over the front and rear axles evenly. Make sure that you do not exceed either front or rear GAWR.
WARNING!
Because the front wheels drive and steer the vehicle, it is important that you do not exceed the maximum front or rear GAWR. A dangerous driving condition can result if either rating is exceeded. You could lose control of the vehicle and have an accident.
328 STARTING AND OPERATING
Overloading The load carrying components (axle, springs, tires, wheels, etc.) of your vehicle will provide satisfactory service as long as you do not exceed the GVWR and front and rear GAWR. The best way to figure out the total weight of your vehicle is to weigh it when it is fully loaded and ready for operation. Weigh it on a commercial scale to insure that it is not over the GVWR. Figure out the weight on the front and rear of the vehicle separately. It is important that you distribute the load evenly over the front and rear axles. Overloading can cause potential safety hazards and shorten useful service life. Heavier axles or suspension components do not necessarily increase the vehicle’s GVWR.
Loading To load your vehicle properly, first figure out its empty weight, axle by axle and side by side. Store heavier items down low and be sure you distribute their weight as evenly as possible. Stow all loose items securely before driving. If weighing the loaded vehicle shows that you have exceeded either GAWR, but the total load is within the specified GVWR, you must redistribute the weight. Improper weight distribution can have an adverse effect on the way your vehicle steers and handles and the way the brakes operate.
STARTING AND OPERATING 329
A loaded vehicle is shown in the illustration. Note that neither the GVWR or the GAWR capacities have been exceeded.
Example Only Empty Weight
Load (Including driver, pas- sengers and cargo)
Total
GAWR
Front Axle Rear Axle 2076 lbs (942 kg ) 890 lbs (404 kg) 2968 lbs (1346 kg) 3035 lbs (1377 kg)
2538 lbs (1151 kg) 223 lbs (101 kg) 2762 lbs (1253 kg) 2826 lbs (1282 kg)
TRAILER TOWING In this section you will find safety tips and information on limits to the type of towing you can reasonably do with your vehicle. Before towing a trailer carefully re- view this information to tow your load as efficiently and safely as possible. To maintain warranty coverage, follow the requirements and recommendations in this manual concerning ve- hicles used for trailer towing.
330 STARTING AND OPERATING
Common Towing Definitions The following trailer towing related definitions will assist you in understanding the following information: Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) The GVWR is the total allowable weight of your vehicle. This includes driver, passengers, cargo and tongue weight. The total load must be limited so that you do not exceed the GVWR. Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) The gross trailer weight (GTW) is the weight of the trailer plus the weight of all cargo, consumables and equipment (permanent or temporary) loaded in or on the trailer in its ⬙loaded and ready for operation⬙ condition. The recom- mended way to measure GTW is to put your fully loaded trailer on a vehicle scale. The entire weight of the trailer must be supported by the scale.
Gross Combination Weight Rating (GCWR) The gross combination weight rating (GCWR) is the total permissible weight of your vehicle and trailer when weighed in combination. (Note that GCWR ratings include a 150 lbs (68 kg) allowance for the presence of a driver). Gross Axle Weight Rating (GAWR) The GAWR is the maximum capacity of the front and rear axles. Distribute the load over the front and rear axles evenly. Make sure that you do not exceed either front or rear GAWR.
WARNING!
It is important that you do not exceed the maximum front or rear GAWR. A dangerous driving condition can result if either rating is exceeded. You could lose control of the vehicle and have an accident.
Tongue Weight (TW) The downward force exerted on the hitch ball by the trailer. In most cases it should not be less than 10% or more than 15% of the trailer load. You must consider this as part of the load on your vehicle. Frontal Area The maximum height and maximum width of the front of a trailer. Trailer Sway Control The trailer sway control is a telescoping link that can be installed between the hitch receiver and the trailer tongue that typically provides adjustable friction associated with the telescoping motion to dampen any unwanted trailer swaying motions while traveling. Weight-Carrying Hitch A weight-carrying hitch supports the trailer tongue weight, just as if it were luggage located at a hitch ball or some other connecting point of the vehicle. These kind of
STARTING AND OPERATING 331
hitches are the most popular on the market today and they’re commonly used to tow small- and medium-sized trailers. Weight-Distributing Hitch A weight-distributing system works by applying lever- age through spring (load) bars. They are typically used for heavier loads, to distribute trailer tongue weight to the tow vehicle’s front axle and the trailer axle(s). When used in accordance with the manufacturers’ directions, it provides for a more level ride, offering more consistent steering and brake control thereby enhancing towing safety. The addition of a friction / hydraulic sway control also dampens sway caused by traffic and crosswinds and contributes positively to tow vehicle and trailer stability. Trailer sway control and a weight distributing (load equalizing) hitch are recommended for heavier Tongue Weights (TW) and may be required depending on Vehicle and Trailer configuration / loading to comply with gross axle weight rating (GAWR) requirements.
332 STARTING AND OPERATING
WARNING!
An improperly adjusted Weight Distributing Hitch system may reduce handling, stability, braking per- formance, and could result in an accident. Weight Distributing Systems may not be compatible with Surge Brake Couplers. Consult with your hitch and trailer manufacturer or a reputable Recreational Vehicle dealer for additional information.
Weight Distributing Hitch System
STARTING AND OPERATING 333
The following chart provides the industry standard for the maximum trailer weight a given trailer hitch class can tow and should be used to assist you in selecting the correct trailer hitch for your intended towing condition. Refer to the Trailer Towing Weights (Maximum Trailer Weight Ratings) chart for the Max. GTW towable for your given drivetrain.
Trailer Hitch Classification
Class
Max. GTW
Class I - Light Duty Class II - Medium Duty Class III - Heavy Duty Class IV - Extra Heavy Duty All trailer hitches should be professionally installed on your vehicle.
(Gross Trailer Wt.) 2,000 lbs (907 kg) 3,500 lbs (1587 kg) 5,000 lbs (2268 kg) 10,000 lbs (4540 kg)
Improper Adjustment of Weight Distributing System
Trailer Hitch Classification Your vehicle may be factory equipped for safe towing of trailers weighing over 2,000 lbs (907 kg) with the optional Trailer Tow Prep Package. See your dealer for package content.
334 STARTING AND OPERATING
Trailer Towing Weights (Maximum Trailer Weight Ratings) The following chart provides the maximum trailer weight ratings towable for your given drivetrain. Engine/Transmission GCWR (Gross Com- bined Wt. Rating) 8,600 lbs (3900 kg)
3.5L & 3.8L Auto- matic
Frontal Area
40 SQ. FT.
8,600 lbs (3900 kg)
40 SQ. FT.
8,600 lbs (3900 kg)
40 SQ. FT.
Max. GTW (Gross
Trailer Wt.)
Up to 2 persons & Luggage 3,500 lbs
(1600 kg)
3 to 4 persons & Luggage 3,000 lbs
(1360 kg)
5 to 6 persons & Luggage 1,000 lbs
(454 kg)
Max. Tongue Wt.
350 lbs (158 kg)
300 lbs (136 kg)
100 lbs (45 kg)
Refer to local laws for maximum trailer towing speeds. NOTE: The trailer tongue weight must be considered as part of the combined weight of occupants and cargo, and should never exceed the weight referenced on the Tire
and Loading Information placard. Refer to the Tire– Safety Information Section in this manual.
Trailer and Tongue Weight Always load a trailer with 60% to 65% of the weight in the front of the trailer. This places 10% to 15% of the Gross Trailer Weight (GTW) on the tow hitch of your vehicle. Loads balanced over the wheels or heavier in the rear can cause the trailer to sway severely side to side which will cause loss of control of the vehicle and trailer. Failure to load trailers heavier in front is the cause of many trailer accidents. Never exceed the maximum tongue weight stamped on your bumper or trailer hitch.
STARTING AND OPERATING 335
Consider the following items when computing the weight on the rear axle of the vehicle: • The tongue weight of the trailer. • The weight of any other type of cargo or equipment • The weight of the driver and all passengers.
put in or on your vehicle.
336 STARTING AND OPERATING
NOTE: Remember that everything put into or on the trailer adds to the load on your vehicle. Also, additional factory-installed options, or dealer-installed options, must be considered as part of the total load on your vehicle. Refer to the Tire and Loading Information plac- ard in the Tire Safety Information Section of this manual for the maximum combined weight of occupants and cargo for your vehicle. Towing Requirements To promote proper break-in of your new vehicle driv- etrain components the following guidelines are recom- mended:
CAUTION!
• Avoid towing a trailer for the first 500 miles (805
km) of vehicle operation. Doing so may damage your vehicle. • During the first 500 miles (805 km) of trailertowing, limit your speed to 50 mph (80 km/h).
Perform the maintenance listed in Section 8 of this manual. When towing a trailer, never exceed the GAWR, or GCWR, ratings.
WARNING!
Improper towing can lead to an injury accident. Follow these guidelines to make your trailer towing as safe as possible: Make certain that the load is secured in the trailer and will not shift during travel. When trailering cargo that is not fully secured, dynamic load shifts can occur that may be difficult for the driver to control. You could lose control of your vehicle and have an accident. • When hauling cargo or towing a trailer, do not over- load your vehicle or trailer. Overloading can cause a loss of control, poor performance or damage to brakes, axle, engine, transmission, steering, suspension, chas- sis structure or tires.
STARTING AND OPERATING 337
• Safety chains must always be used between your vehicle and trailer. Always connect the chains to the frame or hook retainers of the vehicle hitch. Cross the chains under the trailer tongue and allow enough slack for turning corners. • Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. When parking, apply the parking brake on the tow vehicle. Put the tow vehicle automatic transmission in P for Park. Always, block or ⬙chock⬙ the trailer wheels.
• GCWR must not be exceeded. • Total weight must be distributed between the tow vehicle and the trailer such that the following four ratings are not exceeded: 1. GVWR 2. GTW 3. GAWR
338 STARTING AND OPERATING
4. Tongue weight rating for the trailer hitch utilized (This requirement may limit the ability to always achieve the 10% to 15% range of tongue weight as a percentage of total trailer weight).
Towing Requirements — Tires − Do not attempt to tow a trailer while using a compact
spare tire.
− Proper tire inflation pressures are essential to the safe and satisfactory operation of your vehicle. Refer to the Tires–General Information section of this manual on Tire Pressures for proper tire inflation procedures.
− Also, check the trailer tires for proper tire inflation
pressures before trailer usage.
− Check for signs of tire wear or visible tire damage before towing a trailer. Refer to the Tires–General Information section of this manual on Tread Wear Indicators for the proper inspection procedure.
− When replacing tires refer to the Tires–General Infor- mation section of this manual on Replacement Tires for proper tire replacement procedures. Replacing tires with a higher load carrying capacity will not increase the vehicle’s GVWR and GAWR limits. Towing Requirements — Trailer Brakes − Do not interconnect the hydraulic brake system or vacuum system of your vehicle with that of the trailer. This could cause inadequate braking and possible personal injury.
− An electronically actuated trailer brake controller is required when towing a trailer with electronically actuated brakes. When towing a trailer equipped with a hydraulic surge actuated brake system, an electronic brake controller is not required.
− Trailer brakes are recommended for trailers over 1,000
lbs (454 kg) and required for trailers in excess of 2,000
lbs (907 kg).CAUTION!
If the trailer weighs more than 1,000 lbs (454 kg) loaded, it should have its own brakes and they should be of adequate capacity. Failure to do this could lead to accelerated brake lining wear, higher brake pedal effort, and longer stopping distances.
STARTING AND OPERATING 339
WARNING!
Do not connect trailer brakes to your vehicle’s hy- draulic brake lines. It can overload your brake sys- tem and cause it to fail. You might not have brakes when you need them and could have an accident. Towing any trailer will increase your stopping dis- tance. When towing you should allow for additional space between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you. Failure to do so could result in an accident.
Towing Requirements — Trailer Lights & Wiring Whenever you pull a trailer, regardless of the trailer size, stop lights and turn signals on the trailer are required for motoring safety. The Trailer Tow Package may include a 4 and 7 pin wiring harness. Use a factory approved trailer harness and connector.
340 STARTING AND OPERATING
NOTE: Do not cut or splice wiring into the vehicles wiring harness. The electrical connections are all complete to the vehicle but you must mate the harness to a trailer connector. Refer to the following illustrations.
7- Pin Connector
Towing Tips Before setting out on a trip, practice turning, stopping and backing the trailer in an area away from heavy traffic.
4 - Pin Connector
Towing Tips — Automatic Transmission The “D” range can be selected when towing. However, if frequent shifting occurs while in this range, the “3” range should be selected. NOTE: Using the “3” range while operating the vehicle under heavy operating conditions will improve perfor- mance and extend transmission life by reducing exces- sive shifting and heat build up. This action will also provide better engine braking. The automatic transmission fluid and filter should be changed if you REGULARLY tow a trailer for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation. See Schedule “B” in section 8 of this manual for transmission fluid change intervals. NOTE: Check the automatic transmission fluid level before towing.
STARTING AND OPERATING 341
Towing Tips — Electronic Speed Control (If Equipped) − Don’t use in hilly terrain or with heavy loads. − When using the speed control, if you experience speed drops greater than 10 mph (16 km/h), disengage until you can get back to cruising speed.
− Use speed control in flat terrain and with light loads to
maximize fuel efficiency.
Towing Tips — Cooling System To reduce potential for engine and transmission over- heating, take the following actions: − City Driving When stopped for short periods of time, put transmission in neutral but do not increase engine idle speed.
342 STARTING AND OPERATING
− Highway Driving Reduce speed. − Air Conditioning Turn off temporarily. − refer to Cooling System Operating information in the Maintenance section of this manual for more informa- tion.
RECREATIONAL TOWING (BEHIND MOTORHOME, ETC.)
TOWING THIS VEHICLE BEHIND ANOTHER VEHICLE (Flat towing with all four wheels on the ground) Recreational towing for this vehicle is not recommended. If the vehicle requires towing make sure all four NOTE: wheels are off the ground.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
CONTENTS
䡵 Hazard Warning Flasher . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
䡵 If Your Engine Overheats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 345
䡵 Jacking And Tire Changing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
▫ Jack Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 346
▫ Spare Tire Stowage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 348
▫ Preparations For Jacking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 349
▫ Jacking Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 350
䡵 Jump-Starting Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354䡵 Freeing A Stuck Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
䡵 Towing A Disabled Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
▫ With Ignition Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
▫ Without The Ignition Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358
▫ Towing This Vehicle Behind Another Vehicle (Flat Towing With All Four Wheels On The Ground) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 358▫ Towing This Vehicle Behind Another Vehicle
With A Tow Dolly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
344 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
HAZARD WARNING FLASHER
Hazard Flasher Switch
The hazard flasher switch is located in the center of the instrument panel above the center air outlets.
To engage the Hazard Warning Flashers, depress the switch on the instrument panel. When the Hazard Warn- ing Switch is activated, all directional turn signals will flash on and off to warn oncoming traffic of an emer- gency. Push the switch a second time to turn off the flashers.
CAUTION!
This is an emergency warning system and should not be used when the vehicle is in motion. Use it when your vehicle is disabled and is creating a safety hazard for other motorists.
When you must leave the vehicle to seek assistance, the Hazard Warning Flashers will continue to operate even though the ignition switch is OFF.
NOTE: With extended use, the Hazard Warning Flash- ers may wear down your battery.
IF YOUR ENGINE OVERHEATS In any of the following situations, you can reduce the potential for overheating by taking the appropriate ac- tion. • On the highways — Slow down. • In city traffic — While stopped, put transmission in
neutral, but do not increase engine idle speed.
NOTE: There are steps that you can take to slow down an impending overheat condition. If your air conditioner is on, turn it off. The air conditioning system adds heat to the engine cooling system and turning off the A/C removes this heat. You can also turn the Temperature control to maximum heat, the Mode control to floor, and
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 345
the fan control to High. This allows the heater core to act as a supplement to the radiator and aids in removing heat from the engine cooling system.
CAUTION!
Driving with a hot cooling system could damage your vehicle. If temperature gauge reads “H”, pull over and stop the vehicle. Idle the vehicle with the air conditioner turned off until the pointer drops back into the normal range. If the pointer remains on the “H”, turn the engine off immediately, and call for service.
346 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
WARNING!
A hot engine cooling system is dangerous. You or others could be badly burned by steam or boiling coolant. You may want to call a service center if your vehicle overheats. If you decide to look under the hood yourself, see Section 7, Maintenance, of this manual. Follow the warnings under the Cooling System Pressure Cap paragraph.
JACKING AND TIRE CHANGING
Jack Location
Five Passenger Seating The jack and jack-handle are stowed in the rear storage bin located behind the second row bench seat. Pull up on the storage bin cover to access the jack and jack tools.
Jack Location
Remove the scissors jack and jack handle by rotating the small wing nut to the left.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 347
Six Passenger Seating The jack and jack-handle are stowed in the rear storage bin located in the rear cargo floor. Pull up on the storage bin cover and liner to access the jack and jack tools.
Jack Wing Nut
Jack Location
348 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
Spare Tire Stowage
Five Passenger Seating The spare tire is stowed under the rear of the vehicle by means of a cable winch mechanism. To remove or stow the spare, use the jack handle to rotate the “spare tire drive” nut. The nut is located under the plastic cover at the center rear of the cargo floor area, just inside the liftgate opening. Six Passenger Seating The spare tire is stowed under the rear of the vehicle by means of a cable winch mechanism. To remove or stow the spare, use the jack handle to rotate the “spare tire drive” nut. The nut is located under the trim cover at the center of the rear storage bin in the rear cargo floor.
Lowering Spare Tire
Spare Tire Removal Fit the jack-handle over the drive nut. Rotate the nut to the left until the spare is on the ground with enough slack cable to allow you to pull the tire out from under the vehicle.
CAUTION!
The winch mechanism is designed for use with the jack handle only. Use of an air wrench or other power tools is not recommended and can damage the winch.
When the spare is clear, tilt the retainer at the end of the cable and pull it through the center of the wheel. Preparations For Jacking Park the vehicle on a firm level surface, avoid ice or slippery areas, set the parking brake and place the gear selector in PARK. Turn OFF the ignition.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 349
WARNING!
Do not attempt to change a tire on the side of the vehicle close to moving traffic. Pull far enough off the road to avoid the danger of being hit when operating the jack or changing the wheel. • Turn on the Hazard Warning Flasher.
• Block both the front and rear of the wheel diagonally oppo- site the jacking position. For example, if changing the right front tire, block the left rear wheel. • Passengers should not remain in the vehicle when the
vehicle is being jacked.
350 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
Jacking Instructions
WARNING!
• Getting under a jacked-up vehicle is dangerous. The vehicle could slip off the jack and fall on you. You could be crushed. Never get any part of your body under a vehicle that is on a jack. Never start or run the engine while the vehicle is on a jack. If you need to get under a raised vehicle, take it to a service center where it can be raised on a lift. • The jack is designed to use as a tool for changing tires only. The jack should not be used to lift the vehicle for service purposes. The vehicle should be jacked on a firm level surface only. Avoid ice or slippery areas.
WARNING!
raised.
Carefully follow these tire changing warnings to help prevent personal injury or damage to your vehicle: • Always park on a firm, level surface as far from the edge of the roadway as possible before raising the vehicle. • Block the wheel diagonally opposite the wheel to be • Apply the parking brake firmly before jacking. • Never start the engine with the vehicle on a jack. • Do not let anyone sit in the vehicle when it is on a jack. • Do not get under the vehicle when it is on a jack. • Only use the jack in the positions indicated. • If working on or near a roadway, be extremely careful • To assure that spare tires, flat or inflated are securely stowed, spares must be stowed with the value stem facing the ground.
of motor traffic.
1. Remove the spare wheel, scissors jack and jack-handle from stowage. 2. Carefully pry off the wheel center cap if equipped, using the tip of the jack handle. 3. Loosen (but do not remove) the wheel lug nuts by turning them to the left one turn while the wheel is still on the ground. NOTE: Do not oil wheel studs. For chrome wheels, do not substitute with chrome plated wheel nuts. 4. There are two jack engagement locations on each side of the body — refer to the following illustration.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 351
Jack Engagement Locations
5. These locations are on the sill flange on the underside of the body. The jack is to be located, engaging the flanges, 20 cm (8 inches) inward from the edge of the wheel opening closest to the wheel to be changed. Place the wrench on the jack screw and turn to the right until the jack head is properly engaged in the described
352 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
location. Do not raise the vehicle until you are sure the jack is securely engaged. Never jack up the vehicle using any suspension components. 6. Raise the vehicle by turning the jack screw to the right, using the swivel wrench. Raise the vehicle only until the tire just clears the surface and enough clearance is obtained to install the spare tire. Minimum tire lift provides maximum stability.
WARNING!
Raising the vehicle higher than necessary can make the vehicle less stable. It could slip off the jack and hurt someone near it. Raise the vehicle only enough to remove the tire.
7. Remove the wheel lug nuts, for vehicles with wheel covers, remove the cover from the wheel by hand. Do not pry the wheel cover off. Then pull the wheel off the hub. 8. Install the spare wheel, for vehicles with wheel covers, align the notch in the wheel cover with the valve stem on the wheel. Install the cover on the wheel by hand only and install the wheel lug nuts with the cone shaped end of the nut toward the wheel. Lightly tighten the lug nuts. To avoid the risk of forcing the vehicle off the jack, do not tighten the lug nuts fully until the vehicle has been lowered. NOTE: Do not install the wheel cover on the compact spare. Do not use a hammer or force to install the wheel covers. 9. Lower the vehicle by turning the jack screw to the left. 10. Finish tightening the lug nuts. Push down on the wrench while tightening for increased leverage. Alternate
lug nuts until each nut has been tightened twice. Correct wheel nut tightness is 130 N·m (95 ft. lbs). If in doubt about the correct tightness, have them checked with a torque wrench by your dealer or at a service station. 11. Lower the jack to its fully closed position.
WARNING!
A loose tire or jack, thrown forward in a collision or hard stop could endanger the occupants of the ve- hicle. Always stow the jack parts and the spare tire in the places provided.
12. Secure the flat or spare tire as follows: • If your vehicle is equipped with cast aluminum wheels, the center cap of the wheel must be re- moved prior to flat tire stowage. Store the center cap inside the glove box or other storage compartment.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 353
• Turn the wheel so that the valve-stem is down. Slide the wheel retainer through the center of the wheel and position it properly across the wheel opening. • For convenience in checking the spare tire inflation, stow with the valve-stem toward the rear of the vehicle. • Using the jack-handle, rotate the drive nut to the right until the wheel is drawn into place against the underside of the vehicle. • Continue to rotate the nut until you hear the mecha- nism click three times. It cannot be overtightened. Push against the tire several times to be sure it is securely in place.
13. Stow the jack and jack handle. 14. Check the tire pressure as soon as possible. Correct pressure as required.
354 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
NOTE: When reinstalling the wheel center cap, insure that the valve stem symbol on the back of the cap is pointed toward the wheel valve stem. Install the center cap using hand pressure only. Do not use a hammer. Wheel Nuts All wheel nuts should be tightened occasionally to elimi- nate the possibility of wheel studs being sheared or the bolt holes in the wheels becoming elongated. This is especially important during the first few hundred miles of operation, and after each time a tire is changed, to allow the wheel nuts to become properly set. All nuts should first be firmly seated against the wheel. The nuts should then be tightened to recommended torque. Tighten the nuts to final torque in increments. Progress around the bolt circle, tightening the nut opposite to the nut torque is achieved. Recommended torque is 130 N·m (95 ft. lbs).
just previously tightened until
final
JUMP-STARTING PROCEDURE
WARNING!
• Do not attempt to push or tow your vehicle to get it started.
Vehicles equipped with an automatic transmission cannot be started this way. Unburned fuel could enter the catalytic converter and once the engine has started, ignite and damage the converter and vehicle. If the vehicle has a discharged battery, booster cables may be used to obtain a start from another vehicle. This type of start can be dangerous if done improperly, so follow this procedure carefully.
• Battery fluid is a corrosive acid solution; do not allow battery
fluid to contact eyes, skin or clothing. Don’t lean over battery when attaching clamps or allow the clamps to touch each other. If acid splashes in eyes or on skin, flush contaminated area immediately with large quantities of water.
• A battery generates hydrogen gas which is flammable and
explosive. Keep flame or spark away from the vent holes. Do not use a booster battery or any other booster source with an output that exceeds 12 volts.
• Take care to avoid the radiator cooling fan whenever the hood
is raised. It can start anytime the ignition switch is on. You can be hurt by the fan.
Check the Battery Test Indicator (if equipped). If a light or bright colored dot is visible in the indicator (if equipped), DO NOT jump-start the battery. If the indicator (if equipped) is dark or shows a green dot, proceed as follows: 1. Wear eye protection and remove any metal jewelry such as watch bands or bracelets that might make an inadvertent electrical contact. 2. When boost is provided by a battery in another vehicle, park that vehicle within booster cable reach and without letting the vehicles touch. Set the parking brake, place the automatic transmission in PARK and turn the ignition switch to the OFF position for both vehicles. 3. Turn off the heater, radio and all unnecessary electrical loads.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 355
4. Connect one end of a jumper cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery. Connect the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery.
WARNING!
Do not permit vehicles to touch each other as this could establish a ground connection and personal injury could result.
5. Connect the other cable, first to the negative terminal of the booster battery and then to the engine of the vehicle with the discharged battery. Make sure you have a good contact on the engine.
356 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
WARNING!
WARNING!
Do not connect the cable to the negative post of the discharge battery. The resulting electrical spark could cause the battery to explode. During cold weather when temperatures are below freezing point, electrolyte in a discharged battery may freeze. Do not attempt jump starting because the battery could rupture or explode. The battery temperature must be brought up above freezing point before attempting jump start.
6. Start the engine in the vehicle which has the booster battery, let the engine idle a few minutes, then start the engine in the vehicle with the discharged battery. 7. When removing the jumper cables, reverse the above sequence exactly. Be careful of the moving belts and fan.
Any procedure other than above could result in: 1. Personal injury caused by electrolyte squirting out the battery vent; 2. Personal injury or property damage due to battery explosion; 3. Damage to charging system of booster vehicle or of immobilized vehicle.
FREEING A STUCK VEHICLE If your vehicle becomes stuck in mud, sand or snow, it can often be moved by a rocking motion. Turn your steering wheel right and left to clear the area around the front wheels. Then shift back and forth between Reverse and Drive. Usually the least accelerator pedal pressure to maintain the rocking motion without spinning the wheels is most effective.
WARNING!
Fast spinning tires can be dangerous. Forces gener- ated by excessive wheel speeds may cause tire dam- age or failure. A tire could explode and injure someone. Do not spin your vehicle’s wheels faster than 35 mph (55 km/h) when you are stuck. And don’t let anyone near a spinning wheel, no matter what the speed.
CAUTION!
Racing the engine or spinning the wheels too fast may lead to transmission overheating and failure. It can also damage the tires. Do not spin the wheels above 35 mph (55 km/h).
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 357
TOWING A DISABLED VEHICLE
With Ignition Key
Front Wheel Drive Your vehicle may be towed under the following condi- tions: The gear selector must be in NEUTRAL, the distance to be traveled must not exceed 100 miles (160
km), the towing speed must not exceed 44 mph (72
km/h), and both front and rear wheels must be on the ground. Exceeding these towing limits may cause a transmission geartrain failure. If the transmission is not operative, or if the vehicle is to be towed more than 100
miles (160 km), the vehicle must be towed with the front wheels off the ground. All Wheel Drive Your vehicle may be towed under the following conditions: The gear selector must be in NEUTRAL, the distance to be traveled must not exceed 100 miles (160 km), the towing speed must not exceed 44 mph (72 km/h), and both front358 WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES
and rear wheels must be on the ground. If your vehicle must be towed farther or at a higher rate of speed, it must be transported on a flat bed truck. All Transmissions
CAUTION!
• Do not attempt to tow this vehicle from the front with sling type towing equipment. Damage to the front fascia will result. • Always use wheel lift equipment when towing from the front. The only other approved method of towing is with a flat bed truck. • Do not tow the vehicle from the rear. Damage to the rear sheet metal, liftgate and fascia will occur. • Do not push or tow this vehicle with another vehicle as damage to the bumper fascia and trans- mission may result.
If it is necessary to use the accessories while being towed (wipers, defrosters, etc.), the key must be in the ON position, not the ACCESSORY position. Make certain the transmission remains in NEUTRAL. Without The Ignition Key Special care must be taken when the vehicle is towed with the ignition in the LOCK position. The only ap- proved method of towing with out the ignition key is with a flat bed truck. Proper towing equipment is neces- sary to prevent damage to the vehicle. TOWING THIS VEHICLE BEHIND ANOTHER VEHICLE (Flat towing with all four wheels on the ground) Flat towing of vehicles equipped with an automatic transmission, is only permitted within the limitations described in this section.
TOWING THIS VEHICLE BEHIND ANOTHER VEHICLE WITH A TOW DOLLY The manufacturer does not recommend that you tow an All-Wheel Drive (AWD) or front wheel drive vehicle on a tow dolly. Vehicle damage may occur.
WHAT TO DO IN EMERGENCIES 359
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
CONTENTS
䡵 4.0L Engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 364
䡵 3.8L Engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
䡵 Onboard Diagnostic System — OBD II . . . . . . . . 366
▫ Loose Fuel Filler Cap Message . . . . . . . . . . . . 366䡵 Emissions Inspection And Maintenance
Programs
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
䡵 Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
䡵 Dealer Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
䡵 Maintenance Procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369▫ Engine Oil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
▫ Engine Oil Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
▫ Drive Belts — Check Condition And Tension . . 374
▫ Spark Plugs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
▫ Engine Air Cleaner Filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
▫ Catalytic Converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
▫ Maintenance-Free Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
▫ Air Conditioner Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
▫ Power Steering — Fluid Check . . . . . . . . . . . . 379362 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
▫ Front & Rear Suspension Ball Joints . . . . . . . . 380
▫ Steering Shaft Seal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
▫ Steering Linkage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
▫ Drive Shaft Universal Joints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
▫ Body Lubrication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
▫ Windshield Wiper Blades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
▫ Windshield And Rear Window Washers . . . . . 382
▫ Exhaust System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
▫ Cooling System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
▫ Hoses And Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses . . . . . . . 388
▫ Brakes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
▫ Master Cylinder — Brake Fluid Level Check . . 390
▫ Fuel System Hoses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391▫ Automatic Transmission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
▫ All Wheel Drive (AWD) — If Equipped . . . . . 395
▫ Front And Rear Wheel Bearings . . . . . . . . . . . 396
▫ Appearance Care And Protection FromCorrosion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
▫ Cleaning The Center Console Cup Holders . . . 401
䡵 Fuses (Integrated Power Module) . . . . . . . . . . . 402
䡵 Vehicle Storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
䡵 Replacement Light Bulbs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
䡵 Bulb Replacement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
▫ Standard Quad Headlights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
▫ High Intensity Discharge Headlights (HID) —If Equipped . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
▫ Front Park/Turn Signal And Sidemarker
Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409▫ Front Fog Light ▫ Rear Tail, Stop, Turn Signal, Side Marker And
Back-Up Lights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410▫ License Light
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 363
䡵 Fluids And Capacities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
䡵 Fluids, Lubricants And Genuine Parts . . . . . . . . 412
▫ Engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 412
▫ Chassis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413364 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
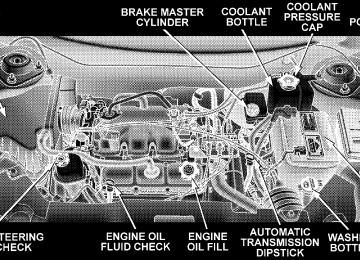
4.0L ENGINES
Engine Compartment 4.0L Engine
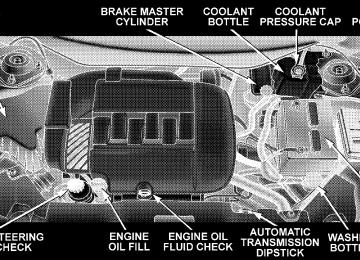
3.8L ENGINES
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 365
Engine Compartment 3.8L Engines
366 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
ONBOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM — OBD II Your vehicle is equipped with a sophisticated onboard diagnostic system called OBD II. This system monitors the performance of the emissions, engine, and automatic transmission control systems. When these systems are operating properly, your vehicle will provide excellent performance and fuel economy, as well as engine emis- sions well within current government regulations. If any of these systems require service, the OBD II system will turn on the “Malfunction Indicator Light.” It will also store diagnostic codes and other information to assist your service technician in making repairs. Al- though your vehicle will usually be drivable and not need towing, see your dealer for service as soon as possible.
CAUTION!
• Prolonged driving with the “Malfunction Indica- tor Light” on could cause further damage to the emission control system. It could also affect fuel economy and driveability. The vehicle must be serviced before any emissions tests can be per- formed. • If the “Malfunction Indicator Light” is flashing while the engine is running, severe catalytic con- verter damage and power loss will soon occur. Immediate service is required.
Loose Fuel Filler Cap Message After fuel is added, the vehicle diagnostic system can determine if the fuel filler cap is loose, improperly installed, or damaged. A loose fuel filler cap message will be displayed in the instrument cluster. Tighten the gas
cap until a ⬙clicking⬙ sound is heard. This is an indication that the gas cap is properly tightened. Press the odometer reset button to turn the message off. If the problem persists, the message will appear the next time the vehicle is started. This might indicate a damaged cap. If the problem is detected twice in a row, the system will turn on the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL). Resolving the problem will turn the MIL light off.
EMISSIONS INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS In some localities, it may be a legal requirement to pass an inspection of your vehicle’s emissions control system. Failure to pass could prevent vehicle registration.
For states, which have an I/M (Inspection and Maintenance) requirement, this check verifies the following: the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 367
is functioning and is not on when the engine is running, and that the OBD (On Board Diagnostic) system is ready for testing. Normally, the OBD system will be ready. The OBD system may not be ready if your vehicle was recently serviced, if you recently had a dead battery, or a battery replacement. If the OBD system should be determined not ready for the I/M test, your vehicle may fail the test. Your vehicle has a simple ignition key actuated test, which you can use prior to going to the test station. To check if your vehicle’s OBD system is ready, you must do the following: 1. Insert your ignition key into the ignition switch. 2. Turn the ignition to the ON position, but do not crank or start the engine. 3. If you crank or start the engine, you will have to start this test over.
368 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
4. As soon as you turn your key to the ON position, you will see your MIL symbol come on as part of a normal bulb check. 5. Approximately 15 seconds later, one of two things will happen:
a. The MIL will flash for about 10 seconds and then return to being fully illuminated until you turn off the ignition key or start the engine. This means that your vehicle’s OBD system is not ready and you should not proceed to the I/M station. b. The MIL will not flash at all and will remain fully illuminated until you turn off the ignition key or start the engine. This means that your vehicle’s OBD system is ready and you can proceed to the I/M station.
If your OBD system is not ready, you should see your authorized dealer or repair facility. If your vehicle was recently serviced or had a battery failure or replacement,
you may need to do nothing more than drive your vehicle as you normally would in order for your OBD system to update. A recheck with the above test routine may then indicate that the system is now ready. Regardless of whether your vehicle’s OBD system is ready or not ready, if the MIL symbol is illuminated during normal vehicle operation, you should have your vehicle serviced before going to the I/M station. The I/M station can fail your vehicle because the MIL symbol is on with the engine running.
REPLACEMENT PARTS Use of genuine Mopar威 parts for normal/scheduled maintenance and repairs is highly recommended to in- sure the designed performance. Damage or failures caused by the use of non-Mopar威 parts for maintenance and repairs will not be covered by the manufacturer’s warranty.
DEALER SERVICE Your dealer has the qualified service personnel, special tools, and equipment to perform all service operations in an expert manner. Service Manuals are available which include detailed service information for your vehicle. Refer to these manuals before attempting any procedure yourself. NOTE: systems can result against you.
Intentional tampering with emissions control in civil penalties being assessed
WARNING!
You can be badly injured working on or around a motor vehicle. Only do service work for which you have the knowledge and the proper equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a competent mechanic.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 369
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES The pages that follow contain the required maintenance services determined by the engineers who designed your vehicle. Besides the maintenance items for which there are fixed maintenance intervals, there are other items that should operate satisfactorily without periodic maintenance. However, if a malfunction of these items does occur, it could adversely affect the engine or vehicle performance. These items should be inspected if a malfunction is observed or suspected. Engine Oil
Checking Oil Level To assure proper engine lubrication, the engine oil must be maintained at the correct level. Check the oil level at regular intervals, such as every fuel stop.
370 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
The best time to check the engine oil level is about 5
minutes after a fully warmed engine is shut off or before starting the engine after it has sat overnight. Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level readings. Maintain the oil level between the MIN and MAX markings on the dipstick. Adding one quart of oil when the reading is at the MIN mark will result in a MAX reading on these engines.Engine Oil Dipstick
CAUTION!
Overfilling or underfilling will cause oil aeration or loss of oil pressure. This could damage your engine.
Change Engine Oil Road conditions and your kind of driving affects the interval at which your oil should be changed. Check the following list to see if any apply to you. • Day or night temperatures are below 32°F (0°C). • Stop and Go driving. • Extensive engine idling. • Driving in dusty conditions. • Short trips of less than 10 miles (16 km). • More than 50% of your driving is at sustained high • Trailer towing. • Taxi, Police or delivery service (commercial service). • Off-Road or desert operation.
speeds during hot weather, above 90°F (32°C).
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 371
If ANY of these apply to you then change your NOTE: engine oil every 3,000 miles (5 000 km) or 3 months, whichever comes first and follow schedule “B” of the ⬙Maintenance Schedules⬙ section of this manual. If none of these apply to you, then change your engine oil at every interval shown on schedule ⬙A⬙ of the ⬙Mainte- nance Schedules⬙ section of this manual. NOTE: Under no circumstances should oil change in- tervals exceed 6000 miles (10 000 km) or 6 months whichever comes first. Engine Oil Selection For best performance and maximum protection under all types of operating conditions, the manufacturer only recommends engine oils that are API certified and meet the requirements of DaimlerChrysler Material Standard MS-6395.
372 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
American Petroleum Institute (API) Engine Oil Identification Symbol
This symbol means that the oil has been certified by the American Petroleum Institute (API). The manufacturer only recommends API Certified engine oils.
Engine Oil Viscosity (SAE Grade) — 4.0 Liter Engines The proper SAE viscosity grade of engine oil should be selected based on the following recommendation and be within the operating temperature shown in the engine oil viscosity chart.
• SAE 10W-30 engine oil is preferred. SAE 5W-30 engine oil is allowed during cold weather only to improve cold weather starting.
Lubricants which do not have both, the engine oil certi- fication mark and the correct SAE viscosity grade num- ber should not be used.
Engine Oil Viscosity (SAE Grade) — 3.8 Liter Engines SAE 5W-20 engine oil is recommended for all operating temperatures. This engine oil improves low temperature starting and vehicle fuel economy. Your engine oil filler cap also shows the recommended engine oil viscosity for your vehicle. For information on engine oil filler cap location, refer to the Engine Compartment illustration in this section. Lubricants which do not have both, the engine oil certi- fication mark and the correct SAE viscosity grade num- ber should not be used. Synthetic Engine Oils There are a number of engine oils being promoted as either synthetic or semi-synthetic. If you chose to use such a product, use only those oils that are American
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 373
Petroleum Institute (API) Certified and have the recom- mended SAE viscosity grade. Follow the maintenance schedule that describes your driving type. Materials Added to Engine Oil The manufacture strongly recommends against the addi- tion of any additives (other than leak detection dyes) to the engine oil. Engine oil is an engineered product and it’s performance may be impaired by supplemental ad- ditives. Disposing of Used Engine Oil And Oil Filters Care should be taken in disposing of used engine oil and oil filters from your vehicle. Used oil and oil filters, indiscriminately discarded, can present a problem to the environment. Contact your dealer, service station, or governmental agency for advice on how and where used oil and oil filters can be safely discarded in your area.
374 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Engine Oil Filter The engine oil filter should be replaced at every engine oil change. Engine Oil Filter Selection This manufacture’s engines have a full-flow type oil filter. Use a filter of this type for replacement. The quality of replacement filters varies considerably. Only high quality filters should be used to assure most efficient service. Mopar Engine Oil Filters are a high quality oil filter and are recommended. Drive Belts — Check Condition and Tension At the mileage indicated in the maintenance schedule, all belts should be checked for condition and proper tension. Improper belt tension can cause belt slippage and failure. Belts should be inspected for evidence of cuts, cracks, or glazing, and replaced if there is indication of damage which could result in belt failure. Low generator belt tension can cause battery failure.
Also check belt routing to make sure there is no interfer- ence between the belts and other engine components. Spark Plugs Spark plugs must fire properly to assure engine perfor- mance and emission control. New plugs should be in- stalled at the specified mileage. The entire set should be replaced if there is any malfunction due to a faulty spark plug. Malfunctioning spark plugs can damage the cata- lytic converter. For proper type of replacement spark plugs, refer to the “Vehicle Emission Control Informa- tion” label in the engine compartment. Engine Air Cleaner Filter Under normal driving conditions, replace the air filter at the intervals shown on Schedule “A”. If, however, you drive the vehicle frequently under dusty or severe con- ditions, the filter element should be inspected periodi- cally and replaced if necessary at the intervals shown on Schedule “B”.
WARNING!
The air cleaner can provide a measure of protection in the case of engine backfire. Do not remove the air cleaner unless such removal is necessary for repair or maintenance. Make sure that no one is near the engine compartment before starting the vehicle with the air cleaner removed. Failure to do so can result in serious personal injury.
Catalytic Converter The catalytic converter requires the use of unleaded fuel only. Leaded gasoline will destroy the effectiveness of the catalyst as an emission control device.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 375
Under normal operating conditions, the catalytic con- verter will not require maintenance. However, it is im- portant to keep the engine properly tuned to assure proper catalyst operation and prevent possible catalyst damage.
CAUTION!
Damage to the catalytic converter can result if your vehicle is not kept in proper operating condition. In the event of engine malfunction, particularly involv- ing engine misfire or other apparent loss of perfor- mance, have your vehicle serviced promptly. Contin- ued operation of your vehicle with a severe malfunction could cause the converter to overheat, resulting in possible damage to the converter and the vehicle.
376 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Intentional tampering with emissions control sys- NOTE: tems can result in civil penalties being assessed against you.
WARNING!
A hot exhaust system can start a fire if you park over materials that can burn. Such materials might be grass or leaves coming into contact with your ex- haust system. Do not park or operate your vehicle in areas where your exhaust system can contact any- thing that can burn.
In unusual situations involving grossly malfunctioning engine operation, a scorching odor may indicate severe and abnormal catalyst overheating. If this occurs, the vehicle should be stopped, the engine shut off and the vehicle allowed to cool. Thereafter, service, including a tune-up to manufacturer’s specifications, should be ob- tained immediately.
To minimize the possibility of catalyst damage: • Do not shut off the engine or interrupt the ignition when the transmission is in gear and the vehicle is in motion. • Do not try to start engine by pushing or towing the • Do not idle the engine with any spark plug wires disconnected or removed, such as when diagnostic testing, or for prolonged periods during very rough idling or malfunctioning operating conditions.
vehicle.
Maintenance-Free Battery The top of the MAINTENANCE-FREE battery is perma- nently sealed. You will never have to add water, nor is periodic maintenance required.
WARNING!
• Battery fluid is a corrosive acid solution and can burn or even blind you. Don’t allow battery fluid to contact your eyes, skin or clothing. Don’t lean over a battery when attaching clamps. If acid splashes in eyes or on skin, flush the area imme- diately with large amounts of water. • Battery gas is flammable and explosive. Keep flame or sparks away from the battery. Don’t use a booster battery or any other booster source with an output greater than 12 volts. Don’t allow cable clamps to touch each other. • Battery posts, terminals and related accessories contain lead and lead compounds. Wash hands after handling.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 377
CAUTION!
• It is essential when replacing the cables on the battery that the positive cable is attached to the positive post and the negative cable is attached to the negative post. Battery posts are marked posi- tive (+) and negative (-) and identified on the battery case. Cable clamps should be tight on the terminal posts and free of corrosion. • If a “fast charger” is used while battery is in vehicle, disconnect both vehicle battery cables before connecting the charger to battery. Do not use a “fast charger” to provide starting voltage.
378 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Air Conditioner Maintenance For best possible performance, your air conditioner should be checked and serviced by an Authorized Dealer at the start of each warm season. This service should include cleaning of the condenser fins and a system performance check. Drive belt tension should also be checked at this time.
WARNING!
• Use only refrigerants and compressor lubricants approved by the manufacturer for your air condi- tioning system. Some unapproved refrigerants are flammable and can explode, injuring you. Other unapproved refrigerants or lubricants can cause the system to fail, requiring costly repairs. Refer to Section 3 of the Warranty Information book for further warranty information. • The air conditioning system contains refrigerant under high pressure. To avoid risk of personal injury or damage to the system, adding refrigerant or any repair requiring lines to be disconnected should be done by an experienced repairman.
Refrigerant Recovery And Recycling R-134a Air Conditioning Refrigerant is a hydrofluorocar- bon (HFC) that is endorsed by the Environmental Pro- tection Agency and is an ozone-saving product. How- ever, the manufacturer recommends that air conditioning service be performed by dealers or other service facilities using recovery and recycling equipment. NOTE: Use only manufacturer approved A/C System Sealers, Stop Leak Products, Seal Conditioners, Compres- sor Oil, or Refrigerants. A/C Air Filter The filter access door is located under the instrument panel on the passenger side. To replace the filter slide the lock toward the rear of the vehicle (unlock position). Remove the access door and pull the filter downward. When installing a new filter, ensure its proper orienta- tion. Align the black arrow on the bottom of the filter
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 379
frame with the direction of airflow (away from the blower motor and towards the center of the car). Refer to the “Maintenance Schedules” section of this manual for the recommended air conditioning filter replacement intervals. Power Steering — Fluid Check Checking the power steering fluid level at a defined service interval is not required. The fluid should only be checked if a leak is suspected, abnormal noises are apparent, and/or the system is not functioning as antici- pated. Coordinate inspection efforts through a certified DaimlerChrysler Dealership.⬙
380 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
WARNING!
Fluid level should be checked on a level surface and with the engine off to prevent injury from moving parts and to insure accurate fluid level reading. Do not overfill. Use only manufacturers recommended power steering fluid.
If necessary, add fluid to restore to the proper indicated level. With a clean cloth, wipe any spilled fluid from all surfaces. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants, and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type. Front & Rear Suspension Ball Joints The suspension ball joints are permanently sealed. No regular maintenance is required for these components.
Steering Shaft Seal The steering shaft seal, at the point where the shaft passes through the bulkhead, is lubricated when it is installed. If the seal becomes noisy when the steering shaft is turned, it should be lubricated with a multi-purpose grease. Mopar multi-purpose lubricant is recommended. Steering Linkage The tie rod end ball joints are permanently lubricated and do not require periodic maintenance. Drive Shaft Universal Joints Your vehicle has constant velocity universal joints. Peri- odic lubrication of these joints is not required. However, the joint boots should be inspected for external leakage or damage when other maintenance is performed. If leakage or damage is evident, the universal joint boot and grease should be replaced immediately.
Continued operation could result in failure of the univer- sal joint due to water and dirt contamination of the grease. This would require complete replacement of the joint assembly. Body Lubrication Locks and all body pivot points, including such items as seat tracks, doors, liftgate and hood hinges, should be lubricated periodically to assure quiet, easy operation and to protect against rust and wear. Prior to the appli- cation of any lubricant, the parts concerned should be wiped clean to remove dust and grit; after lubricating excess oil and grease should be removed. Particular attention should also be given to hood latching compo- nents to insure proper function. When performing other underhood services, the hood latch, release mechanism and safety catch should be cleaned and lubricated.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 381
The external lock cylinders should be lubricated twice a year, preferably in the fall and spring. Apply a small amount of a high quality lubricant such as Mopar威 Lock Cylinder Lubricant directly into the lock cylinder. Windshield Wiper Blades The rubber edges of the wiper blades and the windshield should be cleaned periodically with a sponge or soft cloth and a mild nonabrasive cleaner. This will remove accu- mulations of salt or road film. Operation of the wipers on dry glass for long periods may cause deterioration of the wiper blades. Always use washer fluid when using the wipers to remove salt or dirt from a dry windshield. Avoid using the wiper blades to remove frost or ice from the windshield. Keep the blade rubber out of contact with petroleum products such as engine oil, gasoline, etc.
382 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Windshield and Rear Window Washers The fluid reservoir for the windshield washers and the rear window washer is shared. It is located in the engine compartment and should be checked for fluid level at regular intervals. Fill the reservoir with windshield washer solvent (not radiator antifreeze) and operate the system for a few seconds to flush out the residual water. The washer fluid reservoir will hold a full gallon of fluid when the Low Washer Fluid Light illuminates.
Washer Fluid Reservoir
Exhaust System The best protection against carbon monoxide entry into the vehicle body is a properly maintained engine exhaust system. Whenever a change is noticed in the sound of the exhaust system, when exhaust fumes can be detected inside the
vehicle, or when the underside or rear of the vehicle is damaged, have a competent mechanic inspect the com- plete exhaust system and adjacent body areas for broken, damaged, deteriorated, or mispositioned parts. Open seams or loose connections could permit exhaust fumes to seep into the passenger compartment. In addition, inspect the exhaust system each time the vehicle is raised for lubrication or oil change. Replace as required.
WARNING!
Exhaust gases can injure or kill. They contain carbon monoxide (CO) which is colorless and odorless. Breathing it can make you unconscious and can eventually poison you. To avoid breathing CO, refer to “Exhaust Gas” in the Safety Tips section of this manual.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 383
Cooling System
WARNING!
• When working near the radiator cooling fan, dis- connect the fan motor lead or turn the ignition switch to the OFF position. The fan is temperature controlled and can start at any time the ignition switch is in the ON position. • You or others can be badly burned by hot coolant or steam from your radiator. If you see or hear steam coming from under the hood, don’t open the hood until the radiator has had time to cool. Never try to open a cooling system pressure cap when the radiator is hot.
384 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Engine Coolant Checks Check the engine coolant (antifreeze) protection every 12
months (before the onset of freezing weather, where applicable). If coolant is dirty or rusty in appearance, the system should be drained, flushed and refilled with fresh coolant. Check the front of the A/C condenser for any accumulation of bugs, leaves, etc. If dirty, clean by gently spraying water from a garden hose vertically down the face of the condenser. Check the coolant recovery bottle tubing for brittle rub- ber, cracking, tears, cuts and tightness of the connection at the bottle and radiator. Inspect the entire system for leaks. With the engine at normal operating temperature (but not running), check the cooling system pressure cap for proper vacuum sealing by draining a small amount of coolant from the radiator drain cock. If the cap is sealing properly, the engine coolant (antifreeze) will begin todrain from the coolant recovery bottle. DO NOT RE- MOVE THE COOLANT PRESSURE CAP WHEN THE COOLING SYSTEM IS HOT. Cooling System — Drain, Flush and Refill At the intervals shown on the Maintenance Schedules, the system should be drained, flushed and refilled. If the solution is dirty or contains a considerable amount of sediment, clean and flush with a reliable cooling system cleaner. Follow with a thorough rinsing to remove all deposits and chemicals. Properly dispose of old antifreeze solution. Selection Of Engine Coolant Use only the manufacturers recommended coolant, refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct coolant type.
CAUTION!
Mixing of coolants other than specified HOAT en- gine coolants, may result in engine damage and may decrease corrosion protection. If a non-HOAT cool- ant is introduced into the cooling system in an emergency, it should be replaced with the specified coolant as soon as possible. Do not use plain water alone or alcohol base engine coolant (antifreeze) products. Do not use additional rust inhibitors or antirust products, as they may not be compatible with the radiator engine coolant and may plug the radiator. This vehicle has not been designed for use with Propylene Glycol based coolants. Use of Propylene Glycol based coolants is not recommended.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 385
Adding Engine Coolant Your vehicle has been built with an improved engine coolant that allows extended maintenance intervals. This coolant can be used up to 5 Years or 100,000 miles before replacement. To prevent reducing this extended mainte- nance period, it is important that you use the same coolant throughout the life of your vehicle. Please review these recommendations for using Hybrid Organic Addi- tive Technology (HOAT) coolant. When adding coolant, a minimum solution of 50% rec- ommended Mopar Antifreeze/ Coolant 5 Year / 100,000
Mile Formula HOAT (Hybrid Organic Additive Technol- ogy), or equivalent, in water should be used. Use higher concentrations (not to exceed 70%) if temperatures below ⫺34°F (⫺37°C ) are anticipated. Use only high purity water such as distilled or deionized water when mixing the water/engine coolant solution.386 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
The use of lower quality water will reduce the amount of corrosion protection in the engine cooling system. Please note that it is the owner’s responsibility to main- tain the proper level of protection against freezing ac- cording to the temperatures occurring in the area where the vehicle is operated. NOTE: Mixing coolant types will decrease the life of the engine coolant and will require more frequent coolant changes. Cooling System Pressure Cap The cap must be fully tightened to prevent loss of coolant, and to insure that coolant will return to the radiator from the coolant recovery bottle. The cap should be inspected and cleaned if there is any accumulation of foreign material on the sealing surfaces.
WARNING!
• The warning words “DO NOT OPEN HOT” on the cooling system pressure cap are a safety pre- caution. Never add coolant when the engine is overheated. Do not loosen or remove the cap to cool an overheated engine. Heat causes pressure to build up in the cooling system. To prevent scalding or injury, do not remove the pressure cap while the system is hot or under pressure. • Do not use a pressure cap other than the one specified for your vehicle. Personal injury or engine damage may result.
Disposal of Used Engine Coolant Used ethylene glycol based engine coolant is a regulated substance requiring proper disposal. Check with your local authorities to determine the disposal rules for your community. To prevent ingestion by animals or children
do not store ethylene glycol based engine coolant in open containers or allow it to remain in puddles on the ground. If ingested by a child, contact a physician immediately. Clean up any ground spills immediately. Engine Coolant Level The coolant bottle provides a quick visual method for determining that the coolant level is adequate. With the engine off and cold, the coolant level in the coolant recovery bottle should be between the ranges indicated on the bottle. The radiator normally remains completely full, so there is no need to remove the radiator cap unless checking for coolant freeze point or replacing coolant. Advise your service attendant of this. As long as the engine operating temperature is satisfactory, the coolant bottle need only be checked once a month.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 387
When additional coolant is needed to maintain the proper level, it should be added to the coolant bottle. Do not overfill. Points To Remember NOTE: When the vehicle is stopped after a few miles (a few kilometers) of operation, you may observe vapor coming from the front of the engine compartment. This is normally a result of moisture from rain, snow, or high humidity accumulating on the radiator and being vapor- ized when the thermostat opens, allowing hot coolant to enter the radiator. If an examination of your engine compartment shows no evidence of radiator or hose leaks, the vehicle may be safely driven. The vapor will soon dissipate. • Do not overfill the coolant recovery bottle.
388 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
• Check coolant freeze point in the radiator and in the coolant recovery bottle. If antifreeze needs to be added, contents of coolant recovery bottle must also be protected against freezing. • If frequent coolant additions are required, or if the level in the coolant recovery bottle does not drop when the engine cools, the cooling system should be pres- sure tested for leaks. • Maintain coolant concentration at 50% HOAT engine coolant (minimum) and distilled water for proper corrosion protection of your engine which contains aluminum components. • Make sure that the radiator and coolant recovery bottle overflow hoses are not kinked or obstructed. • Keep the front of the radiator clean. If your vehicle is equipped with air conditioning, keep the front of the condenser clean, also.
• Do not change the thermostat for summer or winter operation. If replacement is ever necessary, install ONLY the correct type thermostat. Other designs may result in unsatisfactory coolant performance, poor gas mileage, and increased emissions.
Hoses And Vacuum/Vapor Harnesses Inspect surfaces of hoses and nylon tubing for evidence of heat and mechanical damage. Hard or soft spots, brittle rubber, cracking, tears, cuts, abrasions, and exces- sive swelling indicate deterioration of the rubber. Pay particular attention to those hoses nearest to high heat sources such as the exhaust manifold. Inspect hose routing to be sure hoses do not come in contact with any heat source or moving component which may cause heat damage or mechanical wear. Insure nylon tubing in these areas has not melted or collapsed.
Inspect all hose connections such as clamps and couplings to make sure they are secure and no leaks are present. Components should be replaced immediately if there is any evidence of wear or damage that could cause failure. Brakes In order to assure brake system performance, all brake system components should be inspected periodically. Suggested service intervals can be found in the Mainte- nance Schedules.
WARNING!
Riding the brakes can lead to brake failure and possibly an accident. Driving with your foot resting or riding on the brake pedal can result in abnormally high brake temperatures, excessive lining wear, and possible brake damage. You wouldn’t have your full braking capacity in an emergency.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 389
Brake And Power Steering Hoses When the vehicle is serviced for scheduled maintenance, inspect surface of hoses and nylon tubing for evidence of heat and mechanical damage. Hard and brittle rubber, cracking, tears, cuts, abrasion, and excessive swelling indicate deterioration of the rubber. Particular attention should be made to examining those hose surfaces nearest to high heat sources, such as the exhaust manifold. Insure nylon tubing in these areas has not melted or collapsed. Inspect all hose connections such as clamps and cou- plings to make sure they are secure and no leaks are present. NOTE: Often, fluid such as oil, power steering fluid, and brake fluid are used during assembly plant opera- tions to facilitate the assembly of hoses to couplings. Therefore, oil wetness at the hose-coupling area is not necessarily an indication of leakage. Actual dripping of
390 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
hot fluid when systems are under pressure (during vehicle operation), should be noted before a hose is replaced based on leakage. Inspection of brake hoses should be performed NOTE: whenever the brake system is serviced and at every engine oil change. Inspect hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing, or worn spots. If there is any evidence of cracking, scuffing, or worn spots, the hose should be replaced immediately! Eventual deterioration of the hose can take place resulting in a possibility of a burst failure.
WARNING!
Worn brake hoses can burst and cause brake failure. You could have an accident. If you see any signs of cracking, scuffing, or worn spots, have the brake hoses replaced immediately.
Master Cylinder — Brake Fluid Level Check The fluid level in the master cylinder should be checked when performing underhood services, or immediately if the brake system warning light indicates system failure. Clean the top of the master cylinder area before removing the cap. Add fluid to bring the level up to the top of the “FULL” mark on the side of the master cylinder reservoir. Overfilling of fluid is not recommended because it may cause leaking in the system. Add enough fluid to bring the level up to the require- ments described on the brake fluid reservoir. With disc brakes, fluid level can be expected to fall as the brake pads wear. However, low fluid level may be caused by a leak and a checkup may be needed. Use only manufacturers recommended brake fluid, refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type.
WARNING!
• Overfilling the brake fluid reservoir can result in spilling brake fluid on hot engine parts and the brake fluid catching fire. • Use of brake fluid that may have a lower initial boiling point or unidentified as to specification, may result in sudden brake failure during hard prolonged braking. You could have an accident.
Use only brake fluid that has been in a tightly closed container to avoid contamination from foreign matter or moisture.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 391
CAUTION!
Do not allow petroleum base fluid to contaminate the brake fluid, all brake seal components could be damaged causing partial or complete brake failure.
Fuel System Hoses Electronic Fuel Injection high pressure fuel systems are designed with hoses and quick connect fittings which have unique material characteristics to provide adequate sealing and resist attack by deteriorated gasoline. You are urged to use only the manufacture specified hoses with quick connect fittings, or their equivalent in material and specification, in any fuel system servicing. It is mandatory to replace any damaged hoses or quick connect fittings that have been removed during service.
392 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Care should be taken in installing quick connect fittings to insure they are properly installed and fully connected. See your authorized dealer for service. Automatic Transmission The automatic transmission and differential assembly are contained within a single housing. All automatic transmissions are equipped with a conven- tional filler tube and dipstick. If fluid is added, it should be added through the dipstick hole in the case. The dipstick is located just behind the radiator, lower right side. Selection of Lubricant It is important that the proper lubricant is used in the transmission to assure optimum transmission perfor- mance. Use only manufacturers recommended transmis- sion fluid, refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts
for correct fluid type. It is important that the transmission fluid be maintained at the prescribed level using the recommended fluid.
CAUTION!
Using a transmission fluid other than the manufac- turers recommended fluid may cause deterioration in transmission shift quality and/or torque converter shudder. Using a transmission fluid other than the manufacturers recommended fluid will result in more frequent fluid and filter changes. Refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 393
3. Fully apply parking brake. 4. Place the gear selector momentarily in each gear position ending with the lever in P (PARK). Wipe the area around the dipstick clean to eliminate the possibility of dirt entering the transmission. 5. Remove the dipstick and determine if the fluid is hot or warm. Hot fluid is approximately 180°F (82°C), which is the normal operating temperature after the vehicle has been driven at least 15 miles (24 km). The fluid cannot be comfortably held between the finger tips. Cold is when the fluid is below 80°F (27°C). 6. Wipe the dipstick clean and reinsert until seated. Remove dipstick and note reading.
a. If the fluid is hot, the reading should be in the crosshatched area marked “HOT” (between the upper two holes in the dipstick).
Procedure For Checking Fluid Level The fluid level in the automatic transmission should be checked whenever the vehicle is serviced. Operation with an improper fluid level will greatly reduce the life of the transmission and of the fluid. To properly check the automatic transmission fluid level, the following procedure must be used: 1. The vehicle must be on level ground. 2. The engine should be running at curb idle speed for a minimum of 60 seconds.
394 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
b. If the fluid is cold, the fluid level should be between the lower two holes in the area marked “COLD”.
If the fluid level indicates low, add sufficient fluid to bring to the proper level.
CAUTION!
Do not overfill. Dirt and water in the transmission can cause serious damage. To prevent dirt and water from entering the transmission after checking or replenishing fluid, make certain that the dipstick cap is reseated properly.
Fluid and Filter Changes Automatic transmission fluid should be changed on all transmissions as follows: Normal Usage — No change necessary
Severe Usage (fluid and filter) — Refer to Maintenance Schedule “B” Severe Usage is defined as: • Police, taxi, limousine, commercial type operation, or trailer towing where the vehicle driven regularly for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation.
NOTE: Refer to Section 8 of this manual for Mainte- nance Schedules. If the transmission is disassembled for any reason, the fluid and filter should be changed. Special Additives Do not add any fluid additives to the transmission. The only exception to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks. The use of transmission sealers should be avoided as they may adversely affect seals.
All Wheel Drive (AWD) — If Equipped Under normal operating conditions, periodic fluid level checks and lubricant changes for the Power Transfer Unit and Rear Carrier, are not required. However when the vehicle is serviced for other reasons, the exterior surface of these components should be inspected for evidence of fluid leaks. Confirmed leaks should be repaired as soon as possible. Power Transfer Unit The fill plug is located on the side of the power transfer unit housing. The fluid should be maintained at a level even with the bottom of the fill plug hole when the vehicle is parked on a level surface. If it becomes neces- sary to add or replace the fluid, use only the manufac- turers recommended fluid, refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 395
Rear Carrier The fill plug is located on the side of the rear carrier housing. The fluid should be maintained at a level even with the bottom of the fill plug hole when the vehicle is parked on a level surface. if it becomes necessary to add or replace the fluid, use only the manufacturers recom- mended fluid, refer to Fluids, Lubricants and Genuine Parts for correct fluid type. Fluid Changes The fluid should be changed as follows: Normal Usage Severe Usage
Power Transfer Unit
Rear Carrier
No Service Required Service Required Refer to Maintenance Schedule “B” Refer to Maintenance Schedule “B”
396 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
Severe Usage is defined as: 1. More than 50% of vehicle operation in stop and go traffic where vehicle is driven regularly for more than 45
minutes of continuous operation, such as in heavy city or in construction zone traffic, 2. Police, taxi, limousine, commercial type operation, or trailer towing where the vehicle driven regularly for more than 45 minutes of continuous operation. NOTE: Refer to Section 8 of this manual for Mainte- nance Schedules. Front And Rear Wheel Bearings Front and rear wheel bearings are permanently sealed. No regular maintenance is required for these compo- nents.Appearance Care and Protection from Corrosion
Protection of Body and Paint from Corrosion Vehicle body care requirements vary according to geo- graphic locations and usage. Chemicals that make roads passable in snow and ice, and those that are sprayed on trees and road surfaces during other seasons, are highly corrosive to the metal in your vehicle. Outside parking, which exposes your vehicle to airborne contaminants, road surfaces on which the vehicle is operated, extreme hot or cold weather and other extreme conditions will have an adverse effect on paint, metal trim, and under- body protection. The following maintenance recommendations will enable you to obtain maximum benefit from the corrosion resistance built into your vehicle. What Causes Corrosion? Corrosion is the result of deterioration or removal of paint and protective coatings from your vehicle.
The most common causes are: • Road salt, dirt and moisture accumulation. • Stone and gravel impact. • Insects, tree sap and tar. • Salt in the air near seacoast localities. • Atmospheric fallout/industrial pollutants. Washing • Wash your vehicle regularly. Always wash your ve- hicle in the shade using Mopar Car Wash or a mild car wash soap, and rinse the panels completely with clear water. • If insects, tar or other similar deposits have accumu- lated on your vehicle, use Mopar Super Kleen Bug and Tar Remover to remove.
MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE 397
• Use Mopar Cleaner Wax to remove road film, stains and to protect your paint finish. Take care never to scratch the paint. • Avoid using abrasive compounds and power buffing that may diminish the gloss or thin out the paint finish.
CAUTION!
Do not use abrasive or strong cleaning materials such as steel wool or scouring powder, which will scratch metal and painted surfaces.
Special Care • If you drive on salted or dusty roads or if you drive near the ocean, hose off the undercarriage at least once a month.
398 MAINTAINING YOUR VEHICLE
• It is important that the drain holes in the lower edges of the doors, rocker panels and trunk be kept clear and open. • If you detect any stone chips or scratches in the paint, touch them up immediately. The cost of such repairs is considered the responsibility of the owner. • If your vehicle is damaged due to an accident or similar cause which destroys the paint and protective coating, have your vehicle repaired as soon as pos- sible. The cost of such repairs is considered the respon- sibility of the owner. • If you carry special cargo such as chemicals, fertilizers, de-icer salt, etc., be sure that such materials are well packaged and sealed. • If a lot of driving is done on gravel roads, consider
mud or stone shields behind each wheel.
• Use Mopar touch up paint on scratches as soon as possible. Your dealer has touch up paint to match the color of your vehicle.
Wheel and Wheel Trim Care All wheels and wheel trim, especially aluminum and chrome plated wheels should be cleaned regularly with a mild soap and water to prevent corrosion. To remove