- 2004 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 2000 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 2001 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 1997 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 2002 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 1998 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 1996 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 1999 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 2005 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- 2003 Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Chevrolet Astro Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
90,000 Miles (150 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j For Two-Wheel-Drive vehicles only: Clean and repack the front wheel
bearings (or at each brake relining, whichever occurs first).
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
(Continued)
7-27
Short Trip/City Scheduled Maintenance
90,000 Miles (150 000 km) (Continued) j Replace fuel filter.
An Emission Control Service. (See footnote [.)
j Replace engine air cleaner filter.
An Emission Control Service.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
93,000 Miles (155 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-28
Short Trip/City Scheduled Maintenance
96,000 Miles (160 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
99,000 Miles (165 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 3 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-29
Short Trip/City Scheduled Maintenance
100,000 Miles (166 000 km) j Inspect spark plug wires.
An Emission Control Service.
j Replace spark plugs.
An Emission Control Service.
j If you haven’t used your vehicle under severe service conditions listed
previously and, therefore, haven’t changed your automatic transmission fluid, change both the fluid and filter.
j Change transfer case fluid. j Inspect Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
An Emission Control Service.
150,000 Miles (240 000 km) j Drain, flush and refill cooling system (or every 60 months since last service, whichever occurs first). See “Engine Coolant” in the Index for what to use. Inspect hoses. Clean radiator, condenser, pressure cap and neck. Pressure test cooling system and pressure cap. An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-30
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
The services shown in this schedule up to 100,000 miles (166 000 km) should be repeated after 100,000 miles (166 000 km) at the same intervals for the life of this vehicle. The services shown at 150,000 miles (240 000 km) should be repeated at the same interval after 150,000 miles (240 000 km) for the life of this vehicle. See “Owner Checks and Services” and “Periodic Maintenance Inspections” following.
Footnotes [ The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency or the California Air Resources Board has determined that the failure to perform this maintenance item will not nullify the emission warranty or limit recall liability prior to the completion of the vehicle’s useful life. We, however, urge that all recommended maintenance services be performed at the indicated intervals and the maintenance be recorded. # Lubricate the front suspension, ball joints and kingpin bushings, steering linkage and transfer case shift linkage, parking brake cable guides, and brake pedal springs. + A good time to check your brakes is during tire rotation. See “Brake System Inspection” under “Periodic Maintenance Inspections” in Part C of this schedule.
7-31
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
7,500 Miles (12 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
15,000 Miles (25 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-32
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
22,500 Miles (37 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-33
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
30,000 Miles (50 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j For Two-Wheel-Drive vehicles only: Clean and repack the front wheel
bearings (or at each brake relining, whichever occurs first).
j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
7-34
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
j Replace fuel filter.
An Emission Control Service. (See footnote [.)
j Replace engine air cleaner filter.
An Emission Control Service.
37,500 Miles (62 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
7-35
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
45,000 Miles (75 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
7-36
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
50,000 Miles (83 000 km) j If you haven’t used your vehicle under severe conditions listed previously and, therefore, haven’t changed your automatic transmission fluid, change both the fluid and filter.
j Change transfer case fluid. 52,500 Miles (87 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
60,000 Miles (100 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
(Continued)
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-37
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
60,000 Miles (100 000 km) (Continued) j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j For Two-Wheel-Drive vehicles only: Clean and repack the front wheel
bearings (or at each brake relining, whichever occurs first).
j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
j Inspect engine accessory drive belt.
An Emission Control Service.
j Replace fuel filter.
An Emission Control Service. (See footnote [.)
j Replace engine air cleaner filter.
An Emission Control Service.
7-38
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
67,500 Miles (112 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
75,000 Miles (125 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
(Continued)
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-39
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
75,000 Miles (125 000 km) (Continued) j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
82,500 Miles (137 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
7-40
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
90,000 Miles (150 000 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j For Two-Wheel-Drive vehicles only: Clean and repack the front wheel
bearings (or at each brake relining, whichever occurs first).
j Change automatic transmission fluid and filter if the vehicle is mainly driven
under one or more of these conditions: – In heavy city traffic where the outside temperature regularly
reaches 90_F (32_C) or higher. – In hilly or mountainous terrain. – When doing frequent trailer towing. – Uses such as found in taxi, police or delivery service. If you do not use your vehicle under any of these conditions, change the fluid and filter every 50,000 miles (83 000 km).
(Continued)
7-41
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
90,000 Miles (150 000 km) (Continued) j Replace fuel filter.
An Emission Control Service. (See footnote [.)
j Replace engine air cleaner filter.
An Emission Control Service.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
97,500 Miles (162 500 km) j Change engine oil and filter (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
An Emission Control Service.
j Lubricate chassis components (or every 12 months, whichever occurs first).
(See footnote #.)
j Check rear/front axle fluid level and add fluid as needed. Check constant
velocity joints and axle seals for leaking.
j Rotate tires. See “Tire Inspection and Rotation” in the Index for proper
rotation pattern and additional information. (See footnote +.)
7-42
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
Long Trip/Highway Scheduled Maintenance
100,000 Miles (166 000 km) j Inspect spark plug wires.
An Emission Control Service.
j Replace spark plugs.
An Emission Control Service.
j If you haven’t used your vehicle under severe service conditions listed
previously and, therefore, haven’t changed your automatic transmission fluid, change both the fluid and filter.
j Change transfer case fluid. j Inspect Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve.
An Emission Control Service.
150,000 Miles (240 000 km) j Drain, flush and refill cooling system (or every 60 months since last service, whichever occurs first). See “Engine Coolant” in the Index for what to use. Inspect hoses. Clean radiator, condenser, pressure cap and neck. Pressure test the cooling system and pressure cap. An Emission Control Service.
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
DATE
ACTUAL MILEAGE
SERVICED BY:
7-43
Part B: Owner Checks and Services Listed in this part are owner checks and services which should be performed at the intervals specified to help ensure the safety, dependability and emission control performance of your vehicle. Be sure any necessary repairs are completed at once. Whenever any fluids or lubricants are added to your vehicle, make sure they are the proper ones, as shown in Part D. At Each Fuel Fill It is important for you or a service station attendant to perform these underhood checks at each fuel fill.
Engine Oil Level Check Check the engine oil level and add the proper oil if necessary. See “Engine Oil” in the Index for further details.
Engine Coolant Level Check Check the engine coolant level and add DEX-COOLR coolant mixture if necessary. See “Engine Coolant” in the Index for further details.
Windshield Washer Fluid Level Check Check the windshield washer fluid level in the windshield washer tank and add the proper fluid if necessary. See “Windshield Washer Fluid” in the Index for further details. At Least Once a Month
Tire Inflation Check Make sure tires are inflated to the correct pressures. Don’t forget to check your spare tire. See “Tires” in the Index for further details. At Least Twice a Year
Restraint System Check Make sure the safety belt reminder light and all your belts, buckles, latch plates, retractors and anchorages are working properly. Look for any other loose or damaged safety belt system parts. If you see anything that might keep a safety belt system from doing its job, have it repaired. Have any torn or frayed safety belts replaced. Also look for any opened or broken air bag coverings, and have them repaired or replaced. (The air bag system does not need regular maintenance.)
7-44
Wiper Blade Check Inspect wiper blades for wear or cracking. Replace blade inserts that appear worn or damaged or that streak or miss areas of the windshield. Also see “Wiper Blades, Cleaning” in the Index.
Spare Tire Check At least twice a year, after the monthly inflation check of the spare tire determines that the spare is inflated to the correct tire inflation pressure, make sure that the spare tire is stored securely. Push, pull, and then try to rotate or turn the tire. If it moves, use the wheel wrench to tighten the cable. See “Storing the Spare Tire and Tools” in the Index.
Weatherstrip Lubrication Silicone grease on weatherstrips will make them last longer, seal better, and not stick or squeak. Apply silicone grease with a clean cloth. During very cold, damp weather more frequent application may be required. See “Recommended Fluids and Lubricants” in the Index.
Automatic Transmission Check Check the transmission fluid level; add if needed. See “Automatic Transmission Fluid” in the Index. A fluid loss may indicate a problem. Check the system and repair if needed. At Least Once a Year
Key Lock Cylinders Service Lubricate the key lock cylinders with the lubricant specified in Part D.
Body Lubrication Service Lubricate all body door hinges, the body hood, fuel door and rear compartment hinges, latches and locks inluding interior glove box and console doors, hood latch assembly, secondary latch, pivots, spring anchor, release pawl and any moving seat hardware. Lubricate the hood safety lever pivot and prop rod pivot. Part D tells you what to use. More frequent lubrication may be required when exposed to a corrosive environment.
7-45
Starter Switch Check
CAUTION:
When you are doing this check, the vehicle could move suddenly. If it does, you or others could be injured. Follow the steps below.
1. Before you start, be sure you have enough room
around the vehicle.
2. Firmly apply both the parking brake and the regular brake. See “Parking Brake” in the Index if necessary. Do not use the accelerator pedal, and be ready to turn off the engine immediately if it starts.
3. Try to start the engine in each gear. The starter
should work only in PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N). If the starter works in any other position, your vehicle needs service.
Automatic Transmission Shift Lock Control System Check
CAUTION:
When you are doing this check, the vehicle could move suddenly. If it does, you or others could be injured. Follow the steps below.
1. Before you start, be sure you have enough
room around the vehicle. It should be parked on a level surface.
2. Firmly apply the parking brake. See “Parking Brake”
in the Index if necessary. Be ready to apply the regular brake immediately if the vehicle begins to move.
3. With the engine off, turn the key to the RUN
position, but don’t start the engine. Without applying the regular brake, try to move the shift lever out of PARK (P) with normal effort. If the shift lever moves out of PARK (P), your vehicle needs service.
7-46
Ignition Transmission Lock Check While parked, and with the parking brake set, try to turn the ignition key to LOCK in each shift lever position. D The key should turn to LOCK only when the shift
lever is in PARK (P).
D The key should come out only in LOCK.
Parking Brake and Automatic Transmission PARK (P) Mechanism Check
CAUTION:
When you are doing this check, your vehicle could begin to move. You or others could be injured and property could be damaged. Make sure there is room in front of your vehicle in case it begins to roll. Be ready to apply the regular brake at once should the vehicle begin to move.
Park on a fairly steep hill, with the vehicle facing downhill. Keeping your foot on the regular brake, set the parking brake. D To check the parking brake’s holding ability: With the engine running and transmission in NEUTRAL (N), slowly remove foot pressure from the regular brake pedal. Do this until the vehicle is held by the parking brake only.
D To check the PARK (P) mechanism’s holding
ability: With the engine running, shift to PARK (P). Then release the parking brake followed by the regular brake.
Underbody Flushing Service At least every spring, use plain water to flush any corrosive materials from the underbody. Take care to clean thoroughly any areas where mud and other debris can collect.
7-47
Part C: Periodic Maintenance Inspections Listed in this part are inspections and services which should be performed at least twice a year (for instance, each spring and fall). You should let your dealer’s service department or other qualified service center do these jobs. Make sure any necessary repairs are completed at once. Proper procedures to perform these services may be found in a service manual. See “Service and Owner Publications” in the Index.
Steering, Suspension and Front Drive Axle Boot and Seal Inspection Inspect the front and rear suspension and steering system for damaged, loose or missing parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect the power steering lines and hoses for proper hook-up, binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Clean and then inspect the drive axle boot seals for damage, tears or leakage. Replace seals if necessary. Exhaust System Inspection Inspect the complete exhaust system. Inspect the body near the exhaust system. Look for broken, damaged, missing or out-of-position parts as well as open seams, holes, loose connections or other conditions which could cause a heat build-up in the floor pan or could let exhaust fumes into the vehicle. See “Engine Exhaust” in the Index.
7-48
Fuel System Inspection Inspect the complete fuel system for damage or leaks. Engine Cooling System Inspection Inspect the hoses and have them replaced if they are cracked, swollen or deteriorated. Inspect all pipes, fittings and clamps; replace as needed. Clean the outside of the radiator and air conditioning condenser. To help ensure proper operation, a pressure test of the cooling system and pressure cap is recommended at least once a year. Throttle System Inspection Inspect the throttle system for interference or binding, and for damaged or missing parts. Replace parts as needed. Replace any components that have high effort or excessive wear. Do not lubricate accelerator and cruise control cables.
Transfer Case and Front Axle (All-Wheel Drive) Inspection Every 12 months or at engine oil change intervals, check front axle and transfer case and add lubricant when necessary. A fluid loss could indicate a problem; check and have it repaired, if needed. Check vent hose at transfer case for kinks and proper installation. Brake System Inspection Inspect the complete system. Inspect brake lines and hoses for proper hook-up, binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect disc brake pads for wear and rotors for surface condition. Also inspect drum brake linings for wear and cracks. Inspect other brake parts, including drums, wheel cylinders, calipers, parking brake, etc. Check parking brake adjustment. You may need to have your brakes inspected more often if your driving habits or conditions result in frequent braking.
7-49
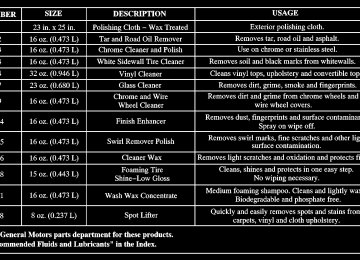
Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants Fluids and lubricants identified below by name, part number or specification may be obtained from your dealer.
USAGE
Engine Oil
Engine Coolant
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Engine oil with the American Petroleum Institute Certified for Gasoline Engines starburst symbol of the proper viscosity. To determine the preferred viscosity for your vehicle’s engine, see “Engine Oil” in the Index.
50/50 mixture of clean, drinkable water and use only GM GoodwrenchR DEX-COOLR or HavolineR DEX-COOLR Coolant. See “Engine Coolant” in the Index.
USAGE
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Hydraulic Brake System
Windshield Washer Solvent
Parking Brake Cable Guides
Power Steering System
Automatic Transmission
Key Lock Cylinders
Delco Supreme 11R Brake Fluid (GM Part No. 12377967 or equivalent DOT-3 brake fluid). GM OptikleenR Washer Solvent (GM Part No. 1051515) or equivalent.
Chassis Lubricant (GM Part No. 12377985 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB.
GM Power Steering Fluid (GM Part No. 1052884 - 1 pint, 1050017 - 1 quart, or equivalent). DEXRONR-III Automatic Transmission Fluid.
Multi-Purpose Lubricant, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12346241 or equivalent).
7-50
USAGE
Chassis Lubrication
Front Wheel Bearings
Front Axle
Rear Axle
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Chassis Lubricant (GM Part No. 12377985 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB.
Wheel bearing lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category GC or GC-LB (GM Part No. 1051344 or equivalent). SAE 80W-90 Axle Lubricant (GM Part No. 1052271 or equivalent). SAE 75W-90 Synthetic Axle Lubricant (GM Part No. 12378261) or equivalent meeting GM Specification 9986115.
USAGE
Transfer Case
FLUID/LUBRICANT AUTO-TRAK II Fluid (GM Part No. 12378508).
Hood Latch Assembly, Secondary Latch, Pivots, Spring Anchor and Release Pawl
Hood and Door Hinges
Weatherstrip Conditioning
LubriplateR Lubricant Aerosol (GM Part No. 12346293 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB.
Multi-Purpose Lubricant, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12346241 or equivalent).
Dielectric Silicone Grease (GM Part No. 12345579 or equivalent).
7-51
Part E: Maintenance Record After the scheduled services are performed, record the date, odometer reading and who performed the service in the boxes provided after the maintenance interval. Any additional information from “Owner Checks and Services” or “Periodic Maintenance” can be added on the following record pages. Also, you should retain all maintenance receipts. Your owner information portfolio is a convenient place to store them.
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-52
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-53
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-54
Section 8 Customer Assistance Information
Here you will find out how to contact Chevrolet if you need assistance. This section also tells you how to obtain service publications and how to report any safety defects.
8-2
8-48-4
8-58-6
8-8Customer Satisfaction Procedure Customer Assistance for Text Telephone (TTY) Users Customer Assistance Offices GM Mobility Program for Persons with Disabilities Chevrolet Roadside Assistance Program Canadian Roadside Assistance
8-8
8-10
8-108-11
8-11
Courtesy Transportation Warranty Information Reporting Safety Defects to the United States Government Reporting Safety Defects to the Canadian Government Reporting Safety Defects to General Motors
8-
8-1
Customer Satisfaction Procedure
Your satisfaction and goodwill are important to your dealer and to Chevrolet. Normally, any concerns with the sales transaction or the operation of your vehicle will be resolved by your dealer’s sales or service departments. Sometimes, however, despite the best intentions of all concerned, misunderstandings can occur. If your concern has not been resolved to your satisfaction, the following steps should be taken: STEP ONE -- Discuss your concern with a member of dealership management. Normally, concerns can be quickly resolved at that level. If the matter has already been reviewed with the sales, service or parts manager, contact the owner of the dealership or the general manager.
8-2
STEP TWO -- If after contacting a member of dealership management, it appears your concern cannot be resolved by the dealership without further help, contact the Chevrolet Customer Assistance Center by calling 1-800-222-1020. In Canada, contact GM of Canada Customer Communication Centre in Oshawa by calling 1-800-263-3777 (English) or 1-800-263-7854 (French). We encourage you to call the toll-free number in order to give your inquiry prompt attention. Please have the following information available to give the Customer Assistance Representative: D Vehicle Identification Number (This is available from the vehicle registration or title, or the plate at the top left of the instrument panel and visible through the windshield.)
D Dealership name and location D Vehicle delivery date and present mileage When contacting Chevrolet, please remember that your concern will likely be resolved at a dealer’s facility. That is why we suggest you follow Step One first if you have a concern.
STEP THREE -- Both General Motors and your dealer are committed to making sure you are completely satisfied with your new vehicle. However, if you continue to remain unsatisfied after following the procedure outlined in Steps One and Two, you should file with the GM/BBB Auto Line Program to enforce any additional rights you may have. Canadian owners refer to your Warranty and Owner Assistance Information booklet for information on the Canadian Motor Vehicle Arbitration Plan (CAMVAP). The BBB Auto Line Program is an out of court program administered by the Council of Better Business Bureaus to settle automotive disputes regarding vehicle repairs or the interpretation of the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. Although you may be required to resort to this informal dispute resolution program prior to filing a court action, use of the program is free of charge and your case will generally be heard within 40 days. If you do not agree with the decision given in your case, you may reject it and proceed with any other venue for relief available to you.
8-3
Customer Assistance Offices Chevrolet encourages customers to call the toll-free number for assistance. If a U.S. customer wishes to write to Chevrolet, the letter should be addressed to Chevrolet’s Customer Assistance Center. United States
Chevrolet Motor Division Chevrolet Customer Assistance Center P.O. Box 33170
Detroit, MI 48232-5170
1-800-222-1020
1-800-833-2438 (For Text Telephone devices (TTYs)) Roadside Assistance: 1-800-CHEV-USAR (243-8872) From: Puerto Rico:1-800-496-9992 (English) 1-800-496-9993 (Spanish) 1-800-496-9994
U.S. Virgin Islands:
Fax Number: 313-381-0022
You may contact the BBB using the toll-free telephone number or write them at the following address:
BBB Auto Line Council of Better Business Bureaus, Inc. 4200 Wilson Boulevard Suite 800
Arlington, VA 22203-1804
Telephone: 1-800-955-5100This program is available in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Eligibility is limited by vehicle age, mileage and other factors. General Motors reserves the right to change eligibility limitations and/or discontinue its participation in this program. Customer Assistance for Text Telephone (TTY) Users To assist customers who are deaf, hard of hearing, or speech-impaired and who use Text Telephones (TTYs), Chevrolet has TTY equipment available at its Customer Assistance Center. Any TTY user can communicate with Chevrolet by dialing: 1-800-833-CHEV (2438). (TTY users in Canada can dial 1-800-263-3830.)
8-4
Canada
General Motors of Canada Limited Customer Communication Centre, 163-005
1908 Colonel Sam Drive Oshawa, Ontario L1H 8P7
1-800-263-3777 (English) 1-800-263-7854 (French) 1-800-263-3830 (For Text Telephone devices (TTYs)) Roadside Assistance: 1-800-268-6800All Overseas Locations Please contact the local General Motors Business Unit. Mexico, Central America and Caribbean Islands/Countries (Except Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands)
General Motors de Mexico, S. de R.L. de C.V. Customer Assistance Center Paseo de la Reforma # 2740
Col. Lomas de Bezares C.P. 11910, Mexico, D.F. 01-800-508-0000
Long Distance: 011-52 - 53 29 0 800GM Mobility Program for Persons with Disabilities
This program, available to qualified applicants, can reimburse you up to $1,000
toward aftermarket driver or passenger adaptive equipment you may require for your vehicle (hand controls, wheelchair/scooter lifts, etc.).This program can also provide you with free resource information, such as area driver assessment centers and mobility equipment installers. The program is available for a limited period of time from the date of vehicle purchase/lease. See your dealer for more details or call the GM Mobility Assistance Center at 1-800-323-9935. Text telephone (TTY) users, call 1-800-833-9935. GM of Canada also has a Mobility Program. Call 1-800-GM-DRIVE (463-7483) for details. When calling from outside Canada, please dial 1-905-644-3063. All TTY users call 1-800-263-3830.
8-5
Roadside Assistance is available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, by calling 1-800-CHEV-USA (243-8872). This toll-free number will provide you over-the-phone roadside assistance with minor mechanical problems. If your problem cannot be resolved over the phone, our advisors have access to a nationwide network of dealer recommended service providers. Roadside membership is free; however some services may incur costs. Roadside offers two levels of service to the customer, Basic Care and Courtesy Care: Roadside Basic Care provides: D Toll-free number, 1-800-CHEV-USA (243-8872), text telephone (TTY) users, call 1-888-889-2438
D Free towing for warranty repairs D Basic over-the-phone technical advice D Available dealer services at reasonable costs (i.e., wrecker services, locksmith/key service, glass repair, etc.)
Chevrolet Roadside Assistance Program
To enhance Chevrolet’s strong commitment to customer satisfaction, Chevrolet is excited to announce the establishment of the Chevrolet Roadside Assistance Center. As the owner of a 2002 Chevrolet, membership in Roadside Assistance is free.
8-6
Roadside Courtesy Care provides: D Roadside Basic Care services (as outlined previously)
Plus:
D FREE Non-Warranty Towing (to the closest dealer
from a legal roadway)
D FREE Locksmith/Key Service (when keys are lost
on the road or locked inside)
D FREE Flat Tire Service (spare installed on the road) D FREE Jump Start (at home or on the road) D FREE Fuel Delivery ($5 of fuel delivered on the road) Chevrolet offers Courtesy Transportation for customers needing warranty service. Courtesy Transportation will be offered in conjunction with the coverage provided by the Bumper-to-Bumper New Vehicle Limited Warranty to eligible purchasers of 2002 Chevrolet passenger cars and light duty trucks. (Please see your selling dealer for details.)
Courtesy Care is available to retail and retail lease customers operating 2002 and newer Chevrolet vehicles for a period of 3 years/36,000 miles (60 000 km), whichever occurs first. All Courtesy Care services must be pre-arranged by Chevrolet Roadside or dealer service management. Basic Care and Courtesy Care are not part of or included in the coverage provided by the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. Chevrolet reserves the right to modify or discontinue Basic Care and Courtesy Care at any time. The Roadside Assistance Center uses companies that will provide you with quality and priority service. When roadside services are required, our advisors will explain any payment obligations that may be incurred for utilizing outside services.
8-7
For prompt assistance when calling, please have the following available to give to the advisor: D Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) D License plate number D Vehicle color D Vehicle location D Telephone number where you can be reached D Vehicle mileage D Description of problem Canadian Roadside Assistance Vehicles purchased in Canada have an extensive Roadside Assistance program accessible from anywhere in Canada or the United States. Please refer to the Warranty and Owner Assistance Information book or call 1-800-268-6800 for emergency services.
Courtesy Transportation Chevrolet has always exemplified quality and value in its offering of motor vehicles. To enhance your ownership experience, we and our participating dealers are proud to offer Courtesy Transportation, a customer support program for new vehicles. The Courtesy Transportation program is offered to retail purchase/lease customers in conjunction with the Bumper-to-Bumper coverage provided by the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. Several transportation options are available when warranty repairs are required. This will reduce your inconvenience during warranty repairs. Plan Ahead When Possible When your vehicle requires warranty service, you should contact your dealer and request an appointment. By scheduling a service appointment and advising your service consultant of your transportation needs, your dealer can help minimize your inconvenience. If your vehicle cannot be scheduled into the service department immediately, keep driving it until it can be scheduled for service, unless, of course, the problem is safety-related. If it is, please call your dealership, let them know this, and ask for instructions.
8-8
If the dealer requests that you simply drop the vehicle off for service, you are urged to do so as early in the work day as possible to allow for same day repair. Transportation Options Warranty service can generally be completed while you wait. However, if you are unable to wait Chevrolet helps minimize your inconvenience by providing several transportation options. Depending on the circumstances, your dealer can offer you one of the following:
Shuttle Service Participating dealers can provide you with shuttle service to get you to your destination with minimal interruption of your daily schedule. This includes a one way shuttle ride to a destination up to 10 miles from the dealership.
Public Transportation or Fuel Reimbursement If your vehicle requires overnight warranty repairs, reimbursement up to $30 per day (five days maximum) may be available for the use of public transportation such as taxi or bus. In addition, should you arrange transportation through a friend or relative, reimbursement for reasonable fuel expenses up to $10 per day (five day maximum) may be available. Claim amounts should reflect actual costs and be supported by original receipts.
Courtesy Rental Vehicle When your vehicle is unavailable due to overnight warranty repairs, your dealer may arrange to provide you with a courtesy rental vehicle or reimburse you for a rental vehicle you obtained, at actual cost, up to a maximum of $30.00 per day supported by receipts. This requires that you sign and complete a rental agreement and meet state, local and rental vehicle provider requirements. Requirements vary and may include minimum age requirements, insurance coverage, credit card, etc. You are responsible for fuel usage charges and may also be responsible for taxes, levies, usage fees, excessive mileage or rental usage beyond the completion of the repair. Generally it is not possible to provide a like-vehicle as a courtesy rental. Additional Program Information Courtesy Transportation is available during the Bumper-to-Bumper warranty coverage period, but it is not part of the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. A separate booklet entitled “Warranty and Owner Assistance Information” furnished with each new vehicle provides detailed warranty coverage information.
8-9
Courtesy Transportation is available only at participating dealers and all program options, such as shuttle service, may not be available at every dealer. Please contact your dealer for specific information about availability. All Courtesy Transportation arrangements will be administered by appropriate dealer personnel. Canadian Vehicles: For warranty repairs during the Complete Vehicle Coverage period of the General Motors of Canada New Vehicle Limited Warranty, alternative transportation may be available under the Courtesy Transportation Program. Please consult your dealer for details. General Motors reserves the right to unilaterally modify, change or discontinue Courtesy Transportation at any time and to resolve all questions of claim eligibility pursuant to the terms and conditions described herein at its sole discretion. Warranty Information Your vehicle comes with a separate warranty booklet that contains detailed warranty information.
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS TO THE UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT If you believe that your vehicle has a defect which could cause a crash or could cause injury or death, you should immediately inform the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), in addition to notifying General Motors. If NHTSA receives similar complaints, it may open an investigation, and if it finds that a safety defect exists in a group of vehicles, it may order a recall and remedy campaign. However, NHTSA cannot become involved in individual problems between you, your dealer or General Motors. To contact NHTSA, you may either call the Auto Safety Hotline toll-free at 1-800-424-9393 (or 366-0123 in the Washington, D.C. area) or write to:
NHTSA, U.S. Department of Transportation Washington, D.C. 20590
You can also obtain other information about motor vehicle safety from the hotline.
8-10
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS TO THE CANADIAN GOVERNMENT If you live in Canada, and you believe that your vehicle has a safety defect, you should immediately notify Transport Canada, in addition to notifying General Motors of Canada Limited. You may write to:
Transport Canada 330 Sparks Street Tower C Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0N5
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS TO GENERAL MOTORS In addition to notifying NHTSA (or Transport Canada) in a situation like this, we certainly hope you’ll notify us. Please call us at 1-800-222-1020, or write:
Chevrolet Motor Division Chevrolet Customer Assistance Center P.O. Box 33170
Detroit, MI 48232-5170In Canada, please call us at 1-800-263-3777 (English) or 1-800-263-7854 (French). Or, write: General Motors of Canada Limited Customer Communication Centre, 163-005
1908 Colonel Sam Drive Oshawa, Ontario L1H 8P78-11
SERVICE PUBLICATIONS ORDERING INFORMATION
Service Manuals Service Manuals have the diagnosis and repair information on engines, transmission, axle, suspension, brakes, electrical, steering, body, etc. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $120.00
Transmission, Transaxle, Transfer Case Unit Repair Manual This manual provides information on unit repair service procedures, adjustments and specifications for GM transmissions, transaxles and transfer cases. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $50.00
Service Bulletins Service Bulletins give technical service information needed to knowledgeably service General Motors cars and trucks. Each bulletin contains instructions to assist in the diagnosis and service of your vehicle.Owner’s Information Owner publications are written specifically for owners and intended to provide basic operational information about the vehicle. The owner’s manual will include the Maintenance Schedule for all models. In-Portfolio: Includes a Portfolio, Owner’s Manual and Warranty Booklet. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $35.00
Without Portfolio: Owner’s Manual only. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $25.00
Current and Past Model Order Forms Service Publications are available for current and past model GM vehicles. To request an order form, please specify year and model name of the vehicle.ORDER TOLL FREE: 1-800-551-4123 – Monday-Friday 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM Eastern Time
Visit Helm, Inc. on the World Wide Web at: www.helminc.com
For Credit Card Orders Only (VISA-MasterCard-Discover)
Helm, Incorporated S P.O. Box 07130 S Detroit, MI 48207
Prices are subject to change without notice and without incurring obligation. Allow ample time for delivery.
Note to Canadian Customers: All listed prices are quoted in U.S. funds. Canadian residents are to make checks payable in U.S. funds.
8-12
2002 Chevrolet Astro
Owner’s Manual
Litho in U.S.A. Part Number C2210 A First Edition
ECopyright General Motors Corporation 6/27/01
All Rights ReservedWe support voluntary technician certification.
For Canadian Owners Who Prefer a French Language Manual: Aux propriétaires canadiens: Vous pouvez vous procurer un exemplaire de ce guide en français chez votre concessionaire ou au:
Helm, Incorporated P.O. Box 07130
Detroit, MI 48207GENERAL MOTORS, GM, the GM Emblem, CHEVROLET, the CHEVROLET Emblem and the name ASTRO are registered trademarks of General Motors Corporation. This manual includes the latest information at the time it was printed. We reserve the right to make changes after that time without further notice. For vehicles first sold in Canada, substitute the name “General Motors of Canada Limited” for Chevrolet Motor Division whenever it appears in this manual. Please keep this manual in your vehicle, so it will be there if you ever need it when you’re on the road. If you sell the vehicle, please leave this manual in it so the new owner can use it.
ii
How to Use this Manual Many people read their owner’s manual from beginning to end when they first receive their new vehicle. If you do this, it will help you learn about the features and controls for your vehicle. In this manual, you’ll find that pictures and words work together to explain things quickly.
Safety Warnings and Symbols You will find a number of safety cautions in this book. We use a box and the word CAUTION to tell you about things that could hurt you if you were to ignore the warning.
CAUTION:
These mean there is something that could hurt you or other people.
In the caution area, we tell you what the hazard is. Then we tell you what to do to help avoid or reduce the hazard. Please read these cautions. If you don’t, you or others could be hurt.
You will also find a circle with a slash through it in this book. This safety symbol means “Don’t,” “Don’t do this” or “Don’t let this happen.”
iii
Vehicle Damage Warnings Also, in this book you will find these notices:
NOTICE:
These mean there is something that could damage your vehicle.
In the notice area, we tell you about something that can damage your vehicle. Many times, this damage would not be covered by your warranty, and it could be costly. But the notice will tell you what to do to help avoid the damage. When you read other manuals, you might see CAUTION and NOTICE warnings in different colors or in different words. You’ll also see warning labels on your vehicle. They use the same words, CAUTION or NOTICE.
Vehicle Symbols Your vehicle may be equipped with components and labels that use symbols instead of text. Symbols, used on your vehicle, are shown along with the text describing the operation or information relating to a specific component, control, message, gage or indicator. If you need help figuring out a specific name of a component, gage or indicator reference the following topics in the Index: D “Engine Compartment Overview” D “Instrument Panel” D “Comfort Controls” D “Audio Systems” Also see “Warning Lights and Gages” in the Index.
iv
These are some examples of vehicle symbols you may find on your vehicle:
Model Reference This manual covers these models:
Cargo Van
Passenger Van
vi
Section 1 Seats and Restraint Systems
Here you’ll find information about the seats in your vehicle and how to use your safety belts properly. You can also learn about some things you should not do with air bags and safety belts.
1-2
1-13
1-171-18
1-18
1-26
1-27
1-27
1-34Seats and Seat Controls Safety Belts: They’re for Everyone Here Are Questions Many People Ask About Safety Belts -- and the Answers How to Wear Safety Belts Properly Driver Position Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy Right Front Passenger Position Air Bag System Rear Seat Passengers
1-38
1-40
1-42
1-48
1-62
1-65
1-65
1-66Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for Children and Small Adults Center Passenger Position (Bench Seat) Children Restraint Systems for Children Older Children Safety Belt Extender Checking Your Restraint Systems Replacing Restraint System Parts After a Crash
1-
1-1
Seats and Seat Controls This section tells you about the seats -- how to adjust them, take them out and put them back in. It also tells you about bucket and bench seats, power seats and head restraints. Manual Front Seats
CAUTION:
You can lose control of the vehicle if you try to adjust a manual driver’s seat while the vehicle is moving. The sudden movement could startle and confuse you, or make you push a pedal when you don’t want to. Adjust the driver’s seat only when the vehicle is not moving.
Two-Way Front Seat
The bucket seats can be adjusted forward or rearward using the lever located under the front of the seat.
Move the seat adjustment lever located under the front of the seat toward the outboard side of the seat to unlock it. Slide the seat to where you want it. Then release the lever and try to move the seat with your body, to make sure that the seat is locked into place.
1-2
Manual Lumbar Support (If Equipped)
Power Seat (If Equipped) If your vehicle has this feature, there will be a control pad located on the inboard side of the driver’s seat.
If your vehicle has this feature, there will be a knob located on the inboard side of the driver’s and passenger’s bucket seats. Turn the knob toward the front of the vehicle to increase lumbar support. Turn the knob toward the rear of the vehicle to decrease lumbar support.
To raise or lower the front of the seat cushion, raise or lower the lever located toward the front of the vehicle. To raise or lower the rear of the seat cushion, raise or lower the lever located toward the rear of the vehicle. To move the entire seat backwards, forward, or up or down, move the center knob.
1-3
Reclining Seatbacks There is a lever located on the inside of the seat to adjust the seatback.
You can adjust the seatback by lifting the lever and leaning back. Release the lever to lock the seatback where you want it. Pull up on the lever, lean forward and the seatback will go to an upright position.
1-4
But don’t have a seatback reclined if your vehicle is moving.
CAUTION:
Sitting in a reclined position when your vehicle is in motion can be dangerous. Even if you buckle up, your safety belts can’t do their job when you’re reclined like this. The shoulder belt can’t do its job because it won’t be against your body. Instead, it will be in front of you. In a crash you could go into it, receiving neck or other injuries. The lap belt can’t do its job either. In a crash the belt could go up over your abdomen. The belt forces would be there, not at your pelvic bones. This could cause serious internal injuries. For proper protection when the vehicle is in motion, have the seatback upright. Then sit well back in the seat and wear your safety belt properly.
Head Restraints
Head restraints are fixed on some models and adjustable on others. Adjust your head restraint so that the top of the restraint is closest to the top of your head. This position reduces the chance of a neck injury in a crash.
1-5
After the latch has been released, push the seatback toward the front of the vehicle until it locks into place. To raise the seatback, unlock the seatback latch by pushing up on the lever while pushing down on the upper edge of the seatback. Move the seatback into the upright position. Make sure the seatback is locked when it is back in the upright position.
CAUTION:
If the seatback isn’t locked, it could move forward in a sudden stop or crash. That could cause injury to the person sitting there. Always press rearward on the seatback to be sure it is locked.
Seatback Latches
The seatback lever is located on the right rear of your seat.
To fold your non-touring bench seatback forward, pull up on the latch release lever while pulling the seatback toward the rear of the vehicle.
1-6
Rear Seats Bucket Seats (If Equipped)
Bench Seats Each bench seat can carry up to three passengers. They can also be removed to increase storage space. The center bench and rear bench seats can be adjusted forward or rearward using the lever at the front of the seat.
Move the seat adjustment lever located at the front of the seat toward the passenger’s side to unlock it. Slide the seat to where you want it. Then release the lever and try to move the seat with your body, to make sure the seat is locked into place.
Your vehicle may have rear bucket seats with an adjustment release bar located under the front of the seats. These seats can be adjusted forward or rearward with the release bar. Pull the release bar up to release the seat bottom. Slide the seat where you want it and then let go of the release bar. Then try to move the seat with your body to make sure the seat is locked into place.
The center bench seat has a pivoting right armrest. The optional bench seats come with moveable armrests, individual reclining seatbacks, adjustable headrests and a fold-down center armrest console.
1-7
To raise or lower the center console, press the button located between the beverage holders. Sit in the center seating position only when the console is in an upright and locked position.
To adjust your seatback, pull up on the lever located on the outboard side of the seat cushion.
For details about headrests, see “Head Restraints” in this section.
1-8
Removing the Rear Seats To remove the rear seats, do the following:
1. If you are removing the center seat, remove the right lap-shoulder belt. To do this, press the tip of a key into the release hole of the safety belt attachment while pulling up on the safety belt.
2. If you have a safety
belt guide on your seat, pull the safety belt all the way out through the guide.
3. To store the safety belt while the second row bench
seat is removed, pull the belt out and put both buckles in the passenger’s side rear storage bin. Route the belt out of the forward edge of the storage bin. Close the cover to retain the belt.
4. Pull up on the seatback latch on the right rear of the
seat. Push the seatback down until it locks into place.
1-9
5. Lift up on the left and the right seat release levers at the same time. The latches are near the floor on the rear legs of the seat.
6. Lift up on the rear of the seat to remove the seat
assembly from the rear latch pins. Then, pull back and lift the seat out of the vehicle. Your seat release latch lever is operated with a two-stage mechanism. To fully release the latch, two levels of lift effort will be required. First, a low effort to overcome the first stage and then a moderate effort to fully release the latch.
1-10
Replacing the Rear Seats
1. Lower the seat into position. Make sure the front
retainers are hooked onto the anchor pins.
2. Pull the seat down to latch the rear retainers. Make sure the seat is locked in by pulling up and down on the seat.
CAUTION:
A seat that isn’t locked into place properly can move around in a collision or sudden stop. People in the vehicle could be injured. Be sure to lock the seat into place properly when installing it.
1-11
3. To raise the seatback, do the following:
A. Unlock the seatback latch by pushing up on the latch release lever at the right rear of the seat, while pushing down on the upper edge of the seatback.
B. Move the seatback into the upright position. Make sure the seatback is locked when it is back in the upright position.
If you are replacing the center seat, connect the right lap-shoulder belt to the attachment on the seat cushion. If you have a safety belt guide on your seat, pull the belt through the guide before reattaching the lap-shoulder belt to the side of the seat. The release hole should be facing outward.
If you installed the safety belt with the release hole facing inward (toward the seat), slide the plastic cover up so you can see the buckle. Disconnect the seat belt. Slide the cover back down and reinstall the belt correctly.
CAUTION:
A safety belt that is improperly routed, not properly attached, or twisted won’t provide the protection needed in a crash. The person wearing the belt could be seriously injured. After installing the seat, always check to be sure that the safety belts are properly routed and attached, and are not twisted.
1-12
Safety Belts: They’re for Everyone This part of the manual tells you how to use safety belts properly. It also tells you some things you should not do with safety belts. And it explains the air bag system.
CAUTION:
Don’t let anyone ride where he or she can’t wear a safety belt properly. If you are in a crash and you’re not wearing a safety belt, your injuries can be much worse. You can hit things inside the vehicle or be ejected from it. You can be seriously injured or killed. In the same crash, you might not be if you are buckled up. Always fasten your safety belt, and check that your passengers’ belts are fastened properly too.
CAUTION:
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in these areas are more likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not allow people to ride in any area of your vehicle that is not equipped with seats and safety belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and using a safety belt properly.
Your vehicle has a light that comes on as a reminder to buckle up. See “Safety Belt Reminder Light” in the Index.
1-13
Why Safety Belts Work When you ride in or on anything, you go as fast as it goes.
In most states and Canadian provinces, the law says to wear safety belts. Here’s why: They work. You never know if you’ll be in a crash. If you do have a crash, you don’t know if it will be a bad one. A few crashes are mild, and some crashes can be so serious that even buckled up a person wouldn’t survive. But most crashes are in between. In many of them, people who buckle up can survive and sometimes walk away. Without belts they could have been badly hurt or killed. After more than 30 years of safety belts in vehicles, the facts are clear. In most crashes buckling up does matter ... a lot!
Take the simplest vehicle. Suppose it’s just a seat on wheels.
1-14
Put someone on it.
Get it up to speed. Then stop the vehicle. The rider doesn’t stop.
1-15
The person keeps going until stopped by something. In a real vehicle, it could be the windshield ...
or the instrument panel ...
1-16
Here Are Questions Many People Ask About Safety Belts -- and the Answers Q: Won’t I be trapped in the vehicle after an
accident if I’m wearing a safety belt?
A: You could be -- whether you’re wearing a
safety belt or not. But you can unbuckle a safety belt, even if you’re upside down. And your chance of being conscious during and after an accident, so you can unbuckle and get out, is much greater if you are belted.
Q: If my vehicle has air bags, why should I have
to wear safety belts?
A: Air bags are in many vehicles today and will be in most of them in the future. But they are supplemental systems only; so they work with safety belts -- not instead of them. Every air bag system ever offered for sale has required the use of safety belts. Even if you’re in a vehicle that has air bags, you still have to buckle up to get the most protection. That’s true not only in frontal collisions, but especially in side and other collisions.
1-17
or the safety belts! With safety belts, you slow down as the vehicle does. You get more time to stop. You stop over more distance, and your strongest bones take the forces. That’s why safety belts make such good sense.
Q: If I’m a good driver, and I never drive far from
home, why should I wear safety belts?
A: You may be an excellent driver, but if you’re in
an accident -- even one that isn’t your fault -- you and your passengers can be hurt. Being a good driver doesn’t protect you from things beyond your control, such as bad drivers.
Most accidents occur within 25 miles (40 km) of home. And the greatest number of serious injuries and deaths occur at speeds of less than 40 mph (65 km/h). Safety belts are for everyone.
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly Adults This part is only for people of adult size. Be aware that there are special things to know about safety belts and children. And there are different rules for smaller children and babies. If a child will be riding in your vehicle, see the part of this manual called “Children.” Follow those rules for everyone’s protection. First, you’ll want to know which restraint systems your vehicle has. We’ll start with the driver position. Driver Position This part describes the driver’s restraint system. Lap-Shoulder Belt The driver has a lap-shoulder belt. Here’s how to wear it properly. 1. Close and lock the door. 2. Adjust the seat so you can sit up straight.
To see how, see “Seats” in the Index.
1-18
3. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Don’t let it get twisted.
4. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure. If the belt isn’t long enough, see “Safety Belt Extender” at the end of this section. Make sure the release button on the buckle is positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on the hips, just touching the thighs. In a crash, this applies force to the strong pelvic bones. And you’d be less likely to slide under the lap belt. If you slid under it, the belt would apply force at your abdomen. This could cause serious or even fatal injuries. The shoulder belt should go over the shoulder and across the chest. These parts of the body are best able to take belt restraining forces. The safety belt locks if there’s a sudden stop or a crash.
1-19
Shoulder Belt Height Adjuster Before you begin to drive, move the shoulder belt adjuster to the height that is right for you.
To move it down, push it in at the top of the arrows and move the height adjuster to the desired position. You can move the adjuster up just by pushing up on the shoulder belt guide. After you move the adjuster to where you want it, try to move it down without pushing in to make sure it has locked into position. Adjust the height so that the shoulder portion of the belt is centered on your shoulder. The belt should be away from your face and neck, but not falling off your shoulder.
1-20
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously hurt if your shoulder belt is too loose. In a crash, you would move forward too much, which could increase injury. The shoulder belt should fit against your body.
A: The shoulder belt is too loose. It won’t give nearly
as much protection this way.
1-21
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if your belt is buckled in the wrong place like this. In a crash, the belt would go up over your abdomen. The belt forces would be there, not at the pelvic bones. This could cause serious internal injuries. Always buckle your belt into the buckle nearest you.
A: The belt is buckled in the wrong place.
1-22
Q: What’s wrong with this?
A: The belt is over an armrest.
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if your belt goes over an armrest like this. The belt would be much too high. In a crash, you can slide under the belt. The belt force would then be applied at the abdomen, not at the pelvic bones, and that could cause serious or fatal injuries. Be sure the belt goes under the armrests.
1-23
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if you wear the shoulder belt under your arm. In a crash, your body would move too far forward, which would increase the chance of head and neck injury. Also, the belt would apply too much force to the ribs, which aren’t as strong as shoulder bones. You could also severely injure internal organs like your liver or spleen.
A: The shoulder belt is worn under the arm. It should
be worn over the shoulder at all times.
1-24
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured by a twisted belt. In a crash, you wouldn’t have the full width of the belt to spread impact forces. If a belt is twisted, make it straight so it can work properly, or ask your dealer to fix it.
A: The belt is twisted across the body.
1-25
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy Safety belts work for everyone, including pregnant women. Like all occupants, they are more likely to be seriously injured if they don’t wear safety belts.
To unlatch the belt, just push the button on the buckle. The belt should go back out of the way. Before you close the door, be sure the belt is out of the way. If you slam the door on it, you can damage both the belt and your vehicle.
1-26
A pregnant woman should wear a lap-shoulder belt, and the lap portion should be worn as low as possible, below the rounding, throughout the pregnancy.
The best way to protect the fetus is to protect the mother. When a safety belt is worn properly, it’s more likely that the fetus won’t be hurt in a crash. For pregnant women, as for anyone, the key to making safety belts effective is wearing them properly. Right Front Passenger Position To learn how to wear the right front passenger’s safety belt properly, see “Driver Position” earlier in this section. The right front passenger’s safety belt works the same way as the driver’s safety belt -- except for one thing. If you ever pull the lap portion of the belt out all the way, you will engage the child restraint locking feature. If this happens, just let the belt go back all the way and start again. Air Bag System This part explains the air bag system. Your vehicle has air bags -- one air bag for the driver and another air bag for the right front passenger. Frontal air bags are designed to help reduce the risk of injury from the force of an inflating air bag. But these air bags must inflate very quickly to do their job and comply with federal regulations.
Here are the most important things to know about the air bag system:
CAUTION:
You can be severely injured or killed in a crash if you aren’t wearing your safety belt -- even if you have air bags. Wearing your safety belt during a crash helps reduce your chance of hitting things inside the vehicle or being ejected from it. Air bags are designed to work with safety belts, but don’t replace them. Air bags are designed to work only in moderate to severe crashes where the front of your vehicle hits something. They aren’t designed to inflate at all in rollover, rear or low-speed frontal crashes, or in many side crashes. And, for some unrestrained occupants, air bags may provide less protection in frontal crashes than more forceful air bags have provided in the past. Everyone in your vehicle should wear a safety belt properly -- whether or not there’s an air bag for that person.
1-27
CAUTION: