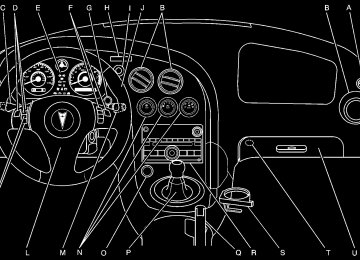
- Download PDF Manual
-
on page 5-80.
H. Engine Oil Fill Cap. See “When to Add Engine Oil”
under Engine Oil on page 5-13.
I. Battery (Out of View). See Battery on page 5-34. J. Engine Oil Dipstick (Out of View). See “Checking
Engine Oil” under Engine Oil on page 5-13.
K. Windshield Washer Fluid Reservoir. See “Adding
Washer Fluid” under Windshield Washer Fluid on page 5-30.
Engine Oil Checking Engine Oil It is a good idea to check your engine oil every time you get fuel. In order to get an accurate reading, the oil must be warm and the vehicle must be on level ground. The engine oil dipstick handle is a yellow loop. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for the location of the engine oil dipstick. 1. Turn off the engine and give the oil several minutes to drain back into the oil pan. If you do not do this, the oil dipstick might not show the actual level.
2. Pull the dipstick and clean it with a paper towel or cloth, then push it back in all the way. Remove it again, keeping the tip down and check the level.
5-13
When to Add Engine Oil
See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for the location of the engine oil fill cap.
If the oil is below the MIN (minimum) mark, you will need to add at least one quart/liter of oil. But you must use the right kind. This section explains what kind of oil to use. For engine oil crankcase capacity, see Capacities and Specifications on page 5-82. Notice: Do not add too much oil. If your engine has so much oil that the oil level gets above the upper mark that shows the proper operating range, your engine could be damaged.
Be sure to add enough oil to put the level somewhere in the proper operating range. Push the dipstick all the way back in when you are through.
5-14
What Kind of Engine Oil to Use
These numbers on an oil container show its viscosity, or thickness. Do not use other viscosity oils such as SAE 20W-50.
Oils meeting these requirements should also have the starburst symbol on the container. This symbol indicates that the oil has been certified by the American Petroleum Institute (API).
Look for two things: (cid:127) GM6094M
Your vehicle’s engine requires oil meeting GM Standard GM6094M. You should look for and use only an oil that meets GM Standard GM6094M.
(cid:127) SAE 5W-30
As shown in the viscosity chart, SAE 5W-30 is best for your vehicle.
You should look for this information on the oil container, and use only those oils that are identified as meeting GM Standard GM6094M and have the starburst symbol on the front of the oil container. Notice: Use only engine oil identified as meeting GM Standard GM6094M and showing the American Petroleum Institute Certified For Gasoline Engines starburst symbol. Failure to use the recommended oil can result in engine damage not covered by your warranty. GM Goodwrench® oil meets all the requirements for your vehicle.
5-15
If you are in an area of extreme cold, where the temperature falls below −20°F (−29°C), it is recommended that you use either an SAE 5W-30
synthetic oil or an SAE 0W-30 oil. Both will provide easier cold starting and better protection for your engine at extremely low temperatures. Engine Oil Additives Do not add anything to your oil. The recommended oils with the starburst symbol that meet GM Standard GM6094M are all you will need for good performance and engine protection. When to Change Engine Oil (Vehicles Without a Driver Information Center) If your vehicle does not have a Driver Information Center (DIC), change the engine oil and filter at the intervals specified in the maintenance schedule. See Scheduled Maintenance on page 6-4. If your vehicle has a Driver Information Center, it has the Engine Oil Life System. See Engine Oil Life System on page 5-16 for information on when to change your engine oil.Engine Oil Life System When to Change Engine Oil (Vehicles With Driver Information Center) If your vehicle has a Driver Information Center (DIC), it has the Engine Oil Life System, a computer system that lets you know when to change the engine oil and filter. This is based on engine revolutions and engine temperature, and not on mileage. Based on driving conditions, the mileage at which an oil change will be indicated can vary considerably. For the oil life system to work properly, you must reset the system every time the oil is changed. When the system has calculated that oil life has been diminished, it will indicate that an oil change is necessary. A CHANGE OIL SOON message will come on. See DIC Warnings and Messages on page 3-38. Change the oil as soon as possible within the next 600 miles (1 000 km). It is possible that, if you are driving under the best conditions, the oil life system may not indicate that an oil change is necessary for over a year. However, the engine oil and filter must be changed at least once a year and at this time the system must be reset. Your dealer has GM-trained service people who will perform this work using genuine GM parts and reset the system. It is also important to check your oil regularly and keep it at the proper level.
5-16
If the system is ever reset accidentally, you must change the oil at 3,000 miles (5 000 km) since the last oil change. Remember to reset the oil life system whenever the oil is changed. How to Reset the Engine Oil Life System The Engine Oil Life System calculates when to change your engine oil and filter based on vehicle use. Anytime your oil is changed, reset the system so it can calculate when the next oil change is required. If a situation occurs where you change your oil prior to a CHANGE OIL SOON message being turned on, reset the system. After changing the engine oil, the system must be reset as follows: 1. Turn the ignition to RUN, with the engine off. 2. Press the information and reset buttons on the DIC at the same time to enter the personalization menu. See DIC Vehicle Personalization on page 3-40.
3. Press the information button to scroll through the
available personalization menu modes until the DIC display shows OIL-LIFE RESET.
4. Press and hold the reset button until the DIC
display shows ACKNOWLEDGED. This will tell you the system has been reset.
5. Turn the key to LOCK. If the CHANGE OIL SOON message comes back on when you start your vehicle, the engine oil life system has not reset. Repeat the reset procedure. What to Do with Used Oil Used engine oil contains certain elements that may be unhealthy for your skin and could even cause cancer. Do not let used oil stay on your skin for very long. Clean your skin and nails with soap and water, or a good hand cleaner. Wash or properly dispose of clothing or rags containing used engine oil. See the manufacturer’s warnings about the use and disposal of oil products. Used oil can be a threat to the environment. If you change your own oil, be sure to drain all the oil from the filter before disposal. Never dispose of oil by putting it in the trash, pouring it on the ground, into sewers, or into streams or bodies of water. Instead, recycle it by taking it to a place that collects used oil. If you have a problem properly disposing of used oil, ask your dealer, a service station or a local recycling center for help.
5-17
Engine Air Cleaner/Filter
See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for the location of the engine air cleaner/filter. When to Inspect the Engine Air Cleaner/Filter Inspect the air cleaner/filter every 15,000 miles (25 000 km) and replace every 45,000 miles (75 000 km). If you are driving in dusty/dirty conditions, inspect the filter at each engine oil change.
5-18
How to Inspect the Engine Air Cleaner/Filter To inspect the air cleaner/filter remove the filter from the vehicle and lightly shake the filter to release loose dust and dirt. If the filter remains caked with dirt, a new filter is required. To inspect or replace the filter, open the clamps that hold the cover on and lift off the cover. Be sure to reinstall the cover tightly.
{CAUTION:
Operating the engine with the air cleaner/filter off can cause you or others to be burned. The air cleaner not only cleans the air; it helps to stop flames if the engine backfires. If it is not there and the engine backfires, you could be burned. Do not drive with it off, and be careful working on the engine with the air cleaner/filter off.
If the air cleaner/filter is off, a backfire can
Notice: cause a damaging engine fire. And, dirt can easily get into your engine, which will damage it. Always have the air cleaner/filter in place when you are driving.
Automatic Transmission Fluid It is not necessary to check the transmission fluid level. A transmission fluid leak is the only reason for fluid loss. If a leak occurs, take your vehicle to the dealership service department and have it repaired as soon as possible. Change the fluid and filter at the intervals listed in the Maintenance Schedule. See Part A: Scheduled Maintenance Services on page 6-4. Be sure to use the transmission fluid listed in Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21. Notice: Use of the incorrect automatic transmission fluid may damage your vehicle, and the damages may not be covered by your warranty. Always use the automatic transmission fluid listed in Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21.
Manual Transmission Fluid It is not necessary to check the manual transmission fluid level. A transmission fluid leak is the only reason for fluid loss. If a leak occurs, take the vehicle to the dealership service department and have it repaired as soon as possible. You may also have your fluid level checked by your dealer when you have your oil changed. See Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21 for the proper fluid to use.
Hydraulic Clutch The hydraulic clutch linkage in your vehicle is self-adjusting. This system does not have its own reservoir. It receives fluid from the brake master cylinder reservoir. See Brakes on page 5-31 for more information.
Engine Coolant The cooling system in your vehicle is filled with DEX-COOL® engine coolant. This coolant is designed to remain in your vehicle for five years or 150,000 miles (240 000 km), whichever occurs first, if you add only DEX-COOL® extended life coolant.
5-19
The following explains your cooling system and how to add coolant when it is low. If you have a problem with engine overheating, see Engine Overheating on page 5-23. A 50/50 mixture of clean, drinkable water and DEX-COOL® coolant will: (cid:127) Give freezing protection down to −34°F (−37°C). (cid:127) Give boiling protection up to 265°F (129°C). (cid:127) Protect against rust and corrosion. (cid:127) Help keep the proper engine temperature. Let the warning lights and gages work as they should.
Notice: Using coolant other than DEX-COOL® may cause premature engine, heater core, or radiator corrosion. In addition, the engine coolant may require changing sooner, at the first maintenance service after each 25,000 miles (41 500 km) or 24 months, whichever occurs first. Any repairs would not be covered by your warranty. Always use DEX-COOL® (silicate-free) coolant in your vehicle.
What to Use Use a mixture of one-half clean, drinkable water and one-half DEX-COOL® coolant which will not damage aluminum parts. If you use this coolant mixture, you do not need to add anything else.
{CAUTION:
Adding only plain water to your cooling system can be dangerous. Plain water, or some other liquid such as alcohol, can boil before the proper coolant mixture will. Your vehicle’s coolant warning system is set for the proper coolant mixture. With plain water or the wrong mixture, your engine could get too hot but you would not get the overheat warning. Your engine could catch fire and you or others could be burned. Use a 50/50 mixture of clean, drinkable water and DEX-COOL® coolant.
5-20
(cid:127) If you use an improper coolant mixture,
Notice: your engine could overheat and be badly damaged. The repair cost would not be covered by your warranty. Too much water in the mixture can freeze and crack the engine, radiator, heater core and other parts. If you have to add coolant more than four times a year, have your dealer check your cooling system. Notice: in your vehicle’s cooling system, you could damage your vehicle. Use only the proper mixture of the engine coolant listed in this manual for the cooling system. See Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21 for more information.
If you use extra inhibitors and/or additives
Checking Coolant
The coolant surge tank is located in the engine compartment on the driver’s side of the vehicle. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for more information on location.
5-21
{CAUTION:
Turning the surge tank pressure cap when the engine and radiator are hot can allow steam and scalding liquids to blow out and burn you badly. Never turn the surge tank pressure cap — even a little — when the engine and radiator are hot.
The vehicle must be on a level surface. When your engine is cold, the coolant level should be at the COLD FILL line. Do not overfill the surge tank. Too much coolant can result in an overflow condition when the fluid is hot.
Adding Coolant If you need more coolant, add the proper DEX-COOL® coolant mixture at the coolant surge tank, but only when the engine is cool. If the coolant surge tank is empty, a special fill procedure is necessary. See Engine Overheating on page 5-23 for instructions on “How to Add Coolant to the Coolant Surge Tank.”
{CAUTION:
You can be burned if you spill coolant on hot engine parts. Coolant contains ethylene glycol, and it will burn if the engine parts are hot enough. Do not spill coolant on a hot engine.
When replacing the pressure cap, make sure it is hand-tight and fully seated.
5-22
Coolant Surge Tank Pressure Cap If the pressure cap is not tightly installed, Notice: coolant loss and possible engine damage may occur. Be sure the cap is properly and tightly secured. The coolant surge tank pressure cap must be fully installed on the coolant surge tank. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for more information on location.
Engine Overheating You will find an engine coolant temperature warning light on your vehicle’s instrument panel. See Engine Coolant Temperature Warning Light on page 3-29 for more information.
If Steam Is Coming From Your Engine
{CAUTION:
Steam from an overheated engine can burn you badly, even if you just open the hood. Stay away from the engine if you see or hear steam coming from it. Just turn it off and get everyone away from the vehicle until it cools down. Wait until there is no sign of steam or coolant before you open the hood. If you keep driving when your engine is overheated, the liquids in it can catch fire. You or others could be badly burned. Stop your engine if it overheats, and get out of the vehicle until the engine is cool. See Overheated Engine Protection Operating Mode on page 5-25 for information on driving to a safe place in an emergency.
5-23
If your engine catches fire because you
Notice: keep driving with no coolant, your vehicle can be badly damaged. The costly repairs would not be covered by your warranty. See Overheated Engine Protection Operating Mode on page 5-25 for information on driving to a safe place in an emergency. If No Steam Is Coming From Your Engine An engine coolant temperature warning can indicate a serious problem. See Engine Coolant Temperature Warning Light on page 3-29. If you get an engine coolant temperature warning, but see or hear no steam, the problem may not be too serious. Sometimes the engine can get a little too hot when you: (cid:127) Climb a long hill on a hot day. (cid:127) Stop after high-speed driving. Idle for long periods in traffic.
If you get the engine coolant temperature warning with no sign of steam, try this for a minute or so: 1. If you have an air conditioner and it is on, turn it off. 2. In heavy traffic, let the engine idle in NEUTRAL (N) while stopped. If it is safe to do so, pull off the road, shift to PARK (P) or NEUTRAL (N) and let the engine idle.
3. Turn on your heater to full hot at the highest fan
speed and open the windows as necessary.
If you no longer have the overheat warning, you can drive. Just to be safe, drive slower for about 10 minutes. If the warning does not come back on, you can drive normally. If the warning continues and you have not stopped, pull over, stop, and park your vehicle right away. If there is still no sign of steam, you can idle the engine for three minutes while you are parked. If you still have the warning, turn off the engine and get everyone out of the vehicle until it cools down. You may decide not to lift the hood but to get service help right away.
5-24
(cid:127) Overheated Engine Protection Operating Mode This emergency operating mode allows your vehicle to be driven to a safe place in an emergency situation. If an overheated engine condition exists, an overheat protection mode which alternates firing groups of cylinders helps prevent engine damage. In this mode, you will notice a significant loss in power and engine performance. An engine coolant temperature warning light will come on in the instrument panel to indicate that an overheat condition exists. Driving extended miles (km) in the overheat protection mode should be avoided. Notice: After driving in the overheated engine protection operating mode, to avoid engine damage, allow the engine to cool before attempting any repair. The engine oil will be severely degraded. Repair the cause of coolant loss, change the oil and reset the oil life system. See Engine Oil on page 5-13.
Cooling System When you decide it is safe to lift the hood, here is what you will see:
A. Electric Engine Cooling Fans B. Coolant Surge Tank and Pressure Cap
5-25
{CAUTION:
{CAUTION:
An electric engine cooling fan under the hood can start up even when the engine is not running and can injure you. Keep hands, clothing and tools away from any underhood electric fan.
If the coolant inside the coolant surge tank is boiling, do not do anything else until it cools down. The vehicle should be parked on a level surface. The coolant level should be at the COLD FILL line. If it is not, you may have a leak at the pressure cap or in the radiator hoses, heater hoses, radiator, water pump, or somewhere in the cooling system.
Heater and radiator hoses, and other engine parts, can be very hot. Do not touch them. If you do, you can be burned. Do not run the engine if there is a leak. If you run the engine, it could lose all coolant. That could cause an engine fire, and you could be burned. Get any leak fixed before you drive the vehicle.
If there seems to be no leak, with the engine on, check to see if the electric engine cooling fans are running. If the engine is overheating, the fans should be running. If they are not, your vehicle needs service. Notice: Engine damage from running your engine without coolant is not covered by your warranty. Notice: Using coolant other than DEX-COOL® may cause premature engine, heater core or radiator corrosion. In addition, the engine coolant may require changing sooner, at 30,000 miles (50 000 km) or 24 months, whichever occurs first. Any repairs would not be covered by your warranty. Always use DEX-COOL® (silicate-free) coolant in your vehicle.
5-26
How to Add Coolant to the Coolant Surge Tank Notice: Your engine has a specific cooling system drain and fill procedure. Failure to follow this procedure could cause your engine to overheat and be severely damaged. If your engine’s cooling system needs to be drained and re-filled, please see your dealer. If you have not found a problem yet, check to see if coolant is visible in the coolant surge tank. If coolant is visible but the coolant level is not at the COLD FILL line, add a 50/50 mixture of clean, drinkable water and DEX-COOL® coolant at the coolant surge tank, but be sure the cooling system, including the coolant surge tank pressure cap, is cool before you do it. See Engine Coolant on page 5-19 for more information.
If no coolant is visible in the coolant surge tank, add coolant as follows:
{CAUTION:
Steam and scalding liquids from a hot cooling system can blow out and burn you badly. They are under pressure, and if you turn the coolant surge tank pressure cap — even a little — they can come out at high speed. Never turn the cap when the cooling system, including the coolant surge tank pressure cap, is hot. Wait for the cooling system and coolant surge tank pressure cap to cool if you ever have to turn the pressure cap.
5-27
{CAUTION:
{CAUTION:
Adding only plain water to your cooling system can be dangerous. Plain water, or some other liquid such as alcohol, can boil before the proper coolant mixture will. Your vehicle’s coolant warning system is set for the proper coolant mixture. With plain water or the wrong mixture, your engine could get too hot but you would not get the overheat warning. Your engine could catch fire and you or others could be burned. Use a 50/50 mixture of clean, drinkable water and DEX-COOL® coolant.
In cold weather, water can freeze and crack
Notice: the engine, radiator, heater core and other parts. Use the recommended coolant and the proper coolant mixture.
You can be burned if you spill coolant on hot engine parts. Coolant contains ethylene glycol and it will burn if the engine parts are hot enough. Do not spill coolant on a hot engine.
1. You can remove the coolant surge tank pressure
cap when the cooling system, including the coolant surge tank pressure cap and upper radiator hose, is no longer hot. Turn the pressure cap slowly counterclockwise about two or two and one-half turns. If you hear a hiss, wait for that to stop. This will allow any pressure still left to be vented out the discharge hose.
2. Then keep turning the
pressure cap slowly, and remove it.
5-28
3. Fill the coolant surge tank with the proper mixture,
to the COLD FILL line. Wait about five minutes, then check to see if the level is below the COLD FILL line. If the level is below the line, add additional coolant to bring the level up to the line. Repeat this procedure until the level remains constant at the COLD FILL line for at least five minutes.
4. With the coolant surge tank pressure cap off, start
the engine and let it run until you can feel the upper radiator hose getting hot. Watch out for the engine cooling fans. By this time, the coolant level inside the coolant surge tank may be lower. If the level is lower than the COLD FILL line, add more of the proper mixture to the coolant surge tank until the level reaches the COLD FILL line.
5. Then replace the pressure cap. Be sure the pressure cap is hand-tight and fully seated. See your dealer, if necessary.
Power Steering Fluid
See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for reservoir location.
5-29
Windshield Washer Fluid What to Use When you need windshield washer fluid, be sure to read the manufacturer’s instructions before use. If you will be operating your vehicle in an area where the temperature may fall below freezing, use a fluid that has sufficient protection against freezing. Adding Washer Fluid
Open the cap with the washer symbol on it. Add washer fluid until the tank is full. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for reservoir location.
When to Check Power Steering Fluid It is not necessary to regularly check power steering fluid unless you suspect there is a leak in the system or you hear an unusual noise. A fluid loss in this system could indicate a problem. Have the system inspected and repaired. How to Check Power Steering Fluid To check the power steering fluid, do the following: 1. Turn the key off and let the engine compartment
cool down.
2. Wipe the cap and the top of the reservoir clean. 3. Unscrew the cap and wipe the dipstick with a
clean rag.
4. Replace the cap and completely tighten it. 5. Remove the cap again and look at the fluid level on
the dipstick.
The level should be between the COLD and HOT marks. If necessary, add only enough fluid to bring the level up to the COLD mark. What to Use To determine what kind of fluid to use, see Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21. Always use the proper fluid. Failure to use the proper fluid can cause leaks and damage hoses and seals.
5-30
Notice: (cid:127) When using concentrated washer fluid,
follow the manufacturer’s instructions for adding water.
(cid:127) Do not mix water with ready-to-use washer fluid.
Water can cause the solution to freeze and damage your washer fluid tank and other parts of the washer system. Also, water does not clean as well as washer fluid. Fill your washer fluid tank only three-quarters full when it is very cold. This allows for expansion if freezing occurs, which could damage the tank if it is completely full.
(cid:127) Do not use engine coolant (antifreeze) in your windshield washer. It can damage your washer system and paint.
Brakes Brake Fluid
Your brake master cylinder reservoir is filled with DOT-3 brake fluid. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for the location of the reservoir.
There are only two reasons why the brake fluid level in the reservoir might go down. The first is that the brake fluid goes down to an acceptable level during normal brake lining wear. When new linings are put in, the fluid level goes back up. The other reason is that fluid is leaking out of the brake and/or clutch hydraulic system. If it is, you should have your brake and/or clutch system fixed, since a leak means that sooner or later your brakes and/or clutch will not work well, or will not work at all.
5-31
(cid:127) So, it is not a good idea to top off your brake/clutch fluid. Adding fluid will not correct a leak. If you add fluid when your brake linings are worn, then you will have too much fluid when you get new brake linings. You should add or remove fluid, as necessary, only when work is done on the brake/clutch hydraulic system.
{CAUTION:
If you have too much brake fluid, it can spill on the engine. The fluid will burn if the engine is hot enough. You or others could be burned, and your vehicle could be damaged. Add brake fluid only when work is done on the brake and/or clutch hydraulic system.
When your brake fluid falls to a low level, your brake warning light will come on. See Brake System Warning Light on page 3-27. What to Add When you do need brake fluid, use only DOT-3 brake fluid. Use new brake fluid from a sealed container only. See Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21.
Always clean the brake fluid reservoir cap and the area around the cap before removing it. This will help keep dirt from entering the reservoir.
{CAUTION:
With the wrong kind of fluid in your brake/clutch system, your brakes/clutch may not work well, or they may not even work at all. This could cause a crash. Always use the proper brake fluid.
Notice: (cid:127) Using the wrong fluid can badly damage
brake/clutch system parts. For example, just a few drops of mineral-based oil, such as engine oil, in your brake/clutch hydraulic system can damage brake/clutch system parts so badly that they will have to be replaced. Do not let someone put in the wrong kind of fluid. If you spill brake fluid on your vehicle’s painted surfaces, the paint finish can be damaged. Be careful not to spill brake fluid on your vehicle. If you do, wash it off immediately. See Washing Your Vehicle on page 5-72.
5-32
(cid:127) Brake Wear Your vehicle has four-wheel disc brakes. Disc brake pads have built-in wear indicators that make a high-pitched warning sound when the brake pads are worn and new pads are needed. The sound may come and go or be heard all the time your vehicle is moving, except when you are pushing on the brake pedal firmly.
{CAUTION:
The brake wear warning sound means that soon your brakes will not work well. That could lead to an accident. When you hear the brake wear warning sound, have your vehicle serviced.
Notice: Continuing to drive with worn-out brake pads could result in costly brake repair. Some driving conditions or climates may cause a brake squeal when the brakes are first applied or lightly applied. This does not mean something is wrong with your brakes.
Properly torqued wheel nuts are necessary to help prevent brake pulsation. When tires are rotated, inspect brake pads for wear and evenly tighten wheel nuts in the proper sequence to GM torque specifications. Brake linings should always be replaced as complete axle sets. Brake Pedal Travel See your dealer if the brake pedal does not return to normal height, or if there is a rapid increase in pedal travel. This could be a sign of brake trouble. Brake Adjustment Every time you apply the brakes, with or without the vehicle moving, your brakes adjust for wear. Replacing Brake System Parts The braking system on a vehicle is complex. Its many parts have to be of top quality and work well together if the vehicle is to have really good braking. Your vehicle was designed and tested with top-quality GM brake parts. When you replace parts of your braking system — for example, when your brake linings wear
5-33
Warning: Battery posts, terminals, and related accessories contain lead and lead compounds, chemicals known to the State of California to cause cancer and reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.
down and you need new ones put in — be sure you get new approved GM replacement parts. If you do not, your brakes may no longer work properly. For example, if someone puts in brake linings that are wrong for your vehicle, the balance between your front and rear brakes can change — for the worse. The braking performance you have come to expect can change in many other ways if someone puts in the wrong replacement brake parts.
Battery Your vehicle has a maintenance free battery. When it is time for a new battery, get one that has the replacement number shown on the original battery’s label. We recommend an ACDelco® replacement battery. See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12 for battery location.
5-34
Vehicle Storage If you are not going to drive your vehicle for 25 days or more, remove the black, negative (−) cable from the battery. This will help keep your battery from running down.
{CAUTION:
Batteries have acid that can burn you and gas that can explode. You can be badly hurt if you are not careful. See Jump Starting on page 5-35 for tips on working around a battery without getting hurt.
Jump Starting If your vehicle’s battery has run down, you may want to use another vehicle and some jumper cables to start your vehicle. Be sure to use the following steps to do it safely.
{CAUTION:
Batteries can hurt you. They can be dangerous because:
(cid:127) They contain acid that can burn you. (cid:127) They contain gas that can explode
(cid:127) They contain enough electricity to
or ignite.
burn you.
If you do not follow these steps exactly, some or all of these things can hurt you.
Ignoring these steps could result in costly
Notice: damage to your vehicle that would not be covered by your warranty. Trying to start your vehicle by pushing or pulling it will not work, and it could damage your vehicle. 1. Check the other vehicle. It must have a 12-volt
battery with a negative ground system.
If the other vehicle’s system is not a 12-volt
Notice: system with a negative ground, both vehicles can be damaged. Only use vehicles with 12-volt systems with negative grounds to jump start your vehicle.
5-35
4. Open the hood on the other vehicle and locate the positive (+) and negative (−) terminal locations on that vehicle. You will not need to access your battery for jump starting. Your vehicle has a remote positive (+) and a remote negative (−) jump starting terminal.
The remote positive (+) terminal is located under a red plastic cover on the engine compartment fuse block. Open the cover to access the terminal.
2. Get the vehicles close enough so the jumper cables can reach, but be sure the vehicles are not touching each other. If they are, it could cause a ground connection you do not want. You would not be able to start your vehicle, and the bad grounding could damage the electrical systems. To avoid the possibility of the vehicles rolling, set the parking brake firmly on both vehicles involved in the jump start procedure. Put an automatic transmission in PARK (P) or a manual transmission in NEUTRAL before setting the parking brake.
If you leave your radio or other accessories
Notice: on during the jump starting procedure, they could be damaged. The repairs would not be covered by your warranty. Always turn off your radio and other accessories when jump starting your vehicle. 3. Turn off the ignition on both vehicles. Unplug
unnecessary accessories plugged into the cigarette lighter or the accessory power outlet. Turn off the radio and all lamps that are not needed. This will avoid sparks and help save both batteries. And it could save the radio!
5-36
The remote negative (−) ground bracket is located in the rear of the engine compartment, on the passenger’s side of the vehicle, and is marked GND (−).
See Engine Compartment Overview on page 5-12
for more information on the location of the positive (+) and negative (−) terminals on your vehicle.{CAUTION:
An electric fan can start up even when the engine is not running and can injure you. Keep hands, clothing and tools away from any underhood electric fan.
{CAUTION:
Using a match near a battery can cause battery gas to explode. People have been hurt doing this, and some have been blinded. Use a flashlight if you need more light. Be sure the battery has enough water. You do not need to add water to the battery installed in your new vehicle. But if a battery has filler caps, be sure the right amount of fluid is there. If it is low, add water to take care of that first. If you don’t, explosive gas could be present. Battery fluid contains acid that can burn you. Do not get it on you. If you accidentally get it in your eyes or on your skin, flush the place with water and get medical help immediately.
5-37
{CAUTION:
Fans or other moving engine parts can injure you badly. Keep your hands away from moving parts once the engine is running.
5. Check that the jumper cables do not have loose or
missing insulation. If they do, you could get a shock. The vehicles could be damaged too. Before you connect the cables, here are some basic things you should know. Positive (+) will go to positive (+) or to a remote positive (+) terminal if the vehicle has one. Negative (−) will go to a heavy, unpainted metal engine part or to a remote negative (−) terminal if the vehicle has one. Do not connect positive (+) to negative (−) or you will get a short that would damage the battery and maybe other parts too. And do not connect the negative (−) cable to the negative (−) terminal on the dead battery because this can cause sparks.
6. Connect the red positive (+) cable to the positive (+)
terminal location on the vehicle with the dead battery. Use a remote positive (+) terminal if the vehicle has one.
7. Do not let the other end touch metal. Connect it to the positive (+) terminal of the good battery. Use a remote positive (+) terminal if the vehicle has one. 8. Now connect the black negative (−) cable to the negative (−) terminal of the good battery. Use a remote negative (−) terminal if the vehicle has one. Do not let the other end touch anything until the next step. The other end of the negative (−) cable does not go to the dead battery. It goes to a heavy, unpainted metal engine part or to a remote negative (−) terminal on the vehicle with the dead battery.
9. Connect the other end of the negative (−) cable to
the negative (−) terminal location on the vehicle with the dead battery. Your vehicle has a remote negative (−) ground bracket for this purpose.
10. Now start the vehicle with the good battery and run
the engine for a while.
11. Try to start the vehicle that had the dead battery.
If it will not start after a few tries, it probably needs service.
5-38
If the jumper cables are connected or
Notice: removed in the wrong order, electrical shorting may occur and damage the vehicle. The repairs would not be covered by your warranty. Always connect and remove the jumper cables in the correct order, making sure that the cables do not touch each other or other metal.
Jumper Cable Removal
A. Heavy, Unpainted Metal Engine Part or Remote
Negative (−) Terminal
B. Good Battery or Remote Positive (+) and Remote
Negative (−) Terminals
C. Dead Battery or Remote Positive (+) Terminal
To disconnect the jumper cables from both vehicles, do the following: 1. Disconnect the black negative (−) cable from the
vehicle that had the dead battery.
2. Disconnect the black negative (−) cable from the
vehicle with the good battery.
3. Disconnect the red positive (+) cable from the
vehicle with the good battery.
4. Disconnect the red positive (+) cable from the
other vehicle.
5. Return the positive (+) terminal cover to its
original position.
Rear Axle When to Check Lubricant It is not necessary to regularly check rear axle fluid unless you suspect there is a leak or you hear an unusual noise. A fluid loss could indicate a problem. Have it inspected and repaired.
5-39
Bulb Replacement For the proper type of replacement bulbs, see Replacement Bulbs on page 5-43. For any bulb changing procedure not listed in this section, contact your dealer.
Halogen Bulbs
{CAUTION:
Halogen bulbs have pressurized gas inside and can burst if you drop or scratch the bulb. You or others could be injured. Be sure to read and follow the instructions on the bulb package.
How to Check Lubricant
To get an accurate reading, the vehicle should be on a level surface. If the level is below the bottom of the filler plug hole, located on the rear axle, you’ll need to add some lubricant. Add enough lubricant to raise the level to the bottom of the filler plug hole. What to Use Refer to the Maintenance Schedule to determine what kind of lubricant to use. See Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-21.
5-40
Headlamps To replace the low/high-beam headlamp bulb, do the following: 1. Open the hood. See Hood Release on page 5-11
for more information.
2. Locate the headlamp bulb socket.
Front Turn Signal, Parking and Fog Lamps
A. Front Turn Signal/
Parking Lamp
B. Fog Lamp (If Equipped)
3. Turn the bulb socket counterclockwise and pull it
from the headlamp assembly.
4. Holding the base of the socket, pull the old bulb
from the socket.
5. Replace with a new bulb. 6. Reverse Steps 2 through 4 to reinstall.
To replace one of these bulbs, do the following:
1. Open the hood. See Hood Release on page 5-11
for more information.
2. Reach underneath the front bumper and locate the
bulb assembly.
3. Turn the bulb socket counterclockwise and pull out
the bulb assembly.
4. Disconnect the bulb socket from the wiring harness. 5. Install a new bulb. 6. Reverse the steps to reinstall the bulb assembly
and headlamp assembly.
5-41
Taillamps, Turn Signal, and Stoplamps To replace one of these bulbs, do the following: 1. Open the trunk. See Trunk on page 2-9 for
more information.
2. Remove the
two screws, which hold the taillamp assembly, from inside the vehicle.
Back-Up Lamps
The back-up lamps are located in the rear bumper.
To replace a bulb, do the following:
1. Reach behind, up and under the rear bumper and
locate the bulb socket.
2. Turn it counterclockwise to remove from the
bulb assembly.
3. Pull the bulb from the bulb socket. 4. Push in a new bulb into the bulb socket. 5. Reinstall the bulb socket by lining up the tabs in the
lamp assembly and turn it clockwise to secure it.
3. Remove the taillamp assembly. 4. Turn the bulb socket counterclockwise to remove. 5. Pull the bulb from the socket. 6. Install a new bulb. 7. Reverse the steps to reinstall the taillamp assembly.
5-42
Replacement Bulbs
Exterior Lamp
Back-Up Lamps Fog Lamp Front Parking/Turn Signal/ DRL Lamp Front Sidemarker Lamp Headlamps, High/Low-Beam Stoplamp, Taillamp and Turn Signal * Uplevel Model
Bulb Number 3057K 898* 3757KA* or 5702KA 194
H133157K
For replacement bulbs not listed here, contact your dealer. Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement Windshield wiper blades should be inspected for wear and cracking. See At Least Twice a Year on page 6-14
for more information.Replacement blades come in different types and are removed in different ways. For proper type and length, see Normal Maintenance Replacement Parts on page 6-23.
To replace the windshield wiper blade assembly do the following: 1. Lift the wiper arm away from the windshield.
5-43
{CAUTION:
Poorly maintained and improperly used tires are dangerous.
(cid:127) Overloading your tires can cause
overheating as a result of too much friction. You could have an air-out and a serious accident. See Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
(cid:127) Underinflated tires pose the same danger as overloaded tires. The resulting accident could cause serious injury. Check all tires frequently to maintain the recommended pressure. Tire pressure should be checked when your tires are cold. See Inflation - Tire Pressure on page 5-50. (cid:127) Overinflated tires are more likely to be cut, punctured or broken by a sudden impact — such as when you hit a pothole. Keep tires at the recommended pressure.
(cid:127) Worn, old tires can cause accidents. If
your tread is badly worn, or if your tires have been damaged, replace them.
2. Push the release lever (B) to disengage the hook and push the wiper arm (A) out of the blade (C).
3. Push the new wiper blade securely on the
wiper arm until you hear the release lever click into place.
Tires Your new vehicle comes with high-quality tires made by a leading tire manufacturer. If you ever have questions about your tire warranty and where to obtain service, see your GM Warranty booklet for details. For additional information refer to the tire manufacturer’s booklet included with your vehicle’s Owner Manual.
5-44
Notice: If your vehicle has P245/45R18 size tires, they are classified as low-profile tires. Low-profile tires are more susceptible to damage from road hazards or curb impact than standard profile tires. Tire and or wheel assembly damage can occur when coming into contact with road hazards like, potholes or sharp edged objects or when sliding into a curb. Your GM warranty does not cover this type of damage. Keep tires set to the correct inflation pressure and when possible avoid contact with curbs, potholes and other road hazards. Winter Tires If you expect to drive on snow or ice covered roads often, you may want to get winter tires for your vehicle. All season tires provide good overall performance on most surfaces but they may not offer the traction you would like or the same level of performance as winter tires on snow or ice covered roads.
See your dealer for details regarding winter tire availability and proper tire selection. Also, see Buying New Tires on page 5-53. If you choose to use snow tires: (cid:127) Use tires of the same brand and tread type on all
four wheel positions.
(cid:127) Use only radial ply tires of the same size,
load range, and speed rating as the original equipment tires.
Winter tires with the same speed rating as your original equipment tires may not be available for H, V, W and ZR speed rated tires. If you choose snow tires with a lower speed rating, never exceed the tire’s maximum speed capability.
5-45
Tire Sidewall Labelling Useful information about a tire is molded into its sidewall. The example below shows a typical passenger (p-metric) tire sidewall.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire Example
(A) Tire Size: The tire size is a combination of letters and numbers used to define a particular tire’s width, height, aspect ratio, construction type and service description. See the “Tire Size” illustration later in this section for more detail.
5-46
(B) TPC Spec (Tire Performance Criteria Specification): Original equipment tires designed to GM’s specific tire performance criteria have a TPC specification code molded onto the sidewall. GM’s TPC specifications meet or exceed all federal safety guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of Transportation): The Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number (TIN): The letters and numbers following DOT code are the Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material: The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG): Tire manufacturers are required to grade tires based on three performance factors: treadwear, traction and temperature resistance. For more information see Uniform Tire Quality Grading on page 5-55.
(G) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit: Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load.
Tire Size The following illustration shows an example of a typical passenger (p-metric) vehicle tire size.
(A) Passenger (P-Metric) Tire: The United States version of a metric tire sizing system. The letter P as the first character in the tire size means a passenger vehicle tire engineered to standards set by the U. S. Tire and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width: The three-digit number indicates the tire section width in millimeters from sidewall to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio: A two-digit number that indicates the tire height-to-width measurements. For example, if the tire size aspect ratio is 60, as shown in item C of the illustration, it would mean that the tire’s sidewall is 60 percent as high as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code: A letter code is used to indicate the type of ply construction in the tire. The letter R means radial ply construction; the letter D means diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter B means belted-bias ply construction.
(E) Rim Diameter: Diameter of the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description: These characters represent the load range and speed rating of the tire. The load index represents the load carry capacity a tire is certified to carry. The load index can range from 1 to 279. The speed rating is the maximum speed a tire is certified to carry a load. Speed ratings range from A to Z.
Tire Terminology and Definitions
Air Pressure: The amount of air inside the tire pressing outward on each square inch of the tire. Air pressure is expressed in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascal (kPa).
Accessory Weight: This means the combined weight of optional accessories. Some examples of optional accessories are, automatic transmission, power steering, power brakes, power windows, power seats, and air conditioning.
Aspect Ratio: The relationship of a tire’s height to its width.
5-47
Belt: A rubber coated layer of cords that is located between the plies and the tread. Cords may be made from steel or other reinforcing materials.
Bead: The tire bead contains steel wires wrapped by steel cords that hold the tire onto the rim.
Bias Ply Tire: A pneumatic tire in which the plies are laid at alternate angles less than 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread.
Cold Inflation Pressure: The amount of air pressure in a tire, measured in pounds per square inch (psi) or kilopascals (kPa) before a tire has built up heat from driving. See Inflation - Tire Pressure on page 5-50.
Curb Weight: This means the weight of a motor vehicle with standard and optional equipment including the maximum capacity of fuel, oil and coolant, but without passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings: A code molded into the sidewall of a tire signifying that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) motor vehicle safety standards. The DOT code includes the Tire Identification Number (TIN), an alphanumeric designator which can also identify the tire manufacturer, production plant, brand and date of production.
GVWR: Gross Vehicle Weight Rating, see Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
5-48
GAWR FRT: Gross Axle Weight Rating for the front axle, see Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
GAWR RR: Gross Axle Weight Rating for the rear axle, see Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
Intended Outboard Sidewall: The side of an asymmetrical tire, that must always face outward when mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa): The metric unit for air pressure.
Light Truck (LT-Metric) Tire: A tire used on light duty trucks and some multipurpose passenger vehicles.
Load Index: An assigned number ranging from 1 to 279 that corresponds to the load carrying capacity of a tire.
Maximum Inflation Pressure: The maximum air pressure to which a cold tire may be inflated. The maximum air pressure is molded onto the sidewall.
Maximum Load Rating: The load rating for a tire at the maximum permissible inflation pressure for that tire.
Maximum Loaded Vehicle Weight: The sum of curb weight; accessory weight; vehicle capacity weight; and production options weight.
Normal Occupant Weight: The number of occupants a vehicle is designed to seat multiplied by 150 lbs (68 kg). See Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
Occupant Distribution: Designated seating positions. Outward Facing Sidewall: The side of an asymmetrical tire that has a particular side that faces outward when mounted on a vehicle. The side of the tire that contains a whitewall, bears white lettering or bears manufacturer, brand, and/or model name molding that is higher or deeper than the same moldings on the other sidewall of the tire. Passenger (P-Metric) Tire: A tire used on passenger cars and some light duty trucks and multipurpose vehicles. Recommended Inflation Pressure: Vehicle manufacturer’s recommended tire inflation pressure and shown on the tire placard. See Inflation - Tire Pressure on page 5-50 and Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29. Radial Ply Tire: A pneumatic tire in which the ply cords that extend to the beads are laid at 90 degrees to the centerline of the tread. Rim: A metal support for a tire and upon which the tire beads are seated. Sidewall: The portion of a tire between the tread and the bead. Speed Rating: An alphanumeric code assigned to a tire indicating the maximum speed at which a tire can operate. Traction: The friction between the tire and the road surface. The amount of grip provided.
Tread: The portion of a tire that comes into contact with the road.
Treadwear Indicators: Narrow bands, sometimes called “wear bars,” that show across the tread of a tire when only 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) of tread remains. See When It Is Time for New Tires on page 5-52.
UTQGS (Uniform Tire Quality Grading Standards): A tire information system that provides consumers with ratings for a tire’s traction, temperature, and treadwear. Ratings are determined by tire manufacturers using government testing procedures. The ratings are molded into the sidewall of the tire. See Uniform Tire Quality Grading on page 5-55.
Vehicle Capacity Weight: The number of designated seating positions multiplied by 150 lbs (68 kg) plus the rated cargo load. See Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
Vehicle Maximum Load on the Tire: Load on an individual tire due to curb weight, accessory weight, occupant weight, and cargo weight.
Vehicle Placard: A label permanently attached to a vehicle showing the vehicle’s capacity weight and the original equipment tire size and recommended inflation pressure. See “Tire and Loading Information Label” under Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29.
5-49
Inflation - Tire Pressure Tires need the correct amount of air pressure to operate effectively. Notice: Do not let anyone tell you that under-inflation or over-inflation is all right. It is not. If your tires do not have enough air (under-inflation), you can get the following:
Too much flexing Too much heat Tire overloading
(cid:127) Premature or irregular wear (cid:127) Poor handling (cid:127) Reduced fuel economy If your tires have too much air (over-inflation), you can get the following: (cid:127) Unusual wear (cid:127) Poor handling (cid:127) Rough ride (cid:127) Needless damage from road hazards
A Tire and Loading Information label is attached to the vehicle’s center pillar (B-pillar), below the driver’s door latch. This label shows your vehicle’s original equipment tires and the correct inflation pressures for your tires when they are cold. The recommended cold tire inflation pressure, shown on the label, is the minimum amount of air pressure needed to support your vehicle’s maximum load carrying capacity. For additional information regarding how much weight your vehicle can carry, and an example of the tire and loading information label, see Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29. How you load your vehicle affects vehicle handling and ride comfort, never load your vehicle with more weight than it was designed to carry. When to Check Check your tires once a month or more. How to Check Use a good quality pocket-type gage to check tire pressure. You cannot tell if your tires are properly inflated simply by looking at them. Radial tires may look properly inflated even when they are under-inflated. Check the tire’s inflation pressure when the tires are cold. Cold means your vehicle has been sitting for at least three hours or driven no more than 1 mile (1.6 km).
5-50
(cid:127) (cid:127) (cid:127) Remove the valve cap from the tire valve stem. Press the tire gage firmly onto the valve to get a pressure measurement. If the cold tire inflation pressure matches the recommended pressure on the Tire and Loading Information label, no further adjustment is necessary. If the inflation pressure is low, add air until you reach the recommended amount. If you overfill the tire, release air by pushing on the metal stem in the center of the tire valve. Re-check the tire pressure with the tire gage. Be sure to put the valve caps back on the valve stems. They help prevent leaks by keeping out dirt and moisture.
Tire Inspection and Rotation Tires should be rotated every 5,000 to 8,000 miles (8 000 to 13 000 km). Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your tires as soon as possible and check wheel alignment. Also check for damaged tires or wheels. See When It Is Time for New Tires on page 5-52 and Wheel Replacement on page 5-56 for more information.
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The first rotation is the most important. See “Scheduled Maintenance” for additional information.
When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation pattern shown here. After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and rear inflation pressures as shown on the Tire and Loading Information label. See Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29, for an example of the tire and loading information label and its location on your vehicle.
5-51
Make certain that all wheel nuts are properly tightened. See “Wheel Nut Torque” under Capacities and Specifications.
{CAUTION:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose after a time. The wheel could come off and cause a crash. When you change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle. In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a scraper or wire brush later, if you need to, to get all the rust or dirt off.
5-52
When It Is Time for New Tires
One way to tell when it is time for new tires is to check the treadwear indicators, which will appear when your tires have only 1/16 inch (1.6 mm) or less of tread remaining.
You need a new tire if any of the following statements are true: (cid:127) You can see the indicators at three or more places
around the tire.
(cid:127) You can see cord or fabric showing through the
tire’s rubber. The tread or sidewall is cracked, cut or snagged deep enough to show cord or fabric. The tire has a bump, bulge or split. The tire has a puncture, cut or other damage that cannot be repaired well because of the size or location of the damage.
(cid:127) (cid:127) (cid:127) Buying New Tires GM has developed and matched specific tires for your vehicle. The original equipment tires installed on your vehicle, when it was new, were designed to meet General Motors Tire Performance Criteria Specification (TPC spec) system rating. If you need replacement tires, GM strongly recommends that you get tires with the same TPC Spec rating. This way, your vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed to give the same performance and vehicle safety, during normal use, as the original tires. GM’s exclusive TPC Spec system considers over a dozen critical specifications that impact the overall performance of your vehicle, including brake system performance, ride and handling, traction control, and tire pressure monitoring performance. GM’s TPC Spec number is molded onto the tire’s sidewall by the tire manufacturer. If the tires have an all-season tread design, the TPC spec number will be followed by a MS, for mud and snow. See Tire Sidewall Labelling on page 5-46 for additional information.
{CAUTION:
Mixing tires could cause you to lose control while driving. If you mix tires of different sizes, brands, or types (radial and bias-belted tires) the vehicle may not handle properly, and you could have a crash. Using tires of different sizes, brands, or types may also cause damage to your vehicle. Be sure to use the correct size, brand, and type of tires on your vehicle’s wheels.
{CAUTION:
If you use bias-ply tires on your vehicle, the wheel rim flanges could develop cracks after many miles of driving. A tire and/or wheel could fail suddenly, causing a crash. Use only radial-ply tires with the wheels on your vehicle.
5-53
If you must replace your vehicle’s tires with those that do not have a TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size, load range, speed rating, and construction type (radial and bias-belted tires) as your vehicle’s original tires. Your vehicle’s original equipment tires are listed on the Tire and Loading Information Label. This label is attached to the vehicle’s center pillar (B-pillar). See Loading Your Vehicle on page 4-29, for more information about the Tire and Loading Information Label.
Different Size Tires and Wheels If you add wheels or tires that are a different size than your original equipment wheels and tires, this may affect the way your vehicle performs, including its braking, ride and handling characteristics, stability and resistance to rollover. Additionally, if your vehicle has electronic systems such as, antilock brakes; traction control; and electronic stability control, the performance of these systems can be affected.
{CAUTION:
If you add different sized wheels, your vehicle may not provide an acceptable level of performance and safety if tires not recommended for those wheels are selected. You may increase the chance that you will crash and suffer serious injury. Only use GM specific wheel and tire systems developed for your vehicle, and have them properly installed by a GM certified technician.
See Buying New Tires on page 5-53 and Accessories and Modifications on page 5-3 for additional information.
5-54
Uniform Tire Quality Grading Quality grades can be found where applicable on the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and maximum section width. For example: Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature A The following information relates to the system developed by the United States National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, which grades tires by treadwear, traction and temperature performance. (This applies only to vehicles sold in the United States.) The grades are molded on the sidewalls of most passenger car tires. The Uniform Tire Quality Grading system does not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver or temporary use spare tires, tires with nominal rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm), or to some limited-production tires. While the tires available on General Motors passenger cars and light trucks may vary with respect to these grades, they must also conform to federal safety requirements and additional General Motors Tire Performance Criteria (TPC) standards.
Treadwear The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one and a half (1.5) times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices and differences in road characteristics and climate. Traction – AA, A, B, C The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A, B, and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance. Warning: The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on straight-ahead braking traction tests, and does not include acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning, or peak traction characteristics.
5-55
Temperature – A, B, C The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a level of performance which all passenger car tires must meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law. Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded. Excessive speed, underinflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance The tires and wheels on your vehicle were aligned and balanced carefully at the factory to give you the longest tire life and best overall performance. Adjustments to wheel alignment and tire balancing will not be necessary on a regular basis. However, if you notice unusual tire wear or your vehicle pulling to one side or the other, the alignment may need to be checked. If you notice your vehicle vibrating when driving on a smooth road, your tires and wheels may need to be rebalanced. See your dealer for proper diagnosis.
Wheel Replacement Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked, or badly rusted or corroded. If wheel nuts keep coming loose, the wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts should be replaced. If the wheel leaks air, replace it (except some aluminum wheels, which can sometimes be repaired). See your dealer if any of these conditions exist. Your dealer will know the kind of wheel you need. Each new wheel should have the same load-carrying capacity, diameter, width, offset and be mounted the same way as the one it replaces.
5-56
If you need to replace any of your wheels, wheel bolts or wheel nuts, replace them only with new GM original equipment parts. This way, you will be sure to have the right wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts for your vehicle.
{CAUTION:
Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel bolts or wheel nuts on your vehicle can be dangerous. It could affect the braking and handling of your vehicle, make your tires lose air and make you lose control. You could have a collision in which you or others could be injured. Always use the correct wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts for replacement.
{CAUTION:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts become loose after a time. The wheel could come off and cause a crash. When you change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle. In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a scraper or wire brush later, if you need to, to get all the rust or dirt off.
{CAUTION:
Notice: The wrong wheel can also cause problems with bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper height, vehicle ground clearance and tire clearance to the body and chassis.
Never use oil or grease on studs or the threads of the wheel nuts. If you do, the wheel nuts might come loose and the wheel could fall off, causing a crash.
5-57
{CAUTION:
Incorrect wheel nuts or improperly tightened wheel nuts can cause the wheel to become loose and even come off. This could lead to a crash. Be sure to use the correct wheel nuts. If you have to replace them, be sure to get new GM original equipment wheel nuts.
Improperly tightened wheel nuts can lead
Notice: to brake pulsation and rotor damage. To avoid expensive brake repairs, evenly tighten the wheel nuts in the proper sequence and to the proper torque specification.
Used Replacement Wheels
{CAUTION:
Putting a used wheel on your vehicle is dangerous. You cannot know how it has been used or how far it has been driven. It could fail suddenly and cause a crash. If you have to replace a wheel, use a new GM original equipment wheel.
5-58
Tire Chains
{CAUTION:
Do not use tire chains. There is not enough clearance. Tire chains used on a vehicle without the proper amount of clearance can cause damage to the brakes, suspension or other vehicle parts. The area damaged by the tire chains could cause you to lose control of your vehicle and you or others may be injured in a crash. Use another type of traction device only if its manufacturer recommends it for use on your vehicle and tire size combination and road conditions. Follow that manufacturer’s instructions. To help avoid damage to your vehicle, drive slowly, re-adjust or remove the device if it is contacting your vehicle, and do not spin your wheels. If you do find traction devices that will fit, install them on the rear tires.
If a Tire Goes Flat Your vehicle has a tire inflator kit. There is no spare tire, no tire changing equipment, and no place to store a tire. It is unusual for a tire to blow out while you are driving, especially if you maintain your tires properly. See Tires on page 5-44. If air goes out of a tire, it is much more likely to leak out slowly. But, if you should ever have a blow out, here are a few tips about what to expect and what to do: If a front tire fails, the flat tire will create a drag that pulls the vehicle toward that side. Take your foot off the accelerator pedal and grip the steering wheel firmly. Steer to maintain lane position, and then gently brake to a stop well out of the traffic lane. A rear blow out, particularly on a curve, acts much like a skid and may require the same correction you would use in a skid. In any rear blow out, remove your foot from the accelerator pedal. Get the vehicle under control by steering the way you want the vehicle to go. It may be very bumpy and noisy, but you can still steer. Gently brake to a stop, well off the road if possible.
5-59
If a tire goes flat, avoid further tire and wheel damage by driving slowly to a level place and stopping. Then do this: 1. Turn on the hazard warning flashers. See Hazard
Warning Flashers on page 3-6.
2. Park your vehicle. If your vehicle has an automatic transmission, set the parking brake firmly and put the shift lever in PARK (P). See Shifting Into Park (P) (Automatic Transmission) on page 2-25. If your vehicle has a manual transmission, move the shift lever to REVERSE (R) and set the parking brake firmly. See Parking Your Vehicle (Manual Transmission) on page 2-27 for additional information.
3. Turn off the engine. 4. Inspect the flat tire. If the tire has been separated from the wheel or has damaged sidewalls or large tears that allow rapid air loss, call a tire repair facility. See Roadside Assistance Program on page 7-6.
If the flat tire is due to a slow leak caused by a nail or other similar road hazard, the tire inflator kit may be used to repair the damaged tire temporarily. The kit uses a liquid tire sealant to seal small punctures in the tread area of the tire. After repairing a tire with the tire inflator kit, take your vehicle to an authorized GM dealer to have the tire inspected and repaired as soon as possible. The tire sealant is a temporary repair only. See Tire Inflator Kit on page 5-60.
Tire Inflator Kit Your vehicle has a tire inflator kit. There is no jack or spare tire. The kit uses a liquid tire sealant and air at the same time to seal small punctures in the tread area of the tire. Be sure to read and follow all of the tire inflator kit instructions.
5-60
The kit includes the following:
After temporarily repairing a tire with the tire inflator kit, take your vehicle to an authorized GM dealer to have the tire inspected and repaired. Accessing the Tire Inflator Kit To access the tire inflator kit, do the following: 1. Make sure the convertible top is in the up position
before accessing the tire inflator kit.
2. Open the trunk. See Trunk on page 2-9 for more
information.
A. Air Compressor B. Tire Sealant
Canister
C. Air Compressor Accessory Plug
D. On/Off Switch E. Air Pressure Gage F. Air Compressor
Inflator Hose
G. Sealant
Filling Hose
If the flat tire is due to a slow leak caused by a nail or other similar road hazard, the tire inflator kit may be used to temporarily repair the damaged tire.
3. Locate the tire inflator kit on the driver’s side of the
vehicle, near the back corner of the trunk.
5-61
Check the tire sealant expiration date on the sealant canister. The sealant may not be as effective beyond the expiration date. If needed, see your GM dealer for a replacement canister. After temporarily repairing a tire using the tire sealant, take your vehicle to an authorized GM dealer to have the tire inspected and repaired. Using the Tire Inflator Kit To use the tire inflator kit, do the following: 1. Place the inflator kit on the ground and unwrap the
sealant filling hose from the compressor.
2. Remove the air compressor accessory plug from
the unit. To do this, pull the top portion of the wrapped cord out first, then the bottom, and then unsnap the plug. Do not insert the plug into an accessory outlet yet.
3. Remove the valve stem cap from the flat tire by
turning it counterclockwise. If an object, such as a nail, has penetrated the tire, do not remove it.
4. Remove the tire inflator
kit strap by squeezing the two tabs of the quick release buckle.
5. Remove the inflator kit from its foam container. Tire Sealant The kit contains a liquid sealant that when injected into a flat tire, may temporarily repair nail holes or cuts in the tread area of the tire. The tire sealant cannot repair tire damage caused while driving on a flat tire or a tire that has had a “blow out” or a tire that has punctures in the sidewall areas. The tire sealant solution is to be used for a single tire and can only be used once.
5-62
{CAUTION:
Idling the engine in a closed-in place or with the climate control system off can cause deadly carbon monoxide (CO). See Engine Exhaust on page 2-28.
6. Start the vehicle. See Starting the Engine on
page 2-19 for more information. The vehicle must be running while using the air compressor.
{CAUTION:
Inflating something too much can make it explode, and you or others could be injured. Be sure to read the inflator instructions, and inflate the tire to its recommended pressure. Do not exceed 36 psi (248 kPa).
7. Move the inflator kit switch to the I (on) position. The inflator kit will force sealant and air into the tire. Sealant may leak from the puncture hole until the vehicle is driven and the hole has sealed.
5-63
4. Attach the sealant filling hose (A) onto the tire valve
stem. Turn it clockwise until it is tight. Make sure the inflator kit on/off switch (B) is in the O (off) position.
5. Plug the air compressor accessory plug (C) into an
accessory power outlet in the vehicle. See Accessory Power Outlet(s) on page 3-15 for more information.
10. Move the inflator kit switch to the O (off) position
once the correct tire pressure is obtained.
11. Turn off the engine. 12. Unplug the air compressor accessory plug from the
accessory power outlet in the vehicle.
13. Disconnect the air compressor inflator hose from the tire valve stem, by turning it counterclockwise, and replace the tire valve stem cap. Be careful when handling the tire inflator components as they may be hot after usage.
14. Wrap the sealant filling hose around the air
compressor channel to stow it in its original location. 15. Stow the air compressor accessory plug back in the air compressor. To do this, wrap the air compressor accessory plug, snap in the plug, and then push in the bottom and then the top of the wrapped air compressor accessory plug.
8. Make sure there is a proper connection between the tire valve stem and the sealant filling hose by looking at the air pressure gage. If there is not a pressure reading while the compressor is running, the connection between the inflator kit and the tire is bad. Check the attachment between the sealant filling hose and the tire valve stem.
9. Inflate the tire up to the recommended inflation
pressure, found on the Tire and Loading Information label located on the vehicle’s center pillar (B-pillar) below the vehicle’s door latch, using the air pressure gage on the top of the unit. The pressure gage reading is slightly high while the compressor is on. Turn the compressor off to get an accurate pressure reading.
If the recommended pressure cannot be
Notice: reached after 15 minutes, the vehicle should not be driven farther. Damage to the tire is severe and the sealant will not be effective. Remove the air compressor plug from the accessory power outlet and unscrew the inflating hose from the tire valve. See Roadside Assistance Program on page 7-6.
5-64
16. If the flat tire was able
to inflate to the recommended inflation pressure, remove the maximum speed label from the sealant canister and place in a highly visible location such as the inside of the upper left corner of the windshield or to the face of the radio/clock.
The maximum speed label reminds you to drive cautiously and not to exceed 55 mph (90 km/h) until you have the damaged tire inspected and repaired.
{CAUTION:
Storing the tire inflator kit or other equipment in the passenger compartment of the vehicle could cause injury. In a sudden stop or collision, loose equipment could strike someone. Store the tire inflator kit in the proper place.
17. Return the equipment to the proper storage location
in the trunk of your vehicle. You may need to loosen the retention strap to wrap it around the inflator kit and foam container. To do this, pull apart the strap and loosen the strap at the quick release buckle. Then snap the buckle together, pull the strap tight, and secure the loose end of the strap by mating the ends.
18. Immediately drive the vehicle 5 miles (8 km) to
distribute the sealant evenly in the tire. Stop at a safe location and check the tire pressure, refer to Steps 1 through 8 under “Using the Air Compressor without Sealant” next in this section. If the tire pressure has fallen more then 10 psi (68 kPa), below the recommended inflation pressure, stop driving the vehicle. The tire is too damaged for the sealant to work. See Roadside Assistance Program on page 7-6. If the tire pressure has not dropped more than 10 psi (68 kPa) from the recommended inflation pressure, you can inflate the tire back up to the recommended inflation pressure.
19. Dispose of the sealant canister at a local GM dealer
or in accordance with your local state codes and practices. After using the sealant canister, replace it with a new canister from a GM dealer.
20. After temporarily repairing a tire with the emergency flat tire repair kit, take your vehicle to an authorized GM dealer to have the tire inspected and repaired.
5-65
Using the Air Compressor without Sealant To use the air compressor by itself to inflate a tire, do the following: 1. Remove the air compressor accessory plug from
the air compressor.
3. Pull the air compressor inflator hose from the
sealant canister.
4. Push the air compressor inflator hose onto the
tire valve stem and push the lever down to secure in place.
5. Ensure proper connection between the tire valve stem and the air compressor hose by looking at the air pressure gage. If there is not a pressure reading while the compressor is running, the connection between the inflator kit and the tire is bad. Check the attachment between the air compressor hose and the tire valve stem.
6. Plug the air compressor accessory plug into an
accessory power outlet in the vehicle. See Accessory Power Outlet(s) on page 3-15 for more information.
2. Unlock the air compressor hose from the sealant
canister by pulling up on the lever.
5-66
{CAUTION:
Idling the engine in a closed-in place or with the climate control system off can cause deadly carbon monoxide (CO). See Engine Exhaust on page 2-28.
7. Start the vehicle. See Starting the Engine on
page 2-19 for more information. The vehicle must be running while using the air compressor.
{CAUTION:
Inflating something too much can make it explode, and you or others could be injured. Be sure to read the inflator instructions, and inflate the tire to its recommended pressure. Do not exceed 36 psi (248 kPa).
8. Move the inflator kit switch to the I (on) position.
9. Inflate the tire up to the recommended inflation pressure using the air pressure gage on the top of the unit.
10. Turn off the air compressor by moving the switch to
the O (off) position.
{CAUTION:
Storing the tire inflator kit or other equipment in the passenger compartment of the vehicle could cause injury. In a sudden stop or collision, loose equipment could strike someone. Store the tire inflator kit in the proper place.
11. Place the equipment in the original location in the
trunk of your vehicle.
5-67
Removal and Installation of the Sealant Canister To remove the sealant canister, do the following:
1. Unlock the air compressor inflator hose from the
sealant canister by pulling the lever up.
2. Disconnect the air compressor inflator hose from
the sealant canister.
3. Turn the sealant canister so the inflator filling hose
is aligned with the slot in the compressor.
4. Lift the sealant canister from the compressor and
replace with a new sealant canister. See your GM dealer for more information.
5-68
To install a new sealant canister, do the following: 1. Align the sealant filling hose with the slot in the
air compressor.
2. Push the sealant canister down and rotate
it clockwise.
3. Push the air compressor inflator hose onto the sealant canister inlet and push the lever down.
Appearance Care
Cleaning the Inside of Your Vehicle Your vehicle’s interior will continue to look its best if it is cleaned often. Although not always visible, dust and dirt can accumulate on your upholstery. Dirt can damage carpet, fabric, leather, and plastic surfaces. Regular vacuuming is recommended to remove particles from your upholstery. It is important to keep your upholstery from becoming and remaining heavily soiled. Soils should be removed as quickly as possible. Your vehicle’s interior may experience extremes of heat that could cause stains to set rapidly. Lighter colored interiors may require more frequent cleaning. Use care because newspapers and garments that transfer color to your home furnishings may also transfer color to your vehicle’s interior.
If you use abrasive cleaners when cleaning
When cleaning your vehicle’s interior, only use cleaners specifically designed for the surfaces being cleaned. Permanent damage may result from using cleaners on surfaces for which they were not intended. Use glass cleaner only on glass. Remove any accidental over-spray from other surfaces immediately. To prevent over-spray, apply cleaner directly to the cleaning cloth.