- 2007 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2012 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2008 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2002 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2003 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2004 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2011 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2010 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2006 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2001 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2009 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- 2005 Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Ford F 350 Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
at the center of the vehicle. 3. Attach the trailer to the vehicle and adjust the hitch equalizers so that the front bumper height is within 0–13 mm (0.5 in) of the reference point. After proper adjustment, the rear bumper should be no higher than in Step 2.
Adjusting an equalizing hitch so the rear bumper of the vehicle is higher than it was unloaded will defeat the function of the
load equalizing hitch and may cause unpredictable handling.
Safety chains Always connect the trailer’s safety chains to the frame or hook retainers of the vehicle hitch. To connect the trailer’s safety chains, cross the chains under the trailer tongue and allow slack for turning corners. If you use a rental trailer, follow the instructions that the rental agency gives to you. Do not attach safety chains to the bumper.
Trailer brakes Electric brakes and manual, automatic or surge-type trailer brakes are safe if installed properly and adjusted to the manufacturer’s specifications. The trailer brakes must meet local and Federal regulations.
160
Driving
Do not connect a trailer’s hydraulic brake system directly to your vehicle’s brake system. Your vehicle may not have enough
braking power and your chances of having a collision greatly increase.
The braking system of the tow vehicle is rated for operation at the GVWR not GCWR.
Trailer lamps Trailer lamps are required on most towed vehicles. Make sure your trailer lamps conform to local and Federal regulations. See your dealer or trailer rental agency for proper instructions and equipment for hooking up trailer lamps.
Using a step bumper (if equipped) The rear bumper is equipped with an integral hitch and only requires a ball with a 25.4 mm (one inch) shank diameter. The bumper has a 2 270 kg (5 000 lb.) trailer weight and 227 kg (500 lb.) tongue weight capacity. If it is necessary to relocate the trailer hitch ball position, a frame-mounted trailer hitch must be installed.
shut off automatically when you are towing on long, steep grades.
Driving while you tow When towing a trailer: • Ensure that you turn off your speed control. The speed control may • Consult your local motor vehicle speed regulations for towing a trailer. • Use a lower gear when towing up or down steep hills. This will eliminate excessive downshifting and upshifting for optimum fuel economy and transmission cooling. • Anticipate stops and brake gradually. Exceeding the GCWR rating may cause internal transmission damage and void your warranty coverage. Servicing after towing If you tow a trailer for long distances, your vehicle will require more frequent service intervals. Refer to your scheduled maintenance guide for more information.
161
Driving
loaded trailer weight.
Trailer towing tips • Practice turning, stopping and backing up before starting on a trip to get the feel of the vehicle trailer combination. When turning, make wider turns so the trailer wheels will clear curbs and other obstacles.
• Allow more distance for stopping with a trailer attached. • The trailer tongue weight should be no more than 10–15% of the • After you have traveled 80 km (50 miles), thoroughly check your • When stopped in traffic for long periods of time in hot weather, place the gearshift in P (Park) (automatic transmissions) or N (Neutral) (manual transmissions). This aids engine cooling and air conditioner efficiency. • Vehicles with trailers should not be parked on a grade. If you must
hitch, electrical connections and trailer wheel lug nuts.
park on a grade, place wheel chocks under the trailer’s wheels.
Launching or retrieving a boat When backing down a ramp during boat launching or retrieval, • Do not allow the static water level to rise above the bottom edge of • Do not allow waves to break higher than 15 cm (6 inches) above the • Disconnect the trailer tow electrical connector to prevent blown fuses
bottom edge of the rear bumper.
the rear bumper and
caused by water entering into your trailer’s electrical wiring. Exceeding these limits may allow water to enter critical vehicle components, adversely affecting driveability, emissions and reliability. Replace front and rear axle lubricants any time the axles have been submerged in water. Axle lubricant quantities are not to be checked unless a leak is suspected.
All Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) vehicles This applies to all cars and 4x2 trucks/sport utilities with rear wheel drive capability. An example of recreational towing is towing your vehicle behind a motorhome. The following recreational towing guidelines are designed to ensure that your transmission is not damaged.
162
Driving
• Place the transmission in N (Neutral). • Maximum speed is 56 km/h (35 mph). • Maximum distance is 80 km (50 miles). If a distance of 80 km (50 miles) or a speed of 56 km/h (35 mph) must be exceeded, you must disconnect the driveshaft. Ford recommends the driveshaft be removed/installed only by a qualified technician. See your local dealer for driveshaft removal/installation. Improper removal/installation of the driveshaft can cause transmission fluid loss, damage to the driveshaft and internal transmission components. RWD vehicles with 4x4 electronic shift transfer case or All Wheel Drive (AWD) vehicles with automatic transmissions Regarding recreational towing or having your vehicle towed, 4x4 vehicles with electronic shift on the fly and AWD vehicles cannot be towed with any wheels on the ground (with the exception of moving it as a disabled vehicle off the road out of traffic).
SNOWPLOWING For low speed snow removal, Ford offers a Snowplow Package as an option. If you do not have this equipment, do not use your vehicle as a snowplow or powertrain and suspension system damage may occur. Do not install a snowplow and plow with your vehicle until it has been driven at least 800 km (500 miles).
Installing the snowplow
Removing the blocker beam without installing snowplow attachment hardware may affect air bag deployment in a crash. Do not operate the truck unless either the blocker beam or snowplow attachment hardware is installed on the vehicle.
Read the following instructions before installing a snowplow: • Front GAWR must not exceed 63% of the GVW. Add ballast weight to the back of the vehicle, if necessary. Refer to the Safety Compliance Certification Label to find Front GAWR.
163
Driving • The Front Axle Accessory Reserve Capacity and the Total Accessory Reserve Capacity listed on the bottom right of the Safety Compliance Certification Label will determine whether or not the addition of a snowplow will overload your vehicle.
• The weight of the snowplow and supporting components distributed to the front axle must not exceed the front accessory reserve capacity. • The total weight of the snowplow and aftermarket equipment must • The weight of the installed snowplow and aftermarket equipment must
not exceed the Total Accessory Reserve Capacity.
not load the vehicle beyond the GAWR (front/rear) and GVWR listed on the Safety Compliance Certification Label. • The total weight of the snowplow and aftermarket equipment must be
considered part of the payload and must not exceed the Gross Combined Weight Rating (GCWR) for towing.
• Federal and most local regulations require additional exterior lamps for snowplow-equipped vehicles. Consult your dealer for additional information. • After installing a snowplow to the vehicle, ensure the vehicle’s front toe alignment and front ride height are within specification (reset if required). These specifications are located in the vehicle’s Workshop Manual. Adherence to the toe, tire pressures and ride height specification is important for proper tire wear, ride, handling and headlight aim. Also, maintain the engine oil and transmission fluid change intervals following the severe duty schedule.
Do not exceed the GVWR or the GAWR specified on the certification label.
Removing snowplow Read the following instructions before removing a snowplow: • After removing a snowplow from the vehicle, ensure the vehicle’s front toe alignment and front ride height are within specification (reset if required). These specifications are located in the vehicle’s Workshop Manual. Adherence to the toe and ride height specification is important for proper tire wear, ride, handling and headlight aim.
164
Driving
Snowplowing with your air bag equipped vehicle Your vehicle is equipped with driver and passenger air bag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). The SRS is designed to activate when the vehicle sustains sufficient longitudinal deceleration.
Careless or high speed driving while plowing snow which results in sufficient vehicle decelerations can deploy the air bag. Such driving also increases the risk of accidents.
All occupants of the vehicle, including the driver, should always properly wear their safety belts, even when an air bag SRS is
provided.
Never remove or defeat the “tripping mechanisms” designed into the snow removal equipment by its manufacturer. Doing so may cause damage to the vehicle and the snow removal equipment as well as possible air bag deployment.
Additional equipment such as snowplow equipment may effect the performance of the air bag sensors increasing the risk of
injury. Please refer to the Body Builders Layout Book for instructions about the appropriate installation of additional equipment.
Do not attempt to service, repair, or modify the Air Bag Supplemental Restraint System or its fuses. See your Ford or
Lincoln Mercury dealer.
165
Driving
Engine temperature while plowing When driving with a plow, your engine may run at a higher temperature than normal because the attached snowplow blade will restrict airflow to the radiator.
If you are driving more than 24 km (15 miles) at temperatures above freezing, angle the plow blade either full left or full right to provide maximum airflow to the radiator. If you are driving less than 24 km (15 miles) at speeds up to 64 km/h (40 mph) in cold weather, you will not need to worry about blade position to provide maximum airflow. 4WD operation while plowing • Shift transfer case to 4x4 LOW (4WD Low) when plowing in small • Shift transfer case to 4x4 HIGH (4WD High) when plowing larger
areas at speeds below 8 km/h (5 mph).
areas or light snow at higher speeds. Do not exceed 24 km/h (15 mph).
• Do not shift the transmission from a forward gear to R (Reverse) until • If the vehicle is stuck, shift the transmission in a steady motion
the engine is at idle and the wheels are stopped.
between forward and reverse gears. Do not rock the vehicle for more than a few minutes. The transmission and tires may be damaged or the engine can overheat.
It is the owner’s responsibility to avoid engine overheating which can cause damage.
Do not spin the wheels at over 35 mph (55 km/h). The tires may fail and injure a passenger or bystander.
166
Roadside emergencies
GETTING ROADSIDE ASSISTANCE To fully assist you should you have a vehicle concern, Ford offers a complimentary roadside assistance program. This program is separate from the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. The service is available: • 24–hours, seven days a week • for the Basic warranty period (Canada) or New Vehicle Limited
Warranty period (U.S.) of three years or 60 000 km (36 000 miles), whichever comes first on Ford and Mercury vehicles, and four years or 80 000 km (50 000 miles) on Lincoln vehicles
Roadside assistance will cover: • changing a flat tire • jump-starts • lock-out assistance • fuel delivery • towing of your disabled vehicle up to 56.3 kms (35 miles) from the point of pickup (this can include to the nearest Ford dealership, or your selling dealer if within the specified distance.) One tow per disablement. Even non-warranty related tows, like accidents or getting stuck in the mud or snow, are covered (some exclusions apply, such as impound towing or repossession).
Using roadside assistance Complete the roadside assistance identification card and place it in your wallet for quick reference. In the United States, this card is found in the Owner Guide portfolio in the glove compartment in Ford vehicles and is mailed to you if you own a Mercury or Lincoln. In Canada, the card is found in the Roadside Assistance book in the glove compartment. To receive roadside assistance in the United States for Ford or Mercury vehicles, call 1–800–241–3673 or if you own a Lincoln vehicle, call 1–800–521–4140. In Canada call 1–800–665–2006. Should you need to arrange roadside assistance for yourself, Ford will reimburse a reasonable amount. To obtain information about reimbursement, call 1–800–241–3673 in the United States for Ford or Mercury vehicles; or if you own a Lincoln vehicle, call 1–800–521–4140. Call 1–800–665–2006 in Canada.
167
Roadside emergencies
Roadside coverage beyond basic warranty In the United States, you may purchase additional roadside assistance coverage beyond this period through the Ford Auto Club by contacting your Ford or Lincoln Mercury dealer. Similarly in Canada, for uninterrupted Roadside Assistance coverage, you may purchase extended coverage prior to your Basic Warranty’s Roadside Assistance expiring. For more information and enrollment, contact 1–877–294–2582 or visit our website at www.ford.ca.
HAZARD FLASHER Use only in an emergency to warn traffic of vehicle breakdown, approaching danger, etc. The hazard flashers can be operated when the ignition is off. • The hazard lights control is
located on top of the steering column.
• Depress hazard lights control to
activate all hazard flashers simultaneously.
• Depress control again to turn the
flashers off.
RESETTING THE FUEL PUMP SHUT-OFF SWITCH FUEL RESET The fuel pump shut-off switch is a device intended to stop the electric fuel pump when your vehicle has been involved in a substantial jolt. After a collision, if the engine cranks but does not start, the fuel pump shut-off switch may have been activated.
168
Roadside emergencies
The fuel pump shut-off switch is located in the passenger’s foot well, by the kick panel.
Use the following procedure to reset the fuel pump shut-off switch. 1. Turn the ignition to the OFF position. 2. Check the fuel system for leaks. 3. If no fuel leak is apparent, reset the fuel pump shut-off switch by pushing in on the reset button. 4. Turn the ignition to the ON position. Pause for a few seconds and return the key to the OFF position. 5. Make a further check for leaks in the fuel system.
169
Roadside emergencies
FUSES AND RELAYS
Fuses If electrical components in the vehicle are not working, a fuse may have blown. Blown fuses are identified by a broken wire within the fuse. Check the appropriate fuses before replacing any electrical components. NOTE: Always replace a fuse with one that has the specified amperage rating. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can cause severe wire damage and could start a fire. Standard fuse amperage rating and color
15
COLOR
Mini fuses
Grey Violet Pink Tan
Brown
Red Blue Yellow Natural Green
— — — — —
Standard
fuses
Grey Violet Pink Tan
Brown
Red Blue Yellow Natural Green
— — — — —
Maxi fuses
— — — — — — —
Yellow
—
Green Orange
Red Blue Tan
Natural
Cartridge
maxi fuses
— — — — — — — Blue — Pink Green Red — — —
Fuse link cartridge
— — — — — — — Blue — Pink Green Red Yellow Brown Black
Fuse rating
2A 3A 4A 5A 7.5A 10A 15A 20A 25A 30A 40A 50A 60A 70A 80A
170
Roadside emergencies
Passenger compartment fuse panel The fuse panel is located below and to the left of the steering wheel by the brake pedal. Remove the panel cover to access the fuses. To remove the fuse panel cover, turn the panel fasteners counterclockwise.
To remove a fuse use the fuse puller tool provided on the fuse panel cover.
171
Roadside emergencies
The fuses are coded as follows.
Fuse/Relay Location
Fuse Amp
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
Rating
Description
20A — 20A 10A
— — 5A 5A — 15A
Turn/Hazard Lamps Not Used Cigar Lighter, Data Link Connector Glove Box Lamp, Map Lamps, Power Mirrors, Underhood Lamp Not Used Not Used Power Window/Lock Switch Illumination Radio, Headlamp Switch Illumination Not Used Dual Fuel Tanks
10
172
Fuse/Relay Location
11
12
1314
15
16
17
18
1920
21
2223
2425
Roadside emergencies
Fuse Amp
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
Rating
30A
15A 20A
10A
5A
15A — 5A 10A
15A — 10A
10A 10A
—
Description
Wiper Motor, Wiper Run/Park Relay Coil, Wiper Hi/LO Relay Coil, Washer Pump Relay Coil Horn Stop Lamps, Center High-mount Stop Lamp, Trailer Tow Stop Lamp, Speed Control Dome Lamp, Cargo Lamp, Courtesy Lamps, Running Board Lamps Stop Lamp Switch (Logic): Generic Electronic Module (GEM), Powertrain Control Module (PCM), Four Wheel Anti-lock Brake System (4WABS) Module, Brake Shift Interlock, Cluster and PCM Keep Alive Memory Instrument Cluster, Hi-beam Headlamps Not Used Audio Auxiliary Powertrain Control Module (APCM) (Diesel only), Instrument Cluster, GEM Module, Overdrive Cancel Switch, Idle Validation Switch (Diesel only), Overhead Console, Diesel PCM via Clutch Starter Motor Relay Coil, Clutch Switch Not Used Passenger Air Bag Activation/Deactivation Switch, Blower Motor Relay Coil Air Bag Module A/C Clutch, Blend Door Actuator, Trailer Tow Battery Charge Relay Coil, Four Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System (4WABS), Turn Signal Not Used
173
Roadside emergencies
Fuse/Relay Location
26
2728
29
30
31
Relay 1
Relay 2
Relay 3
Relay 4
Relay 5Fuse Amp
Passenger Compartment Fuse Panel
Rating
— 10A
15A
5A
30A
5A — — — — —
Description
Not Used Ignition Run Power Feed (Customer Access) Brake Shift Interlock, DRL Relay Coil, Speed Control Module, Backup Lamps, Trailer Tow Backup Lamp Relay Coil, Electronic Shift On The Fly Hub Lock Solenoid, Vacuum Pump Motor Instrument Cluster (Charge and Airbag Warning Lamps) PCM Relay Coil, Ignition Coil (Gasoline only), Fuel Heater (Diesel only), Wastegate Solenoid (Diesel only), Injector Driver Module Relay Coil (Diesel only) Fog Lamp Switch Interior Lamp Relay Not Used Horn Power Window One Touch Down Relay Accessory Delay Relay
174
Roadside emergencies
Power distribution box The power distribution box, trailer tow and electronic shift on the fly relay blocks are located in the engine compartment near the brake master cylinder.
The power distribution box contains high-current fuses that protect your vehicle’s main electrical systems from overloads.
Always disconnect the battery before servicing high current fuses.
Always replace the cover to the Power Distribution Box before reconnecting the battery or refilling fluid reservoirs.
If the battery has been disconnected and reconnected, refer to the Battery section of the Maintenance and care chapter.
175
Roadside emergencies
The high-current fuses and relays are coded as follows. Fuse/Relay Location
Fuse Amp
Power Distribution Box Description
Rating 7.5A * 10A* 7.5A* 20A*
20A*
(Gasoline only)
5A*
(Diesel only)
10A*
Trailer Tow Left Stop/Turn Lamp Washer Pump Trailer Tow Right Stop/Turn Lamp Trailer Tow Backup Lamps, Trailer Tow Park Lamps Gasoline only-PCM, Fuel Pump Relay Coil, Mass Air Flow Sensor, Fuel Injectors Diesel only-Dual Alternator ⬙A⬙ Field
Gasoline only-A/C (CASS) Diesel only-Single or Dual Alternator ⬙A⬙ Field, Regulator
176
Roadside emergencies
Fuse Amp
Power Distribution Box Description
Rating 20A*
(Gasoline only)
5A*
(Diesel only)
15A*
10A* 20A* 10A* 15A*
30A** 60A** 30A** 30A** 30A**
30A** 20A** 50A** 50A** 50A** 40A** 30A**
Gasoline only-Vapor Management Valve, HEGO Sensors, Intake Manifold Communication Control, EVR Solenoid, PCM, Canister Vent Solenoid Diesel only-Dual Alternator ⬙A⬙ Field Trailer Tow Electronic Brake Illumination, Park Lamps, Trailer Tow Park Lamp Relay Coil Left Headlamp (Low Beam) Power Point Right Headlamp (Low Beam) Daytime Running Lamps (DRL) Resistor, Fog Lamps Multi-function Switch, Headlamps Anti-Lock Brake System Heated Seats Trailer Tow Battery Charge Electronic Shift On The Fly Relay, Transfer Case Shift Motor Power Seat, Adjustable Pedals Fuel Pump Motor, PCM Ignition Switch (B4 & B5) Ignition Switch (B1 & B3) Junction Box Battery Feed Blower Motor PCM Power
(Gasoline only)
20A**
(Diesel only)
30A***
Power Windows
Fuse/Relay Location
10
11
1213
14
15
16
1718
19
20
21
22
23
2425
177
Roadside emergencies
Fuse/Relay Location
26
27
28
29
30
31
3233
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41Fuse Amp
Power Distribution Box Description
Rating 20A**
- (Gasoline
only)
30A**
(Diesel only)
30A** 20A**
-- -- --
-- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- —
If equipped with Remote Keyless Entry-Driver Door Unlock Relay Coil, All Door Unlock Relay Coil, All Door Lock Relay Coil, Park Lamp Flash Relay, If not equipped with Remote Keyless Entry-Power Door Lock Motors Gasoline only-Not Used Diesel only-Injector Driver Module
Trailer Tow Electronic Brake Controller Radio PCM Power Relay Blower Motor Relay A/C CASS (Gasoline only), Injector Driver Module Power Relay (Diesel only) Washer Pump Relay Windshield Wiper Park/Run Relay Windshield Wiper HI/LO Relay A/C Clutch Diode PCM Diode Trailer Tow Backup Lamp Relay Trailer Tow Battery Charge Relay Electronic Shift On The Fly Relay #1
Electronic Shift On The Fly Relay #2* Mini Fuses ** Maxi Fuses ***Circuit Breaker
178
Roadside emergencies
CHANGING THE TIRES If you get a flat tire while driving, do not apply the brake heavily. Instead, gradually decrease your speed. Hold the steering wheel firmly and slowly move to a safe place on the side of the road.
Spare tire information Your vehicle may be equipped with a spare tire that can be used as either a spare or a regular tire. The spare tire is not equipped with wheel trim. The wheel trim from the original wheel/tire may be used on the spare. If your vehicle is equipped with 4WD, a spare tire of a different size than the road tires should not be used. Such a tire could result in damage to driveline components and make the vehicle difficult to control. Location of the spare tire and tools The spare tire and tools for your vehicle are stowed in the following locations:
Tool
Spare tire
(pick-up trucks only)
Jack
Jack handle and lug
wrench
Key, spare tire lock
(if equipped)
Location
Under the vehicle, just forward of the rear bumper Regular cab, crew cab and SuperCab without rear bench seat: Fastened to floor pan behind rearmost seat on passenger side SuperCab with rear bench seat: Under rear bench on passenger side On top of the radiator support at the front of the engine compartment In the glove box
Removing the spare tire (with spare tire carrier only) 1. The following tools are required to remove the spare tire: • one handle extension and one typical extension. To assemble, align button with hole and slide parts together. To disconnect, depress button and pull apart.
179
Roadside emergencies • one wheel nut wrench. Slide over
square end of jack handle.
2. If equipped, unlock and remove the spare tire lock from the rear bumper drive tube using the the spare tire lock key and the jack handle. 3. Insert the hooked end of the jack handle into the rear bumper drive tube. The handle will stop moving and you will feel forward resistance to turning when properly engaged. 4. Turn the handle counterclockwise and lower the spare until you can slide the tire rearward and the cable is slack. 5. Remove the retainer through the center of the wheel.
180
Roadside emergencies
Stowing the spare tire 1. Lay the tire on the ground with the valve stem facing up. 2. Slide the wheel under the vehicle and install the retainer through the wheel center. 3. Turn the jack handle clockwise until the tire is raised to its original position underneath the vehicle. The effort to turn the jack handle increases significantly and the spare tire carrier ratchets when the tire is raised to the stowed position. The spare tire carrier has a built-in ratchet feature that will not allow you to overtighten. 4. Check that the tire lies flat to the frame assembly. Push against the tire to make sure it is tightly seated under the vehicle. Loosen or retighten if necessary. 5. If removed, install the spare tire lock into the bumper drive tube with the spare tire lock key and jack handle.
Tire change procedure 1. Park on a level surface, activate hazard flashers and set the parking brake. • Automatic transmission: Place gearshift lever in P (Park). • Manual transmission: Place gearshift lever in R (Reverse). • Electronic Shift On the Fly four wheel drive: Place transfer case in 2WD, 4x4 HIGH or 4x4 LOW. • Manual shift transfer case four wheel drive: Place transfer case in 2H, 4H or 4L.
181
Roadside emergencies
To prevent the vehicle from moving when you change a tire, be sure the parking brake is set, then block (in both directions) the wheel that is diagonally opposite (other side and end of the vehicle) to the tire being changed.
2. Turn engine OFF and block the diagonally opposite wheel (block not provided). 3. Remove the jack, jack handle, lug wrench and spare tire from the stowage locations. 4. Use the tip of the lug wrench to remove any wheel trim. 5. Loosen each wheel lug nut one-half turn counterclockwise but do not remove them until the wheel is raised off the ground.
When one of the rear wheels is off the ground, the transmission alone will not prevent the vehicle from moving or slipping off the
jack, even if the transmission is in P (Park) (automatic transmission) or R (Reverse) (manual transmission). To prevent the vehicle from moving when you change the tire, be sure that the parking brake is set and the diagonally opposite wheel is blocked.
If the vehicle slips off the jack, you or someone else could be seriously injured.
182
Roadside emergencies
The following steps apply to F250/F350 only: 6. Insert the hooked end of the jack handle into the jack and use the handle to slide the jack under the vehicle. 7. Position the jack according to the following guides:
• Front (4x2)
183
Roadside emergencies • Front passenger side (4x4)
• Front driver side (4x4) Make sure the jack fits into the notched area next to the differential housing.
• Rear
184
Roadside emergencies
Never use the front or rear differential as a jacking point.
To lessen the risk of personal injury, do not put any part of your body under the vehicle while changing a tire. Do not start the engine when your vehicle is on the jack. The jack is only meant for changing the tire.
8. Turn the jack handle clockwise until the wheel is completely off the ground and high enough to install the spare tire. 9. Remove the lug nuts with the lug wrench. 10. On single rear wheel vehicles, replace the flat tire with the spare tire, making sure the valve stem is facing outward for all front tires and vehicles equipped with single rear wheels. If replacing an inboard rear tire on a dual rear wheel vehicle, the valve stem must be facing outward. If replacing the outboard wheel, the valve stem must be facing inward. Reinstall the lug nuts until the wheel is snug against the hub. Do not fully tighten the lug nuts until the wheel has been lowered. 11. Lower the wheel by turning the jack handle counterclockwise. Go to step 19.
185
Roadside emergencies
The following steps apply to F350 chassis Cab F450/F550 only: 12. Slide the notched end of the jack handle over the release valve and use the handle to slide the jack under the vehicle. Make sure the valve is closed by turning it clockwise. 13. Position the jack according to the following guides:
• Front (4x2) F350
186
• Front (4x2) F450/550
Roadside emergencies
• Front driver side (4x4)
187
Roadside emergencies • Front passenger side (4x4)
• Rear
188
Roadside emergencies
14. Insert the jack handle into the pump linkage. 15. Use an up-and-down motion with the jack handle to raise the wheel completely off the ground. Hydraulic jacks are equipped with a pressure release valve that prevents lifting loads which exceed the jack’s rated capacity. 16. Remove the lug nuts with the lug wrench. 17. Replace the flat tire with the spare tire, making sure the valve stem is facing outward on all front an inboard rear wheels. If replacing the outboard wheel, the valve stem must be facing inward. Reinstall the lug nuts until the wheel is snug against the hub. Do not fully tighten the lug nuts until the wheel has been lowered. 18. Lower the wheel by slowly turning the release valve counterclockwise. Opening the release valve slowly will provide a more controlled rate of descent.
189
Roadside emergencies
The following steps apply to all vehicles: 19. Remove the jack and fully tighten the lug nuts in the order shown. 20. Stow the flat tire. Refer to Stowing the spare tire if the vehicle is equipped with a spare tire carrier. 21. Stow the jack, jack handle and lug wrench. Make sure the jack is securely fastened so it does not rattle when driving. 22. Unblock the wheels. On vehicles equipped with single rear wheels, retighten the lug nuts to the specified torque at 800 km (500 miles) after any wheel disturbance (tire rotation, changing a flat tire, wheel removal, etc.). On vehicles equipped with dual rear wheels, retighten the wheel lug nuts to the specified torque at 160 km (100 miles), and again at 800 km (500
miles) of new vehicle operation and after any wheel disturbance (tire rotation, changing a flat tire, wheel removal, etc.).Bolt size
Wheel lug nut torque*
Nm 200-225
Lb-ft 150-165
M14 x 1.5
* Torque specifications are for nut and bolt threads free of dirt and rust. Use only Ford recommended replacement fasteners. On all two-piece flat wheel nuts, apply one drop of motor oil between the flat washer and the nut. Do not apply motor oil to the wheel nut threads or the wheel stud threads.When a wheel is installed, always remove any corrosion, dirt or foreign materials present on the mounting surfaces of the wheel or the surface of the front disc brake hub and rotor that contacts the wheel. Installing wheels without correct metal-to-metal contact at the wheel mounting surfaces can cause the wheel nuts to loosen and the wheel to come off while the vehicle is in motion, resulting in loss of control.
190
Roadside emergencies
JUMP STARTING YOUR VEHICLE
The gases around the battery can explode if exposed to flames, sparks, or lit cigarettes. An explosion could result in injury or
vehicle damage.
Batteries contain sulfuric acid which can burn skin, eyes, and clothing, if contacted.
Do not attempt to push-start your vehicle. Automatic transmissions do not have push-start capability; also, the catalytic conveter may become damaged.
Preparing your vehicle When the battery is disconnected or a new battery is installed, the transmission must relearn its adaptive strategy. As a result of this, the transmission may shift firmly. This operation is considered normal and will not affect function or durability of the transmission. Over time, the adaptive learning process will fully update transmission operation to its optimum shift feel. 1. Use only a 12–volt supply to start your vehicle. 2. Do not disconnect the battery of the disabled vehicle as this could damage the vehicle’s electrical system. 3. Park the booster vehicle close to the hood of the disabled vehicle making sure the two vehicles do not touch. Set the parking brake on both vehicles and stay clear of the engine cooling fan and other moving parts. 4. Check all battery terminals and remove any excessive corrosion before you attach the battery cables. Ensure that vent caps are tight and level. 5. Turn the heater fan on in both vehicles to protect any electrical surges. Turn all other accessories off.
191
Roadside emergencies
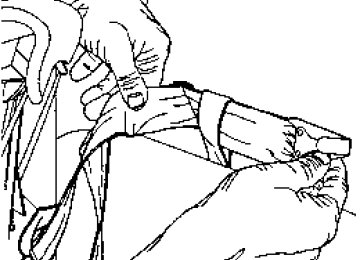
Connecting the jumper cables
+–
+–
1. Connect the positive (+) booster cable to the positive (+) terminal of the discharged battery. Note: In the illustrations, lightning bolts are used to designate the assisting (boosting) battery.
+–
+–
2. Connect the other end of the positive (+) cable to the positive (+) terminal of the assisting battery.
192
Roadside emergencies
+–
+–
3. Connect the negative (-) cable to the negative (-) terminal of the assisting battery.
+–
+–
4. Make the final connection of the negative (-) cable to an exposed metal part of the stalled vehicle’s engine, away from the battery and the carburetor/fuel injection system. Do not use fuel lines, engine rocker covers or the intake manifold as grounding points.
Do not connect the end of the second cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery to be jumped. A spark may cause an
explosion of the gases that surround the battery.
5. Ensure that the cables are clear of fan blades, belts, moving parts of both engines, or any fuel delivery system parts.
193
Roadside emergencies
Jump starting 1. Start the engine of the booster vehicle and run the engine at moderately increased speed. 2. Start the engine of the disabled vehicle. 3. Once the disabled vehicle has been started, run both engines for an additional three minutes before disconnecting the jumper cables.
Removing the jumper cables
+–
+–
Remove the jumper cables in the reverse order that they were connected. 1. Remove the jumper cable from the ground metal surface. Note: In the illustrations, lightning bolts are used to designate the assisting (boosting) battery.
+–
+–
2. Remove the jumper cable on the negative (-) connection of the booster vehicle’s battery.
194
Roadside emergencies
+–
+–
3. Remove the jumper cable from the positive (+) terminal of the booster vehicle’s battery.
+–
+–
4. Remove the jumper cable from the positive (+) terminal of the disabled vehicle’s battery. After the disabled vehicle has been started and the jumper cables removed, allow it to idle for several minutes so the engine computer can relearn its idle conditions. When the battery is disconnected or a new battery is installed, the transmission must relearn its adaptive strategy. As a result of this, the transmission may shift firmly. This operation is considered normal and will not effect function or durability of the transmission. Over time, the adaptive learning process will fully update transmission operation to its optimum shift feel.
195
Roadside emergencies
WRECKER TOWING
If you need to have your vehicle towed, contact a professional towing service or, if you are a member, your roadside assistance center. On 4x2 vehicles, it is acceptable to tow the vehicle with the front wheels on the ground and the rear wheels off the ground using a wheel lift or a slingbelt with T-hooks. On 4x4 vehicles, it is recommended that your vehicle be towed with a wheel lift or flatbed equipment with all the wheels off the ground. However, a slingbelt with T-hooks and a wheel dolly can also be used. If the vehicle is towed by other means or incorrectly, vehicle damage may occur. Ford Motor Company provides a towing manual for all authorized tow truck operators. Have your tow truck operator refer to this manual for proper hook-up and towing procedures for your vehicle.
196
Maintenance and care
SERVICE RECOMMENDATIONS To help you service your vehicle: • We highlight do-it-yourself items in the engine compartment for easy • We provide a scheduled maintenance guide which makes tracking
location.
routine service easy.
If your vehicle requires professional service, your dealership can provide the necessary parts and service. Check your Warranty Guide to find out which parts and services are covered. Use only recommended fuels, lubricants, fluids and service parts conforming to specifications. Motorcraft parts are designed and built to provide the best performance in your vehicle.
PRECAUTIONS WHEN SERVICING YOUR VEHICLE Be especially careful when inspecting or servicing your vehicle. • Do not work on a hot engine. • When the engine is running, keep loose clothing, jewelry or long hair • Do not work on a vehicle with the engine running in an enclosed • Keep all lit cigarettes, open flames and other lit material away from
space, unless you are sure you have enough ventilation.
away from moving parts.
the battery and all fuel related parts.
If you disconnect the battery, the engine must “relearn” its idle conditions before your vehicle will drive properly, as explained in the Battery section in this chapter.
197
Maintenance and care
Working with the engine off • Automatic transmission: 1. Set the parking brake and ensure the gearshift is securely latched in P (Park). 2. Turn off the engine and remove the key. 3. Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving unexpectedly. • Manual transmission: 1. Set the parking brake. 2. Depress the clutch and place the gearshift in 1 (First). 3. Turn off the engine and remove the key. 4. Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving unexpectedly.
Working with the engine on • Automatic transmission: 1. Set the parking brake and ensure the gearshift is securely latched in P (Park). 2. Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving unexpectedly. NOTE:Do not start your engine with the air cleaner removed and do not remove it while the engine is running. • Manual transmission: 1. Set the parking brake, depress the clutch and place the gearshift in neutral. 2. Block the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving unexpectedly. NOTE:Do not start your engine with the air cleaner removed and do not remove it while the engine is running.
The cooling fan is automatic and may come on at any time. Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before
working near the fan.
198
Maintenance and care
OPENING THE HOOD 1. Inside the vehicle, pull the hood release handle located under the bottom left corner of the instrument panel.
HOOD
2. Go to the front of the vehicle and release the auxiliary latch located under the right center of the hood. Slide the handle to release the auxiliary latch. 3. Lift the hood until the lift cylinders hold it open.
199
Maintenance and care
IDENTIFYING COMPONENTS IN THE ENGINE COMPARTMENT
5.4L V8/6.8L V10 gasoline engines Refer to the 7.3 Liter Power Stroke Direct Injection Turbo Diesel Owner’s Guide Supplement for diesel engine component locations.
10
11
1. Engine oil dipstick 2. Clutch fluid reservoir (manual transmission) 3. Brake fluid reservoir 4. Power distribution box 5. Power steering fluid reservoir 6. Air filter assembly 7. Engine coolant reservoir 8. Windshield washer fluid reservoir 9. Battery 10. Engine oil filler cap 11. Transmission fluid dipstick (automatic transmission)
200
Maintenance and care
ENGINE OIL
Checking the engine oil Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the appropriate intervals for checking the engine oil. 1. Make sure the vehicle is on level ground. 2. Turn the engine off and wait a few minutes for the oil to drain into the oil pan. 3. Set the parking brake and ensure the gearshift is securely latched in P (Park) (automatic transmission) or 1 (First) (manual transmission). 4. Open the hood. Protect yourself from engine heat. 5. Locate and carefully remove the engine oil level indicator (dipstick).
MIN
MAX
6. Wipe the indicator clean. Insert the indicator fully, then remove it again. • If the oil level is between the MIN and MAX marks, the oil level is
acceptable. DO NOT ADD OIL.
201
Maintenance and care • If the oil level is below the MIN mark, add enough oil to raise the level within the MIN-MAX range.
• Oil levels above the MAX mark may cause engine damage. Some oil
must be removed from the engine by a service technician.
7. Put the indicator back in and ensure it is fully seated.
Adding engine oil 1. Check the engine oil. For instructions, refer to Checking the engine oil in this chapter. 2. If the engine oil level is not within the normal range, add only certified engine oil of the recommended viscosity. Remove the engine oil filler cap and use a funnel to pour the engine oil into the opening. 3. Recheck the engine oil level. Make sure the oil level is not above the MAX mark on the engine oil level indicator (dipstick). 4. Install the indicator and ensure it is fully seated. 5. Fully install the engine oil filler cap by turning the filler cap clockwise 1/4 of a turn until three clicks are heard until it is latched. To avoid possible oil loss, DO NOT operate the vehicle with the engine oil level indicator and/or the engine oil filler cap removed.
202
Maintenance and care
Engine oil and filter recommendations Look for this certification trademark.
SAE 5W-20 engine oil is recommended. Only use oils “Certified For Gasoline Engines” by the American Petroleum Institute (API). Use Motorcraft or an equivalent oil meeting Ford specification WSS-M2C153–H. SAE 5W-20 oil provides optimum fuel economy and durability performance meeting all requirements for your vehicle’s engine. Do not use supplemental engine oil additives, oil treatments or engine treatments. They are unnecessary and could, under certain conditions, lead to engine damage which is not covered by your warranty. Change your engine oil and filter according to the appropriate schedule listed in the scheduled maintenance guide. Ford production and aftermarket (Motorcraft) oil filters are designed for added engine protection and long life. If a replacement oil filter is used that does not meet Ford material and design specifications, start-up engine noises or knock may be experienced. It is recommended you use the appropriate Motorcraft oil filter (or another brand meeting Ford specifications) for your engine application.
203
Maintenance and care
BRAKE FLUID
Checking and adding brake fluid Brake fluid should be checked and refilled as needed. Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the service interval schedules. 1. Clean the reservoir cap before removal to prevent dirt or water from entering the reservoir.
2. Visually inspect the fluid level. 3. If necessary, add brake fluid from a clean un-opened container until the level reaches MAX. Do not fill above this line. 4. Use only a DOT 3 brake fluid certified to meet Ford specification ESA-M6C25–A. Refer to Lubricant specifications in the Capacities and specifications chapter.
MAX
Brake fluid is toxic. If brake fluid contacts the eyes, flush eyes with running water for 15 minutes. Seek medical attention if
irritation persists. If taken internally, drink water and induce vomiting. Seek medical attention immediately.
If you use a brake fluid that is not DOT 3, you will cause permanent damage to your brakes.
Do not let the reservoir for the master cylinder run dry. This may cause the brakes to fail.
204
Maintenance and care
CLUTCH FLUID (IF EQUIPPED) Check the clutch fluid level. Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the service interval schedules. Use only a DOT 3 brake fluid designed to meet Ford specification ESA-M6C25–A. Refer to Capacities and specifications.
Brake fluid is toxic. If brake fluid contacts the eyes, flush eyes with running water for 15 minutes. Seek medical if irritation persists. If taken internally, drink water and induce vomiting. Seek medical attention immediately.
For vehicles equipped with the 6–speed manual transmission, during normal operation, the fluid level in the clutch reservoir should remain constant or rise slightly. If the fluid level drops, refill the fluid level to the step in the reservoir. For vehicles equipped with the 5–speed manual transmission, during normal operation, the fluid level in the clutch reservoir will drop slightly. As this occurs, refill the fluid level to the step in the reservoir. 1. Clean the reservoir cap before removal to prevent dirt and water from entering the reservoir. 2. Remove cap and rubber diaphragm from reservoir. 3. Add fluid until the level reaches the step in the reservoir. 4. Reinstall rubber diaphragm and cap onto reservoir.
205
Maintenance and care
WINDSHIELD WASHER FLUID
Washer fluid Check the washer fluid whenever you stop for fuel. The reservoir is highlighted with a If the level is low, add enough fluid to fill the reservoir. In very cold weather, do not fill the reservoir all the way.
symbol.
Only use a washer fluid that meets Ford specification . Refer to Lubricant specifications in the Capacities and specifications chapter. State or local regulations on volatile organic compounds may restrict the use of methanol, a common windshield washer antifreeze additive. Washer fluids containing non-methanol antifreeze agents should be used only if they provide cold weather protection without damaging the vehicle’s paint finish, wiper blades or washer system. Do not put washer fluid in the engine coolant reservoir. Washer fluid placed in the cooling system may harm engine and cooling system components.
ENGINE COOLANT
Checking engine coolant The concentration and level of engine coolant should be checked at the mileage intervals listed in the scheduled maintenance guide. The coolant concentration should be maintained at 50/50 coolant and water, which equates to a freeze point of -36° C (-34° F). Coolant concentration testing is possible with a hydrometer or antifreeze tester (such as the Rotunda Battery and Antifreeze Tester, 014–R1060). The level of coolant should be maintained at the “cold full” of “cold fill range” level in the coolant reservoir. If the level falls below, add coolant per the instructions in the Adding Engine Coolant section.
206
Maintenance and care
Your vehicle was factory-filled with a 50/50 engine coolant and water concentration. If the concentration of coolant falls below 40% or above 60%, the engine parts could become damaged or not work properly. A 50–50 mixture of coolant and water provides the following: • Freeze protection down to -36° C (-34° F). • Boiling protection up to 129° C (265° F). • Protection against rust and other forms of corrosion. • Enables calibrated gauges to work properly. When the engine is cold, check the level of the engine coolant in the reservoir.
MAX
MIN
COLD FILL RANGE
• The engine coolant should be at the “cold fill level” or within the “cold
fill range” as listed on the engine coolant reservoir (depending upon application).
• Refer to the Scheduled Maintenance Guide for service interval • Be sure to read and understand Precautions when servicing your
schedules.
vehicle in this chapter.
If the engine coolant has not been checked at the recommended interval, the engine coolant reservoir may become low or empty. If the reservoir is low or empty, add engine coolant to the reservoir. Refer to Adding engine coolant in this chapter. NOTE:Automotive fluids are not interchangeable; do not use engine coolant, antifreeze or windshield washer fluid outside of its specified function and vehicle location.
207
Maintenance and care
Adding engine coolant When adding coolant, make sure it is a 50/50 mixture of engine coolant and distilled water. Add the mixture to the coolant reservoir, when the engine is cool, until the appropriate fill level is obtained.
Do not add engine coolant when the engine is hot. Steam and scalding liquids released from a hot cooling system can burn you badly. Also, you can be burned if you spill coolant on hot engine parts.
Do not put engine coolant in the windshield washer fluid container. If sprayed on the windshield, engine coolant could
make it difficult to see through the windshield.
The cooling system in your vehicle is filled with either green-colored Motorcraft Premium Engine Coolant meeting Ford specification ESE-M97B44–A or yellow-colored Motorcraft Premium Gold Engine Coolant meeting Ford Specification WSS-M97B51–A1. To determine your vehicle’s coolant type (color), check your coolant reservoir. • Add Motorcraft Premium Engine Coolant (green-colored), VC-4–A (U.S.) or CXC-10 (Canada) or Motorcraft Premium Gold Engine Coolant (yellow-colored), VC-7–A, depending on the type of coolant originally equipped in your vehicle. If you are unsure which type of coolant your vehicle requires, check your coolant reservoir or contact your local dealer. • Do not add/mix an orange-colored, extended life coolant such as Motorcraft Speciality Orange Engine Coolant, VC-2 (US) or CXC-209 (Canada), meeting Ford specification WSS-M97B44–D with the factory-filled coolant. Mixing Motorcraft Speciality Orange Engine Coolant or any orange-colored extended life product with your factory filled coolant can result in degraded corrosion protection. • A large amount of water without engine coolant may be added, in case of emergency, to reach a vehicle service location. In this instance, the cooling system must be drained and refilled with a 50/50 mixture of engine coolant and distilled water as soon as possible. Water alone (without engine coolant) can cause engine damage from corrosion, overheating or freezing.
208
Maintenance and care • Do not use alcohol, methanol or brine or any engine coolants mixed with alcohol or methanol antifreeze (coolant). Alcohol and other liquids can cause engine damage from overheating or freezing.
• Do not add extra inhibitors or additives to the coolant. These
can be harmful and compromise the corrosion protection of the engine coolant. • Do not mix with recycled coolant unless from a Ford-approved recycling process (see Use of Recycled Engine Coolant section). For vehicles with overflow coolant systems with a non-pressurized cap on the coolant recovery system, add coolant to the coolant recovery reservoir when the engine is cool. Add the proper mixture of coolant and water to the “cold full” level. For all other vehicles, which have a coolant degas system with a pressurized cap, or if it is necessary to remove the coolant pressure relief cap on the radiator of a vehicle with an overflow system, follow these steps to add engine coolant.
To avoid personal injury, make sure the engine is cool before unscrewing the coolant pressure relief cap. The cooling system is under pressure; steam and hot liquid can come out forcefully when the cap is loosened slightly.
1. Before you begin, turn the engine off and let it cool. 2. When the engine is cool, wrap a thick cloth around the coolant pressure relief cap on the coolant reservoir (an opaque plastic bottle). Slowly turn cap counterclockwise (left) until pressure begins to release. 3. Step back while the pressure releases. 4. When you are sure that all the pressure has been released, use the cloth to turn it counterclockwise and remove the cap. 5. Fill the coolant reservoir slowly with the proper coolant mixture (see above), to within the “cold fill range” or the “cold full” level on the reservoir. If you removed the radiator cap in an overflow system, fill the radiator until the coolant is visible and radiator is almost full. 6. Replace the cap. Turn until tightly installed. (Cap must be tightly installed to prevent coolant loss.)
209
Maintenance and care
After any coolant has been added, check the coolant concentration see Checking Engine Coolant section). If the concentration is not 50/50
(protection to –34°F/–36°C), drain some coolant and adjust the concentration. It may take several drains and additions to obtain a 50/50
coolant concentration. Whenever coolant has been added, the coolant level in the coolant reservoir should be checked the next few times you drive the vehicle. If necessary, add enough 50/50 concentration of engine coolant and distilled water to bring the liquid level to the proper level. If you have to add more than 1.0 liter (1.0 quart) of engine coolant per month, have your dealer check the engine cooling system. Your cooling system may have a leak. Operating an engine with a low level of coolant can result in engine overheating and possible engine damage.Recycled engine coolant Ford Motor Company recommends the use of a recycled engine coolant produced by Ford-approved processes in vehicles originally equipped with Motorcraft Premium Engine Coolant (green-colored). However, not all coolant recycling processes produce coolant that meets Ford specification ESE-M97B44–A. Use of such coolant may harm the engine and cooling system components. Ford Motor Company does NOT recommend the use of recycled engine coolant in vehicles originally equipped with Motorcraft Premium Gold Engine Coolant since a Ford-approved recycling process is not yet available.
Used engine coolant should be disposed of in an appropriate
manner. Follow your community’s regulations and standards for recycling and disposing of automotive fluids.
Coolant refill capacity To find out how much fluid your vehicle’s cooling system can hold, refer to Refill capacities in the Capacities and specifications chapter. Fill your engine coolant reservoir as outlined in Adding engine coolant in this chapter.
Severe climates If you drive in extremely cold climates (less than –36° C [–34° F]), it may be necessary to increase the coolant concentration above 50%.
210
Maintenance and care
Refer to the chart on the coolant container to ensure the coolant concentration in your vehicle will provide adequate freeze protection. Never increase the engine coolant concentration above 60% (protection to –60°F). At a level over 60%, your engine could overheat and become damaged. If you drive in extremely hot climates, it is still necessary to maintain the coolant concentration at 50/50 coolant and water. Do not allow the coolant concentration to fall below 40% coolant. At a concentration less than 40%, the corrosion protection to your engine and cooling components may be compromised and permanent damage may result.
What you should know about fail-safe cooling (if equipped) If the engine coolant supply is depleted, this feature allows the vehicle to be driven temporarily before incremental component damage is incurred. The “fail-safe” distance depends on ambient temperatures, vehicle load and terrain. How fail-safe cooling works If the engine begins to overheat: • The engine coolant temperature gauge will move to the red (hot) area. • The • The Service Engine Soon
symbol will
illuminate.
and
indicator light will illuminate.
If the engine reaches a preset over-temperature condition, the engine will automatically switch to alternating cylinder operation. Each disabled cylinder acts as an air pump and cools the engine. When this occurs the vehicle will still operate. However: • The engine power will be limited. • The air conditioning system will be disabled. Continued operation will increase the engine temperature and the engine will completely shut down, causing steering and braking effort to increase. Once the engine temperature cools, the engine can be re-started. Take your vehicle to a service facility as soon as possible to minimize engine damage.
211
Maintenance and care
When fail-safe mode is activated You have limited engine power when in the fail-safe mode, so drive the vehicle with caution. The vehicle will not be able to maintain high-speed operation and the engine will run rough. Remember that the engine is capable of completely shutting down automatically to prevent engine damage, therefore: 1. Pull off the road as soon as safely possible and turn off the engine. 2. Arrange for the vehicle to be taken to a service facility. 3. If this is not possible, wait a short period for the engine to cool. 4. Check the coolant level and replenish if low.
Never remove the coolant reservoir cap while the engine is running or hot.
5. Re-start the engine and take your vehicle to a service facility. Driving the vehicle without repairing the engine problem increases the chance of engine damage. Take your vehicle to a service facility as soon as possible.
212
Maintenance and care
CHECKING AND ADDING POWER STEERING FLUID Check the power steering fluid. Refer to the scheduled maintenance guide for the service interval schedules. If adding fluid is necessary, use only MERCON威 ATF.
Check the fluid level when it is at ambient temperature, 20° – 80° F (-7° – 25° C): 1. Check the fluid level on the dipstick. It should be between the arrows in the FULL COLD range. Do not add fluid if the level is within this range. 2. If the fluid level is low, start the engine. 3. While the engine idles, turn the steering wheel left and right several times. 4. Turn the engine off. 5. Recheck the fluid level on the dipstick. Do not add fluid if the level is between the arrows in the FULL COLD range. 6. If the fluid is low, add fluid in small amounts, continuously checking the level until it reaches the FULL COLD range. Be sure to put the dipstick back in the reservoir.
213
Maintenance and care
TRANSMISSION FLUID
Checking automatic transmission fluid (if equipped) Refer to your scheduled maintenance guide for scheduled intervals for fluid checks and changes. Your transmission does not consume fluid. However, the fluid level should be checked if the transmission is not working properly, i.e., if the transmission slips or shifts slowly or if you notice some sign of fluid leakage. Automatic transmission fluid expands when warmed. To obtain an accurate fluid check, drive the vehicle until it is at normal operating temperature (approximately 30 km [20 miles]). If your vehicle has been operated for an extended period at high speeds, in city traffic during hot weather or pulling a trailer, the vehicle should be turned off for about 30
minutes to allow fluid to cool before checking. 1. Drive the vehicle 30 km (20 miles) or until it reaches normal operating temperature. 2. Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. 3. With the parking brake engaged and your foot on the brake pedal, start the engine and move the gearshift lever through all of the gear ranges. Allow sufficient time for each gear to engage. 4. Latch the gearshift lever in P (Park) and leave the engine running. 5. Remove the dipstick, wiping it clean with a clean, dry lint free rag. If necessary, refer to Identifying components in the engine compartment in this chapter for the location of the dipstick. 6. Install the dipstick making sure it is fully seated in the filler tube. 7. Remove the dipstick and inspect the fluid level. The fluid should be in the designated area for normal operating temperature or ambient temperature. Low fluid level Do not drive the vehicle if the fluid level is at the bottom of the dipstick and the ambient temperature is above 10°C (50°F).DO NOT ADD
COLD
ADD
HOT
DON'T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCHED AREA (cid:127) CHECK WHEN HOT
IDLING IN PARK
214
Maintenance and care
HOT
ADD
COLD
DO NOT ADD
DON'T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCHED AREA (cid:127) CHECK WHEN HOT
Correct fluid level The transmission fluid should be checked at normal operating temperature 66°C-77°C (150°F-170°F) on a level surface. The normal operating temperature can be reached after approximately 30 km (20 miles) of driving. You can check the fluid without driving if the ambient temperature is above 10°C (50°F). However, if fluid is added at this time, an overfill condition could result when the vehicle reaches normal operating temperature. The transmission fluid should be in this range if at normal operating temperature (66°C-77°C [150°F-170°F]). The transmission fluid should be in this range if at ambient temperature (10°C-35°C [50°F-95°F]). High fluid level Fluid levels above the safe range may result in transmission failure. An overfill condition of transmission fluid may cause shift and/or engagement concerns and/or possible damage. High fluid levels can be caused by an overheating condition. Adjusting automatic transmission fluid levels Before adding any fluid, make sure the correct type is used. The type of fluid used is normally indicated on the dipstick and also in the Lubricant specifications section in the Capacities and specifications chapter. Use of a non-approved automatic transmission fluid may cause internal transmission component damage. If necessary, add fluid in 250 ml (1/2 pint) increments through the filler tube until the level is correct.
DON'T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCHED AREA (cid:127) CHECK WHEN HOT
DON'T ADD IF IN CROSSHATCHED AREA (cid:127) CHECK WHEN HOT
DO NOT ADD
DO NOT ADD
COLD
COLD
IDLING IN PARK
IDLING IN PARK
IDLING IN PARK
ADD
ADD
HOT
HOT
215
Maintenance and care
If an overfill occurs, excess fluid