- 2000 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 1999 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2001 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2007 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2003 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2006 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2005 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2002 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2004 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2008 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 1998 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- 2009 GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- GMC Envoy Owners Manuals
- Download PDF Manual
-
When you are doing this check, your vehicle could begin to move. You or others could be injured and property could be damaged. Make sure there is room in front of your vehicle in case it begins to roll. Be ready to apply the regular brake at once should the vehicle begin to move.
Park on a fairly steep hill, with the vehicle facing downhill. Keeping your foot on the regular brake, set the parking brake. D To check the parking brake’s holding ability: With
the engine running and transmission in NEUTRAL (N), slowly remove foot pressure from the regular brake pedal. Do this until the vehicle is held by the parking brake only.
D To check the PARK (P) mechanism’s holding ability:
With the engine running, shift to PARK (P). Then release the parking brake followed by the regular brake.
Underbody Flushing Service At least every spring, use plain water to flush any corrosive materials from the underbody. Take care to clean thoroughly any areas where mud and other debris can collect.
7-19
Part C: Periodic Maintenance Inspections Listed in this part are inspections and services which should be performed at least twice a year (for instance, each spring and fall). You should let your dealer’s service department or other qualified service center do these jobs. Make sure any necessary repairs are completed at once. Proper procedures to perform these services may be found in a service manual. See “Service and Owner Publications” in the Index. Steering, Suspension and Front Drive Axle Boot and Seal Inspection Inspect the front and rear suspension and steering system for damaged, loose or missing parts, signs of wear or lack of lubrication. Inspect the power steering lines and hoses for proper hook-up, binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Clean and then inspect the drive axle boot seals for damage, tears or leakage. Replace seals if necessary.
Exhaust System Inspection Inspect the complete exhaust system. Inspect the body near the exhaust system. Look for broken, damaged, missing or out-of-position parts as well as open seams, holes, loose connections or other conditions which could cause a heat build-up in the floor pan or could let exhaust fumes into the vehicle. See “Engine Exhaust” in the Index. Fuel System Inspection Inspect the complete fuel system for damage or leaks. Engine Cooling System Inspection Inspect the hoses and have them replaced if they are cracked, swollen or deteriorated. Inspect all pipes, fittings and clamps; replace as needed. Clean the outside of the radiator and air conditioning condenser. To help ensure proper operation, a pressure test of the cooling system and pressure cap is recommended at least once a year.
7-20
Transfer Case and Front Axle (Four-Wheel Drive) Inspection Every 12 months or at engine oil change intervals, check front axle and transfer case and add lubricant when necessary. A fluid loss could indicate a problem; check and have it repaired, if needed. Check vent hose at transfer case for kinks and proper installation. More frequent lubrication may be required on off-road use.
Brake System Inspection Inspect the complete system. Inspect brake lines and hoses for proper hook-up, binding, leaks, cracks, chafing, etc. Inspect disc brake pads for wear and rotors for surface condition. Inspect other brake parts, including calipers, parking brake, etc. Check parking brake adjustment. You may need to have your brakes inspected more often if your driving habits or conditions result in frequent braking.
7-21
Part D: Recommended Fluids and Lubricants Fluids and lubricants identified below by name, part number or specification may be obtained from your dealer.
USAGE
Engine Oil
Engine Coolant
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Engine oil with the American Petroleum Institute Certified for Gasoline Engines starburst symbol of the proper viscosity. To determine the preferred viscosity for your vehicle’s engine, see “Engine Oil” in the Index.
50/50 mixture of clean, drinkable water and use only GM GoodwrenchR DEX-COOLR or HavolineR DEX-COOLR Coolant. See “Engine Coolant” in the Index.
USAGE
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Hydraulic Brake System
Windshield Washer Solvent
Parking Brake Cable Guides
Power Steering System
Automatic Transmission
Delco Supreme 11R Brake Fluid (GM Part No. 12377967 or equivalent DOT-3 brake fluid). GM OptikleenR Washer Solvent (GM Part No. 1051515) or equivalent.
Chassis Lubricant (GM Part No. 12377985 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB. GM Power Steering Fluid (GM Part No. 1052884 - 1 pint, 1050017 - 1 quart, or equivalent). DEXRONR-III Automatic Transmission Fluid.
7-22
USAGE
FLUID/LUBRICANT
USAGE
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Key Lock Cylinders
Multi-Purpose Lubricant, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12346241 or equivalent).
Chassis Lubrication
Front and Rear Axle
Automatic Transfer Case
Chassis Lubricant (GM Part No. 12377985 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB. SAE 75W-90 Synthetic Axle Lubricant (GM Part No. 12378261) or equivalent meeting GM Specification 9986115. AUTO-TRAK II Fluid (GM Part No. 12378508).
Rear Driveline Center Spline and Universal Joints
Constant Velocity Universal Joint
Hood Latch Assembly, Secondary Latch, Pivots, Spring Anchor and Release Pawl
Chassis Lubricant (GM Part No. 12377985 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB. Chassis Lubricant (GM Part No. 12377985 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB. LubriplateR Lubricant Aerosol (GM Part No. 12346293 or equivalent) or lubricant meeting requirements of NLGI # 2, Category LB or GC-LB.
7-23
USAGE
FLUID/LUBRICANT
USAGE
FLUID/LUBRICANT
Multi-Purpose Lubricant, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12346241 or equivalent). Multi-Purpose Lubricant, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12346241 or equivalent).
Hood and Door Hinges
Body Door Hinge Pins, Liftgate Hinge and Linkage, Folding Seats and Fuel Door Hinge
Outer Tailgate Handle Pivot Points and Hinges
Weatherstrip Conditioning
Weatherstrip Squeaks
Multi-Purpose Lubricant, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12346241 or equivalent).
Dielectric Silicone Grease (GM Part No. 12345579 or equivalent).
Synthetic Grease with Teflon, SuperlubeR (GM Part No. 12371287 or equivalent).
7-24
Part E: Maintenance Record After the scheduled services are performed, record the date, odometer reading and who performed the service in the boxes provided after the maintenance interval. Any additional information from “Owner Checks and Services” or “Periodic Maintenance” can be added on the following record pages. Also, you should retain all maintenance receipts. Your owner information portfolio is a convenient place to store them.
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-25
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-26
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-27
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-28
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-29
DATE
ODOMETER
READING
SERVICED BY
MAINTENANCE PERFORMED
Maintenance Record
7-30
Section 8 Customer Assistance Information
Here you will find out how to contact GMC if you need assistance. This section also tells you how to obtain service publications and how to report any safety defects.
8-2
8-48-4
8-58-6
8-7Customer Satisfaction Procedure Customer Assistance for Text Telephone (TTY) Users Customer Assistance Offices GM Mobility Program for Persons with Disabilities Roadside Assistance Canadian Roadside Assistance
8-8
8-10
8-108-11
8-11
Courtesy Transportation Warranty Information Reporting Safety Defects to the United States Government Reporting Safety Defects to the Canadian Government Reporting Safety Defects to General Motors
8-
8-1
Customer Satisfaction Procedure
Your satisfaction and goodwill are important to your dealer and to GMC. Normally, any concerns with the sales transaction or the operation of your vehicle will be resolved by your dealer’s sales or service departments. Sometimes, however, despite the best intentions of all concerned, misunderstandings can occur. If your concern has not been resolved to your satisfaction, the following steps should be taken: STEP ONE -- Discuss your concern with a member of dealership management. Normally, concerns can be quickly resolved at that level. If the matter has already been reviewed with the sales, service or parts manager, contact the owner of the dealership or the general manager.
8-2
STEP TWO -- If after contacting a member of dealership management, it appears your concern cannot be resolved by the dealership without further help, contact the GMC Consumer Relations Manager by calling 1-800-GMC-8782 (1-800-462-8782, Customer Assistance prompt). In Canada, contact GM of Canada Customer Communication Centre in Oshawa by calling 1-800-263-3777 (English) or 1-800-263-7854 (French). We encourage you to call the toll-free number in order to give your inquiry prompt attention. Please have the following information available to give the Customer Assistance Representative: D Vehicle Identification Number (This is available from the vehicle registration or title, or the plate at the top left of the instrument panel and visible through the windshield.)
D Dealership name and location D Vehicle delivery date and present mileage When contacting GMC, please remember that your concern will likely be resolved at a dealer’s facility. That is why we suggest you follow Step One first if you have a concern.
STEP THREE -- Both General Motors and your dealer are committed to making sure you are completely satisfied with your new vehicle. However, if you continue to remain unsatisfied after following the procedure outlined in Steps One and Two, you should file with the GM/BBB Auto Line Program to enforce any additional rights you may have. Canadian owners refer to your Warranty and Owner Assistance Information booklet for information on the Canadian Motor Vehicle Arbitration Plan (CAMVAP). The BBB Auto Line Program is an out of court program administered by the Council of Better Business Bureaus to settle automotive disputes regarding vehicle repairs or the interpretation of the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. Although you may be required to resort to this informal dispute resolution program prior to filing a court action, use of the program is free of charge and your case will generally be heard within 40 days. If you do not agree with the decision given in your case, you may reject it and proceed with any other venue for relief available to you.
8-3
Customer Assistance Offices GMC encourages customers to call the toll-free number for assistance. If a U.S. customer wishes to write to GMC, the letter should be addressed to GMC’s Customer Assistance Center. United States
Pontiac-GMC Customer Assistance Center P.O. Box 33172
Detroit, MI 48232-5172
1-800-GMC-8782 (462-8782) 1-800-GMC-8583 (462-8583)(For Text Telephone devices (TTYs))
Roadside Assistance: 1-800-GMC-8782 (462-8782) From: Puerto Rico:
1-800-496-9992 (English) 1-800-496-9993 (Spanish) 1-800-496-9994
U.S. Virgin Islands:
Fax Number: 313-381-0022
You may contact the BBB using the toll-free telephone number or write them at the following address:
BBB Auto Line Council of Better Business Bureaus, Inc. 4200 Wilson Boulevard Suite 800
Arlington, VA 22203-1804
Telephone: 1-800-955-5100This program is available in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Eligibility is limited by vehicle age, mileage and other factors. General Motors reserves the right to change eligibility limitations and/or discontinue its participation in this program. Customer Assistance for Text Telephone (TTY) Users To assist customers who are deaf, hard of hearing, or speech-impaired and who use Text Telephones (TTYs), GMC has TTY equipment available at its Customer Assistance Center. Any TTY user can communicate with GMC by dialing: 1-800-GMC-8583 (462-8583). (TTY users in Canada can dial 1-800-263-3830.)
8-4
Canada
General Motors of Canada Limited Customer Communication Centre, 163-005
1908 Colonel Sam Drive Oshawa, Ontario L1H 8P7
1-800-263-3777 (English) 1-800-263-7854 (French) 1-800-263-3830 (For Text Telephone devices (TTYs)) Roadside Assistance: 1-800-268-6800All Overseas Locations Please contact the local General Motors Business Unit. Mexico, Central America and Caribbean Islands/Countries (Except Puerto Rico and U.S. Virgin Islands)
General Motors de Mexico, S. de R.L. de C.V. Customer Assistance Center Paseo de la Reforma # 2740
Col. Lomas de Bezares C.P. 11910, Mexico, D.F. 01-800-508-0000
Long Distance: 011-52 - 53 29 0 800GM Mobility Program for Persons with Disabilities
This program, available to qualified applicants, can reimburse you up to $1,000
toward aftermarket driver or passenger adaptive equipment you may require for your vehicle (hand controls, wheelchair/scooter lifts, etc.).This program can also provide you with free resource information, such as area driver assessment centers and mobility equipment installers. The program is available for a limited period of time from the date of vehicle purchase/lease. See your dealer for more details or call the GM Mobility Assistance Center at 1-800-323-9935. Text telephone (TTY) users, call 1-800-833-9935. GM of Canada also has a Mobility Program. Call 1-800-GM-DRIVE (463-7483) for details. When calling from outside Canada, please dial 1-905-644-3063. All TTY users call 1-800-263-3830.
8-5
Roadside Assistance
GMC’s Roadside Assistance provides stranded owners with over-the-phone roadside repairs, location of the nearest GMC dealer or the following special services: Flat Tire Change: Installation of spare tire will be covered at no charge (customer is responsible for repair or replacement of tire).
8-6
Fuel Delivery: Delivery of enough fuel for the customer to get to the nearest service station (up to $5.00) will be covered. Jump Start: No-start situations which require a battery jump start will be covered at no charge. Lock Out: Replacement keys or locksmith service will be covered at no charge if you are unable to gain entry into your vehicle. Delivery of the replacement key will be covered at no charge within 10 miles (16 km). Emergency Towing Service: Towing to the nearest GMC dealer for warranty related disablements will be covered. Trip Routing: Custom-made, computerized highlighted maps using the most direct or scenic route are provided free of charge. Maps include points of interest and a list of GMC dealers along the route. Also included is a list of hotels along the route that are discounted through affiliation with “Quest International.” Trip Routing is available through Roadside Assistance by calling 1-800-GMC-8782 (462-8782). Please be prepared to provide your Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). Allow five working days for fulfillment.
Trip Interruption Assistance: GMC will reimburse any reasonable trip interruption expenses (up to $500.00) when directly associated with warranty disablement. Trip Interruption service covers expenses such as meals and overnight lodging if vehicle disablement occurs at least 150 miles (240 km) from your home or rental property. You will be required to obtain prior approval from GMC Roadside Assistance and pay for expenses at the time of disablement. Original receipts should be submitted to GMC Roadside Assistance for reimbursement. A service representative will provide assistance when you call. The Roadside Assistance services listed are available to retail and retail lease customers operating 2002 GMC light duty trucks for a period of 3 years/36,000 miles (60 000 km). All services must be pre-arranged by GMC Roadside Assistance. Over-the-phone assistance, such as providing the name of the closest dealer or minor technical advice, etc., is available to all owner/operators of GMC trucks, regardless of vehicle or mileage. Just dial GMC Roadside Assistance at 1-800-GMC-8782
(1-800-462-8782, Roadside Assistance prompt) to reach a qualified representative who can assist you. Text telephone (TTY) users, call 1-888-889-2438.Your Roadside Assistance representative will ask for the following information when your call is received: D Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) D Name and home address D Telephone number and location from which you
are calling
D Location, license plate number and color of your
GMC truck
D Mileage of vehicle and description of problem Roadside Assistance is available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, 365 days a year, including weekends and holidays. Should you have any questions about roadside assistance, call the GMC Roadside Assistance Center or contact your dealer. Roadside Assistance is not part of or included in the coverage provided by the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. GMC reserves the right to make any changes or discontinue the Roadside Assistance program at any time without notification. Canadian Roadside Assistance Vehicles purchased in Canada have an extensive Roadside Assistance program accessible from anywhere in Canada or the United States. Please refer to the separate brochure provided by the dealer or call 1-800-268-6800 for emergency services.
8-7
Courtesy Transportation GMC has always exemplified quality and value in its offering of motor vehicles. To enhance your ownership experience, we and our participating dealers are proud to offer Courtesy Transportation, a customer support program for new vehicles. The Courtesy Transportation program is offered to retail purchase/lease customers in conjunction with the Bumper-to-Bumper coverage provided by the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. Several transportation options are available when warranty repairs are required. This will reduce your inconvenience during warranty repairs. Plan Ahead When Possible When your vehicle requires warranty service, you should contact your dealer and request an appointment. By scheduling a service appointment and advising your service consultant of your transportation needs, your dealer can help minimize your inconvenience.
If your vehicle cannot be scheduled into the service department immediately, keep driving it until it can be scheduled for service, unless, of course, the problem is safety-related. If it is, please call your dealership, let them know this, and ask for instructions. If the dealer requests that you simply drop the vehicle off for service, you are urged to do so as early in the work day as possible to allow for same day repair. Transportation Options Warranty service can generally be completed while you wait. However, if you are unable to wait GMC helps minimize your inconvenience by providing several transportation options. Depending on the circumstances, your dealer can offer you one of the following:
Shuttle Service Participating dealers can provide you with shuttle service to get you to your destination with minimal interruption of your daily schedule. This includes a one way shuttle ride to a destination up to 10 miles from the dealership.
8-8
Public Transportation or Fuel Reimbursement If your vehicle requires overnight warranty repairs, reimbursement up to $30 per day (five days maximum) may be available for the use of public transportation such as taxi or bus. In addition, should you arrange transportation through a friend or relative, reimbursement for reasonable fuel expenses up to $10 per day (five day maximum) may be available. Claim amounts should reflect actual costs and be supported by original receipts.
Courtesy Rental Vehicle When your vehicle is unavailable due to overnight warranty repairs, your dealer may arrange to provide you with a courtesy rental vehicle or reimburse you for a rental vehicle you obtained, at actual cost, up to a maximum of $30.00 per day supported by receipts. This requires that you sign and complete a rental agreement and meet state, local and rental vehicle provider requirements. Requirements vary and may include minimum age requirements, insurance coverage, credit card, etc.
You are responsible for fuel usage charges and may also be responsible for taxes, levies, usage fees, excessive mileage or rental usage beyond the completion of the repair. Generally it is not possible to provide a like-vehicle as a courtesy rental. Additional Program Information Courtesy Transportation is available during the Bumper-to-Bumper warranty coverage period, but it is not part of the New Vehicle Limited Warranty. A separate booklet entitled “Warranty and Owner Assistance Information” furnished with each new vehicle provides detailed warranty coverage information. Courtesy Transportation is available only at participating dealers and all program options, such as shuttle service, may not be available at every dealer. Please contact your dealer for specific information about availability. All Courtesy Transportation arrangements will be administered by appropriate dealer personnel.
8-9
Canadian Vehicles: For warranty repairs during the Complete Vehicle Coverage period of the General Motors of Canada New Vehicle Limited Warranty, alternative transportation may be available under the Courtesy Transportation Program. Please consult your dealer for details. General Motors reserves the right to unilaterally modify, change or discontinue Courtesy Transportation at any time and to resolve all questions of claim eligibility pursuant to the terms and conditions described herein at its sole discretion. Warranty Information Your vehicle comes with a separate warranty booklet that contains detailed warranty information.
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS TO THE UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT If you believe that your vehicle has a defect which could cause a crash or could cause injury or death, you should immediately inform the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), in addition to notifying General Motors. If NHTSA receives similar complaints, it may open an investigation, and if it finds that a safety defect exists in a group of vehicles, it may order a recall and remedy campaign. However, NHTSA cannot become involved in individual problems between you, your dealer or General Motors. To contact NHTSA, you may either call the Auto Safety Hotline toll-free at 1-800-424-9393 (or 366-0123 in the Washington, D.C. area) or write to:
NHTSA, U.S. Department of Transportation Washington, D.C. 20590
You can also obtain other information about motor vehicle safety from the hotline.
8-10
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS TO THE CANADIAN GOVERNMENT If you live in Canada, and you believe that your vehicle has a safety defect, you should immediately notify Transport Canada, in addition to notifying General Motors of Canada Limited. You may write to:
REPORTING SAFETY DEFECTS TO GENERAL MOTORS In addition to notifying NHTSA (or Transport Canada) in a situation like this, we certainly hope you’ll notify us. Please call us at 1-800-GMC-8782
(1-800-462-8782), or write:Transport Canada 330 Sparks Street Tower C Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0N5
Pontiac-GMC Customer Assistance Center P.O. Box 33172
Detroit, MI 48232-5172In Canada, please call us at 1-800-263-3777 (English) or 1-800-263-7854 (French). Or, write: General Motors of Canada Limited Customer Communication Centre, 163-005
1908 Colonel Sam Drive Oshawa, Ontario L1H 8P78-11
2002 GMC SERVICE PUBLICATIONS ORDERING INFORMATION
The following publications covering the operation and servicing of your vehicle can be purchased by filling out
the Service Publication Order Form in this book and mailing it in with your check, money order,
or credit card information to Helm, Incorporated (address below.)
CURRENT PUBLICATIONS FOR 2002 GMC
SERVICE MANUALS Service Manuals have the diagnosis and repair information on engines, transmission, axle, suspension, brakes, electrical, steering, body, etc. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $120.00
OWNER’S INFORMATION Owner publications are written directly for Owners and intended to provide basic operational information about the vehicle. The owner’s manual will include the Maintenance Schedule for all models.
TRANSMISSION, TRANSAXLE, TRANSFER CASE UNIT REPAIR MANUAL This manual provides information on unit repair service procedures, adjustments and specifications for the 2002 GM transmissions, transaxles and transfer cases. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $50.00
SERVICE BULLETINS Service Bulletins give technical service information needed to knowledgeably service General Motors cars and trucks. Each bulletin contains instructions to assist in the diagnosis and service of your vehicle.
PLEASE COMPLETE THE ORDER FORM SHOWN ON THE FOLLOWING PAGE AND MAIL TO:
Helm, Incorporated S P.O. Box 07130 S Detroit, MI 48207
8-12
In-Portfolio: Includes a Portfolio, Owner’s Manual and Warranty Booklet. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $20.00
Without Portfolio: Owner’s Manual only. RETAIL SELL PRICE: $15.00
CURRENT & PAST MODEL ORDER FORMS Service Publications are available for current and past model GM vehicles. To request an order form, please specify year and model name of the vehicle.
OR ORDER TOLL FREE: 1-800-551-4123
Monday-Friday 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM Eastern Time Visit Helm, Inc. on the World Wide Web at: www.helminc.com For Credit Card Orders Only (VISA–MasterCard–Discover)
ORDER TOLL FREE
(NOTE: For Credit Card Holders Only)
1-800-551-4123
(Monday-Friday 8:00 AM – 6:00 PM EST)
FAX Orders Only 1-313-865-5927 www.helminc.com
Orders will be mailed within 10 days of receipt. Please allow adequate time for postal service. If further information is needed, write to the address shown below or call 1-800-551-4123. Material cannot be returned for credit without packing slip with return information within 30 days of delivery. On returns, a re-stocking fee may be applied against the original order.
PUBLICATION FORM PUBLICATION FORM
NUMBER NUMBER
ITEM DESCRIPTION
Service Manual Car & Light Truck Transmission Unit Repair
Owner’s Manual In Portfolio
Owner’s Manual Without Portfolio
VEHICLE MODEL
NAME
TOTAL PRICE
YEAR 2002
2002
2002
2002
QTY.
PRICE EACH*
$120.00
$50.00
$20.00
$15.00
NOTE: Dealers and Companies please provide dealer or company name, and also the name of the person to whose attention the shipment should be sent. Mail completed order form to:
HELM, INCORPORATED S P.O. Box 07130 S Detroit, MI 48207
For purchases outside U.S.A. please write to the above address for quotation.(CUSTOMER’S NAME)
(ATTENTION)
(STREET ADDRESS—NO P.O. BOX NUMBERS)
(CITY)
(STATE)
DAYTIME TELEPHONE NO.
( )
AREA CODE
(ZIP CODE)
Check or Money Order payable to Helm, Inc. (USA funds only — do not send cash.)
MasterCard
VISA
Discover
Account Number: Expiration Date mo/yr:
CUSTOMER SIGNATURE
TOTAL MATERIAL
Michigan Purchasers add 6% sales tax U.S. Order Processing Canadian customers add $3.00 to U.S. order processing
GRAND TOTAL
$6.50
Check here if your billing address is different from your shipping address shown.
GM-GMC-ORD99
*(Prices are subject to change without notice and without incurring obligation. Allow ample time for delivery.)
Note to Canadian Customers: All listed prices are quoted in U.S. funds. Canadian residents 8-13
are to make checks payable in U.S. funds.2002 GMC Envoy Owner's Manual
Litho in U.S.A. Part Number X2238 A First Edition
© Copyright General Motors Corporation 2000
All Rights ReservedTable of Contents
Section 1
Seats and Seat Controls Safety Belts
Seats and Restraint Systems
Air Bag Systems Restraint Systems for Children
Windows Keys and Door Locks Remote Keyless Entry System Liftgate/Liftglass Automatic Transmission Four-Wheel Drive (If Equipped) Parking Brake Tilt Wheel Turn Signal/Multifunction Lever Windshield Wipers
Features and Controls
Cruise Control Exterior and Interior Lamps Mirrors Storage Compartments Luggage Carrier Accessory Power Outlets OnStar® System (If Equipped) Sunroof (Option) HomeLink® Transmitter Instrument Panel, Warning Lights and Gages
Section 2
ii
Table of Contents (cont'd)
Comfort Controls and Audio Systems
Section 3
Heating and Air Conditioning Setting the Radio Clock Radio/Cassette Player/CD Player
Radio Theft-Deterrent Feature Steering Wheel Controls (If Equipped)
Section 4
Section 5
Your Driving and the Road
Your Driving, the Road and Your Vehicle Defensive Driving Drunken Driving Control of a Vehicle Braking Steering
Driving Tips for Various Road Conditions Off-Road Driving Recreational Vehicle Towing Loading Your Vehicle Towing a Trailer
Hazard Warning Flashers Jump Starting Towing Your Vehicle
Problems on the Road
Engine Overheating Changing a Flat Tire If You're Stuck
iii
Table of Contents (cont'd)
Service and Appearance Care
Section 6
Fuel Checking Fluids and Lubricants Engine Air Cleaner/Filter Brakes Bulb Replacement Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
Tires and Wheels Appearance Care Electrical System/Fuses and Circuit Breakers Capacities and Specifications Normal Maintenance Replacement Parts
Section 7
Scheduled Maintenance Owner Checks and Services Periodic Maintenance Inspections
Maintenance Schedule
Recommended Fluids and Lubricants Maintenance Records
iv
Table of Contents (cont'd)
Customer Assistance Information
Section 8
Customer Satisfaction Procedures Customer Assistance Offices Roadside Assistance and Courtesy Transportation
Warranty Information (See Warranty Manual) Reporting Safety Defects on page 8-10
Service PublicationsSection 9
In the Index you will find an alphabetical listing of almost every subject in this manual.
You can use it to quickly find something you want to read.
Index
Please refer to the last page of this manual for your Service Station Guide
We support voluntary technician certification.
GENERAL MOTORS, GM, the GM Emblem, GMC, the GMC Emblem and the name ENVOY are registered trademarks of General Motors Corporation. This manual includes the latest information at the time it was printed. We reserve the right to make changes after that time without further notice. For vehicles first sold in Canada, substitute the name “General Motors of Canada Limited” for GMC whenever it appears in this manual. Please keep this manual in your vehicle, so it will be there if you ever need it when you’re on the road. If you sell the vehicle, please leave this manual in it so the new owner can use it.
For Canadian Owners Who Prefer a French Language Manual: Aux propriétaires canadiens: Vous pouvez vous procurer un exemplaire de ce guide en français chez votre concessionaire ou au:
Helm, Incorporated P.O. Box 07130
Detroit, MI 48207vi
4-Door Utility
About Driving Your Vehicle As with other vehicles of this type, failure to operate this vehicle correctly may result in loss of control or an accident. Be sure to read the “on-pavement” and “off-road” driving guidelines in this manual. (See “Your Driving, the Road and Your Vehicle” and “Off-Road Driving with Your Four-Wheel-Drive Vehicle” in the Index.) How to Use this Manual Many people read their owner’s manual from beginning to end when they first receive their new vehicle. If you do this, it will help you learn about the features and controls for your vehicle. In this manual, you’ll find that pictures and words work together to explain things quickly.
Safety Warnings and Symbols You will find a number of safety cautions in this book. We use a box and the word CAUTION to tell you about things that could hurt you if you were to ignore the warning.
CAUTION:
These mean there is something that could hurt you or other people.
In the caution area, we tell you what the hazard is. Then we tell you what to do to help avoid or reduce the hazard. Please read these cautions. If you don’t, you or others could be hurt.
vii
You will also find a circle with a slash through it in this book. This safety symbol means “Don’t,” “Don’t do this” or “Don’t let this happen.”
Vehicle Damage Warnings Also, in this book you will find these notices:
NOTICE:
These mean there is something that could damage your vehicle.
In the notice area, we tell you about something that can damage your vehicle. Many times, this damage would not be covered by your warranty, and it could be costly. But the notice will tell you what to do to help avoid the damage.
viii
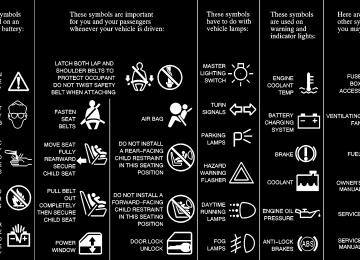
When you read other manuals, you might see CAUTION and NOTICE warnings in different colors or in different words. You’ll also see warning labels on your vehicle. They use the same words, CAUTION or NOTICE. Vehicle Symbols Your vehicle may be equipped with components and labels that use symbols instead of text. Symbols, used on your vehicle, are shown along with the text describing the operation or information relating to a specific component, control, message, gage or indicator. If you need help figuring out a specific name of a component, gage or indicator reference the following topics in the index:
D “Engine Compartment Overview” D “Instrument Panel” D “Comfort Controls” D “Audio Systems”
Also see “Warning Lights and Gages” in the Index. Here are some examples of symbols you may find on your vehicle:
ix
Service Station Guide
Windshield Washer
Fluid
See Section 6
Cooling System See Section 5
Tire Pressure See Section 6
Spare Tire Pressure
See Section 6
For a More
Detailed Look at
What's Under the Hood
See Section 6
Hood Release See Section 6
Battery
See Section 6
Engine Oil Dipstick
See Section 6
Oil Viscosity Engine Oil See Section 6
Fuel
Use unleaded only.
See Section 6
for octane ratings.
Section 1 Seats and Restraint Systems
Here you’ll find information about the seats in your vehicle and how to use your safety belts properly. You can also learn about some things you should not do with air bags and safety belts.
1-2
1-8
1-121-13
1-14
1-20
1-21
1-21
1-30Seats and Seat Controls Safety Belts: They’re for Everyone Here Are Questions Many People Ask About Safety Belts -- and the Answers How to Wear Safety Belts Properly Driver Position Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy Right Front Passenger Position Air Bag Systems Rear Seat Passengers
1-33
1-35
1-39
1-54
1-57
1-57
1-57Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for Children and Small Adults Children Restraint Systems for Children Older Children Safety Belt Extender Checking Your Restraint Systems Replacing Restraint System Parts After a Crash
1-
1-1
Seats and Seat Controls This section tells you about the power seats -- how to adjust them, and also about the reclining front seatbacks, memory seats, lumbar adjustments and heated seats. Power Seats
The power seat controls are located on the outboard side of the front seat cushions.
D Move the front of the seat control up or down to
adjust the front portion of the cushion.
D Move the rear of the seat control up or down to
adjust the rear portion of the cushion.
D Lift up or push down on the center of the seat control
to move the entire seat up or down.
1-2
D To move the seat forward or rearward, slide the seat
control forward or rearward.
D To recline the seatback, press the vertical control rearward. To raise the seatback, press the vertical control forward.
Four-Way Power Lumbar Control
The driver’s and passenger’s seatback lumbar support can be adjusted four ways by moving a single control located on the outboard side of the seat cushions.
To increase or decrease support, hold the control forward or rearward. To move the lumbar up or down, hold the control up or down. Keep in mind that as your seating position changes, as it may during long trips, so should the position of your lumbar support. Adjust the seat as needed.
Memory Seat (If Equipped)
If your vehicle has this feature the controls are located on the driver’s door, and are used to program and recall memory settings for the driver’s seating and outside mirror positions.
Adjust the driver’s seat (including the seatback recliner and lumbar) and both of the outside mirrors to the desired position. Then press and hold button 1 (for driver 1) for three seconds. A chime will sound to let you know that the position has been stored. A second mirror and seating position can be programmed by repeating the procedure with a second driver and pressing button 2 for three seconds. Each time button 1 or 2 is pressed and released while the vehicle is in PARK (P), the memory position will be recalled. Each time a memory button is pressed, a single chime will sound.
If you use the unlock button on the remote keyless entry transmitter to enter your vehicle, the preset driver’s seat and mirror positions will be recalled if programmed to do so through the Driver Information Center (DIC). The numbers on the back of the transmitters, 1 or 2, correspond to the numbers on the memory controls. The seat and mirror positions can also be recalled by placing the key in the ignition if programmed to do so through the Driver Information Center (DIC). To stop recall movement of the memory feature at any time, press one of the power seat controls or memory buttons. Two personalized exit positions can be set by first recalling the driver’s position (by pressing 1 or 2), then positioning the seat in the desired exit position for that driver. Then press and hold the button with the exit symbol for three seconds. A chime will sound to let you know that the position has been stored. With the vehicle in PARK (P), the exit position for that driver can be recalled by pressing the exit button. The mirrors, power lumbar and recline positions will not be stored or recalled for the exit positions.
1-3
Programming for automatic seat and mirror movement can be done through the Driver Information Center (DIC). You can choose to either select or not select automatic seat and mirror movement by using the remote keyless entry transmitter, by placing your key in the ignition, or when exiting the vehicle. For programming information, see “Vehicle Programming and Personalization Features” in the Index. Heated Front Seats (Option)
Your vehicle may have heated front seats. The buttons used to control this feature are located on the front door armrests. The engine must be running for the heated seat feature to work.
The horizontal button with the heated seat symbol is used to control the temperature settings high, medium and low. Press the button to cycle through the temperature settings and to turn the heated seat off. An indicator light will glow beside the temperature selected. The low setting warms the seatback and cushion until the seat temperature is near body temperature. The medium and high settings heat the seatback and seat cushion to a slightly higher temperature. You will be able to feel heat in about two minutes. To heat only the seatback, press the vertical button with the heated seatback symbol. Press the vertical button again to heat the whole seat. The feature will shut off automatically when the ignition is turned off.
1-4
Power Reclining Front Seatback The vertical power seat control described earlier allows the seatback to recline.
CAUTION:
Sitting in a reclined position when your vehicle is in motion can be dangerous. Even if you buckle up, your safety belts can’t do their job when you’re reclined like this. The shoulder belt can’t do its job. In a crash, you could go into it, receiving neck or other injuries. The lap belt can’t do its job either. In a crash the belt could go up over your abdomen. The belt forces would be there, not at your pelvic bones. This could cause serious internal injuries. For proper protection when the vehicle is in motion, have the seatback upright. Then sit well back in the seat and wear your safety belt properly.
1-5
But don’t have a seatback reclined if your vehicle is moving.
Head Restraints
Rear Seats Your vehicle has a folding rear seat which lets you fold the seatbacks down for more cargo space.
Slide the head restraint up or down so that the top of the restraint is closest to the top of your head. This position reduces the chance of a neck injury in a crash. On some models, the head restraints tilt forward and rearward also. The head restraints lock into place when raised. To release the head restraint and lower it, press the tab located on the top of the seatback. 1-6
Pull up on the tab located where the seat cushion meets the seatback to fold the seat cushion up and out of the way. This will allow the seatback to fold flat and increase the cargo area.
The rear seatback handles are located on the outboard side of the rear seatbacks.
Pull the seatback toward you as you lift up on the handle. The head restraint will automatically fold out of the way when the seatback is folded down. To raise the seatbacks, lift up the seatbacks and push on them until they lock into the upright position. Push and pull on the seatbacks to make sure that they are latched securely. Then fold the bottom seat cushion back into place.
To return the head restraint to the upright position, reach behind the seat and pull the restraint up until it locks into place. Push and pull on the head restraint to make sure that it is latched securely.
1-7
Safety Belts: They’re for Everyone This part of the manual tells you how to use safety belts properly. It also tells you some things you should not do with safety belts. And it explains the air bag system.
CAUTION:
Don’t let anyone ride where he or she can’t wear a safety belt properly. If you are in a crash and you’re not wearing a safety belt, your injuries can be much worse. You can hit things inside the vehicle or be ejected from it. You can be seriously injured or killed. In the same crash, you might not be if you are buckled up. Always fasten your safety belt, and check that your passengers’ belts are fastened properly too.
CAUTION:
It is extremely dangerous to ride in a cargo area, inside or outside of a vehicle. In a collision, people riding in these areas are more likely to be seriously injured or killed. Do not allow people to ride in any area of your vehicle that is not equipped with seats and safety belts. Be sure everyone in your vehicle is in a seat and using a safety belt properly.
Your vehicle has a light that comes on as a reminder to buckle up. See “Safety Belt Reminder Light” in the Index.
1-8
In most states and Canadian provinces, the law says to wear safety belts. Here’s why: They work. You never know if you’ll be in a crash. If you do have a crash, you don’t know if it will be a bad one. A few crashes are mild, and some crashes can be so serious that even buckled up a person wouldn’t survive. But most crashes are in between. In many of them, people who buckle up can survive and sometimes walk away. Without belts they could have been badly hurt or killed. After more than 30 years of safety belts in vehicles, the facts are clear. In most crashes buckling up does matter ... a lot! Why Safety Belts Work When you ride in or on anything, you go as fast as it goes.
Take the simplest vehicle. Suppose it’s just a seat on wheels.
1-9
Put someone on it.
Get it up to speed. Then stop the vehicle. The rider doesn’t stop.
1-10
The person keeps going until stopped by something. In a real vehicle, it could be the windshield ...
or the instrument panel ...
1-11
Here Are Questions Many People Ask About Safety Belts -- and the Answers Q: Won’t I be trapped in the vehicle after an
accident if I’m wearing a safety belt?
A: You could be -- whether you’re wearing a safety belt or not. But you can unbuckle a safety belt, even if you’re upside down. And your chance of being conscious during and after an accident, so you can unbuckle and get out, is much greater if you are belted.
Q: If my vehicle has air bags, why should I have to
wear safety belts?
A: Air bags are in many vehicles today and will be in
most of them in the future. But they are supplemental systems only; so they work with safety belts -- not instead of them. Every air bag system ever offered for sale has required the use of safety belts. Even if you’re in a vehicle that has air bags, you still have to buckle up to get the most protection. That’s true not only in frontal collisions, but especially in side and other collisions.
or the safety belts! With safety belts, you slow down as the vehicle does. You get more time to stop. You stop over more distance, and your strongest bones take the forces. That’s why safety belts make such good sense.
1-12
Q: If I’m a good driver, and I never drive far from
home, why should I wear safety belts?
A: You may be an excellent driver, but if you’re in an accident -- even one that isn’t your fault -- you and your passengers can be hurt. Being a good driver doesn’t protect you from things beyond your control, such as bad drivers.
Most accidents occur within 25 miles (40 km) of home. And the greatest number of serious injuries and deaths occur at speeds of less than 40 mph (65 km/h). Safety belts are for everyone.
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly Adults This part is only for people of adult size. Be aware that there are special things to know about safety belts and children. And there are different rules for smaller children and babies. If a child will be riding in your vehicle, see the part of this manual called “Children.” Follow those rules for everyone’s protection. First, you’ll want to know which restraint systems your vehicle has. We’ll start with the driver position.
1-13
Driver Position This part describes the driver’s restraint system. Lap-Shoulder Belt The driver has a lap-shoulder belt. Here’s how to wear it properly. 1. Close and lock the door. 2. Adjust the seat so you can sit up straight. To see
how, see “Seats” in the Index.
3. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Don’t let it get twisted.
4. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure. If the belt isn’t long enough, see “Safety Belt Extender” at the end of this section. Make sure the release button on the buckle is positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
1-14
5. To make the lap part tight, pull down on the buckle end of the belt as you pull up on the shoulder belt.
The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on the hips, just touching the thighs. In a crash, this applies force to the strong pelvic bones. And you’d be less likely to slide under the lap belt. If you slid under it, the belt would apply force at your abdomen. This could cause serious or even fatal injuries. The shoulder belt should go over the shoulder and across the chest. These parts of the body are best able to take belt restraining forces. The safety belt locks if there’s a sudden stop or crash, or if you pull the belt very quickly out of the retractor.
1-15
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously hurt if your shoulder belt is too loose. In a crash, you would move forward too much, which could increase injury. The shoulder belt should fit against your body.
A: The shoulder belt is too loose. It won’t give nearly
as much protection this way.
1-16
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if your belt is buckled in the wrong place like this. In a crash, the belt would go up over your abdomen. The belt forces would be there, not at the pelvic bones. This could cause serious internal injuries. Always buckle your belt into the buckle nearest you.
A: The belt is buckled in the wrong place.
1-17
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured if you wear the shoulder belt under your arm. In a crash, your body would move too far forward, which would increase the chance of head and neck injury. Also, the belt would apply too much force to the ribs, which aren’t as strong as shoulder bones. You could also severely injure internal organs like your liver or spleen.
A: The shoulder belt is worn under the arm. It should
be worn over the shoulder at all times.
1-18
Q: What’s wrong with this?
CAUTION:
You can be seriously injured by a twisted belt. In a crash, you wouldn’t have the full width of the belt to spread impact forces. If a belt is twisted, make it straight so it can work properly, or ask your dealer to fix it.
A: The belt is twisted across the body.
1-19
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy Safety belts work for everyone, including pregnant women. Like all occupants, they are more likely to be seriously injured if they don’t wear safety belts.
To unlatch the belt, just push the button on the buckle. The belt should go back out of the way. Before you close the door, be sure the belt is out of the way. If you slam the door on it, you can damage both the belt and your vehicle.
1-20
A pregnant woman should wear a lap-shoulder belt, and the lap portion should be worn as low as possible, below the rounding, throughout the pregnancy.
The best way to protect the fetus is to protect the mother. When a safety belt is worn properly, it’s more likely that the fetus won’t be hurt in a crash. For pregnant women, as for anyone, the key to making safety belts effective is wearing them properly. Right Front Passenger Position To learn how to wear the right front passenger’s safety belt properly, see “Driver Position” earlier in this section. The right front passenger’s safety belt works the same way as the driver’s safety belt -- except for one thing. If you ever pull the shoulder portion of the belt out all the way, you will engage the child restraint locking feature. If this happens, just let the belt go back all the way and start again.
Air Bag Systems This part explains the frontal and side impact air bag systems. Your vehicle has four air bags -- a frontal air bag for the driver, another frontal air bag for the right front passenger, a side impact air bag for the driver, and another side impact air bag for the right front passenger. Frontal air bags are designed to help reduce the risk of injury from the force of an inflating frontal air bag. But these air bags must inflate very quickly to do their job and comply with federal regulations.
1-21
Here are the most important things to know about the air bag systems:
CAUTION: (Continued)
CAUTION:
You can be severely injured or killed in a crash if you aren’t wearing your safety belt -- even if you have air bags. Wearing your safety belt during a crash helps reduce your chance of hitting things inside the vehicle or being ejected from it. Air bags are designed to work with safety belts but don’t replace them. Frontal air bags for the driver and right front passenger are designed to work only in moderate to severe crashes where the front of your vehicle hits something. They aren’t designed to inflate at all in rollover, rear, side or low-speed frontal crashes. And, for some unrestrained occupants, frontal air bags may provide less protection in frontal crashes than more forceful air bags have provided in the past. The side impact air bags for the driver and right front passenger are designed to inflate only in moderate to severe crashes
CAUTION: (Continued)
1-22
where something hits the side of your vehicle. They aren’t designed to inflate in frontal, in rollover or in rear crashes. Everyone in your vehicle should wear a safety belt properly -- whether or not there’s an air bag for that person.
CAUTION:
Both frontal and side impact air bags inflate with great force, faster than the blink of an eye. If you’re too close to an inflating air bag, as you would be if you were leaning forward, it could seriously injure you. Safety belts help keep you in position for air bag inflation before and during a crash. Always wear your safety belt, even with frontal air bags. The driver should sit as far back as possible while still maintaining control of the vehicle. Front occupants should not lean on or sleep against the door.
CAUTION:
Anyone who is up against, or very close to, any air bag when it inflates can be seriously injured or killed. Air bags plus lap-shoulder belts offer the best protection for adults, but not for young children and infants. Neither the vehicle’s safety belt system nor its air bag system is designed for them. Young children and infants need the protection that a child restraint system can provide. Always secure children properly in your vehicle. To read how, see the part of this manual called “Children.”
There is an air bag readiness light on the instrument panel, which shows the air bag symbol.
The system checks the air bag electrical system for malfunctions. The light tells you if there is an electrical problem. See “Air Bag Readiness Light” in the Index for more information.
How the Air Bag Systems Work
Where are the air bags?
The driver’s frontal air bag is in the middle of the steering wheel.
1-23
The right front passenger’s frontal air bag is in the instrument panel on the passenger’s side.
The driver’s side impact air bag is in the side of the driver’s seatback closest to the door.
1-24
The right front passenger’s side impact air bag is in the side of the passenger’s seatback closest to the door.
CAUTION:
If something is between an occupant and an air bag, the bag might not inflate properly or it might force the object into that person causing severe injury or even death. The path of an inflating air bag must be kept clear. Don’t put anything between an occupant and an air bag, and don’t attach or put anything on the steering wheel hub or on or near any other air bag covering. Don’t let seat covers block the inflation path of a side impact air bag.
1-25
When should an air bag inflate? The driver’s and right front passenger’s frontal air bags are designed to inflate in moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal crashes. But they are designed to inflate only if the impact speed is above the system’s designed “threshold level.” If your vehicle goes straight into a wall that doesn’t move or deform, the threshold level is about 9 to 16 mph (14 to 26 km/h). The threshold level can vary, however, with specific vehicle design, so that it can be somewhat above or below this range. If your vehicle strikes something that will move or deform, such as a parked car, the threshold level will be higher. The driver’s and right front passenger’s frontal air bags are not designed to inflate in rollovers, side impacts, or rear impacts, because inflation would not help the occupant.
The side impact air bags are designed to inflate in moderate to severe side crashes. A side impact air bag will inflate if the crash severity is above the system’s designed “threshold level.” The threshold level can vary with specific vehicle design. Side impact air bags are not designed to inflate in frontal or near-frontal impacts, rollovers or rear impacts, because inflation would not help the occupant. A side impact air bag will only deploy on the side of the vehicle that is struck. In any particular crash, no one can say whether an air bag should have inflated simply because of the damage to a vehicle or because of what the repair costs were. For frontal air bags, inflation is determined by the angle of the impact and how quickly the vehicle slows down in frontal and near-frontal impacts. For side impact air bags, inflation is determined by the location and severity of the impact. The air bag system is designed to work properly under a wide range of conditions, including off-road usage. Observe safe driving speeds, especially on rough terrain. As always, wear your safety belt. See “Off-Road Driving” in the Index for more tips on off-road driving.
1-26
What makes an air bag inflate? In an impact of sufficient severity, the air bag sensing system detects that the vehicle is in a crash. For both frontal and side impact air bags, the sensing system triggers a release of gas from the inflator, which inflates the air bag. The inflator, air bag and related hardware are all part of the air bag modules inside the steering wheel, instrument panel and the side of the front seatbacks closest to the door.
How does an air bag restrain? In moderate to severe frontal or near frontal collisions, even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel or the instrument panel. In moderate to severe side collisions, even belted occupants can contact the inside of the vehicle. The air bag supplements the protection provided by safety belts. Air bags distribute the force of the impact more evenly over the occupant’s upper body, stopping the occupant more gradually. But the frontal air bags would not help you in many types of collisions, including rollovers, rear impacts, and side impacts, primarily because an occupant’s motion is not toward the air bag. Side impact air bags would not help you in many types of collisions, including frontal or near frontal collisions, rollovers, and rear impacts, primarily because an occupant’s motion is not toward those air bags. Air bags should never be regarded as anything more than a supplement to safety belts, and then only in moderate to severe frontal or near-frontal collisions for the driver’s and right front passenger’s frontal air bags, and only in moderate to severe side collisions for the driver’s and right front passenger’s side impact air bags.
1-27
What will you see after an air bag inflates? After an air bag inflates, it quickly deflates, so quickly that some people may not even realize the air bag inflated. Some components of the air bag module -- the steering wheel hub for the driver’s air bag, the instrument panel for the right front passenger’s bag, the side of the seatback closest to the door for the driver and right front passenger’s side impact air bags -- will be hot for a short time. The parts of the bag that come into contact with you may be warm, but not too hot to touch. There will be some smoke and dust coming from the vents in the deflated air bags. Air bag inflation doesn’t prevent the driver from seeing or being able to steer the vehicle, nor does it stop people from leaving the vehicle.
CAUTION:
When an air bag inflates, there is dust in the air. This dust could cause breathing problems for people with a history of asthma or other breathing trouble. To avoid this, everyone in the vehicle should get out as soon as it is safe to do so. If you have breathing problems but can’t get out of the vehicle after an air bag inflates, then get fresh air by opening a window or a door.
Your vehicle has a feature that will automatically unlock the doors and turn the interior lamps on when the air bags inflate (if battery power is available). You can lock the doors again and turn the interior lamps off by using the door lock and interior lamp controls.
1-28
In many crashes severe enough to inflate an air bag, windshields are broken by vehicle deformation. Additional windshield breakage may also occur from the right front passenger air bag. D Air bags are designed to inflate only once. After an air bag inflates, you’ll need some new parts for your air bag system. If you don’t get them, the air bag system won’t be there to help protect you in another crash. A new system will include air bag modules and possibly other parts. The service manual for your vehicle covers the need to replace other parts.
D Your vehicle is equipped with a crash sensing and
diagnostic module, which records information about the frontal air bag system. The module records information about the readiness of the system, when the system commands air bag inflation and driver’s safety belt usage at deployment. The module also records speed, engine rpm, brake and throttle data.
D Let only qualified technicians work on your air bag systems. Improper service can mean that an air bag system won’t work properly. See your dealer for service.
NOTICE:
If you damage the covering for the driver’s or the right front passenger’s air bag, or the air bag covering on the driver’s and right front passenger’s seatback, the bag may not work properly. You may have to replace the air bag module in the steering wheel, both the air bag module and the instrument panel for the right front passenger’s air bag, or both the air bag module and seatback for the driver’s and right front passenger’s side impact air bag. Do not open or break the air bag coverings.
1-29
Rear Seat Passengers It’s very important for rear seat passengers to buckle up! Accident statistics show that unbelted people in the rear seat are hurt more often in crashes than those who are wearing safety belts. Rear passengers who aren’t safety belted can be thrown out of the vehicle in a crash. And they can strike others in the vehicle who are wearing safety belts. Rear Seat Passenger Positions
Servicing Your Air Bag-Equipped Vehicle Air bags affect how your vehicle should be serviced. There are parts of the air bag systems in several places around your vehicle. Your dealer and the service manual have information about servicing your vehicle and the air bag systems. To purchase a service manual, see “Service and Owner Publications” in the Index.
CAUTION:
For up to 10 seconds after the ignition key is turned off and the battery is disconnected, an air bag can still inflate during improper service. You can be injured if you are close to an air bag when it inflates. Avoid yellow connectors. They are probably part of the air bag systems. Be sure to follow proper service procedures, and make sure the person performing work for you is qualified to do so.
The air bag systems do not need regular maintenance.
1-30
Lap-Shoulder Belt All three rear seating positions have lap-shoulder belts. Here’s how to wear one properly.
When the shoulder belt is pulled out all the way, it will lock. If it does, let it go back all the way and start again. If the belt is not long enough, see “Safety Belt Extender” at the end of this section. Make sure the release button on the buckle is positioned so you would be able to unbuckle the safety belt quickly if you ever had to.
1. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Don’t let it get twisted.
2. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks. Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure.
3. To make the lap part tight, pull down on the buckle end of the belt as you pull up on the shoulder part.
1-31
CAUTION:
You can be seriously hurt if your shoulder belt is too loose. In a crash, you would move forward too much, which could increase injury. The shoulder belt should fit against your body.
The lap part of the belt should be worn low and snug on the hips, just touching the thighs. In a crash, this applies force to the strong pelvic bones. And you’d be less likely to slide under the lap belt. If you slid under it, the belt would apply force at your abdomen. This could cause serious or even fatal injuries. The shoulder belt should go over the shoulder and across the chest. These parts of the body are best able to take belt restraining forces.
1-32
To unlatch the belt, just push the button on the buckle.
Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for Children and Small Adults Rear shoulder belt comfort guides will provide added safety belt comfort for older children who have outgrown booster seats and for small adults. When installed on a shoulder belt, the comfort guide better positions the belt away from the neck and head. There is one guide for each of the outside passenger positions in the rear seat. To provide added safety belt comfort for children who have outgrown child restraints and for smaller adults, the comfort guides may be installed on the shoulder belts. Here’s how to install a comfort guide and use the safety belt:
1. Slide the guide off of its storage clip located between the interior body and the seatback.
1-33
2. Slide the guide under and past the belt. The elastic cord must be under the belt. Then, place the guide over the belt, and insert the two edges of the belt into the slots of the guide.
3. Be sure that the belt is not twisted and it lies flat.
The elastic cord must be under the belt and the guide on top.
1-34
Children Everyone in a vehicle needs protection! This includes infants and all other children. Neither the distance traveled nor the age and size of the traveler changes the need, for everyone, to use safety restraints. In fact, the law in every state in the United States and in every Canadian province says children up to some age must be restrained while in a vehicle. Infants and Young Children Every time infants and young children ride in vehicles, they should have the protection provided by the appropriate restraint. Young children should not use the vehicle’s safety belts, unless there is no other choice.
1-35
4. Buckle, position and release the safety belt as
described in “Rear Seat Passenger Positions” earlier in this section. Make sure that the shoulder belt crosses the shoulder.
To remove and store the comfort guides, squeeze the belt edges together so that you can take them out of the guides. Slide the guide back on its storage clip located between the interior body and the seatback.
CAUTION: (Continued)
For example, in a crash at only 25 mph (40 km/h), a 12-lb. (5.5 kg) baby will suddenly become a 240-lb. (110 kg) force on a person’s arms. A baby should be secured in an appropriate restraint.
CAUTION:
People should never hold a baby in their arms while riding in a vehicle. A baby doesn’t weigh much -- until a crash. During a crash a baby will become so heavy it is not possible to hold it.
CAUTION: (Continued)
1-36
CAUTION:
Children who are up against, or very close to, any air bag when it inflates can be seriously injured or killed. Air bags plus lap-shoulder belts offer outstanding protection for adults and older children, but not for young children and infants. Neither the vehicle’s safety belt system nor its air bag system is designed for them. Young children and infants need the protection that a child restraint system can provide.
Q: What are the different types of add-on
child restraints?
A: Add-on child restraints, which are purchased by
the vehicle’s owner, are available in four basic types. Selection of a particular restraint should take into consideration not only the child’s weight, height and age but also whether or not the restraint will be compatible with the motor vehicle in which it will be used.
For most basic types of child restraints, there are many different models available. When purchasing a child restraint, be sure it is designed to be used in a motor vehicle. If it is, the restraint will have a label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle safety standards. The restraint manufacturer’s instructions that come with the restraint state the weight and height limitations for a particular child restraint. In addition, there are many kinds of restraints available for children with special needs.
1-37
CAUTION:
CAUTION:
Newborn infants need complete support, including support for the head and neck. This is necessary because a newborn infant’s neck is weak and its head weighs so much compared with the rest of its body. In a crash, an infant in a rear-facing seat settles into the restraint, so the crash forces can be distributed across the strongest part of an infant’s body, the back and shoulders. Infants always should be secured in appropriate infant restraints.
The body structure of a young child is quite unlike that of an adult or older child, for whom the safety belts are designed. A young child’s hip bones are still so small that the vehicle’s regular safety belt may not remain low on the hip bones, as it should. Instead, it may settle up around the child’s abdomen. In a crash, the belt would apply force on a body area that’s unprotected by any bony structure. This alone could cause serious or fatal injuries. Young children always should be secured in appropriate child restraints.
1-38
Restraint Systems for Children
An infant car bed (A), a special bed made for use in a motor vehicle, is an infant restraint system designed to restrain or position a child on a continuous flat surface. Make sure that the infant’s head rests toward the center of the vehicle.
A rear-facing infant seat (B) provides restraint with the seating surface against the back of the infant. The harness system holds the infant in place and, in a crash, acts to keep the infant positioned in the restraint.
1-39
A forward-facing child seat (C-E) provides restraint for the child’s body with the harness and also sometimes with surfaces such as T-shaped or shelf-like shields.
A booster seat (F-G) is a child restraint designed to improve the fit of the vehicle’s safety belt system. Some booster seats have a shoulder belt positioner, and some high-back booster seats have a five-point harness. A booster seat can also help a child to see out the window.
1-40
Q: How do child restraints work? A: A child restraint system is any device designed for use in a motor vehicle to restrain, seat, or position children. A built-in child restraint system is a permanent part of the motor vehicle. An add-on child restraint system is a portable one, which is purchased by the vehicle’s owner. For many years, add-on child restraints have used the adult belt system in the vehicle. To help reduce the chance of injury, the child also has to be secured within the restraint. The vehicle’s belt system secures the add-on child restraint in the vehicle, and the add-on child restraint’s harness system holds the child in place within the restraint. One system, the three-point harness, has straps that come down over each of the infant’s shoulders and buckle together at the crotch. The five-point harness system has two shoulder straps, two hip straps and a crotch strap. A shield may take the place of hip straps. A T-shaped shield has shoulder straps that are attached to a flat pad which rests low against the child’s body. A shelf- or armrest-type shield has straps that are attached to a wide, shelf-like shield that swings up or to the side.
When choosing a child restraint, be sure the child restraint is designed to be used in a vehicle. If it is, it will have a label saying that it meets federal motor vehicle safety standards. Then follow the instructions for the restraint. You may find these instructions on the restraint itself or in a booklet, or both. These restraints use the belt system in your vehicle, but the child also has to be secured within the restraint to help reduce the chance of personal injury. When securing an add-on child restraint, refer to the instructions that come with the restraint which may be on the restraint itself or in a booklet, or both, and to this manual. The child restraint instructions are important, so if they are not available, obtain a replacement copy from the manufacturer.
1-41
Where to Put the Restraint Accident statistics show that children are safer if they are restrained in the rear rather than the front seat. General Motors, therefore, recommends that child restraints be secured in a rear seat outside position including an infant riding in a rear-facing infant seat, a child riding in a forward-facing child seat and an older child riding in a booster seat. Never put a rear-facing child restraint in the front passenger seat. Here’s why:
1-42
CAUTION:
A child in a rear-facing child restraint can be seriously injured or killed if the right front passenger’s air bag inflates. This is because the back of the rear-facing child restraint would be very close to the inflating air bag. Always secure a rear-facing child restraint in a rear seat outside position. You may secure a forward-facing child restraint in the right front seat, but before you do, always move the front passenger seat as far back as it will go. It’s better to secure the child restraint in a rear seat outside position.